The Circle and Some Related Terms
Circle–The set of all points in a plane at a given distance from a given point.
- The set of all point equidistant from a given point called the center of the circle.
- The given point is the center of the circle and the given distance is the radius.
Radius–It is defined as a segment connecting the center with a point on the circle. (radii –plural)
Chord–A segment whose endpoints lie on the circle.
Diameter–A chord that contains the center of the circle.
- Not all chords can be a diameter.
- It divides a circle into two congruent arcs called semicircles
Arc–A portion of a circle where two distinct points on a circle divides the circle into two parts.
- Two distinct points on a circle divide the circle into parts called arcs.
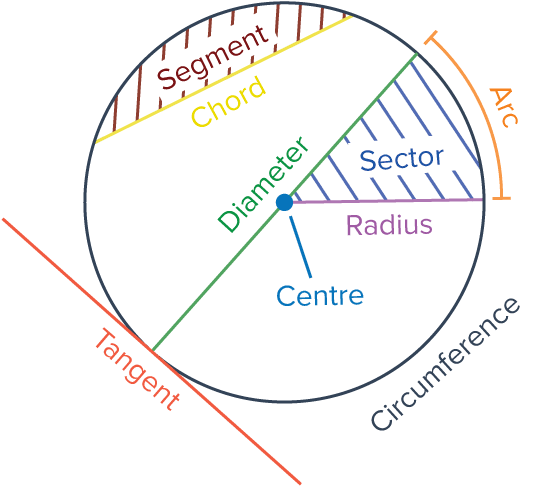
==3 Classifications of Arcs==
- Minor Arc–Less than 180 degrees
- Major Arc–Greater than 180 degrees
- Semicircle–Exactly 180 degrees
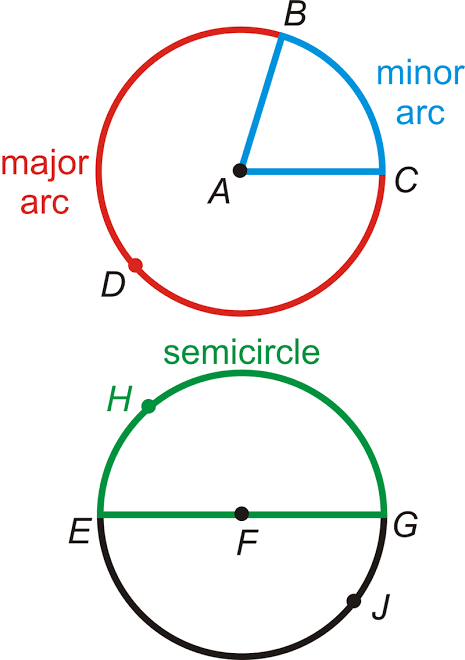
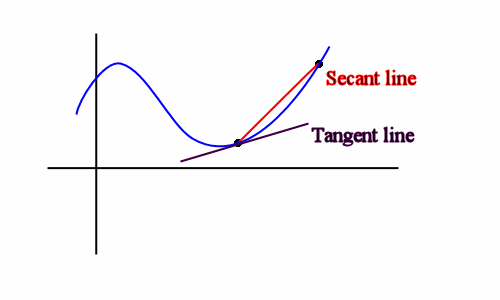
Tangent Line–A tangent to a circle is a line, coplanar with the circle that intersects the circle in exactly one point.
Secant Line–A secant line is a line that intersects the circle in two points. It is always composed of a chord.
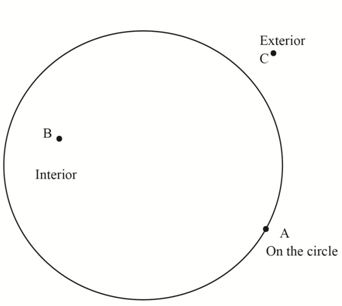
Exterior of the circle–It is a set of points in the plane of the circle whose distance from the center is greater than the radius.
The circle is divided into 3 parts: Exterior, Interior and the circle itself
Central Angle–It is an angle in the plane of the circle whose vertex is the center of the circle.
Inscribed Angle–An angle whose vertex lies on the circles and whose sides contain points of the circle.
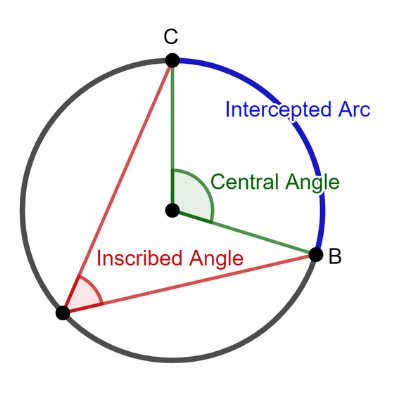
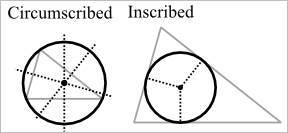
Inscribed Polygon–It is a polygon whose sides are chords of a circle. The polygon is inscribed in a circle, and the circle is circumscribed about the polygon.
Circumscribed Polygon–The polygon is outside the circle.
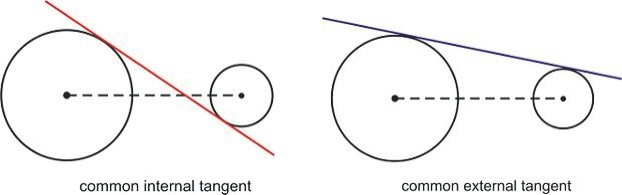
Common Tangent –It is a tangent to each of coplanar lines.
Common External Tangent–The line did not intersect the center of the circle
Concentric Circles–Two or more circles with the same center.
Congruent Circles–The circles have the same radius.