Geology Lab Quiz #2 (Minerals) (copy)
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Hardness
Measure of relative ability of mineral to resist scratching
Color
The impurities in the mineral determine this
Luster
The reflective ability of a mineral, the way a mineral scatters light
Crystal Habit
The mineral’s shape
Streak
The powdered form of a mineral
Incongruent Streak
Streak color differs from the actual color of the mineral. Example: Chalcopyrite-mineral is shiny gold, yet streaks black
Specific Gravity
The density of the mineral. Example-weight juxtaposed to water
Minerals w/highest specific gravity
Gold-19.32; Lead-11.34; Copper-8.95; Iron-7.8; Galena-7.4
Is Mohs scale of hardness used for rocks or minerals?
Minerals
What minerals on Mohs scale can cut glass?
Minerals w/hardness of 5.5 and greater. Ex: Diamond(10); Corundum(9); Quartz(7); Orthoclase(6)
Minerals used as raw ORE for extracting metals through smelting process
Hematite; Magnetite; Limonite; Azurite; Malachite
Minerals that leave a streak
Ones with hardness less than 7. Ex-Graphite; Talc; Satin Spar; Alabaster
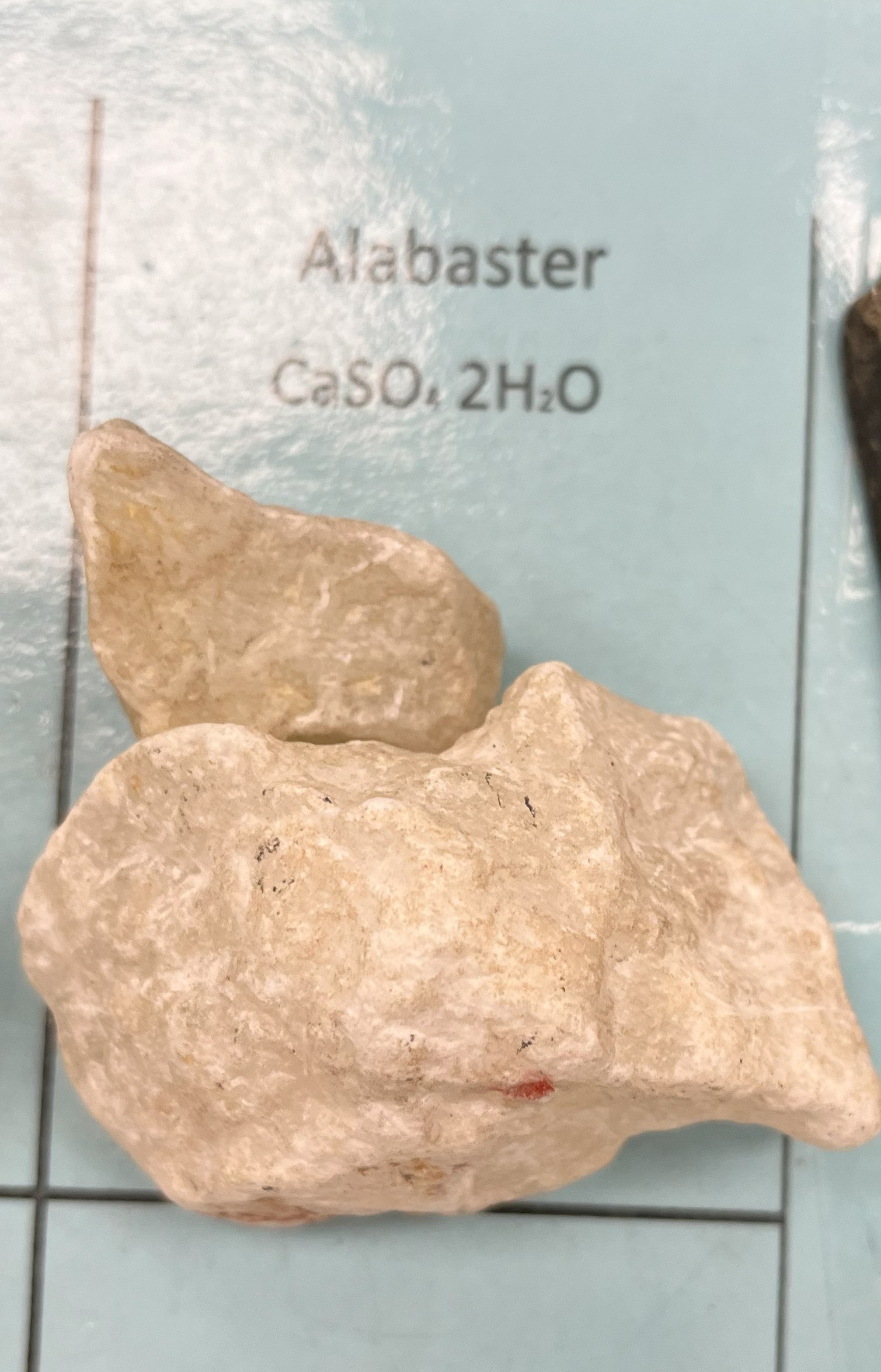

Alabaster
Gypsum/Calcite
Mohs Hardness 2
Forms in layers due to evaporating sea water. Chalky, white color
Uses-sculpting and industrial
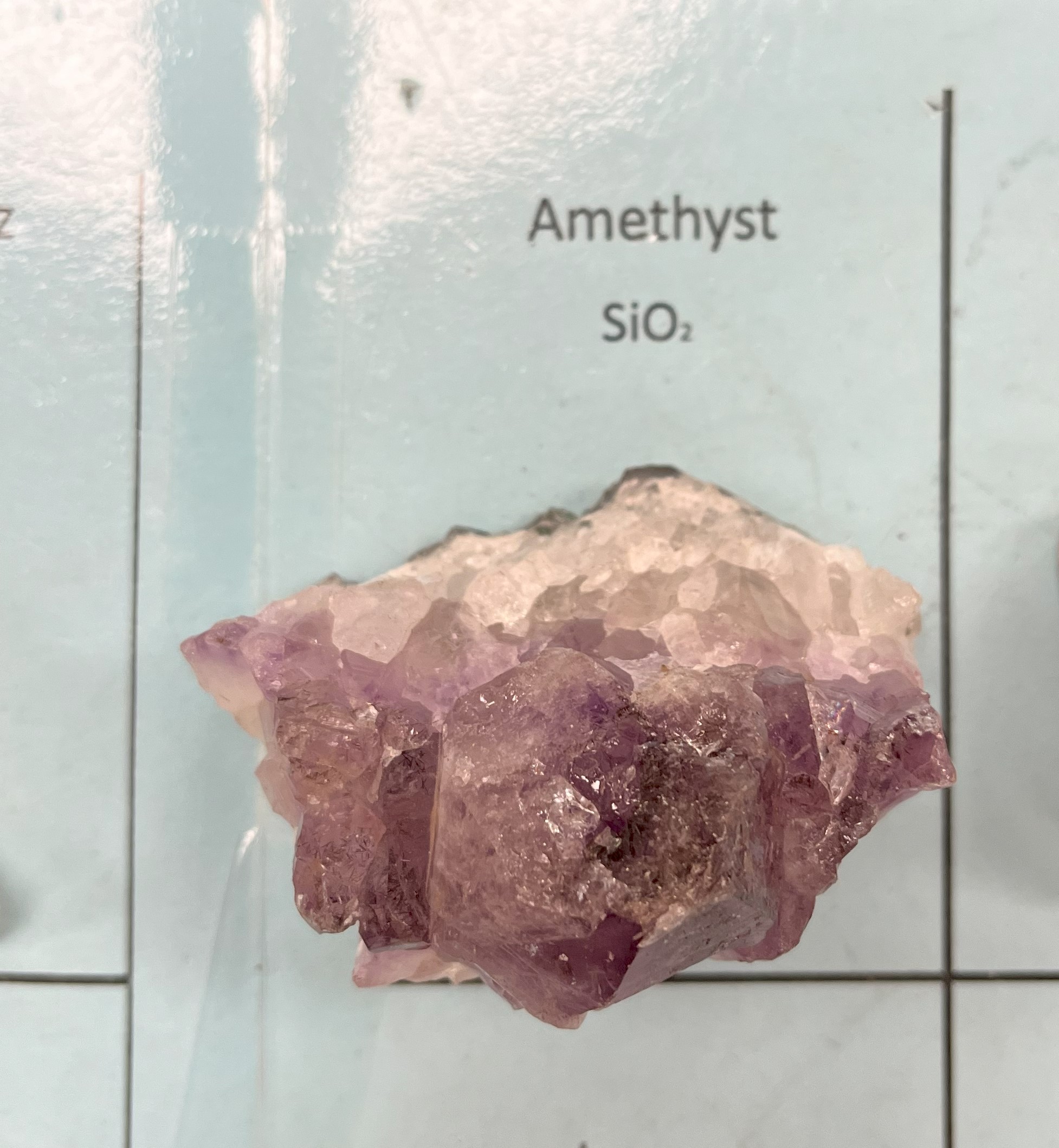
Amethyst
Color: Light to dark purple
Mohs Hardness: 7
Transparency: Transparent to translucent
Specific gravity: 2.6–2.7
Luster: Vitreous (glassy)
Crystal structure: Hexagonal, when combined w/rock it makes a geode
Uses; Jewelry
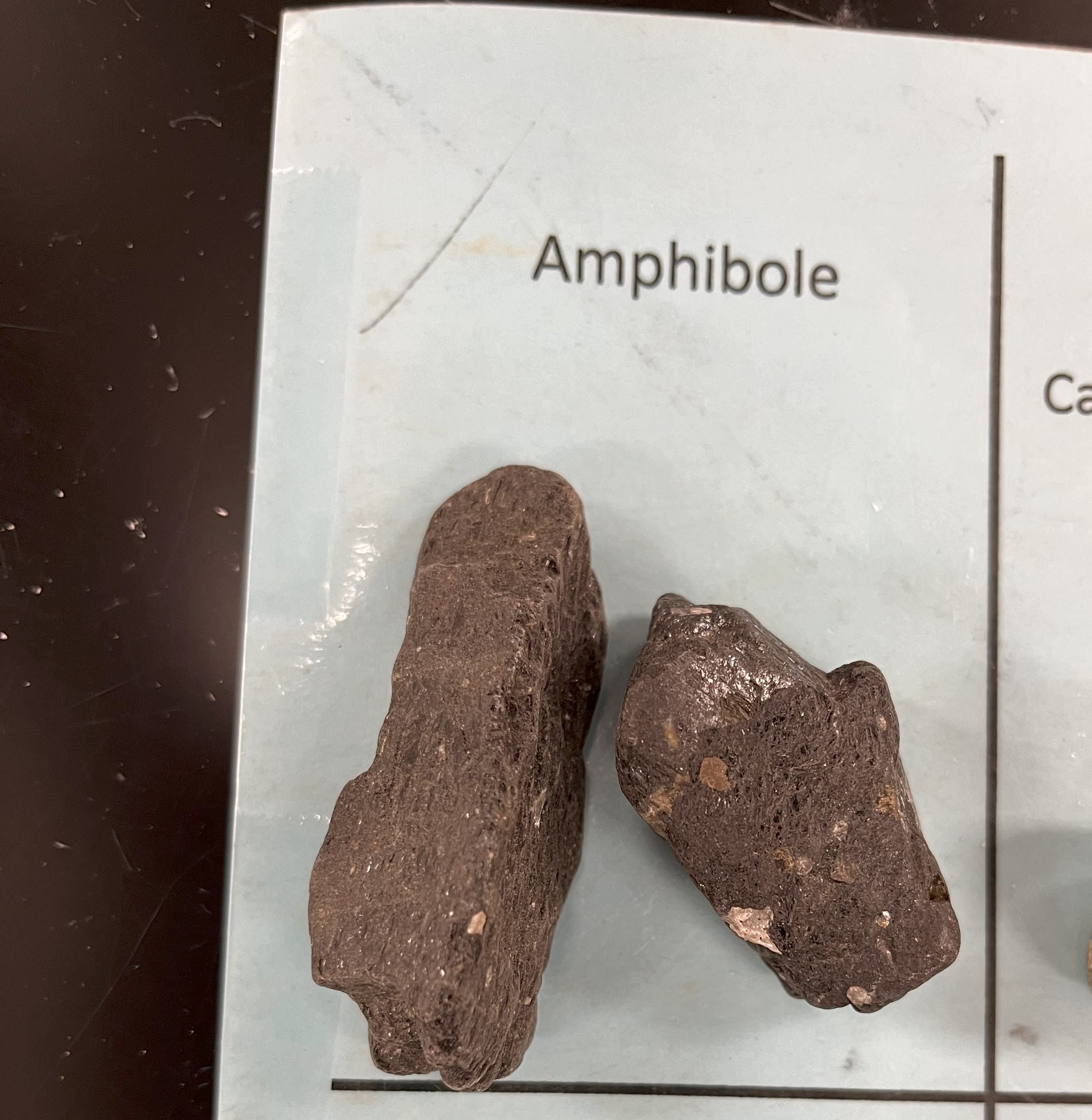

Amphibole
Crystal habit: Long prismatic or fibrous
Mohs hardness: 5–6
Usually black with straight-line orientation
Luster: Vitreous, dull, or opaque
Uses: paving stones and as a veneer or facing on buildings

Apatite
Color: Usually green but can also be brown, blue, yellow, purple, pink, or colorless
Mohs Hardness: 5
Specific gravity: 3.1 to 3.3
Crystal habit: Elongated, small, hexagonal crystal structure
Uses: Industrial; fertilizer; or gemstone
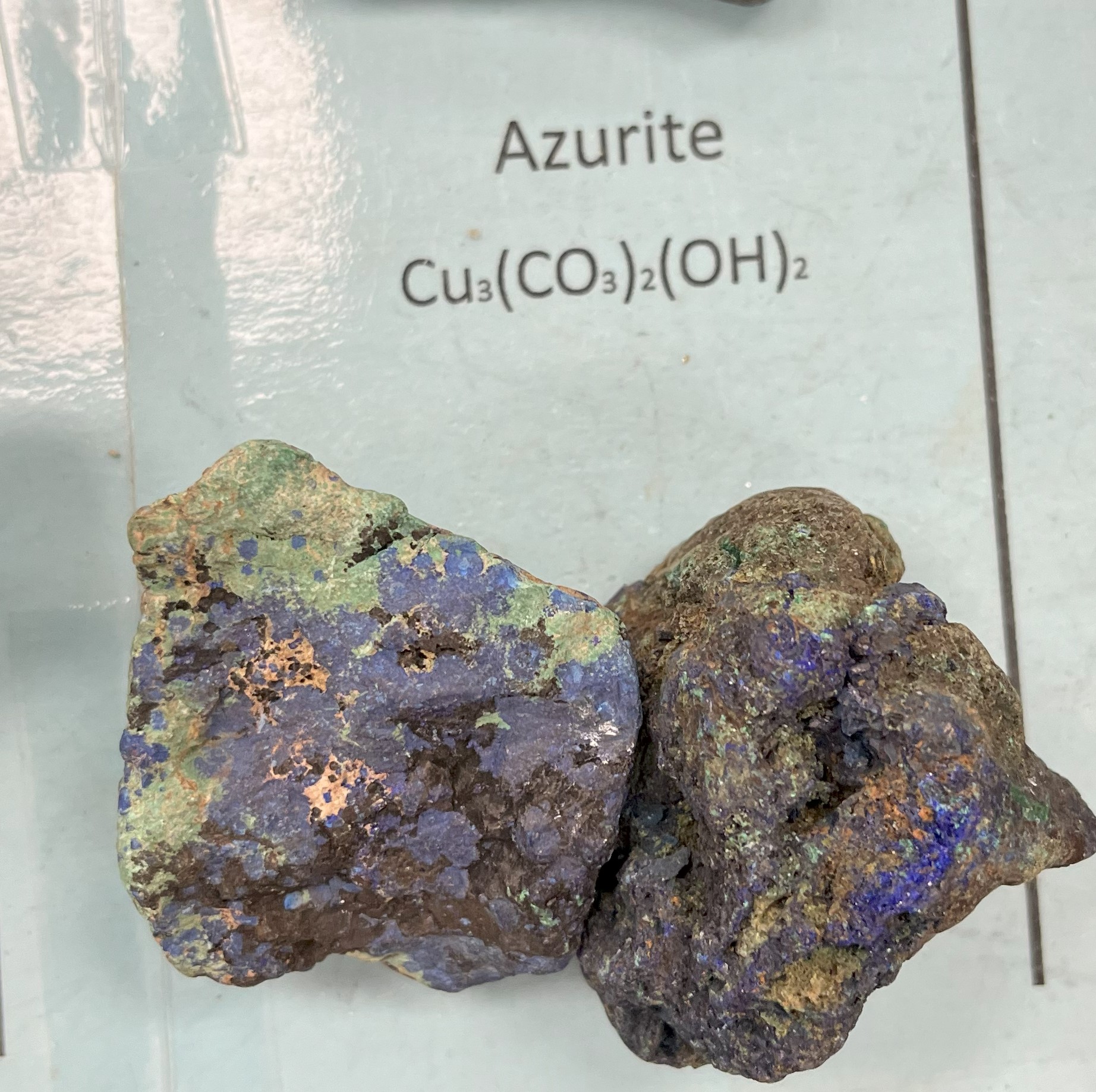

Azurite
Color: Azure-blue, deep blue
Crystal habit: Monoclinic
Copper ore
Luster : vitreous
Mohs scale hardness: 3.5 to 4
Specific gravity: 3.773
Uses: jewelry, as an ornamental stone, and as a pigment for painting
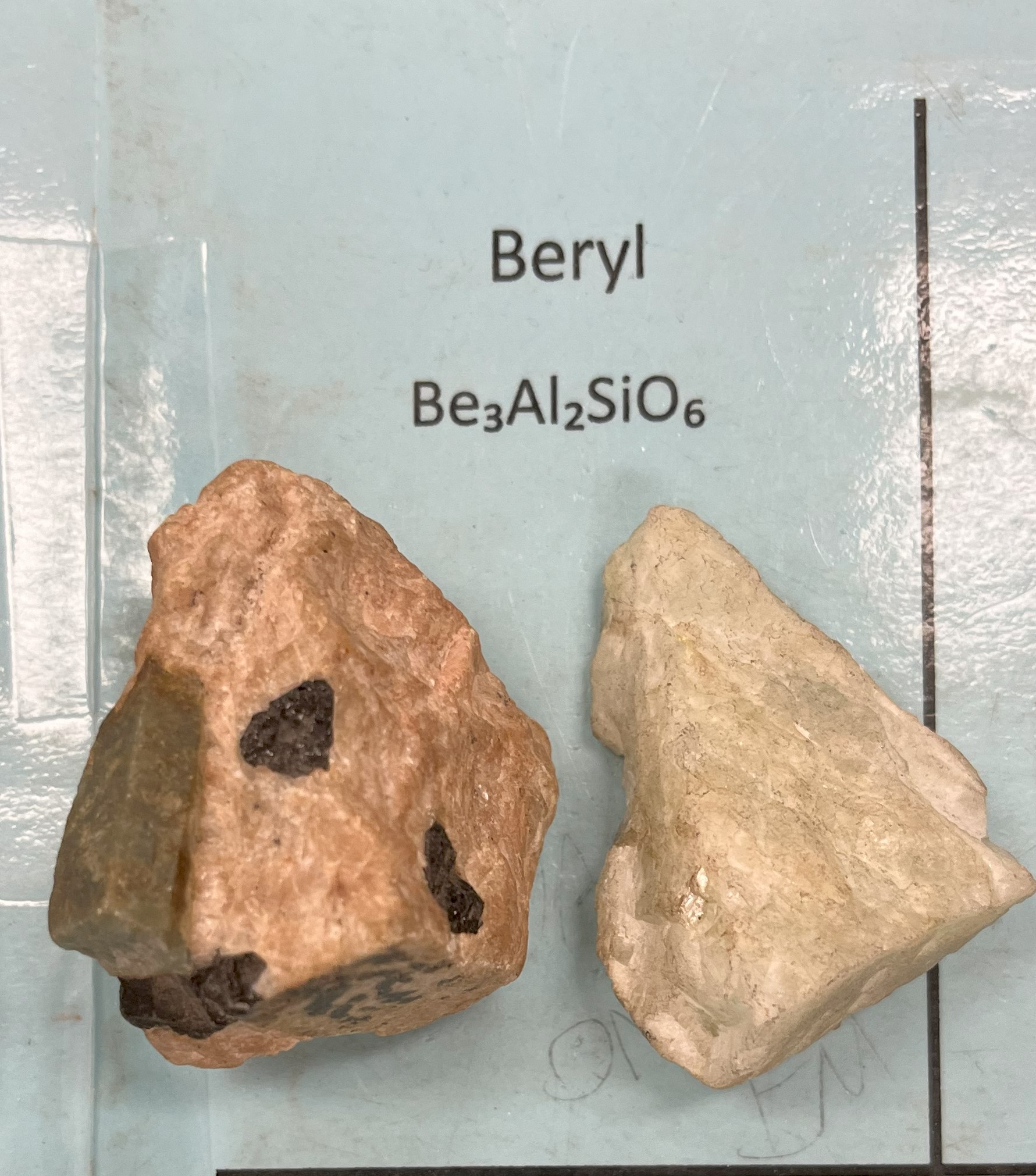

Beryl
Color: green
Mohs Hardness: 7.5–8
Luster: Vitreous to resinous /transparent to translucent
Breaks messily and rarely shows crystal habit. True form hides in rock. Will shatter
Specific gravity: 2.63–2.92
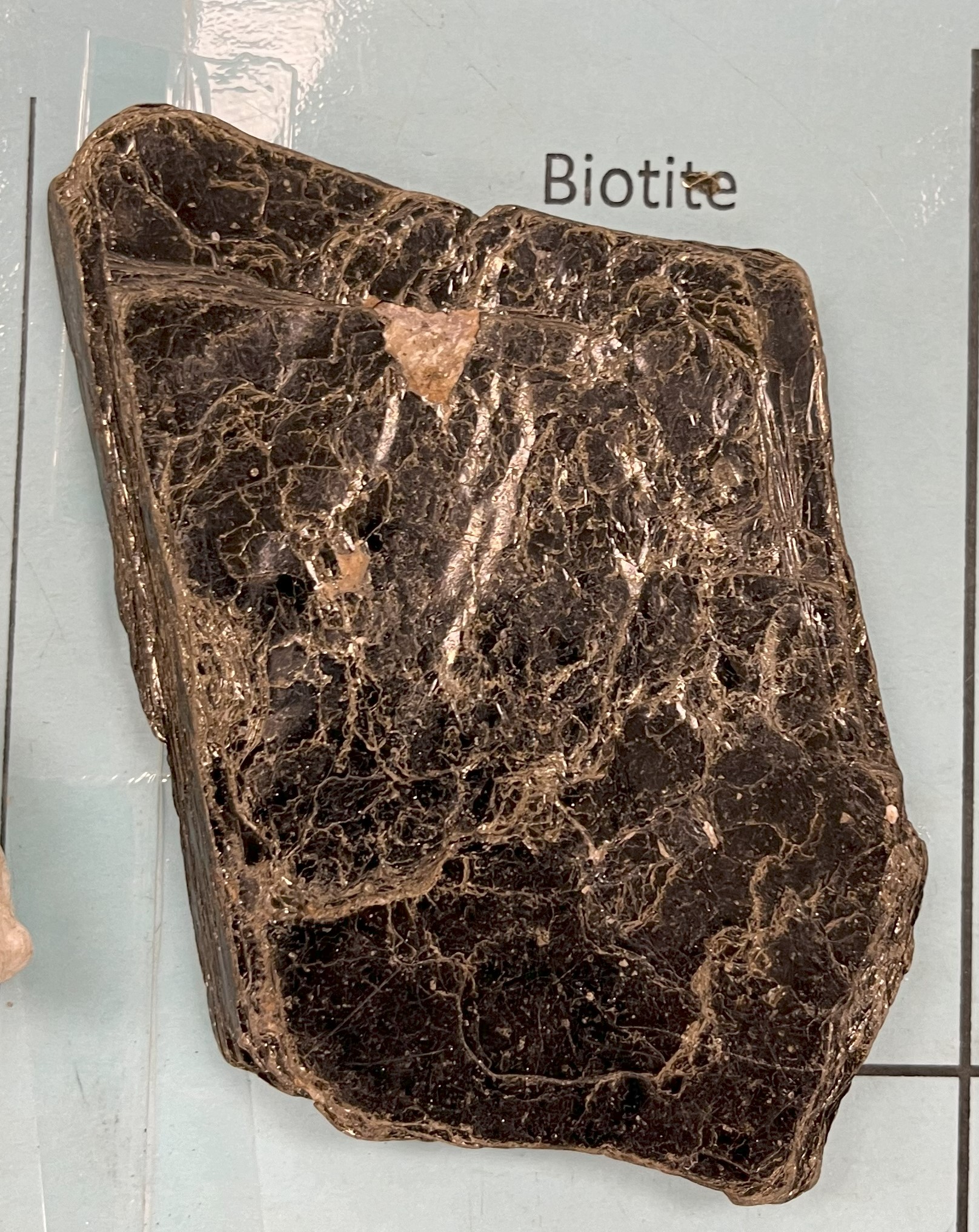

Biotite
Color: Black, dark brown, dark green, reddish black, yellow, and white
Streak: White or gray
Hardness: 2.5–3 on the Mohs scale
Transparency: Translucent to opaque
Luster: Pearly to submetallic
Specific gravity: 2.7–3.1 g/cm3
Crystal forms: Thick flakes, micaceous masses, tabular, foliated, flaky, and scaly
Uses: commercial; paint filler, rubber products, roofing shingles, asphalt

Chalcopyrite
Color: Brassy to golden yellow
Hardness: 3.5–4
Luster: Metallic
Streak: Greenish black soft & powdery (Incongruent streak)
Diaphaneity: Opaque
Specific gravity: 4.1–4.3
Optical properties: Opaque
Crystal system: Tetragon

Corundum (Rubies and Sapphires)
Color: Golden-brown, blue, red, pink, yellow, grey,
Mohs Hardness: 9 making it one of the hardest minerals
Streak: White when scratched on a streak plate
Luster: Adamantine, vitreous, and pearly
Density: 4.02 g/cm3
Transparency: Transparent, translucent, opaque
Tenacity: Brittle
Parting: Rhombohedral sometimes perfect
Uses: gemstones, industrial, sandpaper

Flint
Mohs Hardness 7, can scratch steel.
Color: Flint can be black, gray, brown, white. Translucent or semi-translucent.
Concordial fracture, Flint breaks with a glasslike fracture that can produce sharp edges.
Flint can produce sparks when struck with steel. This property makes it useful for starting fires and making tools.
Small crystal size makes it tougher than many other rocks and stones.
Texture: sharp, slick
Flint also has a waxy or dull luster and can be translucent or opaque. It takes a good polish and then has a vitreous luster.
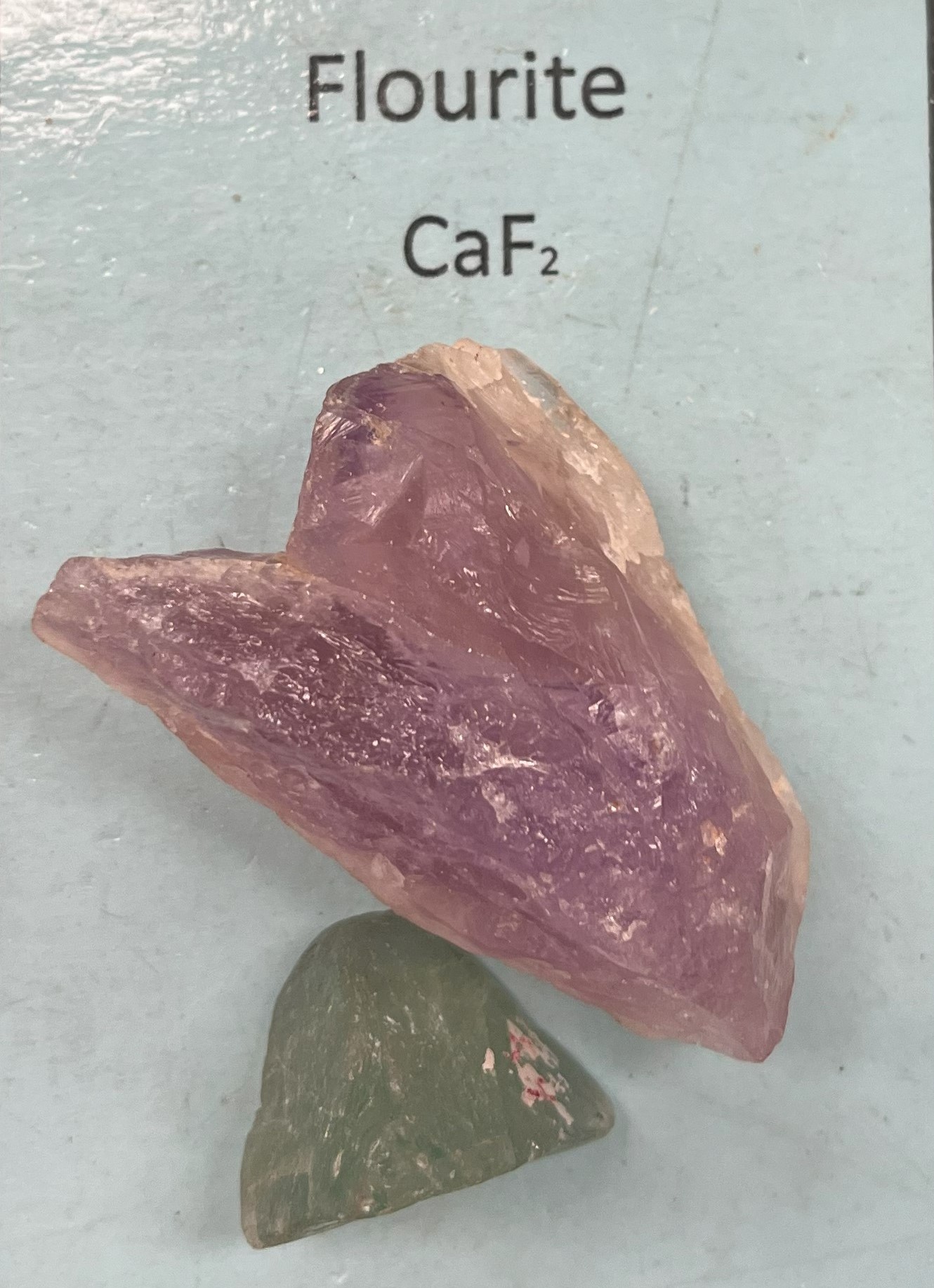

Flourite
Mohs Hardness: 4 softer than nail
Light green or purple
Crystal system: Isometric
Crystal forms: Cube, octahedron, dodecahedron, tetrahexahedron, trapezohedron, trisoctahedron, and hexoctahedron
Luster: Vitreous, resinous, or dull
Specific gravity: 3.2
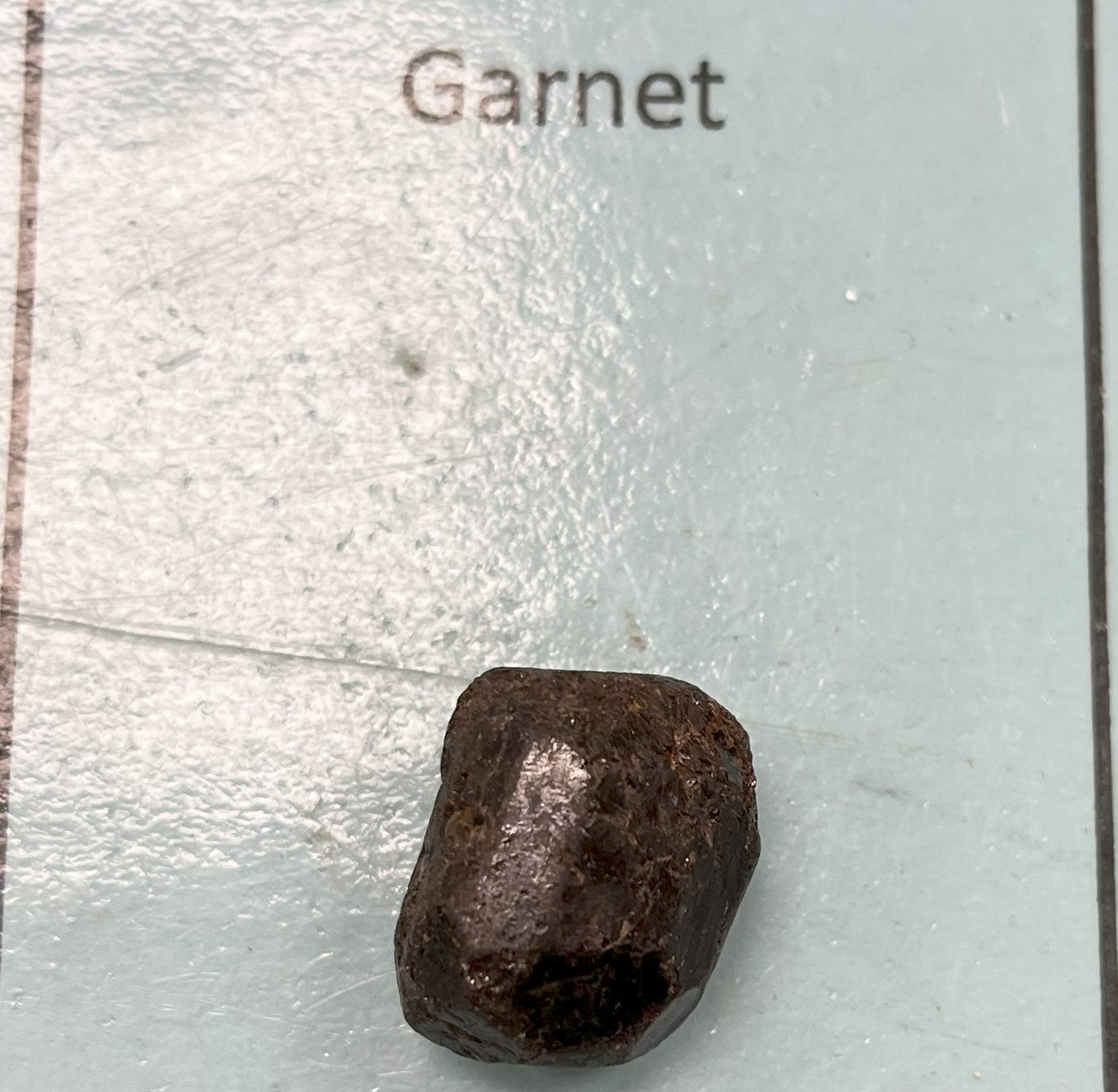

Garnet
Color: red, burgundy, black or tan Crystal habit: 12 sides, dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
Mohs Hardness | 6.5 – 7.5 (very hard) |
Specific Gravity | 3.6 – 4.3 (increases with iron content) |
Luster | Vitreous (glass-like) to resin-like, transparent to translucent. |
Streak | White (or pale shade of sample's color) |
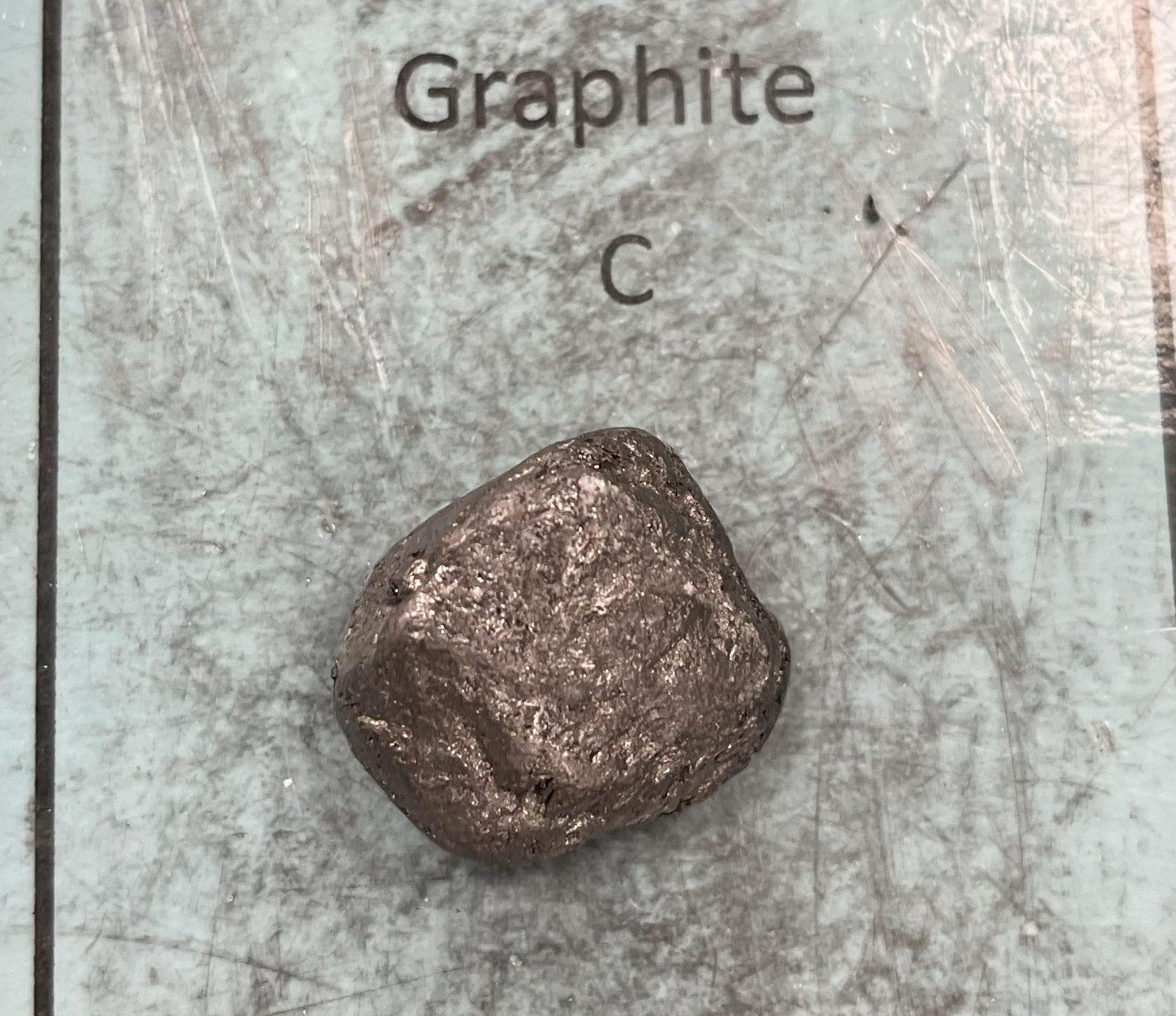

Graphite
Mohs Hardness: of 1–2
Color: Graphite is dark gray to black, opaque, and shiny.
Feel: Graphite has a greasy feel and a low specific gravity.
Structure: Graphite has a hexagonal, multi-layer planar microstructure with alternating layers.
Metallic and non-metallic properties. Made from carbon just like diamonds, except graphite is made closer to the earth’s surface.
Uses: Graphite is used in high-temperature lubricants, brushes for electrical motors, friction materials, battery and fuel cells, and pencil "lead". Graphite is also used in furnaces and brake linings.
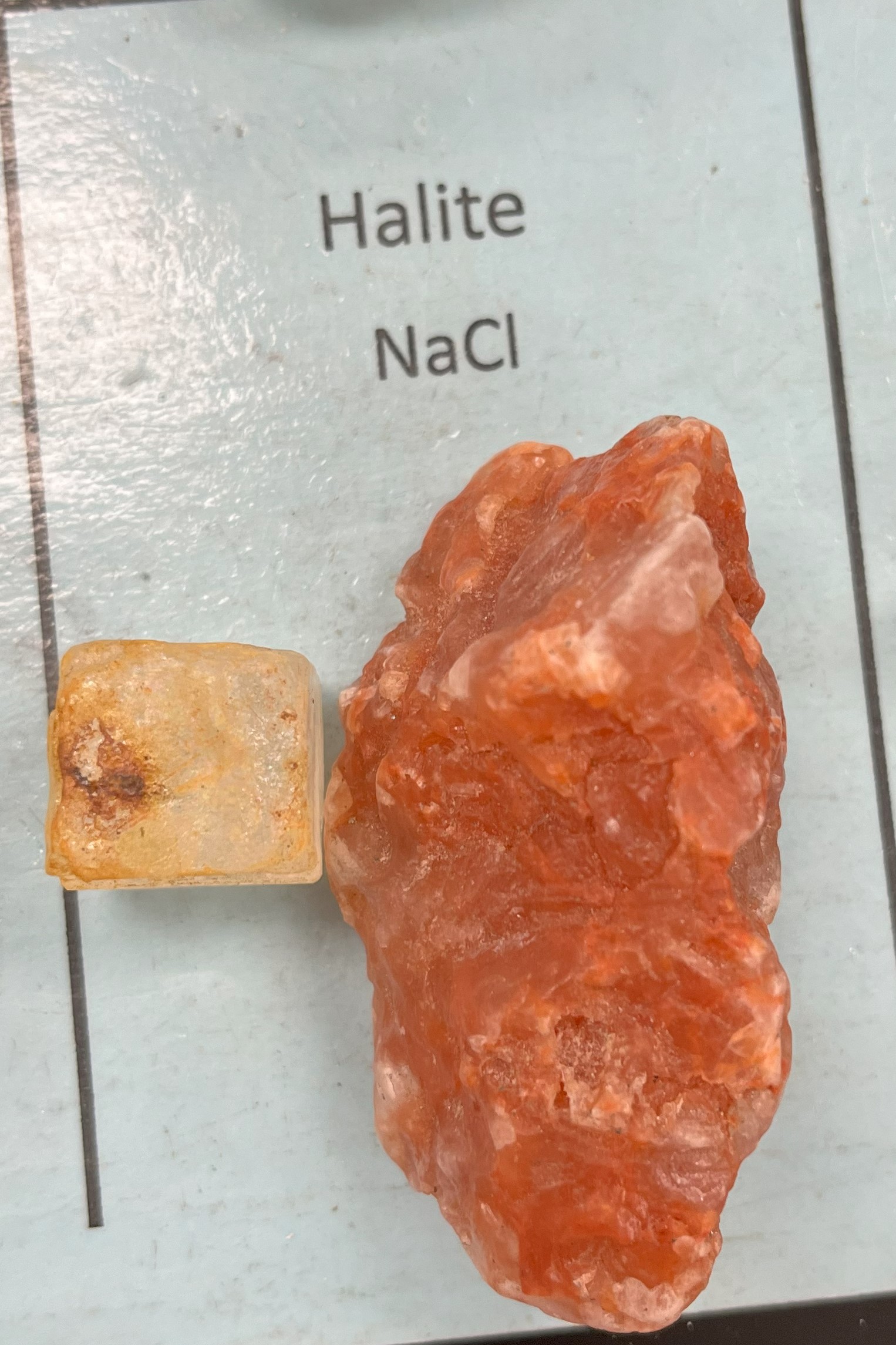

Halite
Color: Usually clear or white, but can be red or orange with impurities
Mohs Hardness: 2.5 (soft)
Fracture: Conchoidal
Streak: White
Luster: Vitreous
Crystals: Isometric, cubic
Taste: Salt
Uses: Rock salt

Hematite
Mohs Hardness: 5 - 6
Color: Black to silver gray, in earthy forms is red to brown
Iron ore
1st mineral identified on Mars
Specific gravity: 5.3 feels heavy
Streak: Distinctive reddish-brown streak
Forms in aquatic environments

Jasper
Mohs Hardness 6.5 -7 will scratch glass
Color: Brown, reddish brown
Crystal habit; hexagonal breaks with a smooth surface can be highly polished
Specific gravity 2.5- 2.9
Uses: ornamentation or as gemstone or items such as vases, seals and snuff boxes
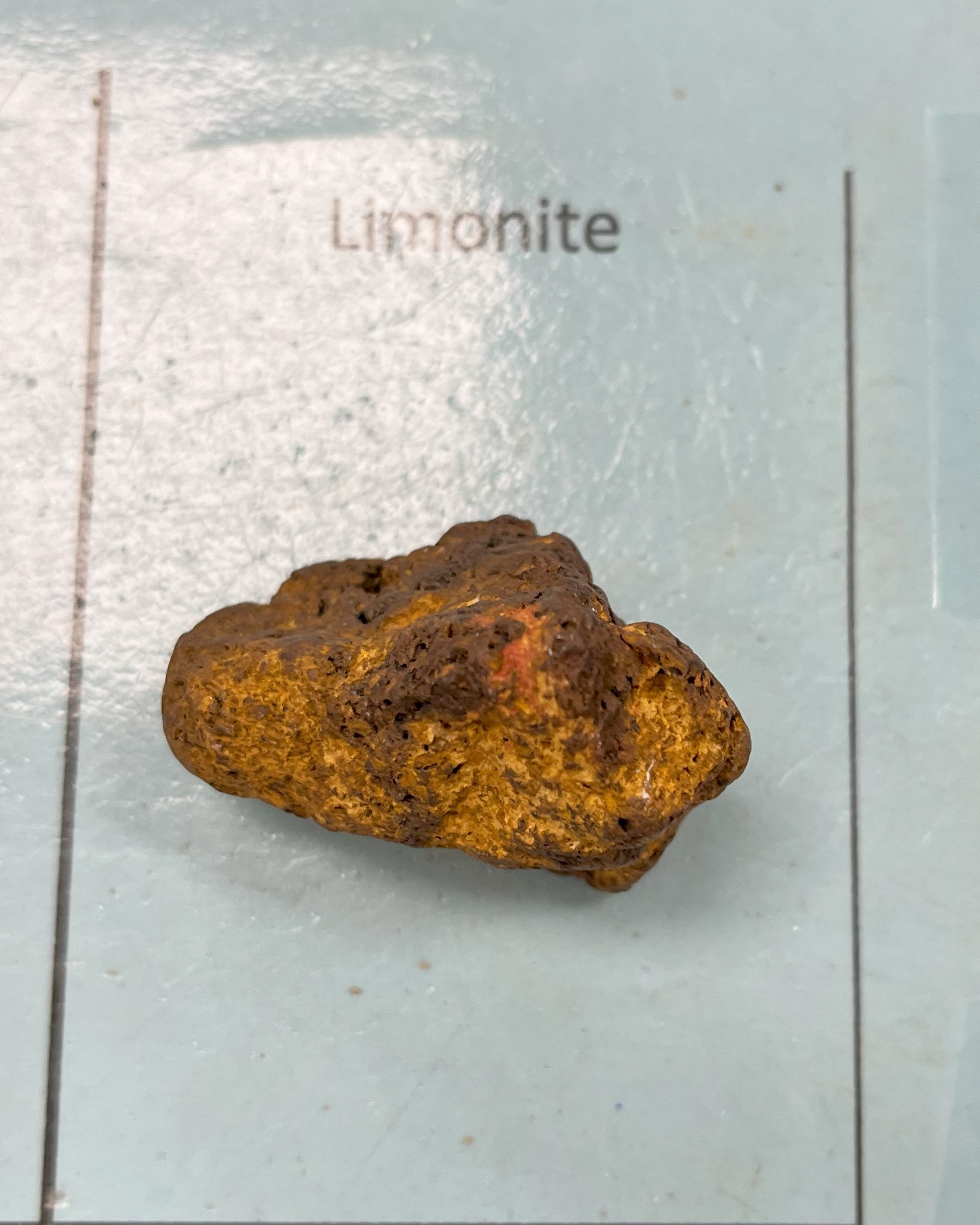

Limonite (Iron Ore)
Color: Yellow, brown, or reddish-brown
Streak: Yellowish brown
Mohs Hardness: 4–5.5
Luster: Dull, vitreous, or silky porous
Specific gravity: 2.7–4.3
Transparency: Opaque
Fracture: Splintery, uneven
Tenacity: Brittle

Magnetite
Color: Black or brownish-black
Hardness: 5.5–6.5
Specific gravity: 5.2
iron ions
Lustre: Metallic, sub-metallic
Streak: Black
Density: 5.175 g/cm
Crystal system: Isometric
Ferromagnetic: Meaning it is strongly attracted to magnetic fields

Malachite (copper ore)
Mohs Hardness: 3½ - 4
Colour: Bright green, with crystals deeper shades of green, even very dark to nearly black; green to yellowish green in transmitted light.
Streak: Light green.
Mohs Hardness: 3½ - 4
Luster: silky, earthy. Transparency: Opaque.
Patinas in the copper ore is what turns it green, just like the Statue of Liberty because it also is made with Malachite

Milky Quartz
Silicate dioxide (SiO2)
Hardness: 7 will scratch glass
Crystal system: Rhombohedral
Fracture: Conchoidal
Luster: Vitreous to greasy
Streak: White

Muscovite
Form of Mica, sheet silicate
Color: Usually colorless, white, or silver, but can also be yellow or brown
Formation: produces thin sheets or flakes
Mohs Hardness: 2 to 2.5
Crystal structure: Aluminum silicate sheets weakly bound together by layers of positive ions
Lustre: Vitreous, silky, pearly
Transparency: Transparent, translucent
Streak: white
Specific gravity: 2.8–2.9
Uses: industrial filler, lubricant, electrical and thermal insulator
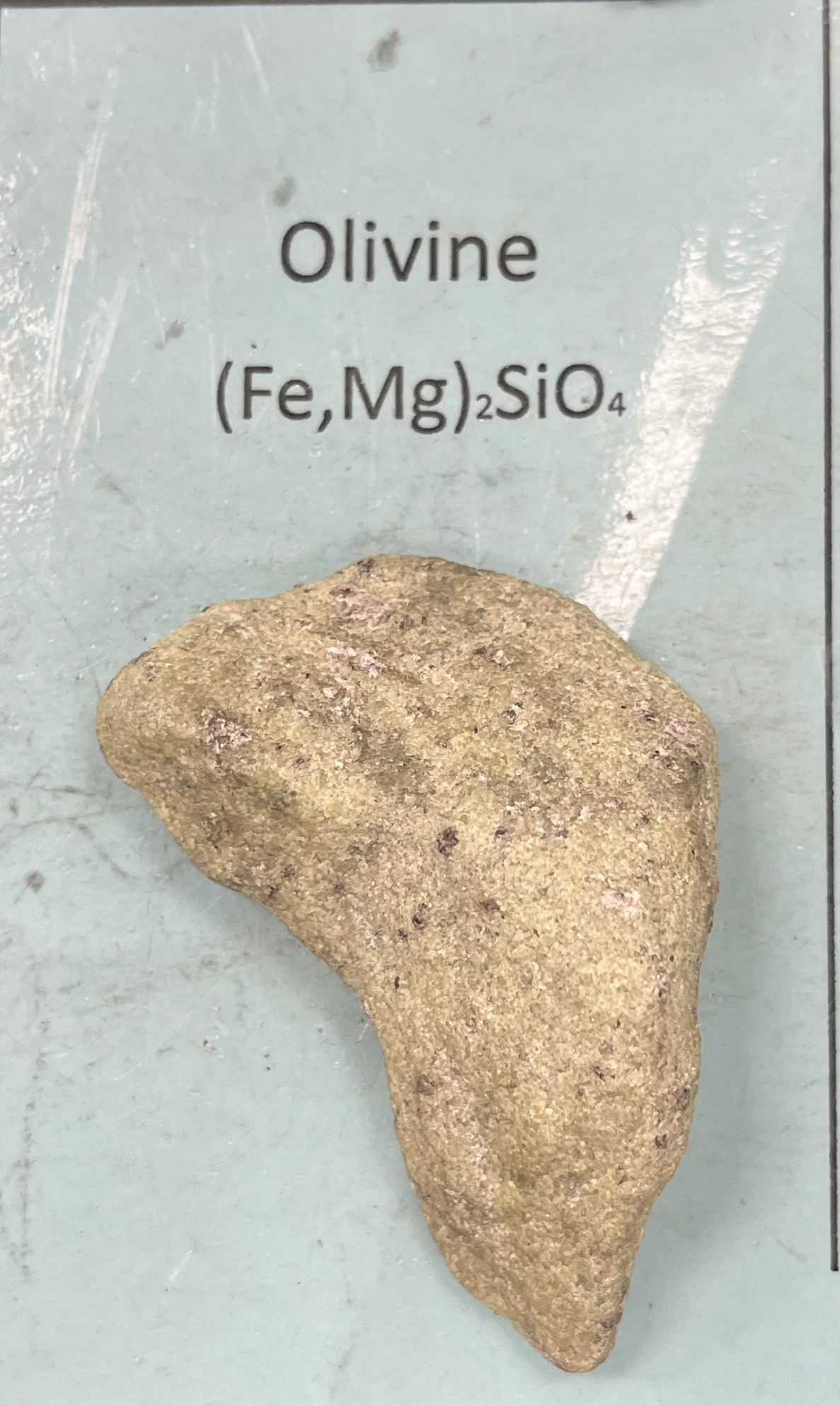

Olivine
Color: Olive green, yellow green.
Gritty texture
Uses: Industrial abrasives, refractory sand in steel manufacturing
Mohs Hardness | 6.5 to 7 (very hard) |
Specific Gravity | 3.2 (Mg-rich variety) to 4.3 (Iron-rich variety) (average weight) |

Orthoclase
Mohs Hardness 6
Color: salmon, peach, cream, tan, beige, white
Texture: high luster, craggly, scraggly look in the shine

Plagioclase
Color: gray, tan, beige, white, cream
Mohs hardness 6-6.5
HIgh luster
Texture: high luster, craggly scraggly look in shine has straight line orientation
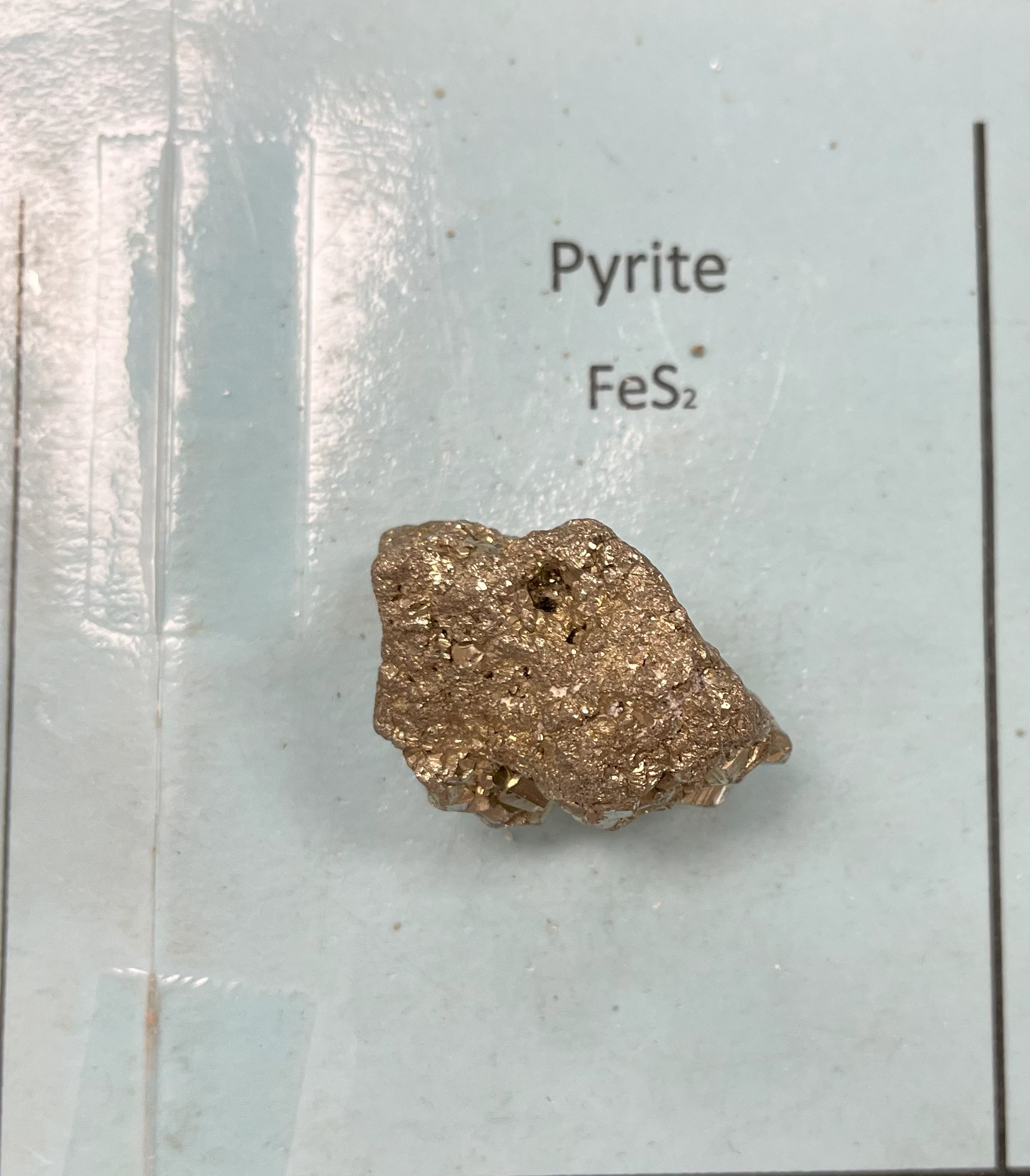

Pyrite
Mohs 6- 6.5
Color, brassy gold, shiney, has incongruent black streak

Rock Crystal Quartz
Chemistry: silicon oxide.
Mohs Hardness: 7
Refractive Index: 1.544.
Specific gravity: 2.65.
Lustre: vitreous.
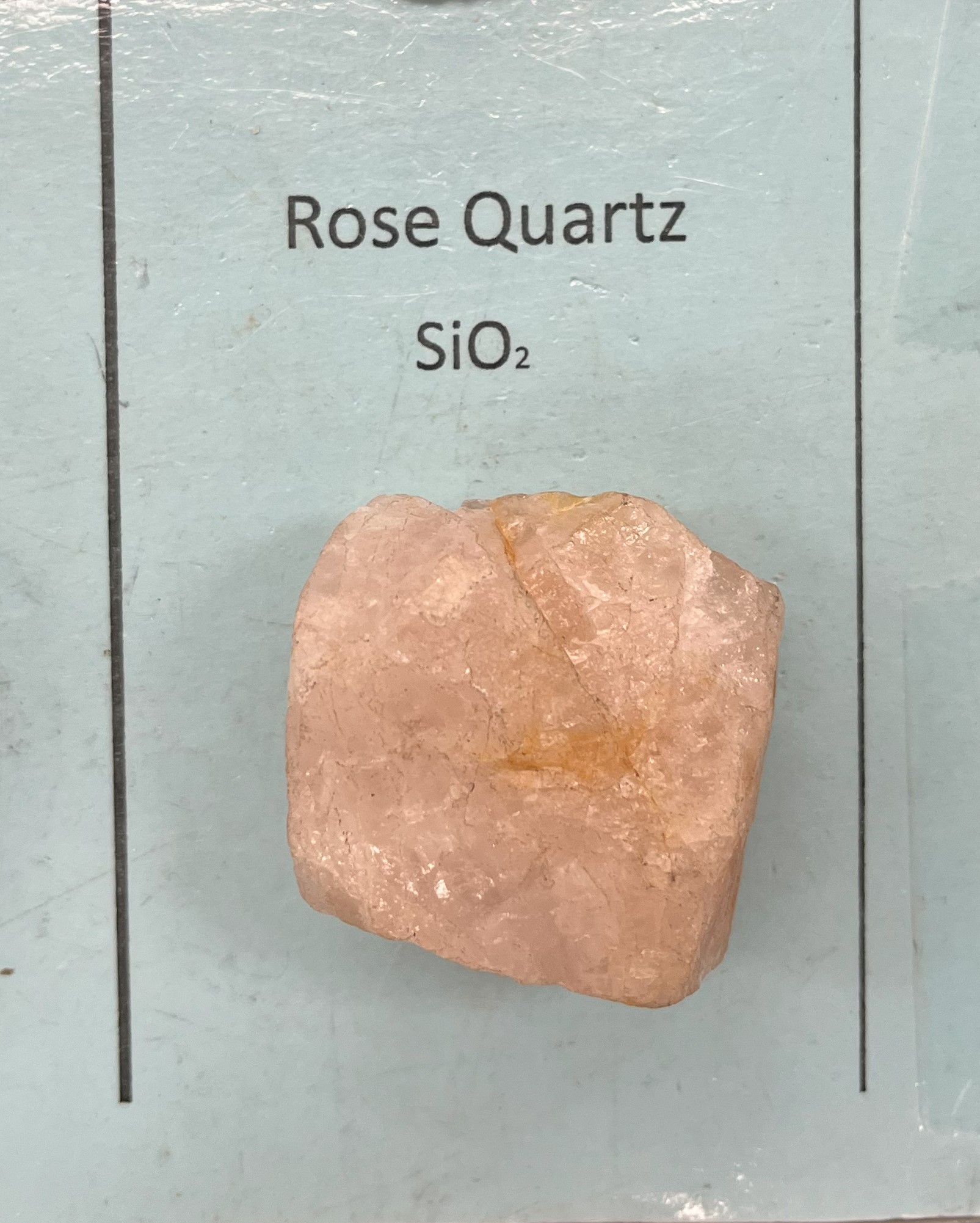
Rose Quartz
Mohs 7
Trigonal crystal system
Color: pink
Uses: jewelry and decoration

Satin Spar
Mohs 2, fibrous crystal habit that forms in sticks and can have high luster if not scratched alot.
Also a form of gypsum
Color: milky white or clear
Lustre: vitreous, translucent to opaque. Will dissolve in water

Selenite
Mohs 2
Also a gypsum
Forms in sheets
Has high luster if not scratched alot transparent to translucent
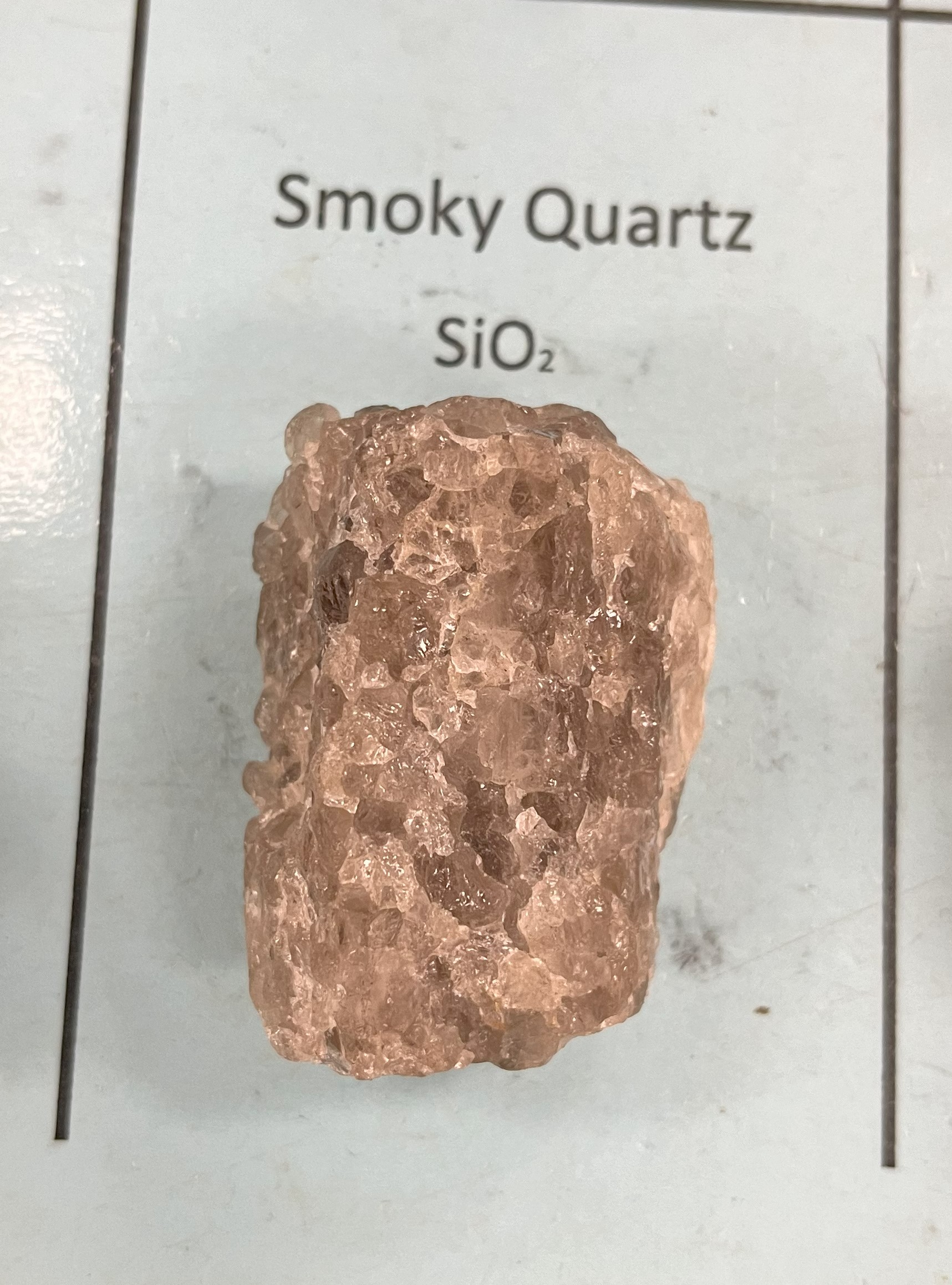

Smokey Quartz
Mohs 7
Color: dark brown

Sphalerite
Crystal habit: dodecahedral. In pure form, it is a semiconductor, but transitions to a conductor as the iron content increases. It’s many facets (flat parts) or “faces” cause it to look glittery.
Color: brown, tan, grey, or black. High luster very shiny
Mohs 3.5 to 4
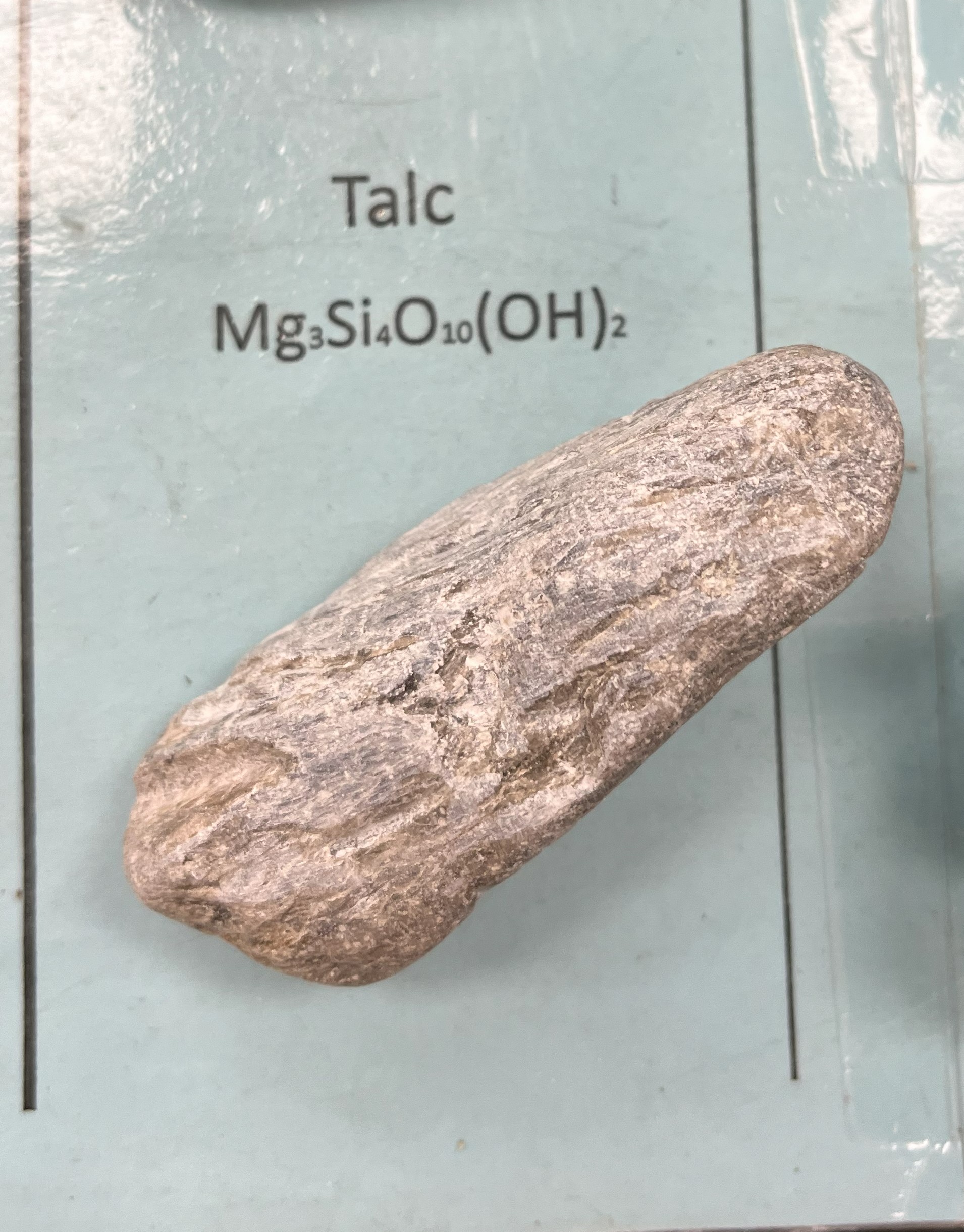

Talc
Mohs 1 softest mineral
Color: white, milky
Crystal habit: layered and feels very slick
Uses: loose powders for chafing (e.g., talcum powder, baby powder, blush, eyeshadow), and in other forms (e.g., pressed powder, liquid makeup). It is also used in some food items, such as rice and chewing gum, and to manufacture pill tablets.
#1 use is an industrial lubricant. Also absorbs well