3.01 thermodynamics and enzymes
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
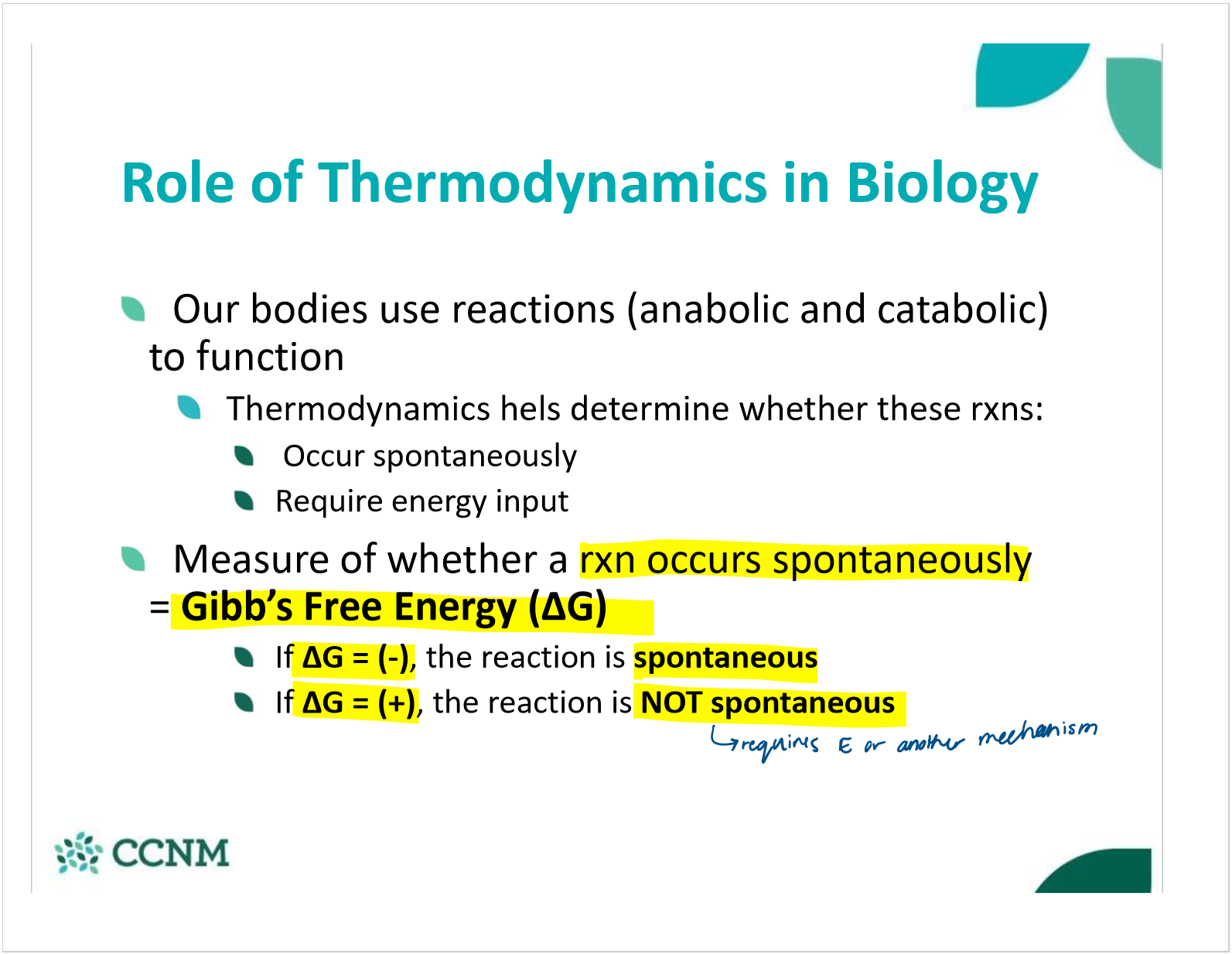
in terms of Gibb’s free energy when is a reaction spontaneous vs non-spontaneous?
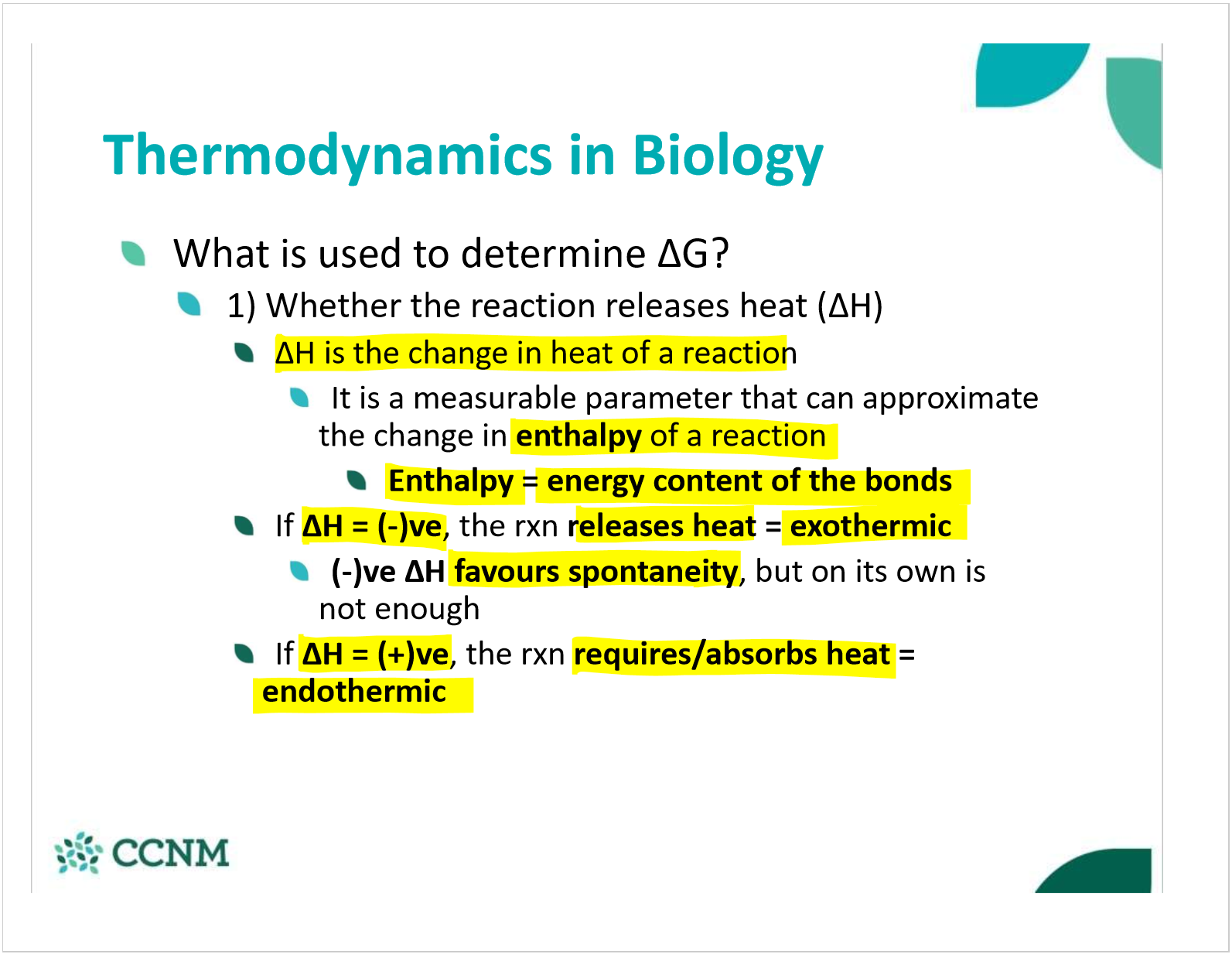
what is enthalpy? when does it favor spontaneity? non-spontaneity?
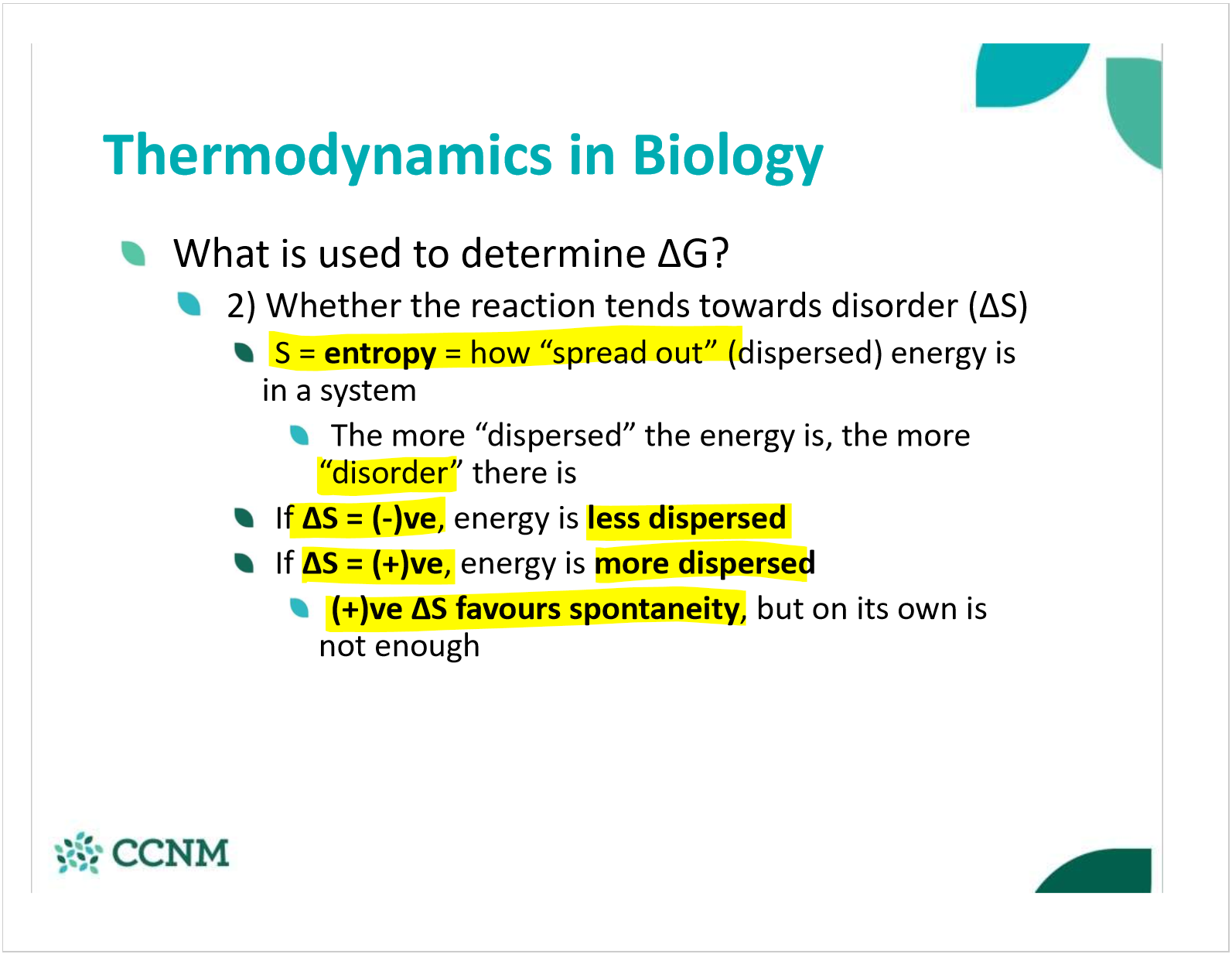
what is entropy? when does it favor spontaneity? non-spontaneity?
what is the thermodynamic/gibbs free energy equation?
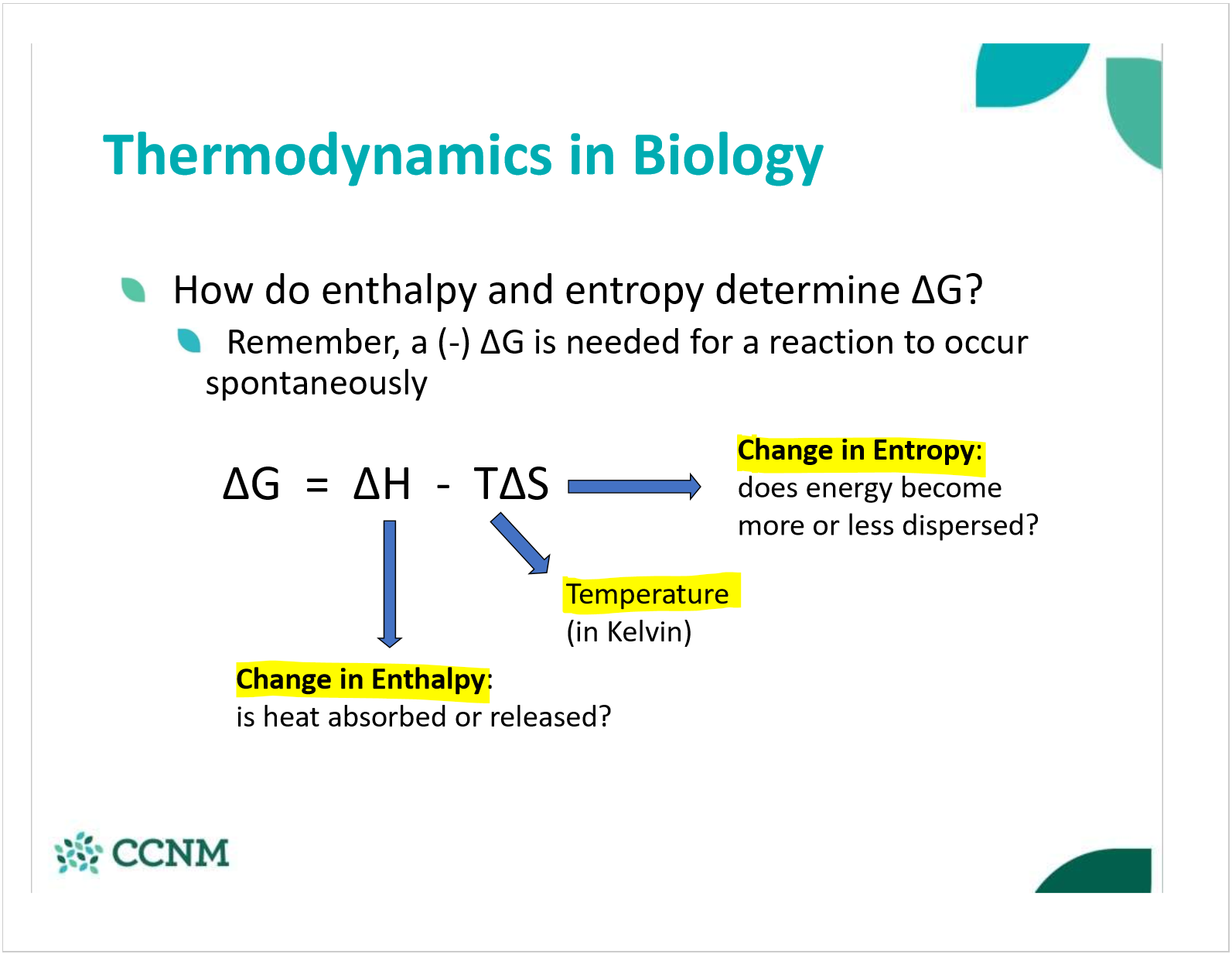
what is Gibb’s free energy for exergonic rxns? endergonic? EQM?
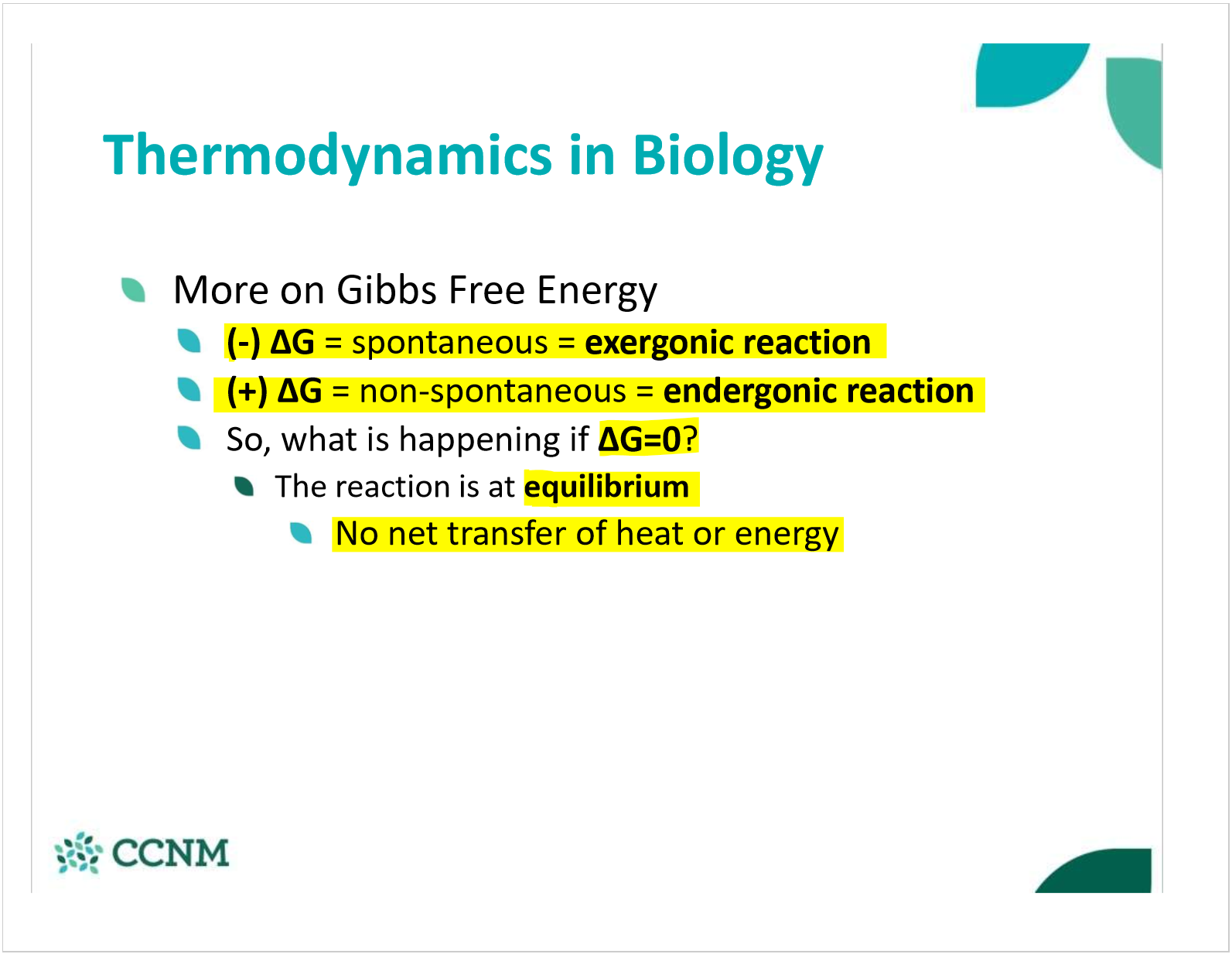
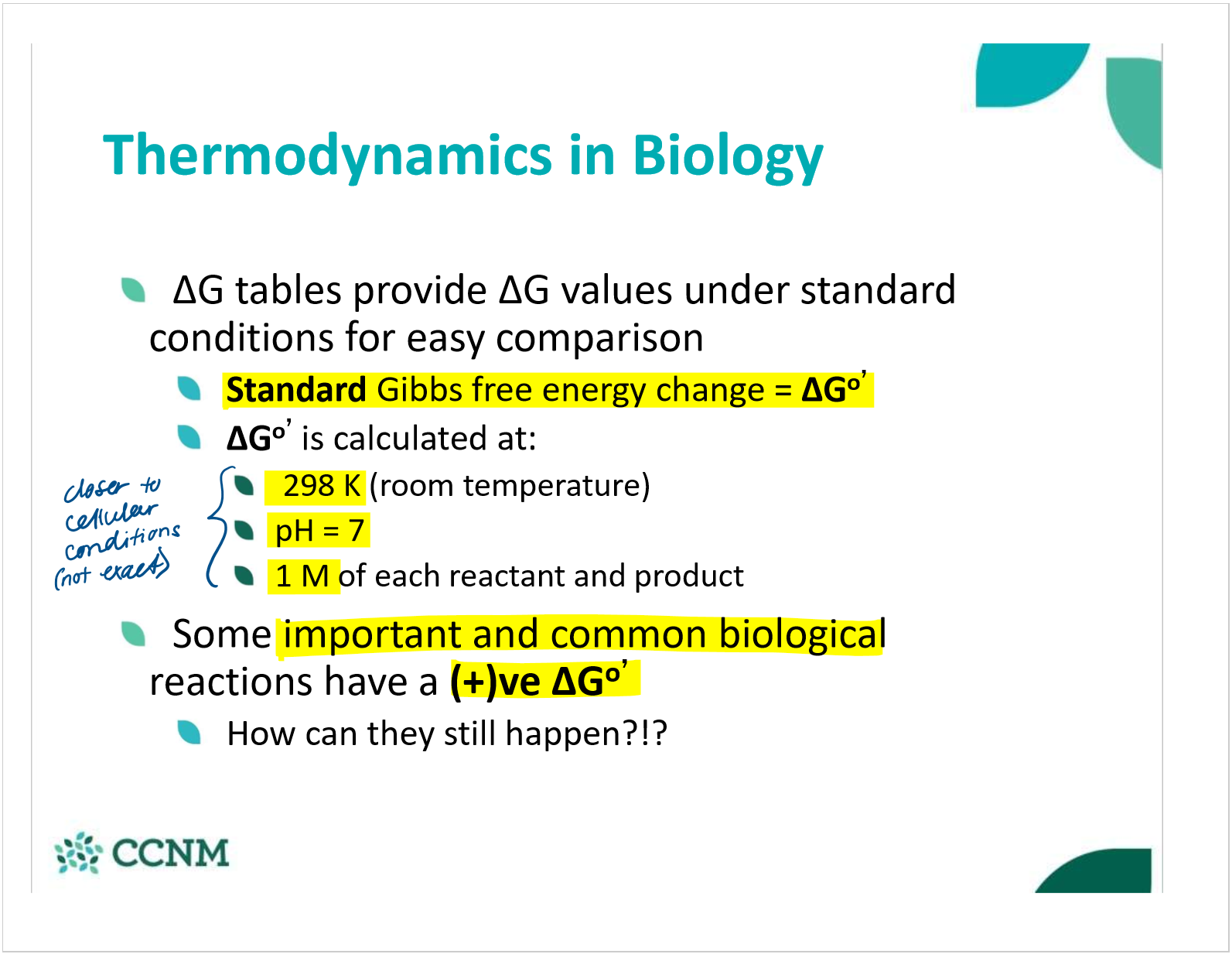
what are the standard conditions that standard gibbs free energy is calculated at? why is this useful
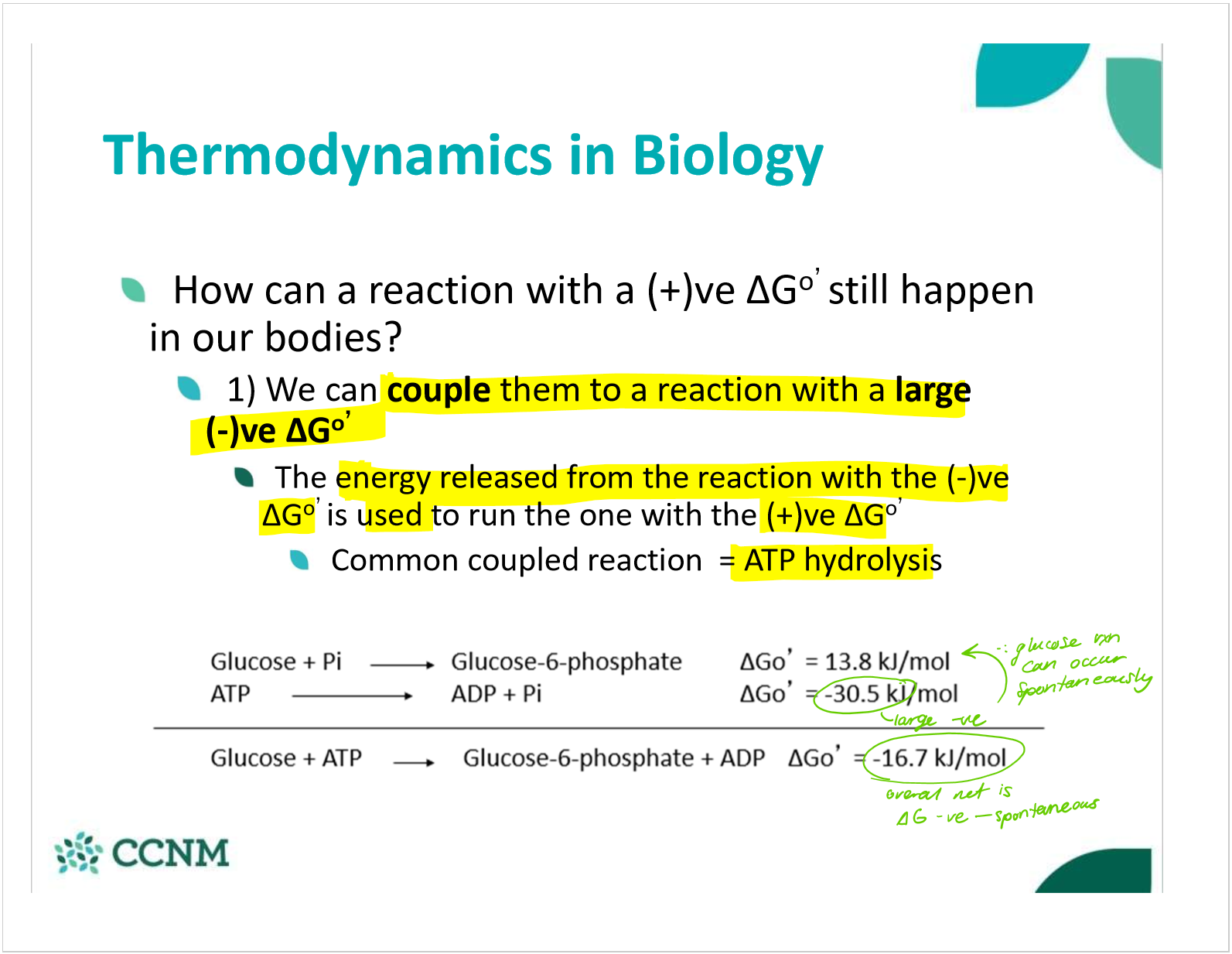
describe the use of coupling reactions
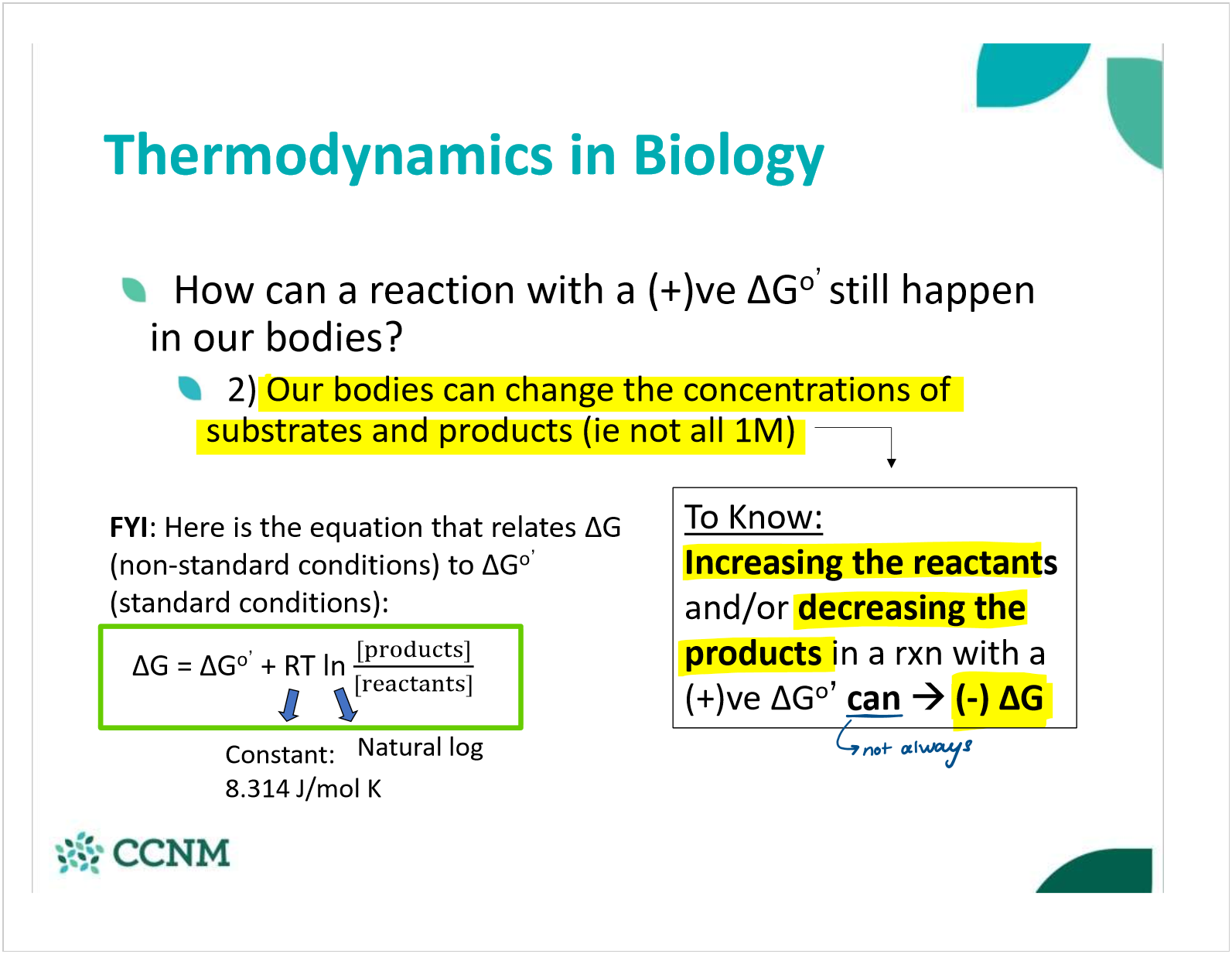
describe how changing concentration can allow a +gibbs free energy rxn to occur
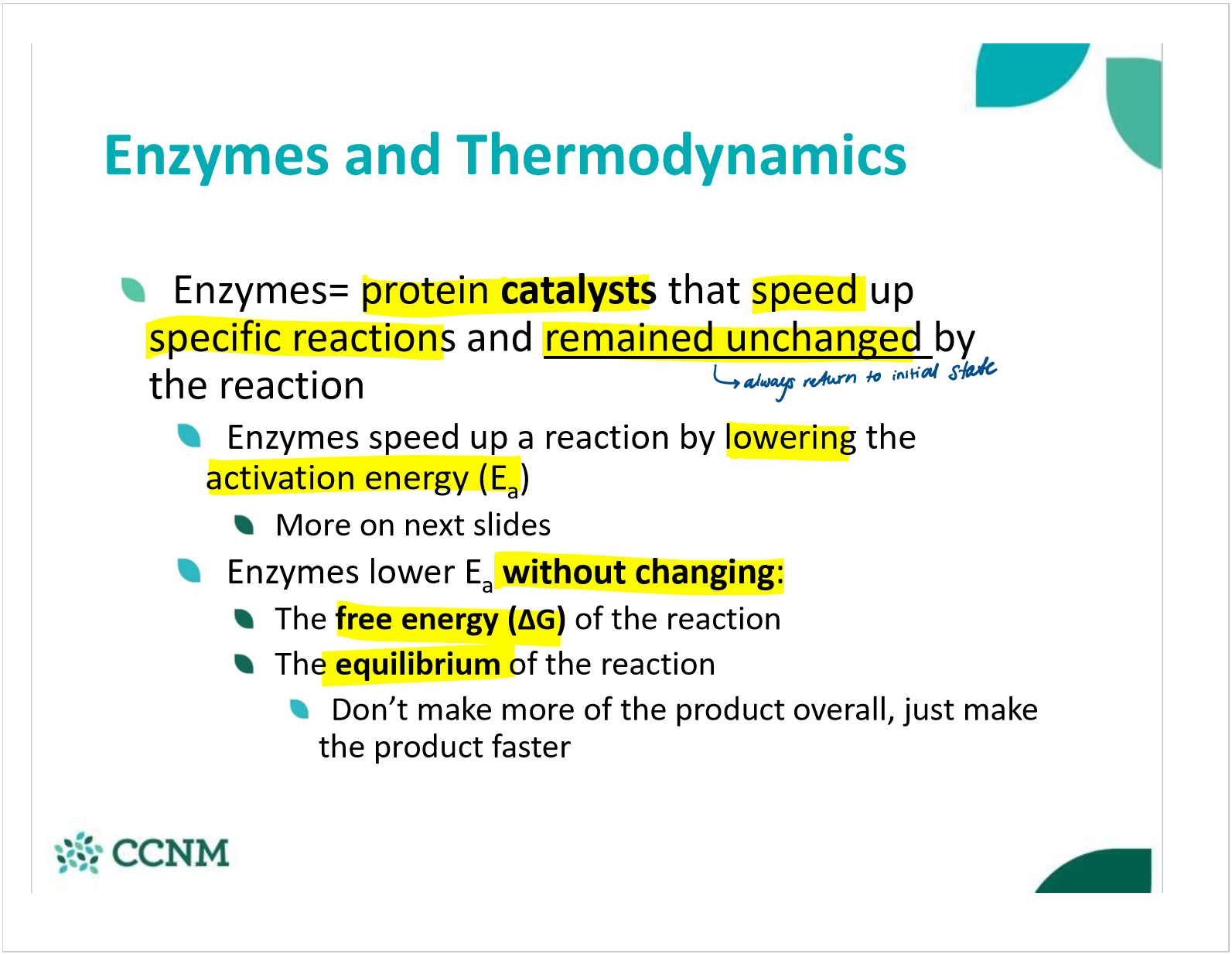
define enzymes and explain how they speed up rxns
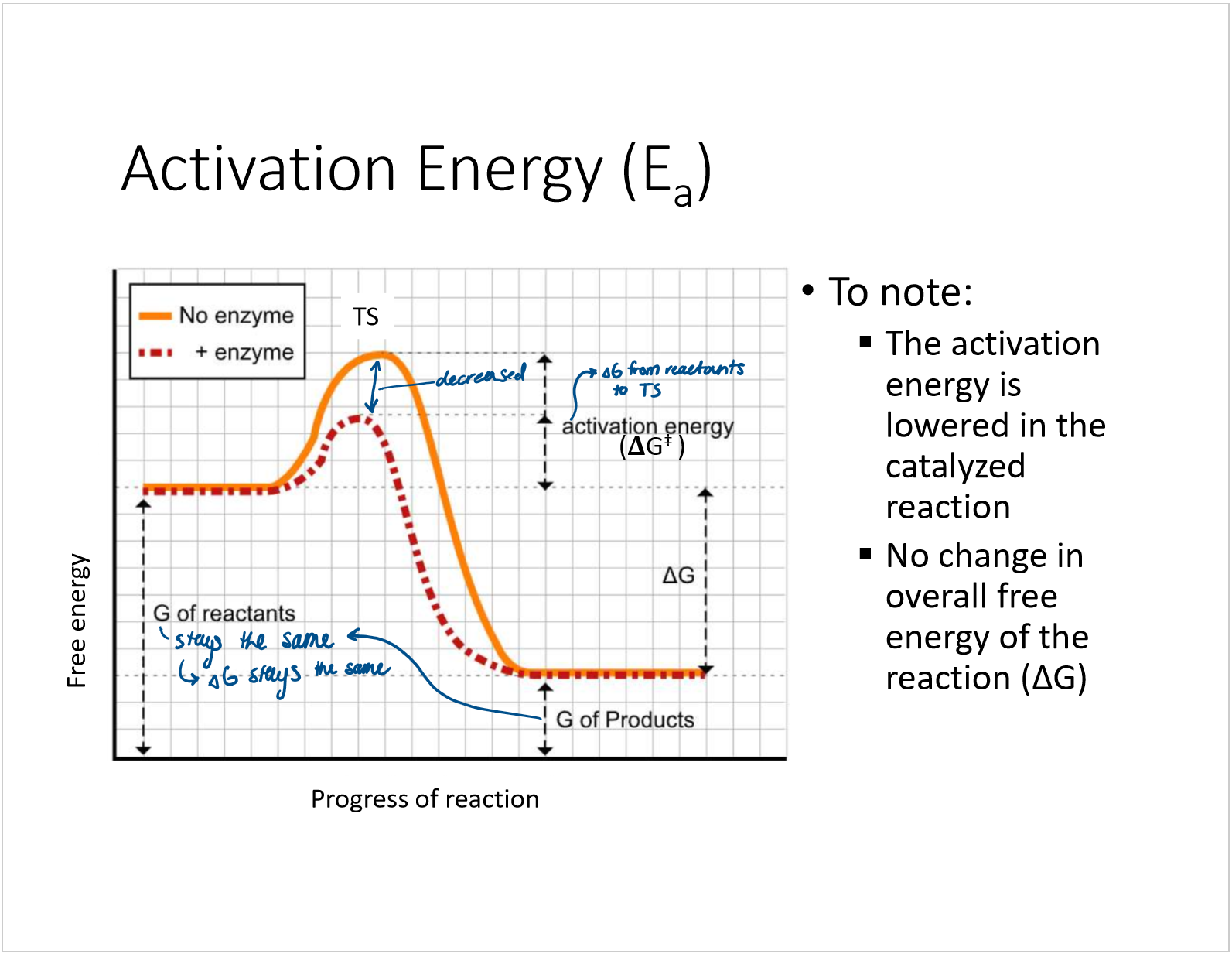
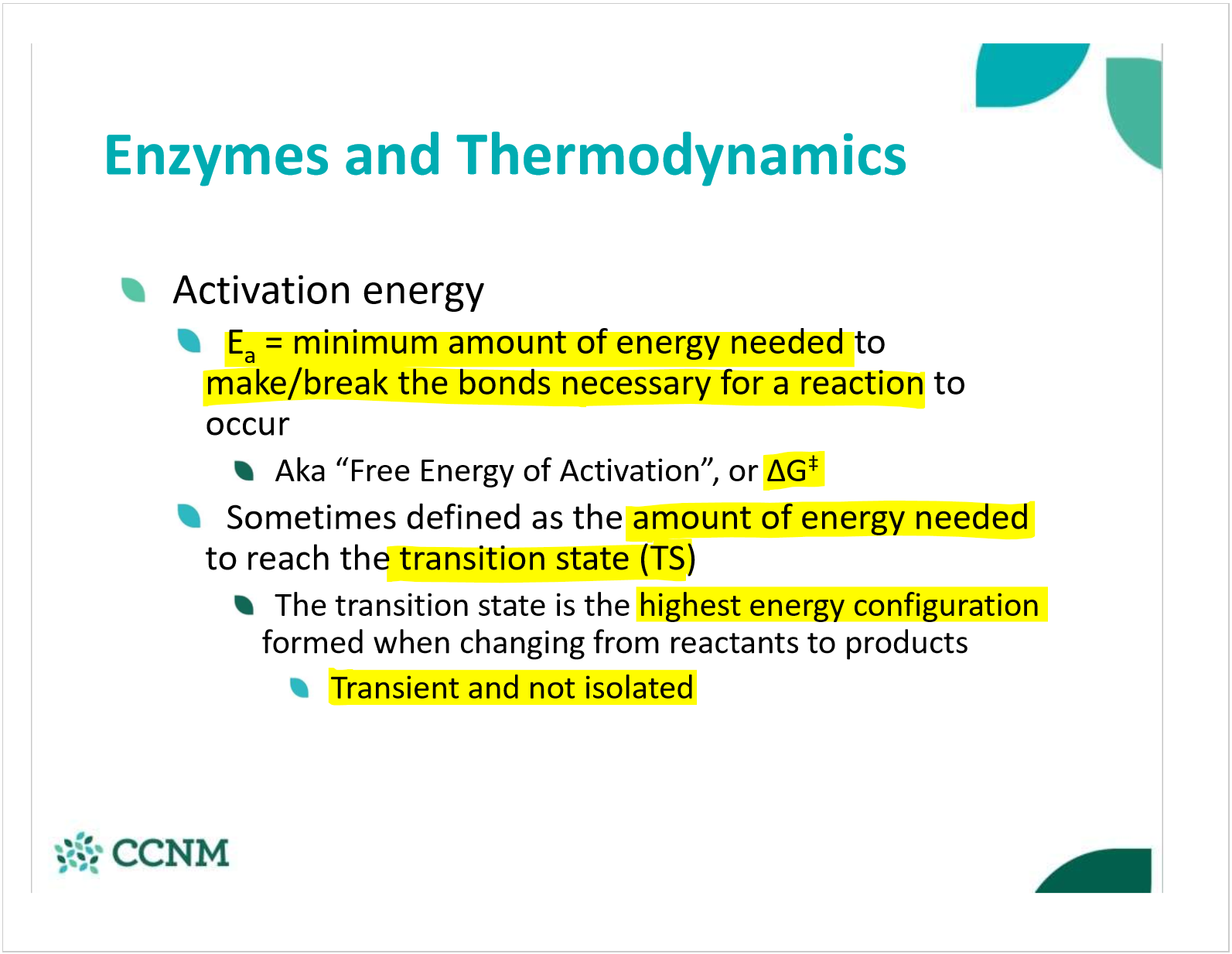
what is activation energy?
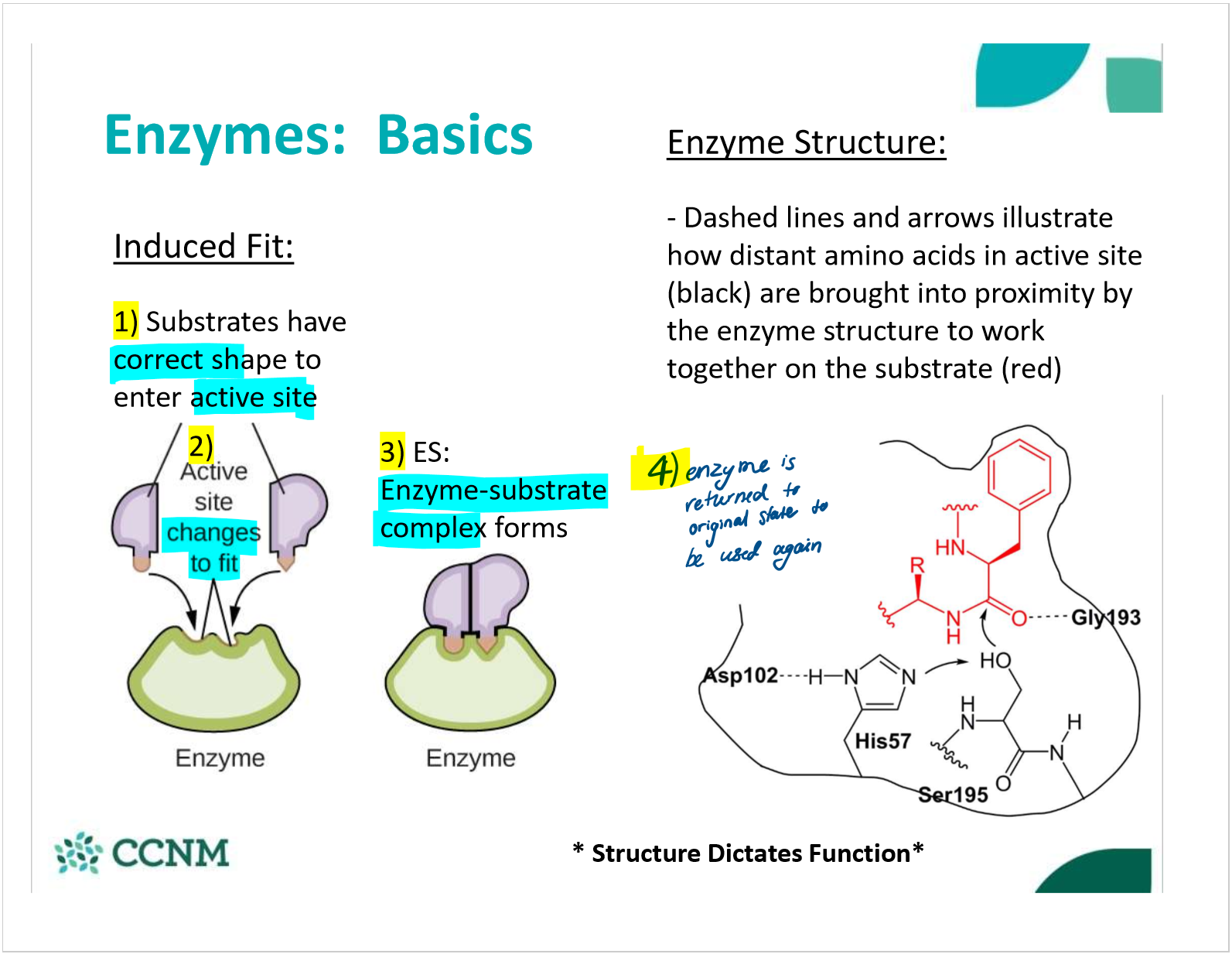
what is an enzyme active site?

describe the enzyme-substrate complex

describe the induced fit model
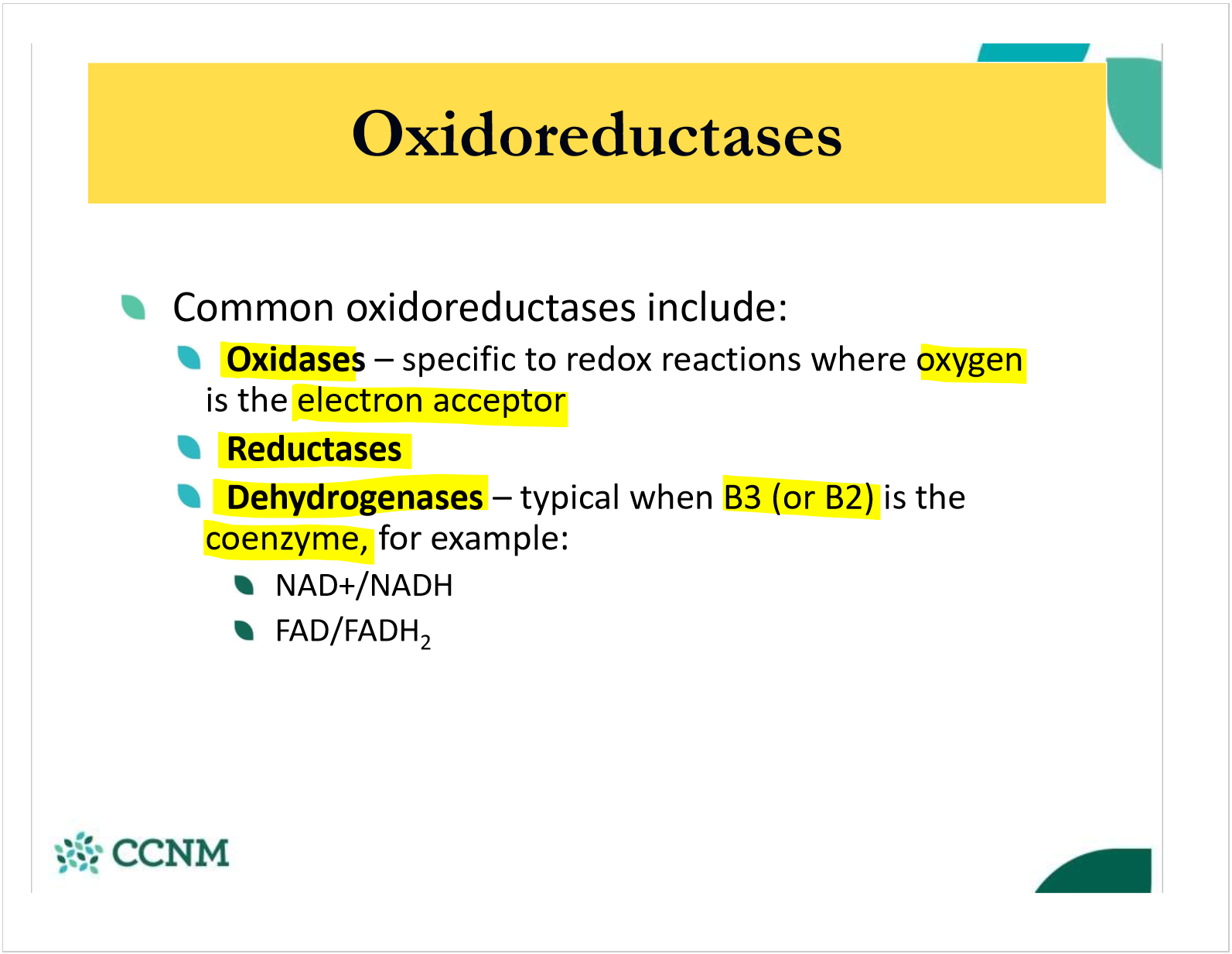
what are oxidoreductases?

what are the 3 common types of oxidoreductase?
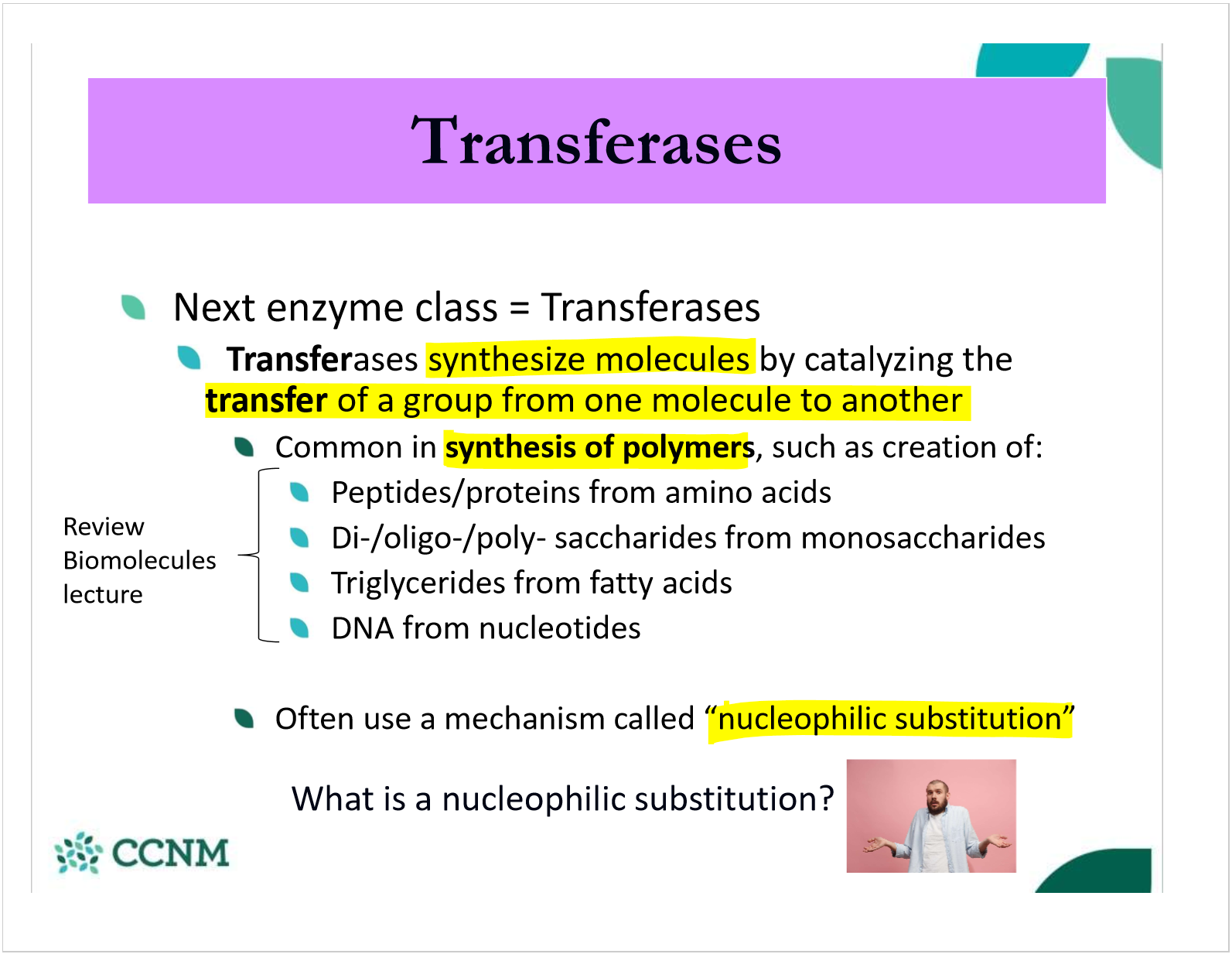
what are transferases/what do they do?
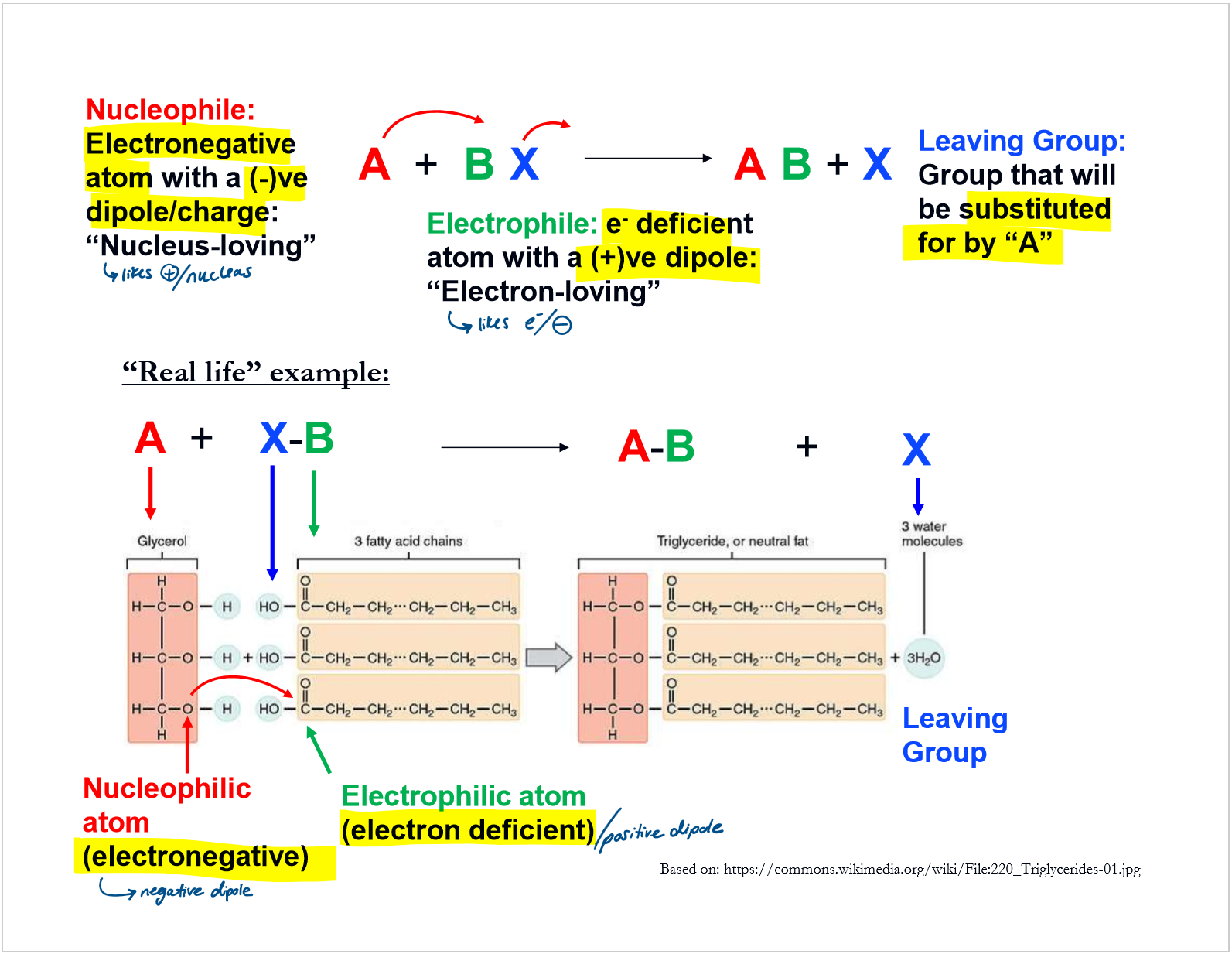
describe nucleophillic substituion
what are the 3 common transferases classes
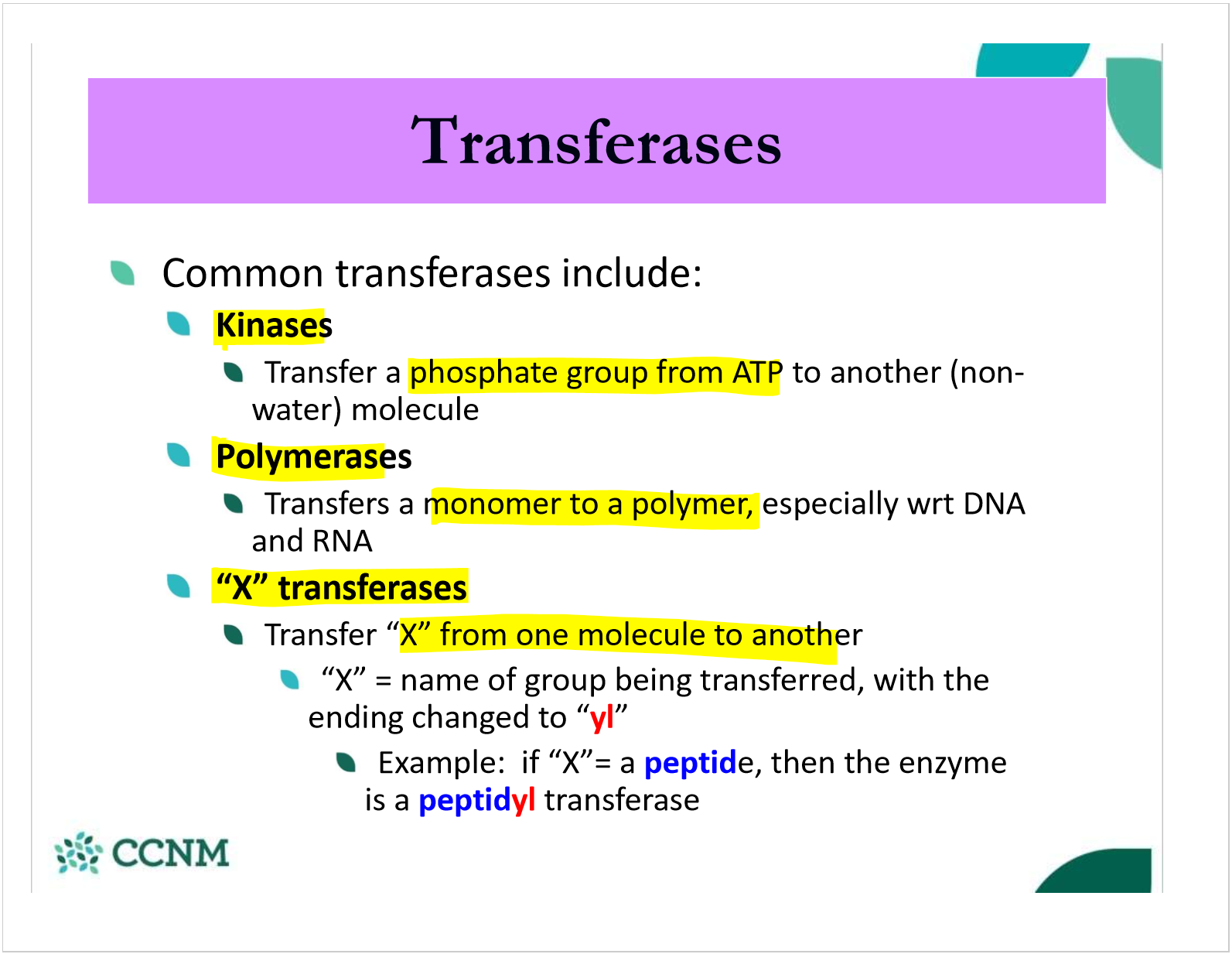
what are carriers?

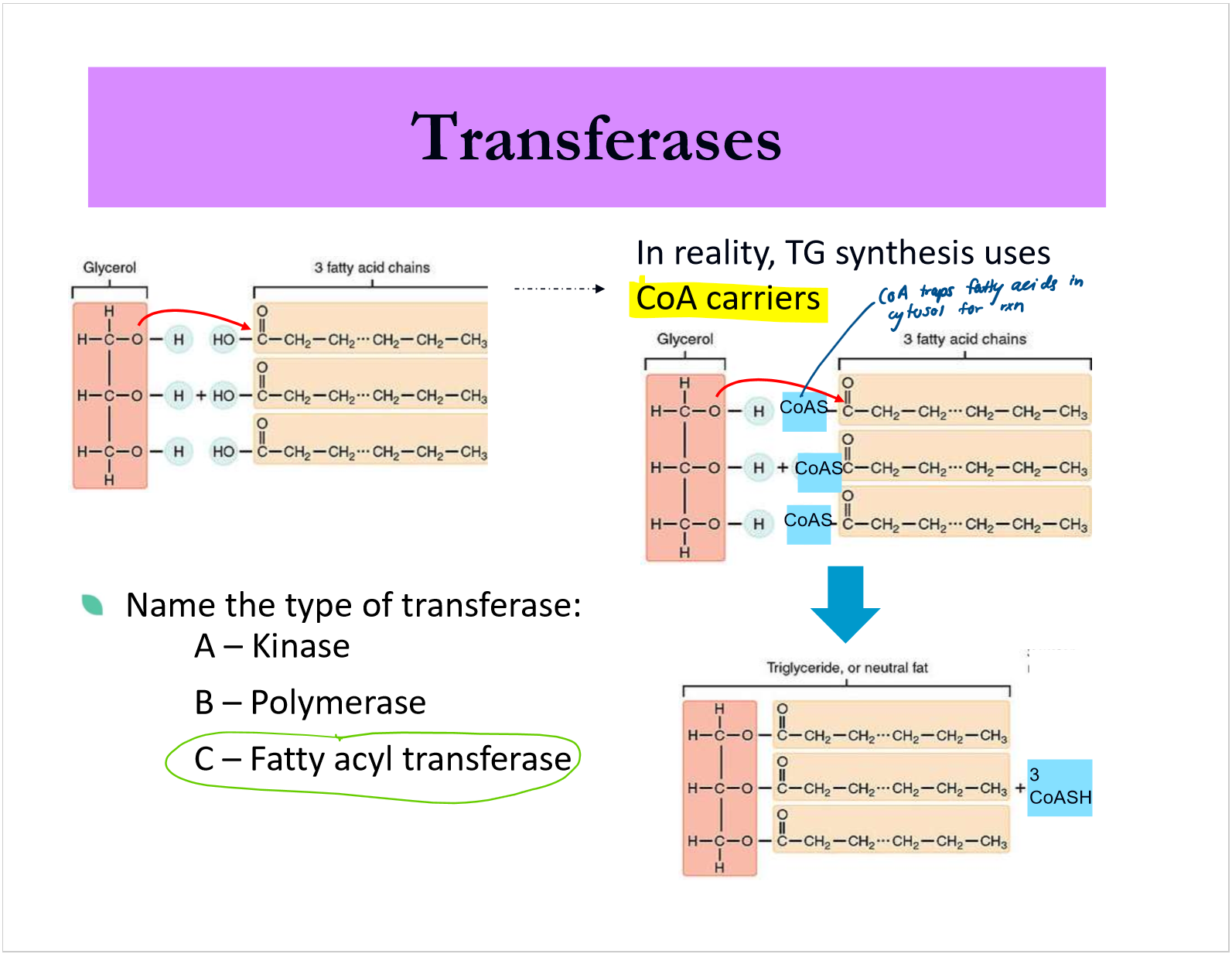
how is CoA used in triglyceride synthesis?
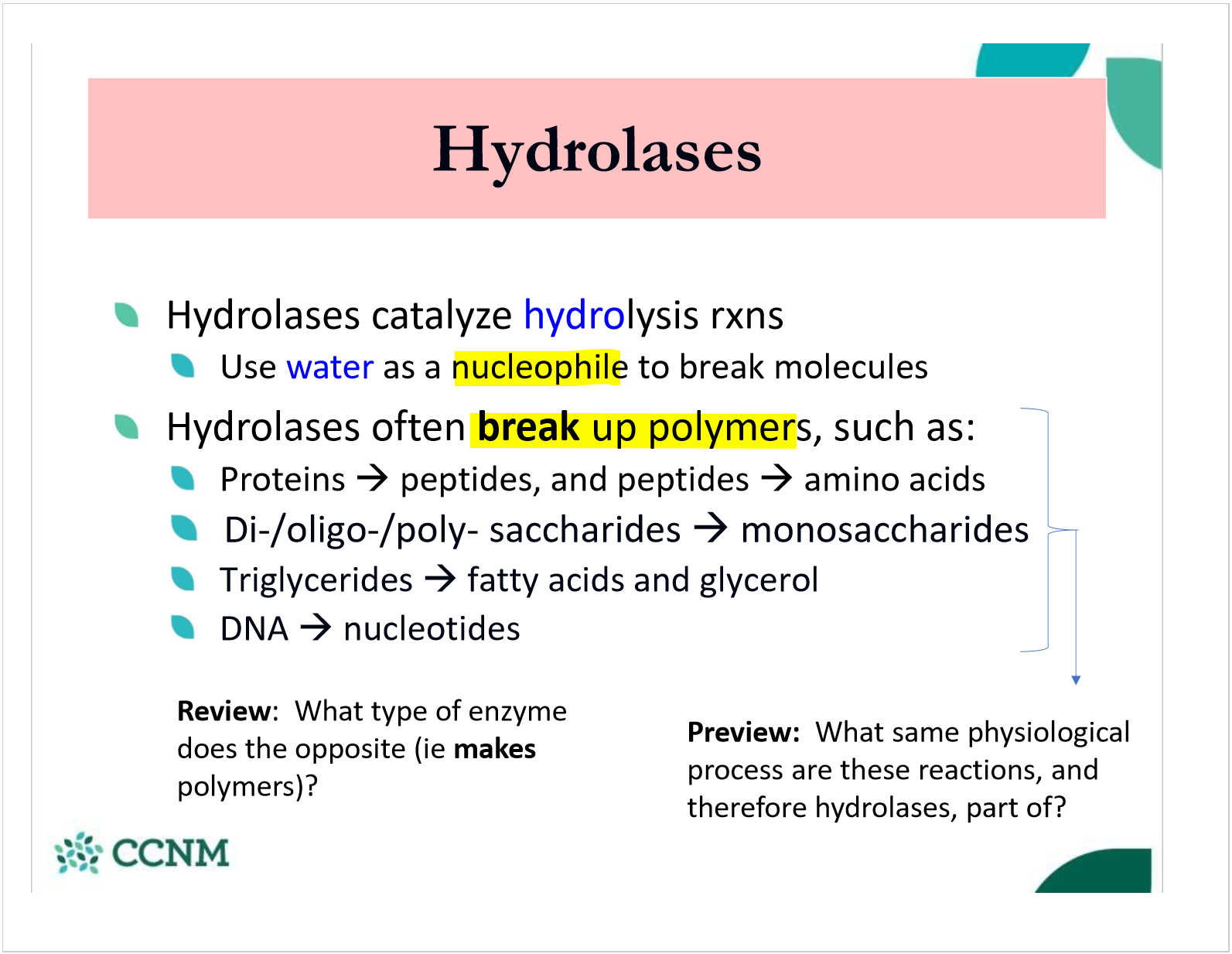
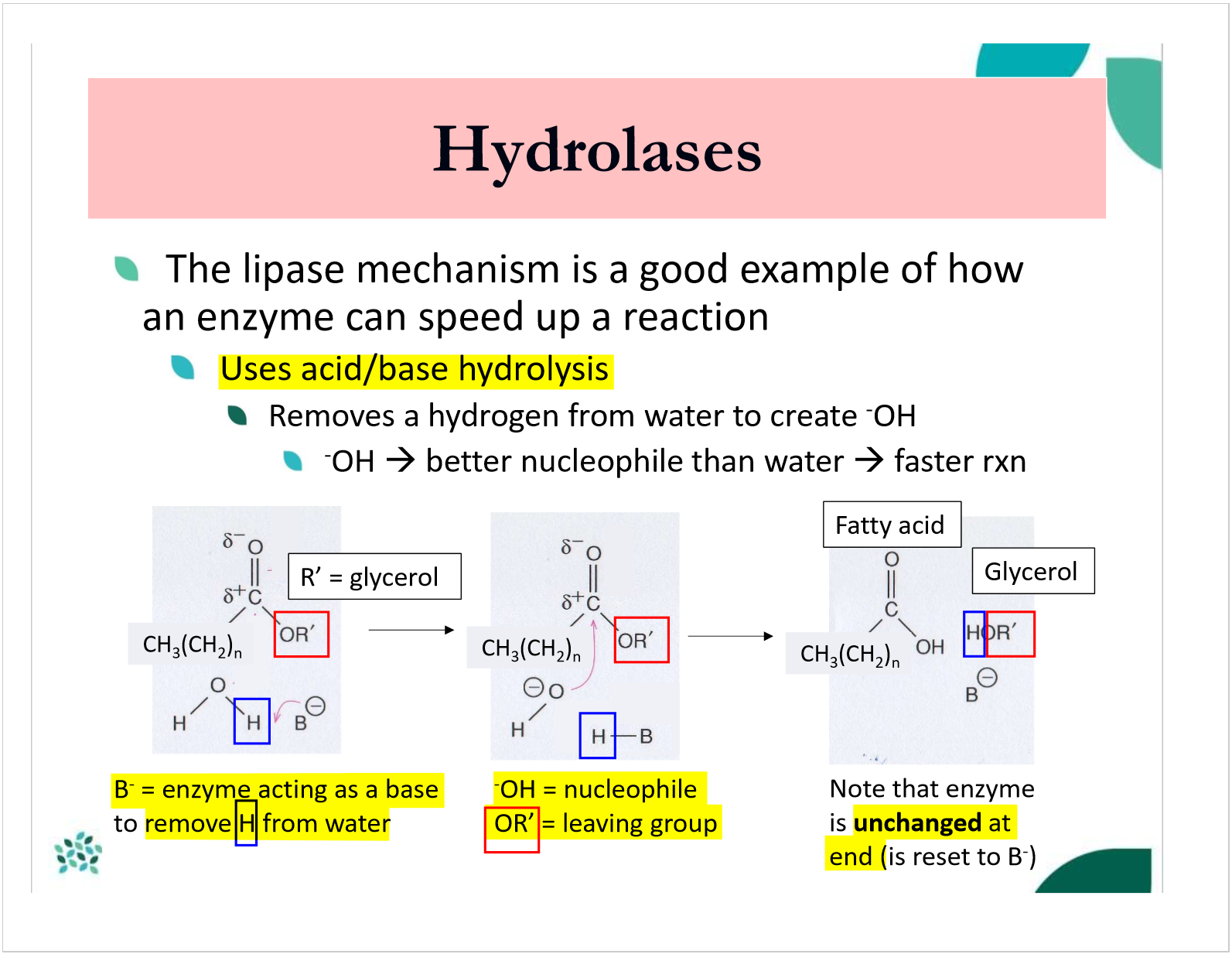
what are hydrolases?
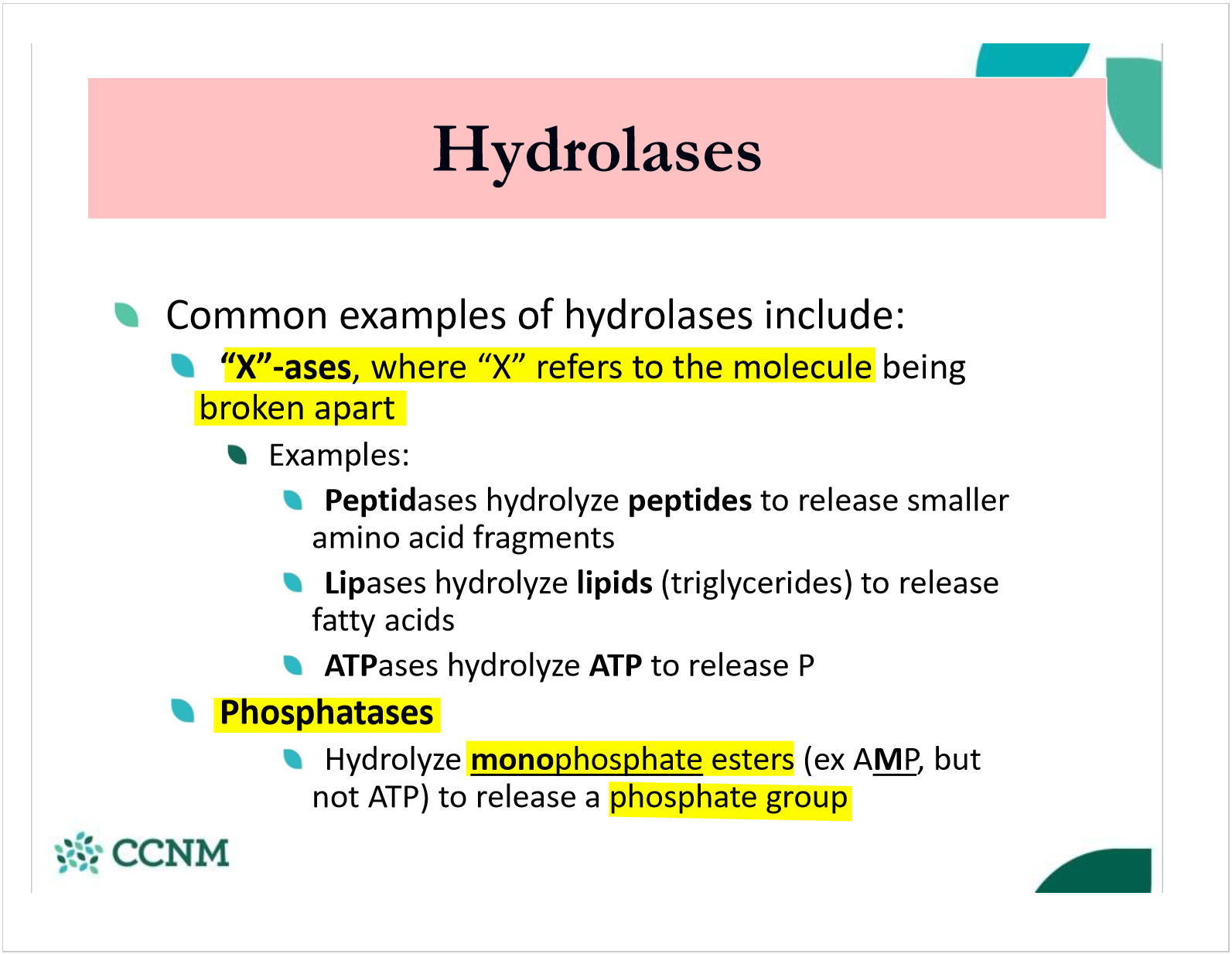
what are the common clases of hydrolases
how do hydrolases use acid/base hydrolysis?
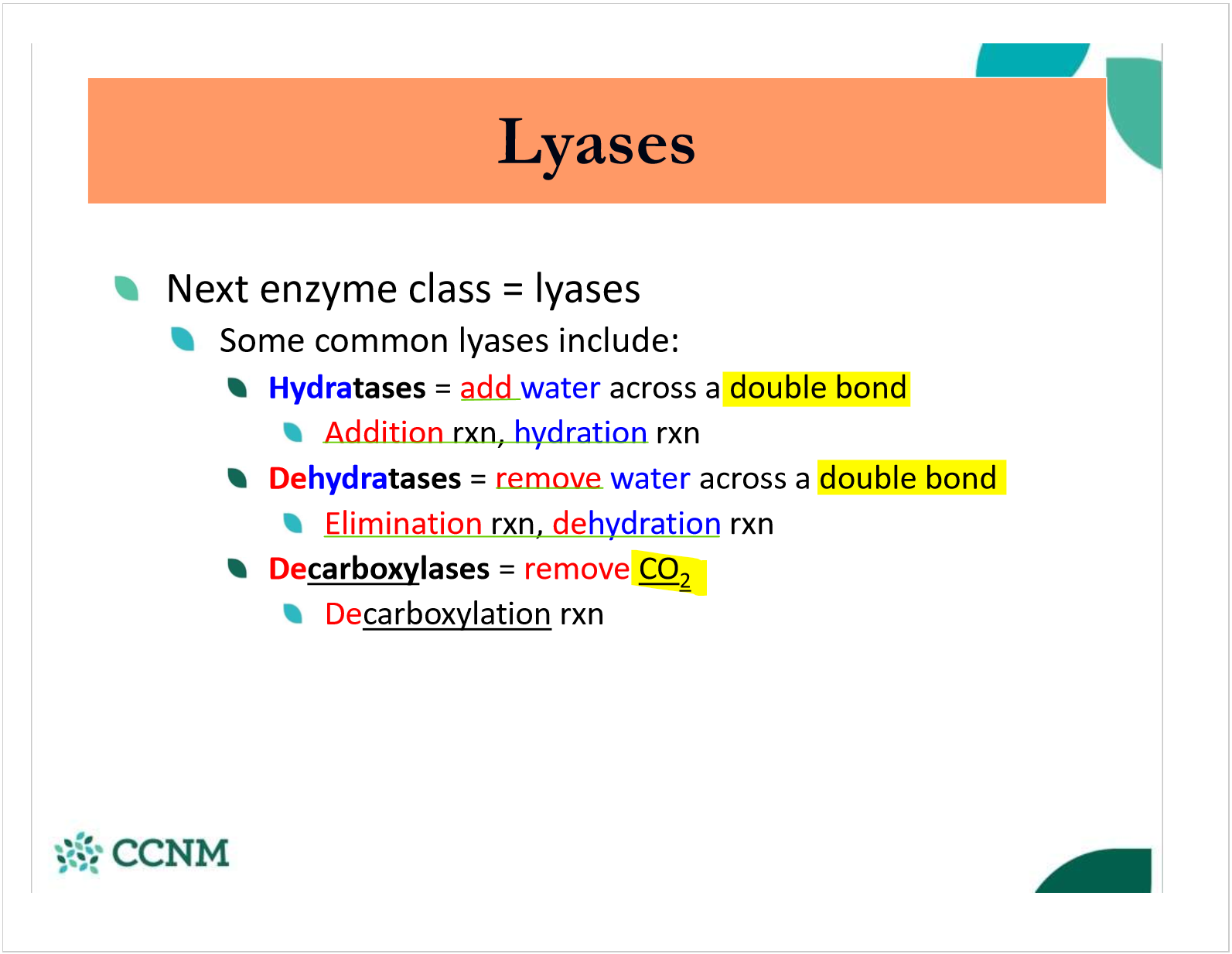
what are the common lyases?
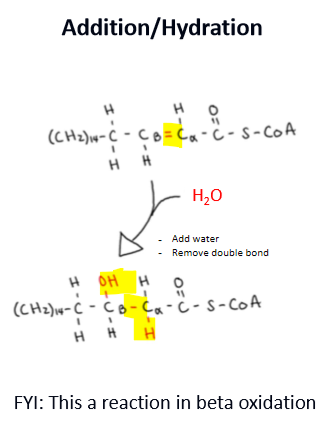
describe an addition/hydration rxn
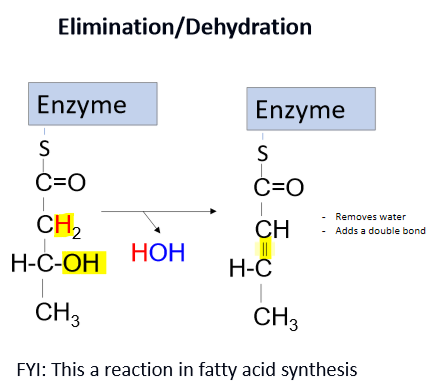
describe an elimination/dehydration rxn
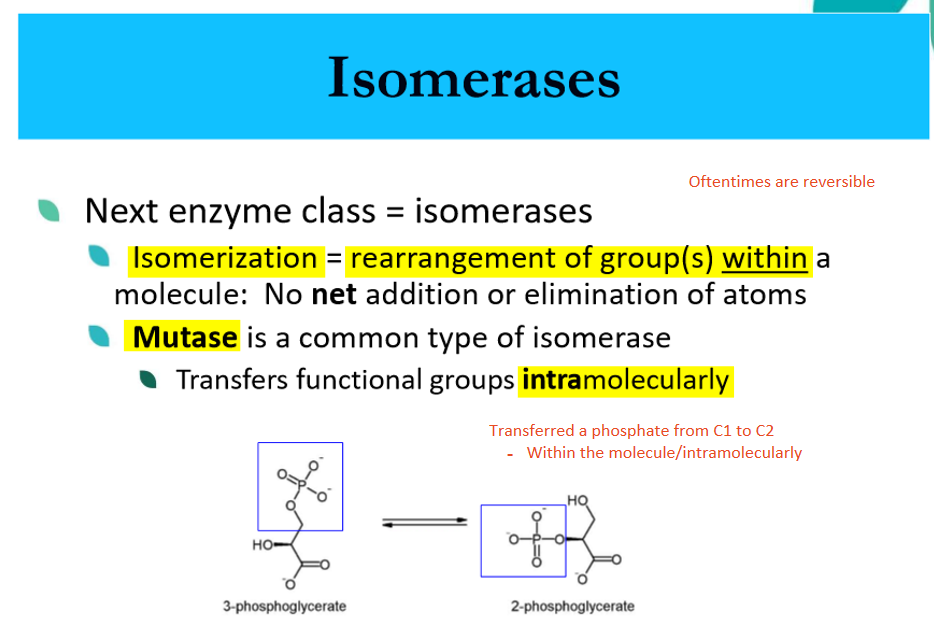
describe isomerases
mutases
what are ligases?
what are the classes?
adds amino acids together AT THE EXPENSE OF ATP
Does not use protein synthesis machinery to form peptide bond = can be made by any cell (even RBCs

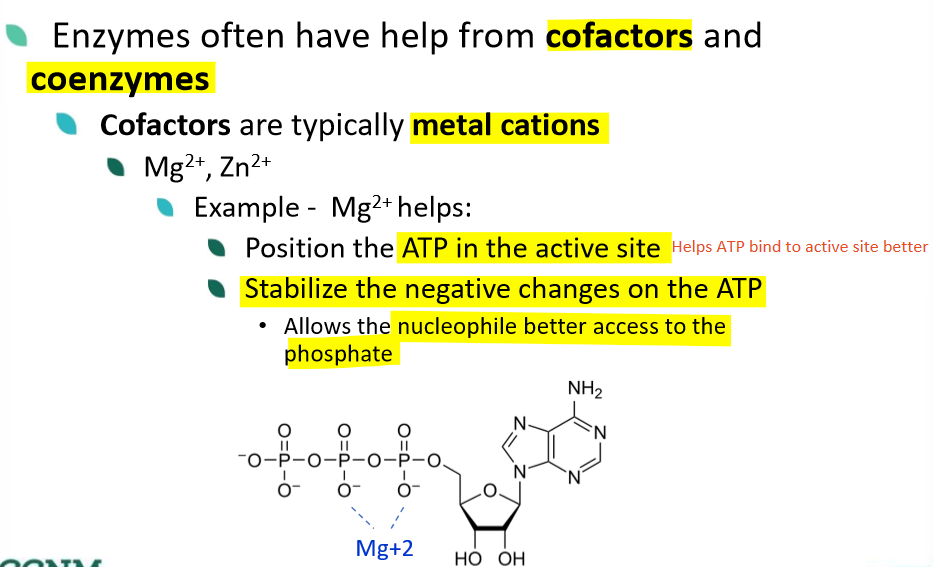
how do enzymes use cofactors?
how do enzymes use coenzymes?

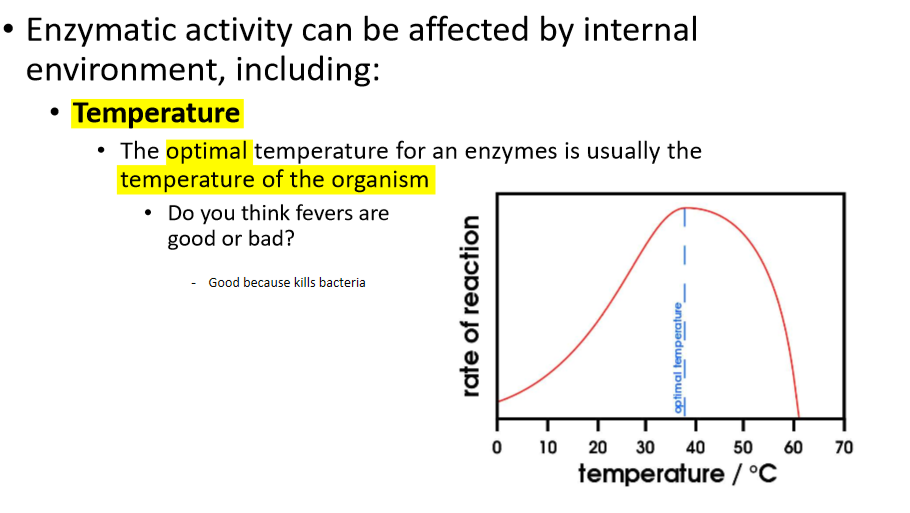
what is the optimal temperature for an enzyme?
how does pH effect an enzyme?

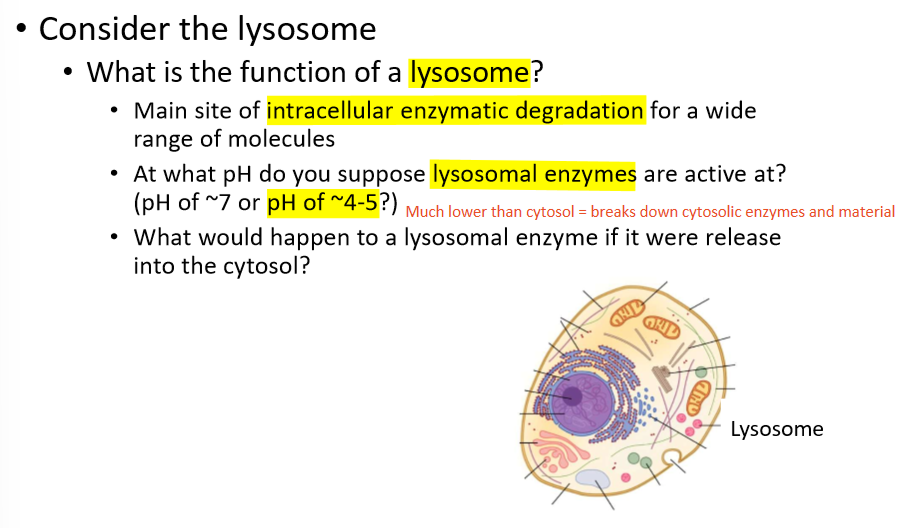
how do lysosomes effect enzymes?