Physics - Radiation doses and effects on humans
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Radiation in daily lives
90% of our annual exposure is from the surrounding environment and doesn’t pose a significant risk to our health.
High levels of ionising radiation from radioactive sources is harmful to biological tissue.
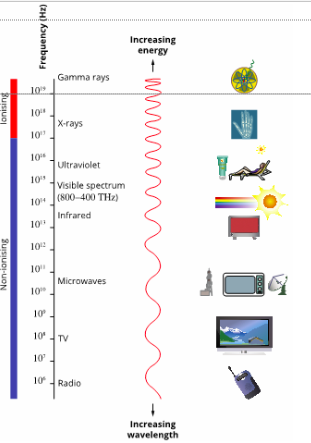
Ionising radiation
Ionising radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a frequency above 2 × 10^16 Hz (Starting at UV-C and higher)
High energy neutrons (alpha and beta particles)
Dose equivalent
(in Sieverts) is a measurement which incorporates quality factor. 1 Sievert of any type of radiation will have the same biological effect.
takes into account the absorbed dose and the type of radiation. (The actual effect of the radiation to the tissue)
Effects of ionising radiation on humans
The effects of radiation on our bodies is due to the damage that occur at the cellular level. The magnitude of this effect is proportional to the radiation dose equivalent. Exposure can be monitored with the use of a dosimeter.
Medical applications of radiation
Radiation is often used for cancer treatment because cancerous cells can be damaged to radiation than healthy tissue therefore to hinder the division of these cells, doctors use radiation.
Radioisotopes can be used to detect cancerous growth in drugs.