NSG 3111: Week 3 - Transition to Parenthood
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Attachment and bonding
Process by which parent and child come to love and accept each other over time
En face position
Position in which the adult's face and the infant's face are approximately 8 inches apart and on the same plane, as when the mother holds the infant up in front of her face or when she nurses the infant

Entrainment
Process of synchronizing a biological rhythm to an environmental stimulus; infant moving with parent's voice
Biorhythmicity
The infant being in tune with the mother's natural rhythms; infant soothed by the maternal heart rate
Reciprocity and synchrony
Mutually gratifying interaction among mother, infant, father
False
True or false? Skin to skin and rooming in are essential to the development of parent-infant attachment
Breastfeeding
Direct transfer of human milk from the breastfeeding parent to the infant
Exclusive breastfeeding
Infant receives no other liquid or solid foods besides the breastmilk
Human milk feeding
Infant is fed expressed breastmilk from the breastfeeding parent or a donor milk bank
True
True or false? The WHO recommends that infants be exclusively breastfed for the first 6 months of life and past 6 months in combination with food
6 months
When should complementary foods high in iron be introduced?
1 year
When can you stop giving vitamin D supplement drops?
Newborn galactosemia
Genetic deficiency of the enzyme required to break down lactose and galactose; contraindication to breast feedings
True
True or false? Alcohol can disrupt the release of oxytocin and prolactin, decreasing breast milk production and availability
Galactogogue
Agent that promotes the flow of milk; ex. domperidone
False
True or false? Oligosaccharides are in both formula and breastmilk
Vitamin D, K, B12
BM contains all required vitamins except...
It's mineral content is too high
Why should you not feed babies cow's milk?
Prolactin
Facilitates milk production; produced from the anterior pituitary, prepares breast to synthesize/secrete milk, levels elevate throughout lactation
Oxytocin
Facilitates in moving the milk, produced from posterior pituitary
Milk ejection reflex
Release of breast milk in response to oxytocin, also called the let-down reflex
Nipple erection reflex
Helps stimulate the infant's palate to latch; initiated by oxytocin
Stage I of lactogenesis
Begins 16-18 weeks pregnancy to birth; colostrum
Stage II of lactogenesis
Begins with delivery of placenta (drop in progesterone and estrogen trigger prolactin release); day 3-5 colostrum transitions to transitional milk; day 5-10 rapid volume increase & transition to mature milk
Stage III lactogenesis
10-14 days after birth, mature milk established
Colostrum
Yellow-orange colored milk rich in antibodies and proteins, low in fat; laxative action
Transitional milk
Mixture of colostrum and mature breast milk
Foremilk
Type of mature milk contained at the beginning of the feed; increased water content
Hindmilk
Type of mature milk released later in the feeding (10-20 minutes in) which has increased fat and energy content
Early hunger signs
Awake/restless, licking/smacking lips, sticking out tongue, sucking on hands, rooting
Late hunger signs
Crying, agitation/distress, frantically turning head from side to side
Laid-back breastfeeding
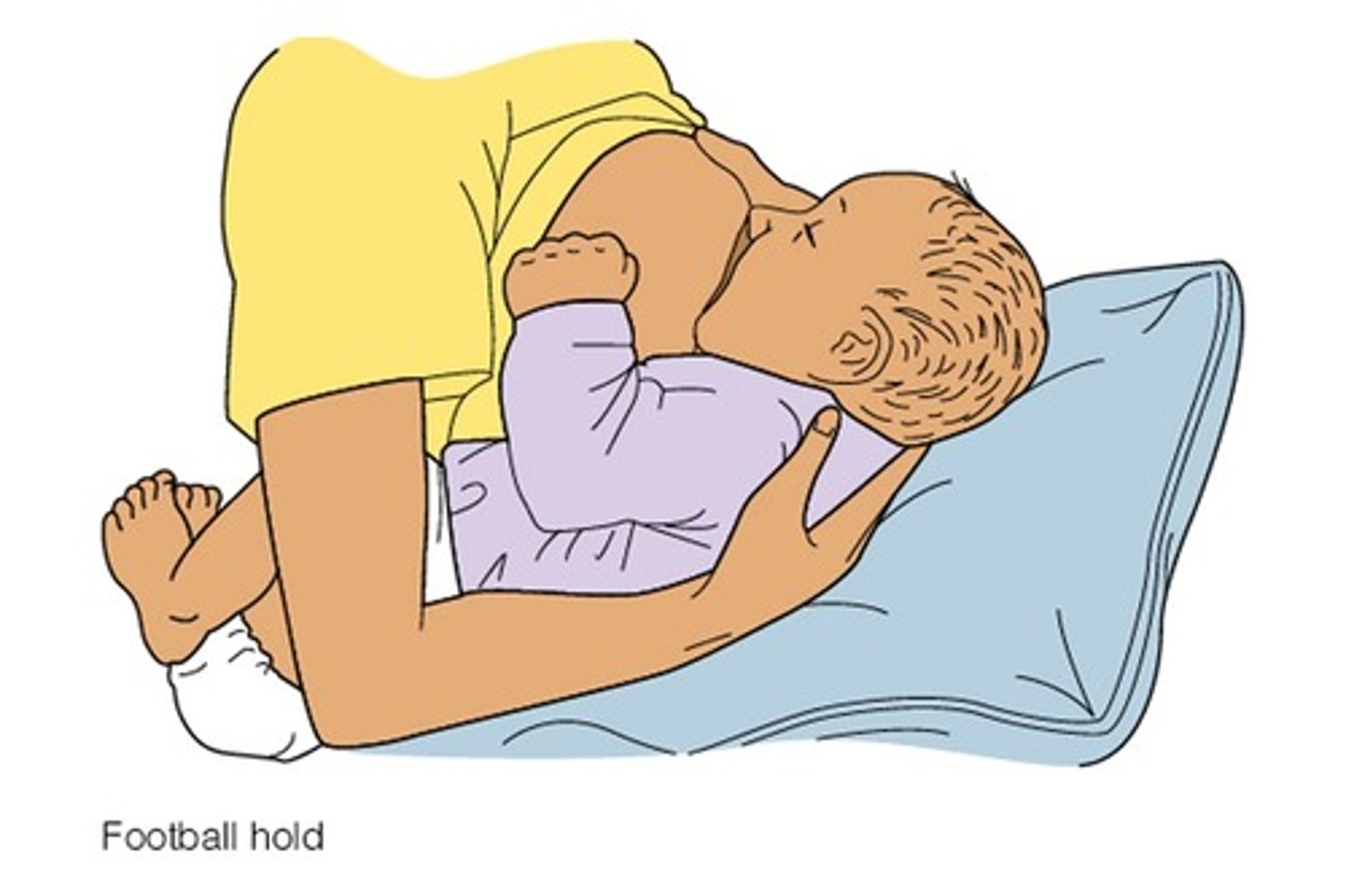
Football hold
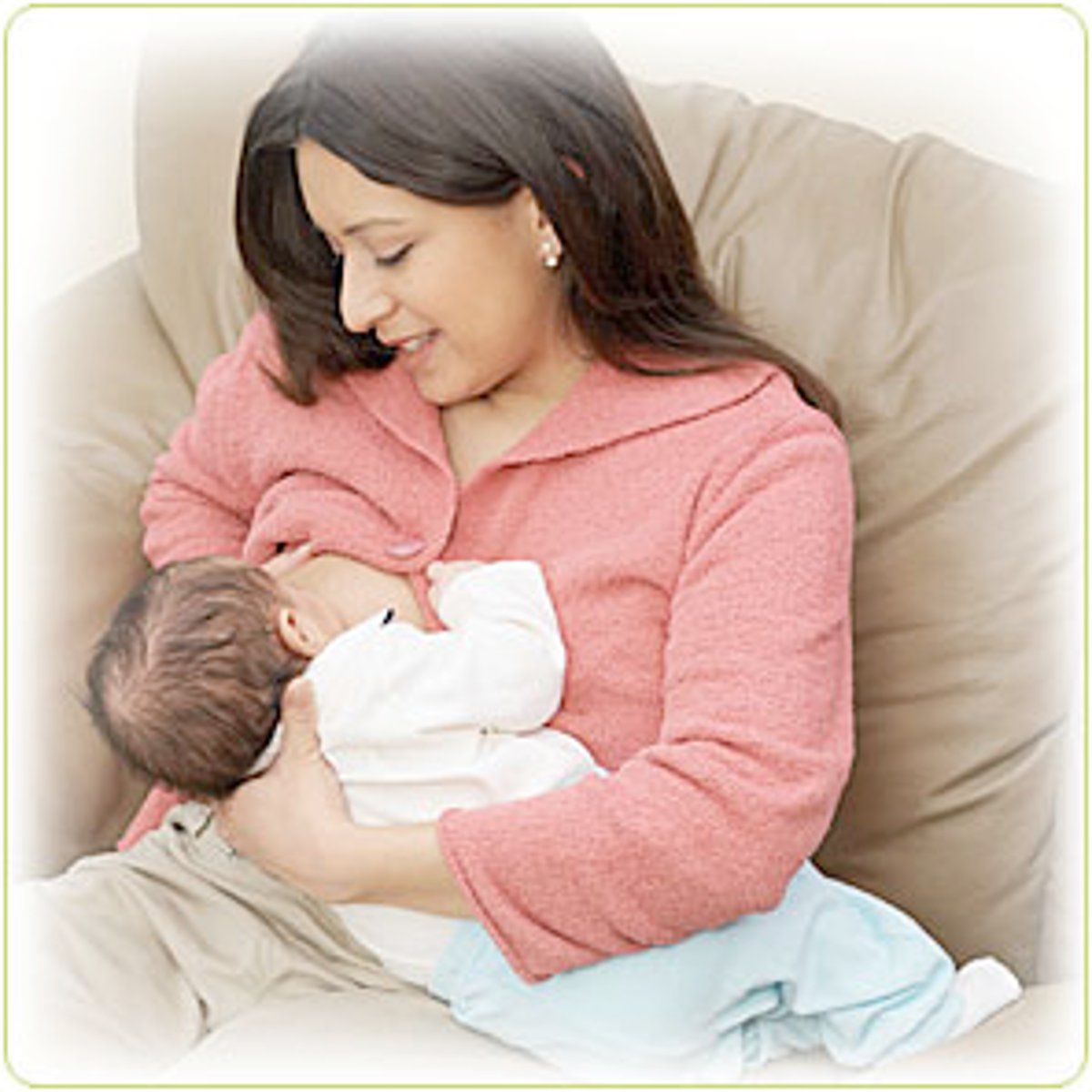
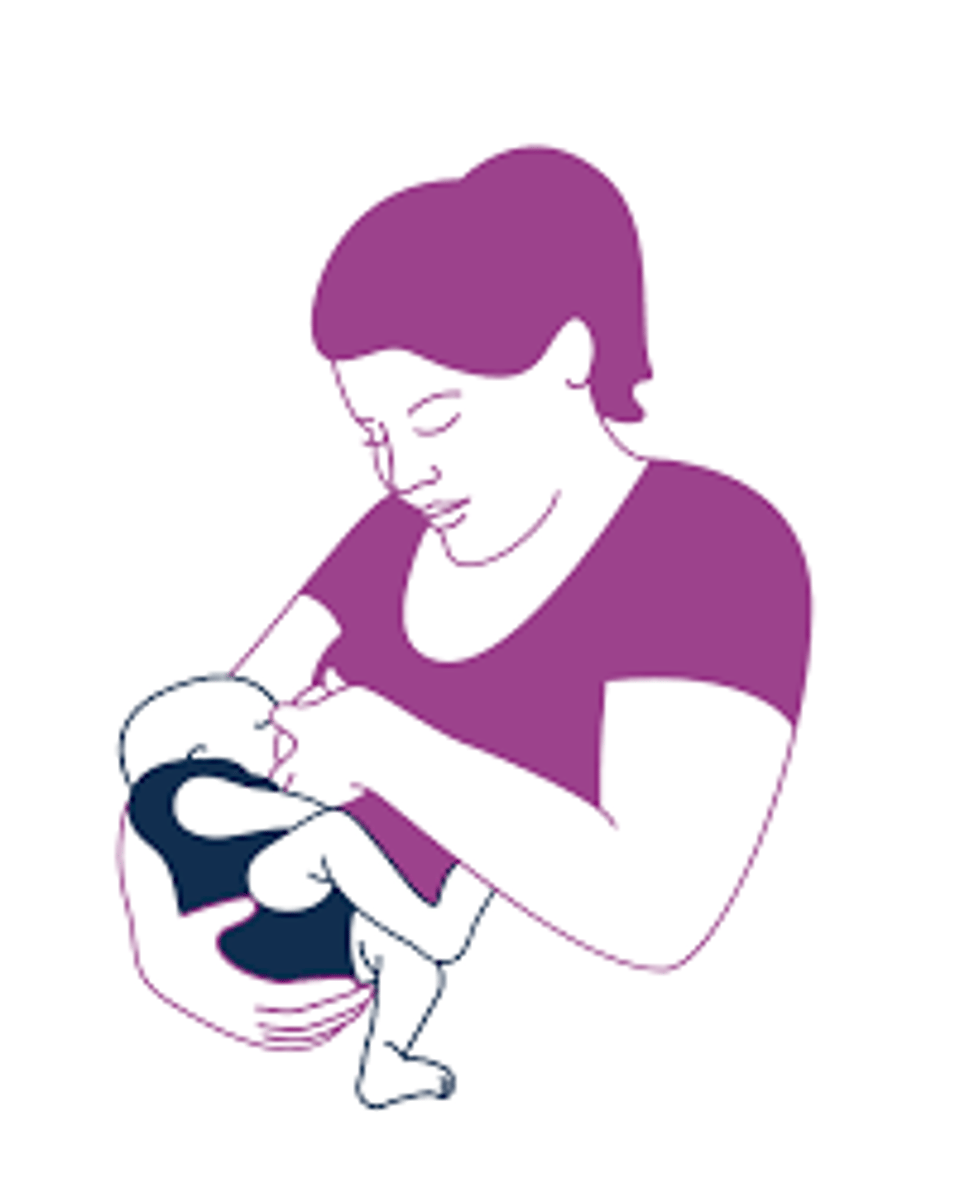
Cross cradle
You are holding the baby with the arm opposite to the breast they are feeding on; allows for more control of upper body

Cradling
You are holding the baby with the arm on the same side as the breast they are feeding on
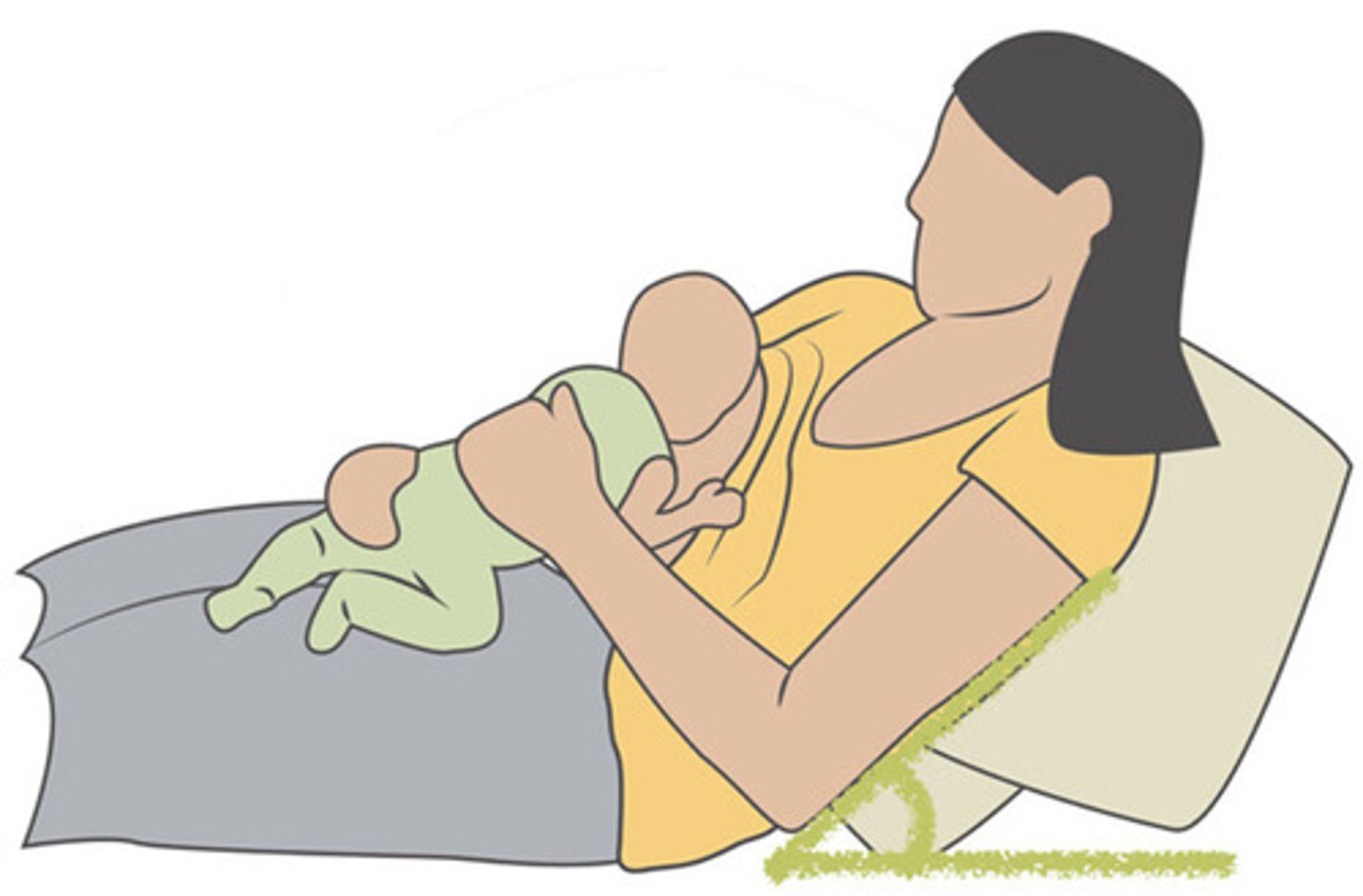
Side-lying position

Purpose of manual expression
Enticing infant to feed, stimulating milk flow/priming milk ducts, collection for infants unable to breastfeed, relieving breast fullness, antiseptic for sore nipples
Nape of neck
Where should you place your hand when the supporting the infant's head during breastfeeding?
False
True or false? When educating the patient on breastfeeding, you should explain the rule of "breast to baby, not baby to breast."
Sign of milk transfer
'suck-suck-pause-swallow' and audible 'ca' sound when swallowing
Insert finger into baby's mouth
How does one break the latch when breastfeeding?
8 or more in 24
What should you teach the breastfeeding patient about the frequency of feedings?
20-30 minutes to 1 hour
How long is a typical feed?
NB satiation cues
Slowed suck/swallow patterns, fall asleep, come off breast, arms and legs extended
7% by day 3 (then gaining weight)
What percent of weight is lost in NBs?
2 weeks
By when should the newborn return to their birthweight?
1 void, 1-2 BM
How many voids and BMs should we expect to see from the newborn on day 1?
≤ 6 hours
How long can you leave freshly expressed breast milk out at room temperature?
2 hours
How long can you leave warmed EBM or breast milk that the infant has started feeding from out at room temperature?
≤ 5 days
How long can you leave EBM in the refrigerator?
≤ 6 months
How long can you leave EBM in the freezer within the fridge?
≤ 12 months
How long can you leave EBM in a deep freeze?
3-4 weeks
How long should you delay bottle feeding if you are doing combined (breast & bottle) feeding?
Causes of insufficient milk supply
Ineffective/infrequent feeds, breast surgery, medication side effects, stress/fatigue
Treatment of insufficient milk supply
Increase feeding frequency or breast pump, increase rest, promote adequate nutrition, introduce galactagogues (domperidone)
Engorgement
Swelling of the breasts resulting from increased blood flow, edema, and milk stasis
Treated by promoting milk removal, warm shower prior to feeding, cold compress bt feedings, frequent/effective feeds
Blocked ducts
Plugged or clogged milk ducts; palpable mass on breast; does not resolve with BF, localized pain
Caused by inadequate duct drainage, milk stasis
Treated by feeding frequently, changing feeding positions, massaging duct after feed
Mastitis
Can be unilateral or bilateral; inflammation and infection of mammary gland caused by milk stasis
Treated by
Candida
Yeast infection of breast caused by transfer from vaginal yeast infection, antibiotic use, or nipple damage
S&S: shooting pains in breast throughout the entire feed, rash on areola; thrush in baby's mouth, fussy, gassy
Treatment: antifungal agents for mother and baby, hand hygiene & keeping nipple dry to prevent
10-30 mL
How much formula should you feed the baby in the first 24-48 hours?
Signs of distress during formula feeding
Wide eyes, sputtering, drooling formula, repeated swallowing without pausing, turning head, arching back, moving arms
Premature or LBW newborns (risk of infection)
What population of newborns should not receive powdered formula for the first 2 months?
False
True or false? Microwaving formula is okay if there is no access to a bottle warmer or boiling water
After 48 hours
When should you discard ready-to-feed and concentrated formula that has been in the fridge after openeing?
After 24 hours
When should you discard powdered formula that has been in the fridge after preparing?
Within 1 hour
When should you discard any remaining formula in the bottle after a feed?
>6 months
When can solid foods be introduced?