2.4: Exchanging creates a circular flow and division of labour
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
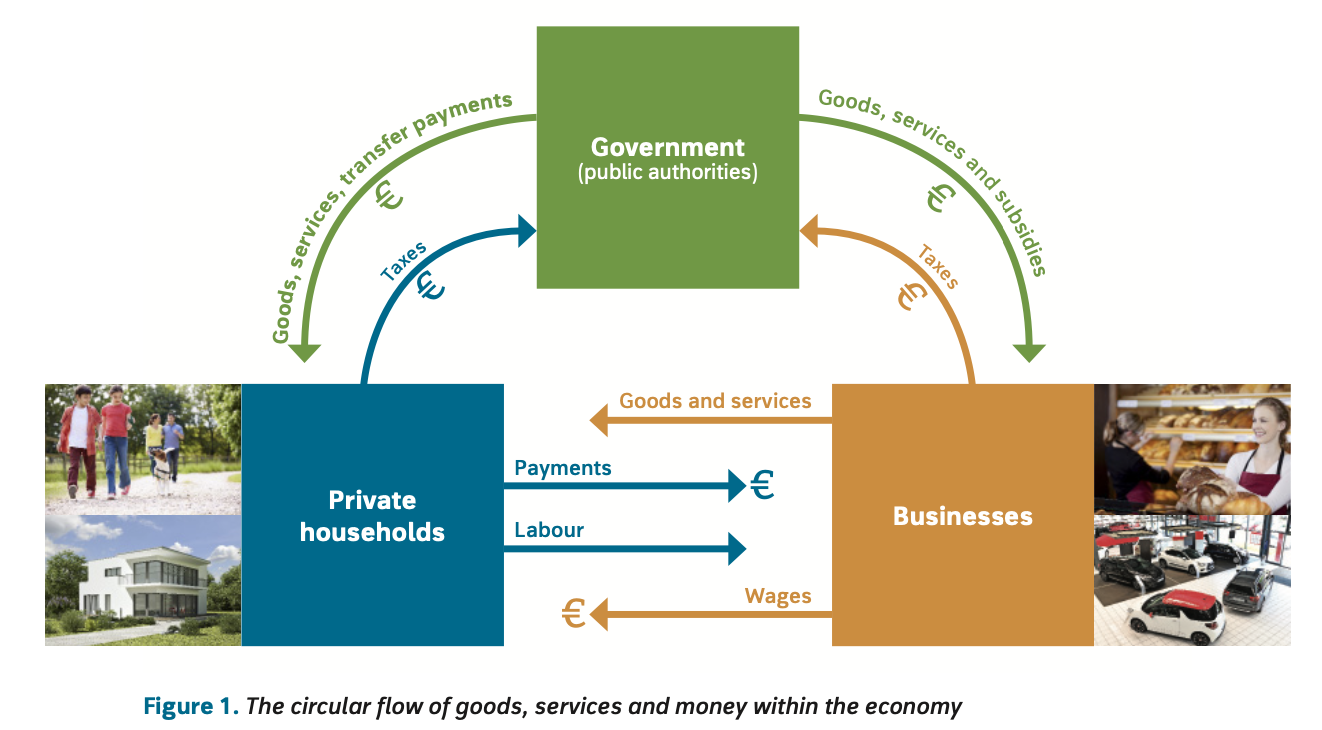
how is a circular flow of goods, services and money created
households offer labour and wages
businesses offer goods and services bought by households and other businesses
businesses recieve money for what they sell
why are exchanges carried out easily
money is a widely used and accepted means of exchange
what does money allow for
flexibility of exchange (medium of exchange)
express value of things (unit of account)
stores value over time (store of value)
why does money fulfill these functions best
it remains stable over time
what could the fluctuation of currency cost
general rise in prices = you can only buy a lower amount of goods and services
purchasing power (Value) of money declines
price indexes
allow us to measure extent of inflation
low inflation
can be tolerated
below 2% per year seen as beneficial to the economy
high inflation
purchasing power of money decreases considerably
amount of goods and services that can be bought for a certain amount of money decreases
role of public authority in the circular flow of the economy
levy taxes from households and businesses
use money to provide goods, transfer payments and subsidies
infrastructure and services like national defence, security need to provided by governments and financed by taxation
there’s a demand for the former but private businesses wouldn’t want to supply them as ‘free riders’ cannot be excluded from enjoying them
in some countries healthcare and education are also provided by public authority
division of labour and specialisation
individuals and businesses concentrate on what they do best
levels of specialisation
within households - individuals concentrate on ie. shopping, cooking, cleaning
within businesses - production, procurement, sales, finances, HR
between businesses
same level of production: special range of products
some offer all kinds of furniture
others offer just beds and couches
different levels of production
first level: production of wood and iron
second level: production of boards and nails
third level: production of tables
final level: selling them
international level
countries differ in characteristics (climate, resources, geography)
they differ in conditions for different industries and business functions
disadvantages of division of labour:
specialised workers get bored over time
less flexibility = hard to develop other skills and competencies
risky if specialisation isn’t needed anymore