Lymphatic System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Diffuse lymphatic tissue
Not surrounded by a capsule
Lymphatic nodules
Small lymphocytes called primary nodules
Secondary nodules
More abundant
Pale central region called germinal center
Thin, darker region called corona
Germinal center
Contains large immature lymphocytes, B cells, macrophages
Cites of B cell clonal expansion, somatic hypermutation, affinity based selection that results in production of high-affinity antibodies
Why does the germinal center appear less stained?
Predominant euchromatin in the nuclei of immature lymphocytes
Corona
Highly packed with small lymphocytes
Lymphatic tissue is responding to antigens
The presence of secondary nodules is an indication that the_________
Parenchyma of lymphatic tissue
Lymphocytes and less abundant immune cells
Storms
Connective tissue capsule and septa
Storma cells
Reticular cells, follicular dendritic cells, endothelial cells
Cells in the thymus and bursa
Epithelial-reticular cells
Provide support for lymphocyte precursors and produce critical paracrine factors influencing lymphocyte differentiation and survival
Reticular fibers
type III collagen fibers
Same banding pattern as collagen
No bundles but networks
Argyrophillic (silver stain)
Produced by fibroblasts and reticular cells
Where are lymphocytes derived from?
Multipotent lymphoid stem cells that give rise to precursors of B cells, T cells and NK cells
Thymus and Bursa
Primary lymphoid organs
Where lymphoid cell precursors become functional and self-tolerant T and B cells
Provides cells with specific antigen receptors
Bursa
Not preset in mammals
Bone marrow
Primary lymphoid organ in mammals
Where B cell instruction occurs
Secondary lymphoid organs
Lymph nodes, spleen, MALT, etc.
Where are lymphatic organs found?
Intercalated in lymph nodes and blood circulations (spleen), beneath select surface epithelia (MALT)
MALT
Supervises tissue with high exposure to pathogens such as GI and respiratory tracts
Lymph nodes
Deal with pathogens that succeeded in crossing epithelial barriers and invaded deeper tissues
Spleen
Looks for pathogens that having violated all barriers circulate freely in blooD
Critical for the surveillance of the immune system
Ability of lymphocytes and other immune cells (macrophages and DCs) to circulate in lymph and blood and move back and forth into tissues
ECF from tissues
Enters blind-ended lymphatic capillaries and circulates in valves vessels similar to veins called lymphatic vessels where it is called lymph
What surrounds lymph nodes?
White adipose tissue and a thin dense connective tissue capsule that gives rise to short partitions called trabeculae
Parenchyma of the lymph node
Divided into:
peripheral dark cortex
Central pale medullary
Cortex of lymph nodes
Dense mass of lymphatic tissue containing nodules of the secondary type and the paracortical region
Paracortical region
Non-modular lymphatic tissue located between the nodules and the medulla
Medulla
Non-nodule lymphatic tissue arranged as branding cords called medullary cords
Sinuses
Interconnecting channels making up the lymph nodes
Endothelium-lined spaced used for lymph circulation
Subsapsular sinuses
Afferent lymphatic vessels delivered here
Located between node’s capsule and cortex
Send lymph to trabecular sinuses
Path of lymph in the lymph nodes
Afferent lymph vessels > subcapsular sinuses > trabecular sinuses > medullary sinuses
Lymph leaving
From medullary sinuses leaves the LN through efferent lymph vessels that emerge at the hilium of the LN
High endothelial venues (HEVs)
Venues leaving nodules
Lined by simple cuboideal or columnar endothelial cells
Posses receptors from lymphocytes called homing receptors
Homing receptors
Signal lymphocytes to leave the circulation and migrate into the lymph node parenchyma
Cortical nodules
Rich in B cells
Paracortex
Populated by T cells and DCs
Germinal centers of secondary nodules
Sites of B cells Provide support activation and generation of memory cells
B cells found in all stages of differentiation into plasma cells
Follicular dendritic cells
Stromal cells located in germinal centers
Multiple, thin, hair-like branching of cytoplasmic processes that interdigitate between B cells in the germinal centers
Important for generation of memory B cells
Visualizing lymphocytes in LNs
With H&E all lymphocytes look the same
Lymphocytes and other immune cells express cell-type specific proteins, use of antibodies specific for those markers would allows for identification via immunofluorescence (IF) or immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Confocal microscope
Enables reconstruction of the image for all fluorochromes
Swine lymph nodes
Medullary tissue is found in cortex and medulla
Cortical tissue is concentrated in the center of the organ
Hemal nodes
Lymph node-like structures intercalated int eh blood circulation of ruminants
Lack medullary region
Found in sublumbar ara along vena Cava and aorta
Birds
Lack lymph nodes
Have abundant modular and diffuse lymphatic tissue associated with many organs
No lymph or hemal nodes
LN Functional considerations
sites their pathogens and their products are concentrated and exposed to immune cells
Sites of lymphocyte activation, clonal expansion, differentiation as well as sites of generation of memory cells
Chances for immune cells to be exposed to antigens are increased because lymph circulation in the sinus system is slow due to presence of the reticular meshwork
Sites for lymphocyte sequestration (HEVs) from blood
Major sites of phagocytosis, antibody production and killing of infected cells
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ, intercalated in the bloodstream
Consist of lymphatic tissue and specialized vascular spaces or channels
Spleen stroma
Dense connective tissue capsule form which trabeculae extend
Splenic pulp
Spleen parenchyma
Red pulp: blood vessels, large amount of immune and RBCs
White pulp: lymphatic tissue
Splenic artery
Enters spleen gives rise to smaller arteries that follow the trabeculae (trabecular arteries) > give rise to arteries of white pulp central arterioles
Periaterial lymphatic sheath (PALS)
Lymphocytes aggregate around a central artery
Roughly cylindrical configuration that conforms to the course of the central artery
T cell zones
Marginal zone of the white pulp
Rich in B cells and macrophages
May contain lymphatic nodules
Red pulp of the spleen
splenic cords separated by the splenic sinuses
Large # of RBCs
Splenic cords
Meshwork of reticular cells and fibers containing large number of macrophages, RBCs, lymphocytes, DCs, plasma cells and granulocytes
Where are aged or damaged macrophages and RBCs removed from the circulation via phagocytosis?
Spleen
Other sites; liver and bone marrow
Splenic sinuses
Long endothelial cells running parallel to the direction of the vessel
Immunologic functions of the spleen (mostly in white pulp)
capture antigens from blood
Antigen presentation by macrophages and DCs to T cells
Activation of T cells and B cells; antibody production
Other functions of the spleen (mostly in red pulp)
removal and destruction of senescent or damaged erythrocytes
Retrieval of iron from hemoglobin
Formation of blood cells (fetal life only)
Storage of blood (Horses and dogs)
Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT)
Beneath surface epithelia
First encounters to pathogens enter body they GI, respiratory and genitourinary systems
Sites of antigen capture and activation of B and T cells
Waldeyer’s ring
Lymphatic tissue distributed in or close to the pharynx
Include lingual tonsil, palatine tonsils, tubal tonsils and pharyngeal tonsils
Palatine tonsil
Located on depressions (tonsillar fossae) at both sides of the oropharynx
Immediately beneath the squamous stratified epithelium
Lack Afferent lymphatic vessels
Fossulae
Sites where the surface epithelium invaginated to form crypts
Peyer’s Patch
Collection of nodular and non-nodular lymph tissue embedded in intestine wall
Aggregation of immune cells cause the wall to project and form domes
Domes contain M cells
M cells (microfold)
folding of their luminal surface
sample foreign material from the lumen and deliver it via transcyotsis to APCs in M cell basal pockets
Thymus
Cranial to the hart
Capsulated non-nodular lymph organ
Trabeculae extend into thymus creating thymic lobules
Dark basophillic peripheral cortex, and pale central medulla
Lacks lymphatic nodules!!!
Epithelial reticular cells
Make up thymic stroma
Produce epithelial-like intermediate filaments (keratin)
Numerous cell-to-cell junctions
Stellate cells with thin cytoplasmic extensions
Paracrine and juxtacrine communication with thymocytes
Large, ovoid spherical nuclei
Hassall’s corpuscles
Formed by epithelial reticular cells
Acidophillic due to increasing levels of keratin
Function unknown, morphological feature important for histologial differentiation of thymus
Blood-thymus barrier
Endothelium, macrophage rich perivascular CT layer, outer sheath of epithelial reticular cells
Selective barrier that separates blood from developing T cells in the cortex
Tight junctions present
Limits access of foreign material to the cortex
Absent in cortico-medullary region where mature T cells leave thymus and enter circulation
Bursa of Fabricius
Primary lymphatic organ in birds
Seeded by lymphoid cells precursors, site of lymphocyte differentiation and regresses at the time of sexual maturity
Produces B cells
Capsule: connective and smooth muscle tissues
Parenchyma: longitudinal folds of epithelium, folds contain lymphatic tissue with dark peripheral zone and light central zone
Histological Differentiation
thymus: parenchyma organized into lobules, individual lobules consisting of a central medulla and peripheral cortex
LN: single medulla surrounded by single cortex, lymphatic nodules and medullary cords found in cortex and medulla
Spleen: red pulp interrupted by white pulp, white pulp contains central artery and lymphatic nodule
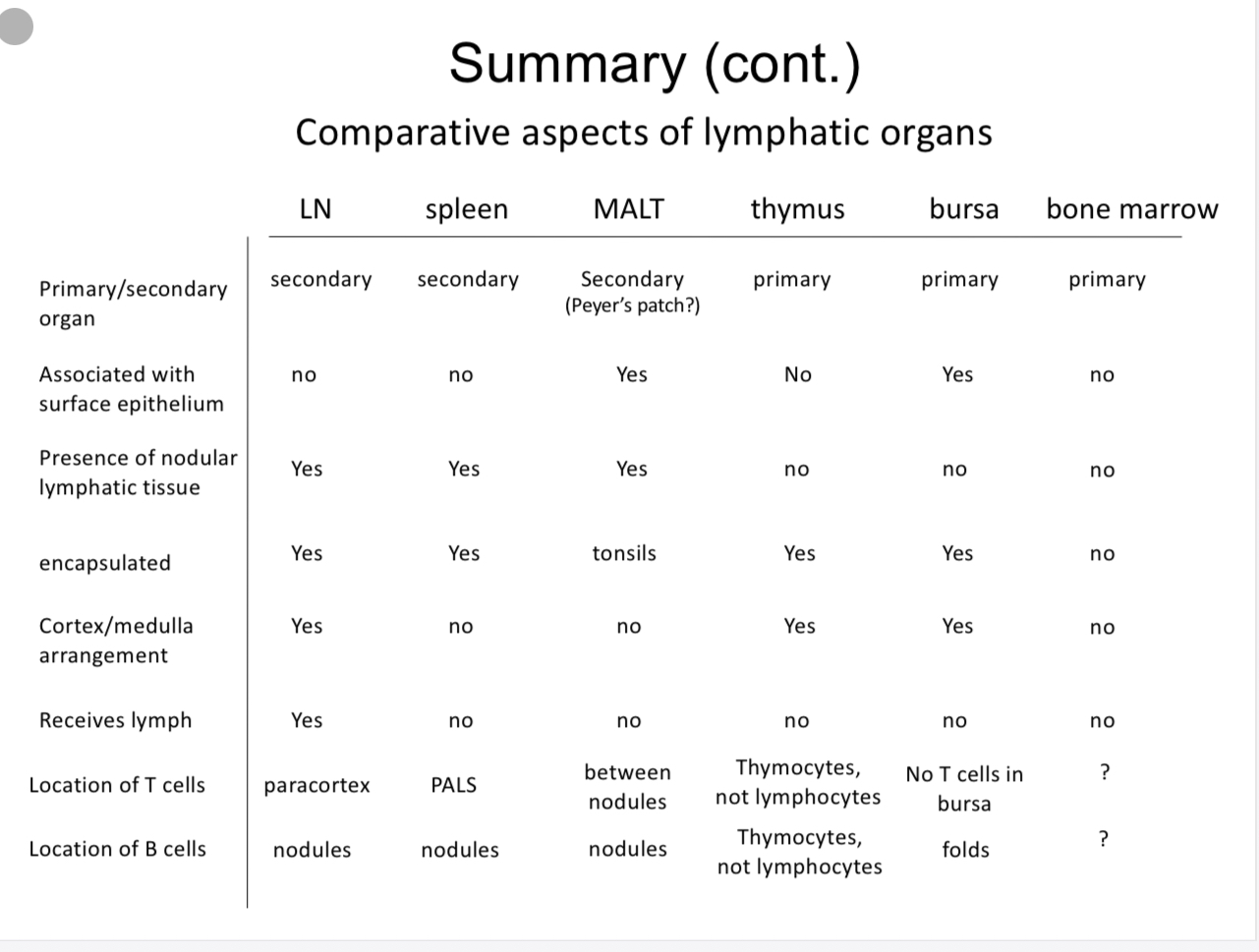
Summary chart