Spinal Orthotics Midterm: Practice Questions
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What orthotic intervention can help manage pubic symphysis pain in pregnant women
sacroiliac orthosis
Spinal trauma can be associated with injury to which structures
vertebrae, spinal cord, ligaments, intervertebral discs
what ligament contributes to the stability of C2 in the presence of a Jefferson fracture
transverse ligament
which orthosis can be donned without moving the pt and is best at limiting cervical spine flexion
SOMI
which imaging technique should be utilized to identify potential damage to soft tissues in the spine
MRI
functional spinal unit consists of
2 vertebral bodies, facet joints, ligaments, intervertebral disc
which vertebral column is required for spinal stability
middle
severe flexion with rotation (bilateral facet dislocation)
what is the most likely mechanism of injury
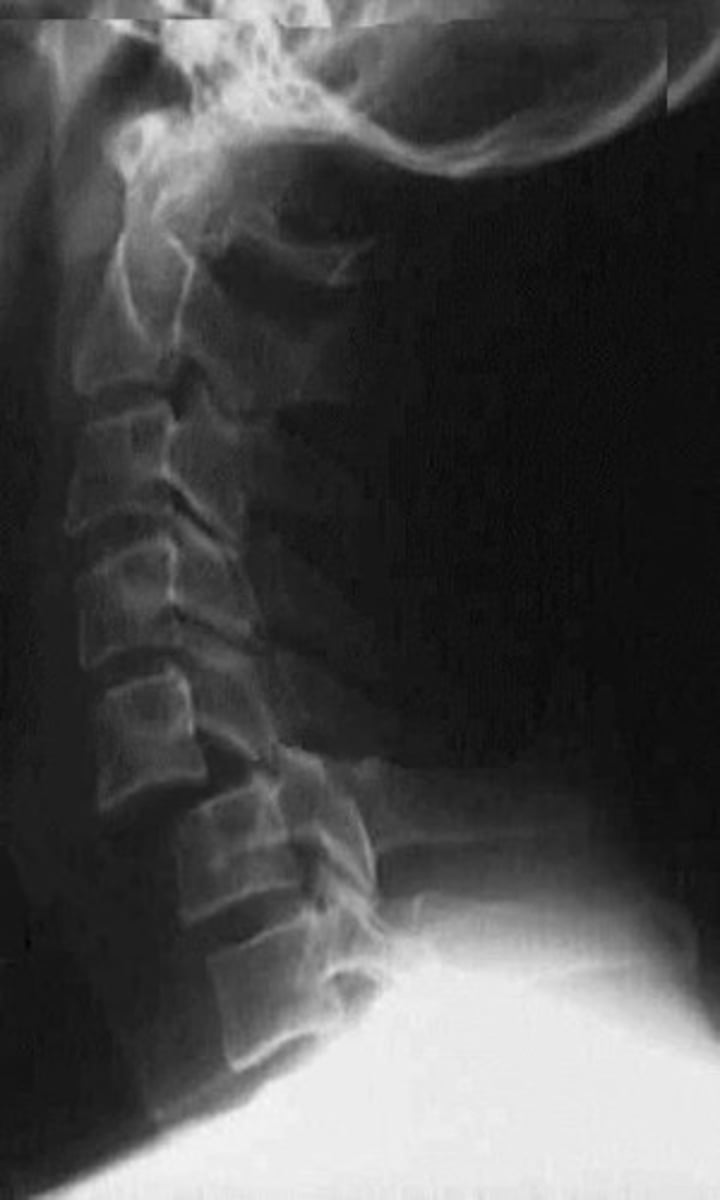
which of the fractures are at the highest risk for neurologic injury
burst and chance
____ should be performed on all identified bony injuries of the spine as it provides significantly more detail on the fracture morphology compared to an x-ray
CT scan
which of the following is a true statement regarding custom fit orthosis and/or custom fab orthosis
a custom fab orthosis may be indicated instead of a custom fit orthosis in the presence of unusual bony habitus (or an unstable fracture)
which ligament is required to be intact to maximize spinal stability
posterior longitudinal ligament
what is included in the "on-site" evaluation of a spinal trauma
assessment of vehicular fatalities, assessment of mechanism of injury, extrication time and evaluation of exposure to the environment
the vast majority of spinal injuries occur in what region of the spine
thoracolumbar
spinal radiographs of a ____ fracture show a wedge shaped vertebrae with or without loss of height of the vertebrae
compression fracture
what can be used to improve stability for injuries below L4
hip spica
the spinous process of the thoracic spine are approximately level with what
the vertebral body below
if a pt presents with an injury at the T9 vertebral body, the orthosis must cover which range of spinal levels
T6-T12
the structure of the Dens allow for what natural spinal movement
rotation
what type of orthosis would you most likely use for a pt with a pathology to the anterior column at T10
hyperextension orthosis (CASH or Jewett)
which of the following is NOT a goal of surgical treatment for neuromuscular scoliosis
-increase repositioning (you want to dec.)
**IS a goal: prevent curve progression, improve sitting balance and skin tolerance in sitting, improve cardiopulmonary function
spondylolisthesis is typically associated with unilateral fracture of the pars interarticularis and anterior slippage of one vertebra on another
False (bilateral fracture)
Complications related to the HALO
nerve damage, infection, pin loosening, pin discomfort, scarring, dysphagia and pin site bleeding
possible clinical presentations of spondylolisthesis
-tingling, numbness or weakness in one or both legs
-tight hamstrings
-difficulty walking
_________ is a condition that involves only a defect or stress fracture in the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch
spondylolysis
a pt presents with fractures at T3, T9 and L3. What is the most appropriate orthotic recommendation
CTLSO
the best orthotic recommendation for hypotonic pts with neuromuscular scoliosis is
soft TLSO
neuromuscular scoliosis may be divided into 2 major subtypes
myopathic and neuropathic
the posterior trimline of a custom TLSO extends superiorly to what anatomical landmark
spine of the scapula
______ is one example of an upper motor neuron lesion that could result in neuromuscular scoliosis
Parkinsons
__________ is one example of a lower motor neuron lesion that could result in neuromuscular scoliosis
Guillan Barre
the spine of the scapula is an anatomical landmark for which vertebral level
T3
what spinal orthosis restricts flexion at the atlantoaxial and C2-C3 segments better than any other CTO
SOMI
what are the goals of treatment for adult/geriatric pts with neuromuscular scoliosis
-improve sitting comfort and sitting tolerance
-provide mild realignment of the trunk and pelvis
-facilitate care
complete slippage of one vertebra on another is known as:
spondyloptosis
the HALO is indicated for complete immobilization of _____ and/or ________
C1 and C2
_______________ is the anatomical landmark for the T2 vertebra
sternal notch
Spondylolisthesis is most common at what spinal level
L4-L5 and L5-S1
What are some of the most common goals for utilizing the LSO anterior overlap orthosis for treatment of spondylolisthesis/spondylosis
dec. lordosis, dec. pain and inc. intra-abdominal pressure
in the non-operative management of neuromuscular scoliosis, goals for the pt include:
improve upper extremity function, slow curve progression and maintain or improve cardiopulmonary function
the goal of orthotic intervention in treating neuromuscular scoliosis is to prevent curve progression
false (just slow progression)
where would you provide compression during a bivalve casting to prevent rotation of the TLSO and help hold it in place
the waist
which of the following diagnoses is not considered to be caused by an upper motor neuron lesion
Guillan Barre Syndrome
Multiple Sclerosis
Parkinson's
Spinal Cord Tumor
Guillan Barre
curve progression can continue beyond skeletal maturity in a pt with neuromuscular scoliosis
true
Which is NOT a reason to use an orthosis in the treatment of neuromuscular scoliosis
Correct curve progression
Delay surgical intervention
Improve function by freeing hands
Improve sitting balance
correct curve progression
the orientation of the facet joints determine what motion is available between vertebra. The orientation of the facets on the thoracic vertebra allow thoracic ________ and limit _______
lateral flexion
flexion and extension
where are lower motor neuron lesions located
peripheral nervous system
a unilateral pars defect without forward slippage
spondylolysis
this is the primary motion achieved from the atlanto-axial joint
rotation
facet joints are in the closed position during
extension
Scheurmanns kyphosis is classified by
-thoracic kyphosis >45 degrees
-wedging of at least 3 vertebra
-narrowing of the disc space
what percentage of slippage is a grade 3 spondy
75%
what test provides the most detail on fracture morphology for bony injuries of the spine
CT scan
how many spinal levels above and below should a stable injury be included in an orthosis
3 above and 3 below
what ligament must be intact for maximal spinal stability
posterior longitudinal ligament
what spinal level is most commonly affected by spondylolisthesis
L5-S1 and L4-L5
what pathology/pathologies are best treated by a hyperextension orthosis
anterior compression fracture
when should orthotic treatment begin for a pt with neuromuscular scoliosis
> 20-25 degrees
scoliosis is a two dimensional abnormality of the spine
false (3D)
what symptoms are included in the clinical presentation of spondylolisthesis
back pain, inc. pain with standing but dec. pain with sitting, pain radiating in buttocks
Which of the following is NOT a complicating factor of Neuromuscular Scoliosis?
Seizures
Incontinence
Increased sensation
Dislocating hips
Increased sensation (a complicating factor is dec. sensation)
what is the mechanism of injury for bilateral facet joint dislocations
flexion and rotation
what are the indications of minerva orthosis
C3-T4 fractures
what is the forehead strap in the SOMI used for
to allow the pt to eat
who is most likely to need an SI belt
a young gymnast
a pregnant woman
an elderly man
a toddler
a pregnant woman
burst fractures are often unstable
true
the anterior trimline of a custom TLSO extends superiorly to what anatomical landmark
sternal notch
You obtain a prescription from the doctor that states the patient is in need of an orthosis to help with healing an anterior compression fracture at T12. The patient is 65 y/o and 130bs.
What are the considerations?
-What spinal levels need to be included in the trimlines: T9-L3
-Is this fracture stable or unstable?: Stable
-What do you need to consider when deciding the device you want to fit on this pt: Age, weight, abnormal anatomy, activity level, donning/doffing, pain, hyperextension moment
You obtain a prescription from the doctor that states the patient is in need of an orthosis to help with healing an anterior compression fracture at T12. The patient is 65 y/o and 130bs.
What is your orthotic recommendation?
CASH hyperextension orthosis; Sternal pad sits ½" below sternal notch, pubic pad sits ½" above pubic symphysis, posterior pad should avoid putting pressure on injured vertebre
Your patient has been in a car accident and has a hangman's fracture at C2. The patient is 25 y/o and 200 lbs
What are your considerations?
-What is the mechanism of injury of the hangman fracture: Hyperextension followed by distraction
-What are some considerations for this pt: Level/ type of fracture, fractures to other anatomy, abnormalities
-What is your orthotic recommendation if the fracture is stable: Minvera, CTO
Your patient has been in a car accident and has a hangman's fracture at C2. The patient is 25 y/o and 200 lbs
What is your orthotic recommendation?
the HALO
A 6 year old female patient presents with a diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy and a scoliosis curve of 24.° She is 38 inches tall and weighs 32 pounds. The patient has limited ambulation and most often uses a wheelchair to get around.
What type of neruomuscular scoliosis is this?
Neuropathic (upper motor neuron)
A 6 year old female patient presents with a diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy and a scoliosis curve of 24.° She is 38 inches tall and weighs 32 pounds. The patient has limited ambulation and most often uses a wheelchair to get around.
What potential non-anatomical landmarks would you mark during castin?
baclofen pump/G-tube
A 6 year old female patient presents with a diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy and a scoliosis curve of 24.° She is 38 inches tall and weighs 32 pounds. The patient has limited ambulation and most often uses a wheelchair to get around.
Discuss the 4 main goals of non-operative management of neuromuscular scoliosis
-maintain balance of spine over level pelvis
-improve upper extremity function
-reduce risk of skin breakdown (pressure, friction, temperature, moisture)
A 6 year old female patient presents with a diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy and a scoliosis curve of 24.° She is 38 inches tall and weighs 32 pounds. The patient has limited ambulation and most often uses a wheelchair to get around.
Orthotic recommendation
Thermoplastic TLSO with liner
-CP usually present with spasticity
-max control of pelvis
-excellent costal margin purchase
-3 opening designs: anterior, posterior and bivalve