Chapter 5 Section 2
5.0(1)Studied by 15 people
Card Sorting
1/23
Last updated 5:10 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Photosynthesis Equation
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight = Sugar + Oxygen
2
New cards
Three Stages of Photosynthesis
1. Light is captured from sunlight
2. Light energy is converted to chemical energy (stored in ATP & NADPH)
3. Energy in ATP & NADPH make organic compounds.
2. Light energy is converted to chemical energy (stored in ATP & NADPH)
3. Energy in ATP & NADPH make organic compounds.
3
New cards
1. Chlorophyll "a"
2. Chlorophyll "b"
2. Chlorophyll "b"
1. Captures red wavelengths
2. Captures blue wavelengths
2. Captures blue wavelengths
4
New cards
Chain 1 and Chain 2 Products
1. ATP
2. NADPH
2. NADPH
5
New cards
C-C-C-C-C-C (Carbon Fixation)
C-C-C (starch, sucrose) C-C-C (used again in Calvin Cycle)
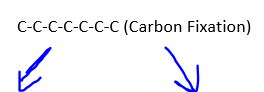
6
New cards
Stage 1 Summary
Stage 2 Summary
Stage 3 Summary
Stage 2 Summary
Stage 3 Summary
1. Absorption of Light
2. Conversion of Light
3. Storage of Energy
2. Conversion of Light
3. Storage of Energy
7
New cards
Thylakoid
Contains Chlorophyll
Disk in Granum
Disk in Granum
8
New cards
Stage 1 and 2
Light Dependent Reactions
9
New cards
Stage 3
Light Independent (Calvin Cycle)
10
New cards
Calvin Cycle
A series of enzyme assisted chemical reactions that convert CO2 and hydrogen-carrier compounds into glucose.
11
New cards
Increases Rate of Photosynthesis
Increase Light Intensity
12
New cards
Granum
Stack of Thylakoids
13
New cards
"Excited" Chlorophyll Splits
Water Molecules
14
New cards
Splitting H2O
H20 -> O2 + H+ + energized electrons
15
New cards
Stage 1 Used
Stage 2 Used
Stage 3 Used
Stage 2 Used
Stage 3 Used
1. Light, Water
2. Electrons, Hydrogen ions
3. ATP, NADPH, CO2
2. Electrons, Hydrogen ions
3. ATP, NADPH, CO2
16
New cards
How is oxygen produced?
When sunlight excites the electrons and splits the water
17
New cards
Stroma
Gel-like fluid/matrix (protein rich)
18
New cards
Light Independent Reactions
Reactions happen whether light is present or not
19
New cards
Light Dependent Reactions
Reactions happen when light is present
20
New cards
Stage 1 Produced
Stage 2 Produced
Stage 3 Produced
Stage 2 Produced
Stage 3 Produced
1. Oxygen, Hydrogen ions
2. ATP, NADPH
3. Organic Compounds
2. ATP, NADPH
3. Organic Compounds
21
New cards
Light Dependent Reactions Located
Thylakoid
22
New cards
Light Independent Reactions Located
Stroma
23
New cards
Stage 1 Operations
Electrons pass through protein and lose energy to pump H+ into thylakoid helps ADP + P -> ATP
24
New cards
Stage 2 Operations
Provides energy to make NADPH