Lecture 21 - Ocean Acidification & Coral Reefs
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is seawater made of?
Na+ / Cl- /Ca+ / Mg+ / K+
CO2 / O2 / H2O
where do these ion and gases originate
organisms respiring will release CO2
atmosphere → CO2
hydrothermal vents → underwater volcanoes
composition of the atmosphere
nitrogen gas (78%)
oxygen gas (21%)
argon gas (1%)
minute concentrations of
carbon dioxide
methane
nitrous oxide
ozone
chlorofluorocarbons
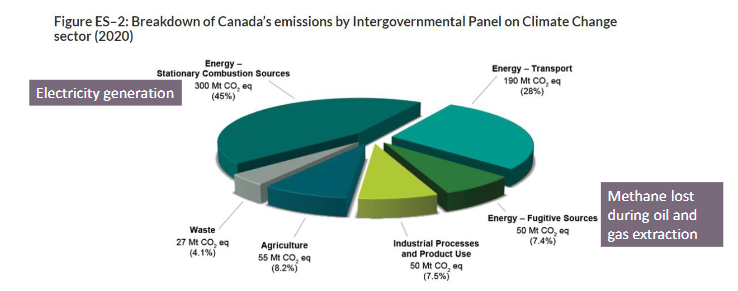
where do greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions come from in Canada?
energy production
transportation
industrial processes
fugitive sources (methane lost during oil and gas extraction)
agriculture
waste
what was happening in the 1700/1800s
industrial revolution → CO2 emissions increase
how much CO2 is absorbed by the ocean
25-30%
increases CO2 in atmosphere = _______
increased CO2 in the ocean
pH of freshwater and saltwater
freshwater: 6.5-8
saltwater: 8.2
ocean acidification process
reactions can go either way depending on how much CO2 is dissolved.
currently moving left → right bc of our actions
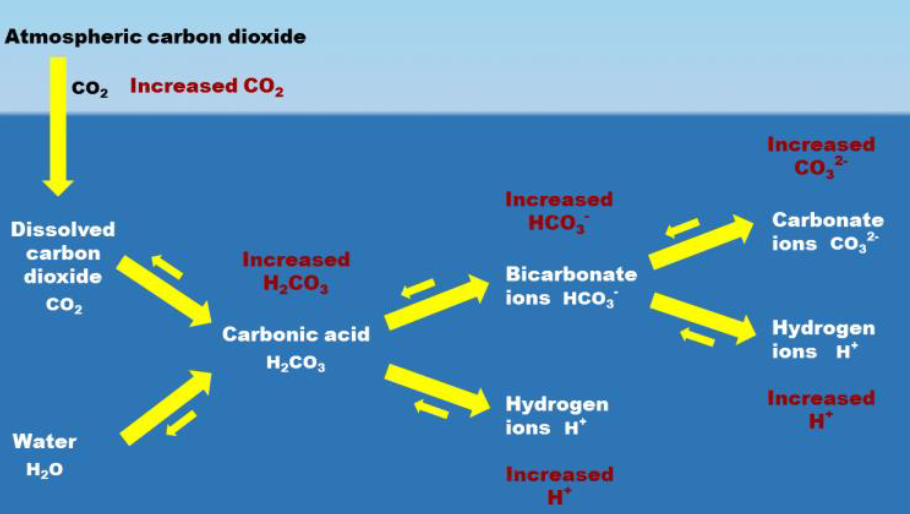
acidity ______, as pH decreases
increases
what is coral skeleton made of?
calcium carbonate
aragonite crystals
calcium abundant in seawater
carbonate can change depending on levels of dissolved CO2
acidification alters ocean chemistry and…
calcification
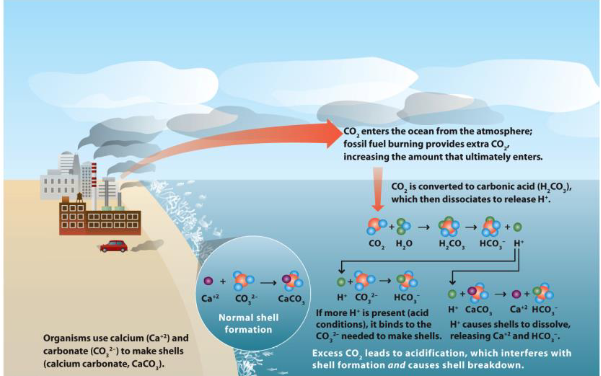
what will happen to coral as ocean water becomes more acidic
can’t grow their skeletons/weaken bc of poor calcification
decreased growth rates
less dense → more fragile → increase bioerosion/storm damage
may use more energy to keep growth rates up → limits energy for things like reproduction
how can we test coral
lab experiments
field experiments
look to natural environments
study coral biochemistry
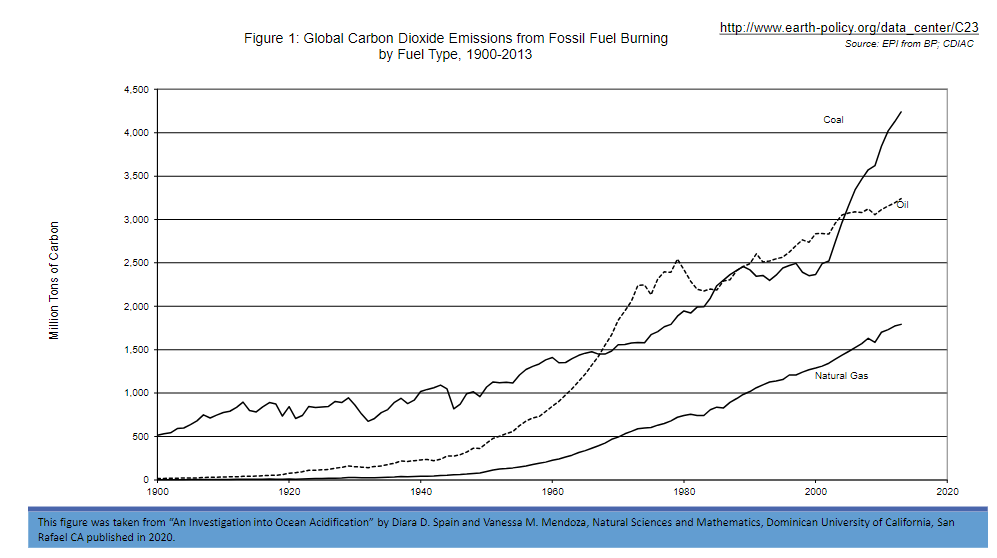
Fill in the correct answer after examining Figure 1.
In the 1900s the primary contributor to global emissions was _____. This trend continued and by 1920 another major contributor emerged, _____. Emissions from _____ became the third contributor after the 1950’s. After 1950 the total amount of carbon dioxide emissions began to _____ to more rapidly. By 1970 the top contributor was clearly _____ with _____ as the second major source. ______ ___has steadily increased from 1940 to 2013. In contrast, there has been a sharp increase in the contributor, _____, since 2000.
In the 1900s the primary contributor to global emissions was coal. This trend continued and by 1920 another major contributor emerged, oil. Emissions from natural gas became the third contributor after the 1950’s. After 1950 the total amount of carbon dioxide emissions began to increase more rapidly. By 1970 the top contributor was clearly oil with coal as the second major source. Natural gas has steadily increased from 1940 to 2013. In contrast, there has been a sharp increase in the contributor, coal, since 2000.
Complete the paragraph to help explain how pH has changed over time.
The pH level of the ocean has _____ over time. Since atmospheric _______ is _____, the amount of CO2 that the water takes in _____ as well. When there is more CO2 in ocean water, this changes ocean chemistry. The ending chemical reaction in the ocean results in an increase in _____ ions, which will result in a pH decrease, thus causing the ocean to become more _____.
The pH level of the ocean has decreased over time. Since atmospheric carbon dioxide is increasing, the amount of CO2 that the water takes in increases as well. When there is more CO2 in ocean water, this changes ocean chemistry. The ending chemical reaction in the ocean results in an increase in hydrogen ions, which will result in a pH decrease, thus causing the ocean to become more acidic.
If human continue to emit CO2 at the amount we do right now, what does that mean for the future? Summarize in your own words.
pH decrease
organisms that rely of calcium carbonate will have trouble forming skeletons
food sources of coral, such as plankton, may also decrease
What are some things that you can do to decrease your carbon footprint and help decrease the overall emission of CO2?
walk, bike, public transportation > cars
eat locally, but also look at how the food is grown (ecologically grown)
move away from industrial farming
eat less meat
turn off unnecessaries lights and water
more energy efficient homes
turn to renewable sources of energy
reduce materialistic consumption → buy secondhand