Bootcamp.com - Plants
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
what are the three main components of a seed?
seed coat; storage material; embryo
the _____ is a hard outer layer that covers and protects the seed from various external forces
seed coat
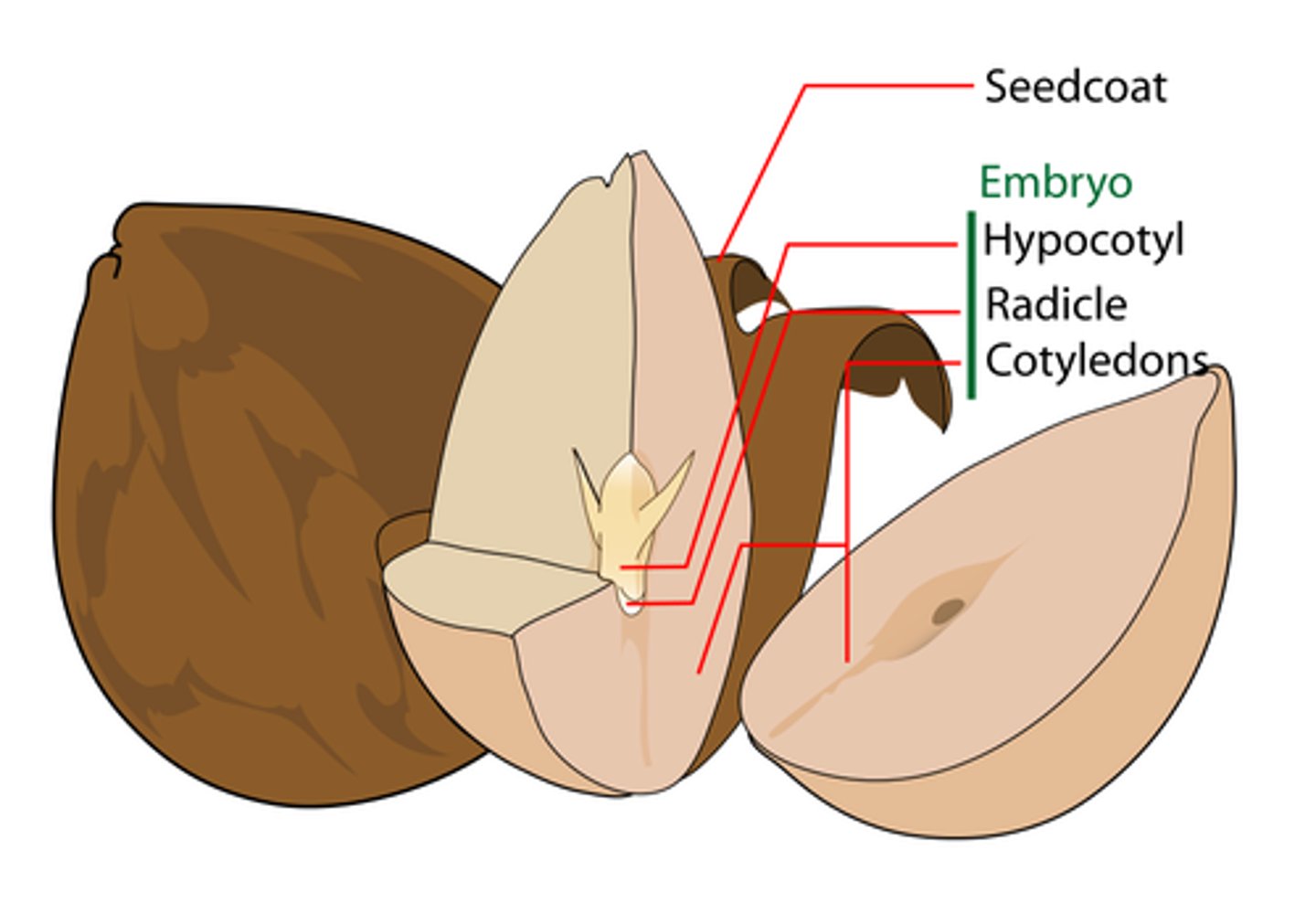
the _____ stores nutrients for the embryo in a seed
endosperm
the _____ refers to the first leaves that appear on a seedling
cotyledon
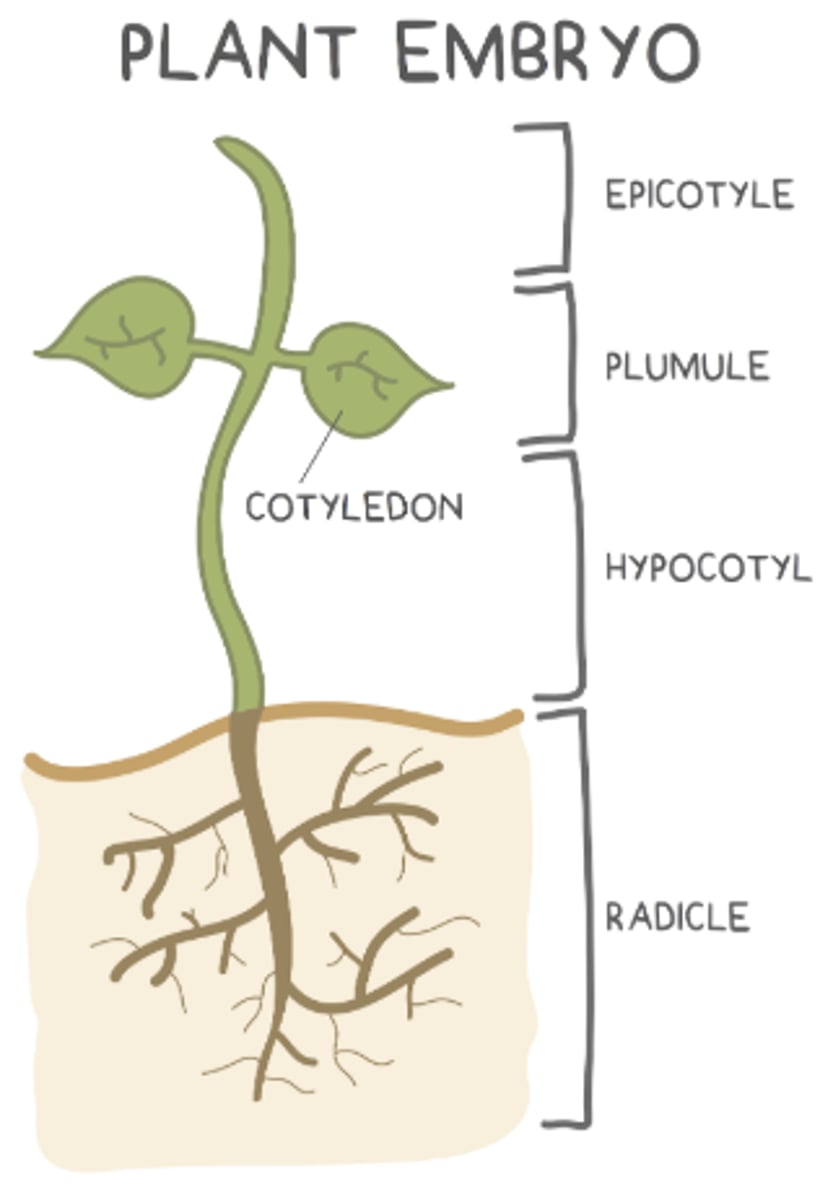
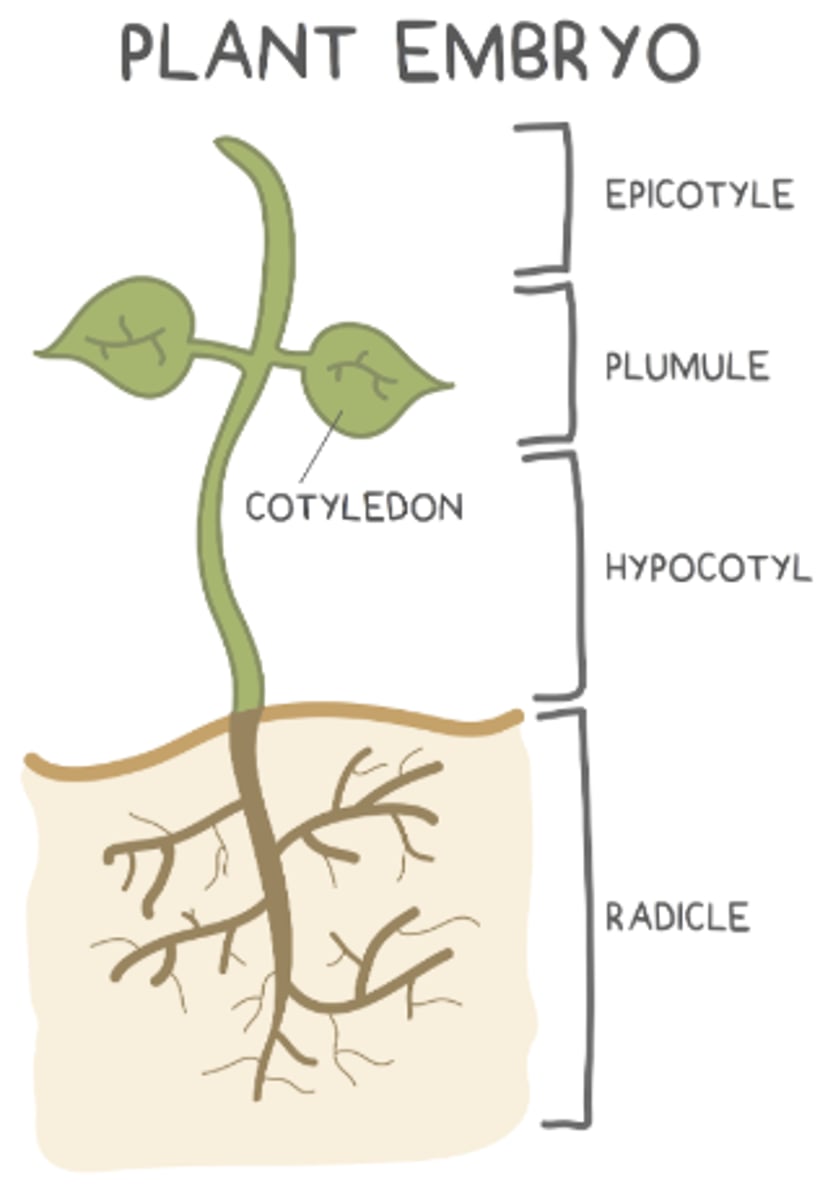
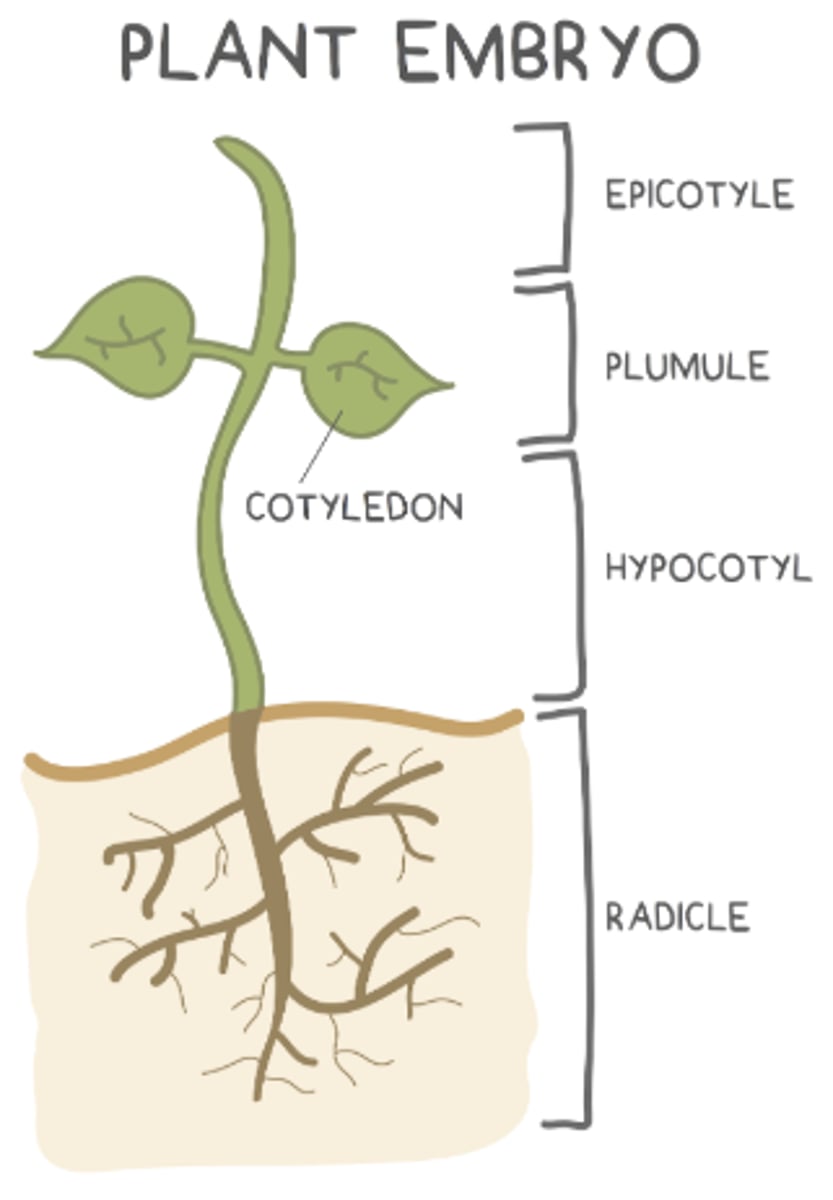
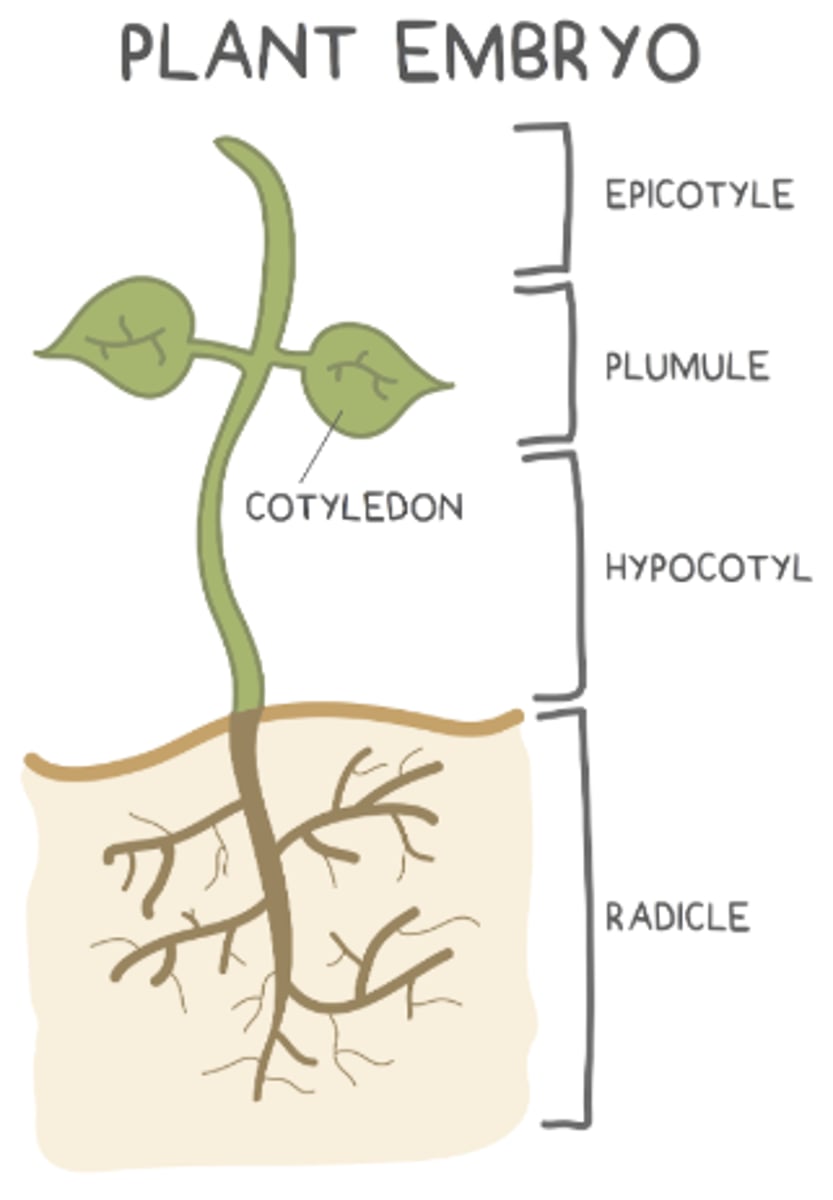
what are the 4 main parts of the embryo of a seed?
radicle; hypocotyl; plumule; epicotyl
the _____ is the part of the embryo that develops into the young root
radicle
the _____ is the first to emerge from the seed coat, and it anchors the plant into the soil
radicle
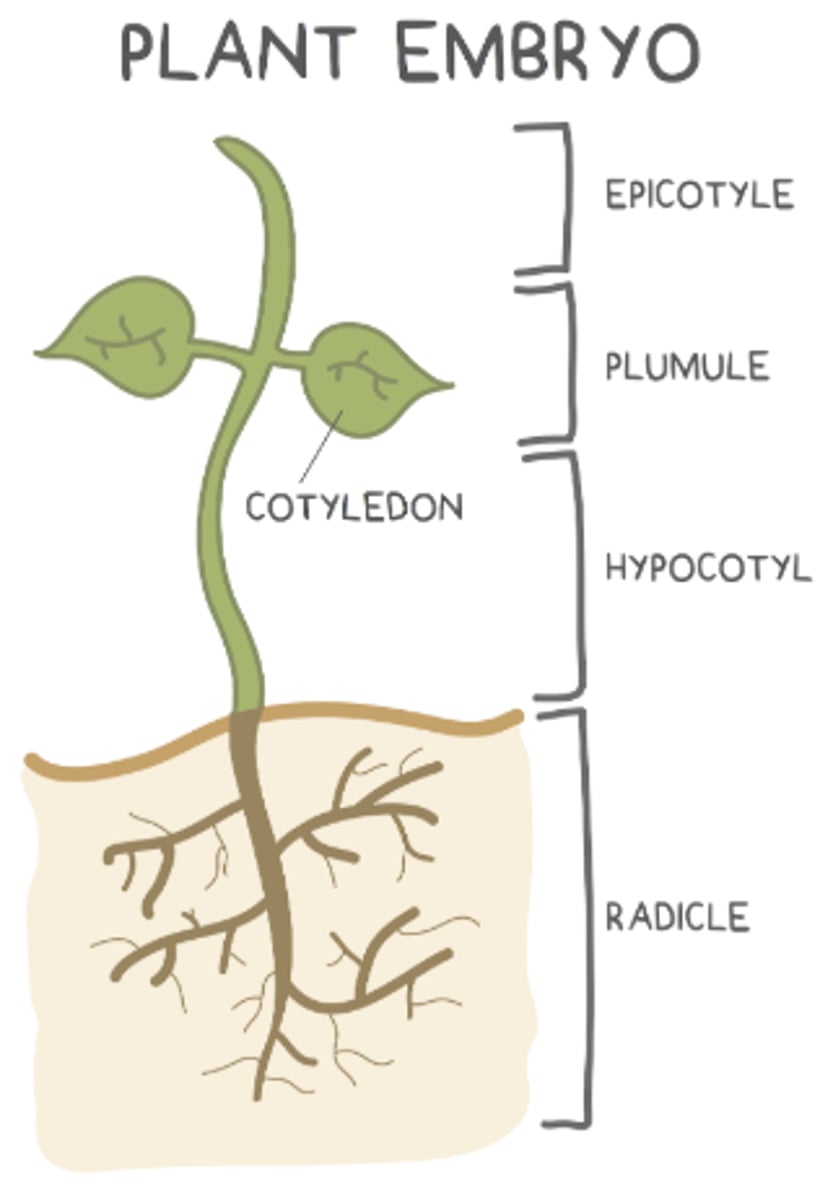
what makes up the young shoot (things above the soil)?
hypocotyl, plumule, and epicotyl
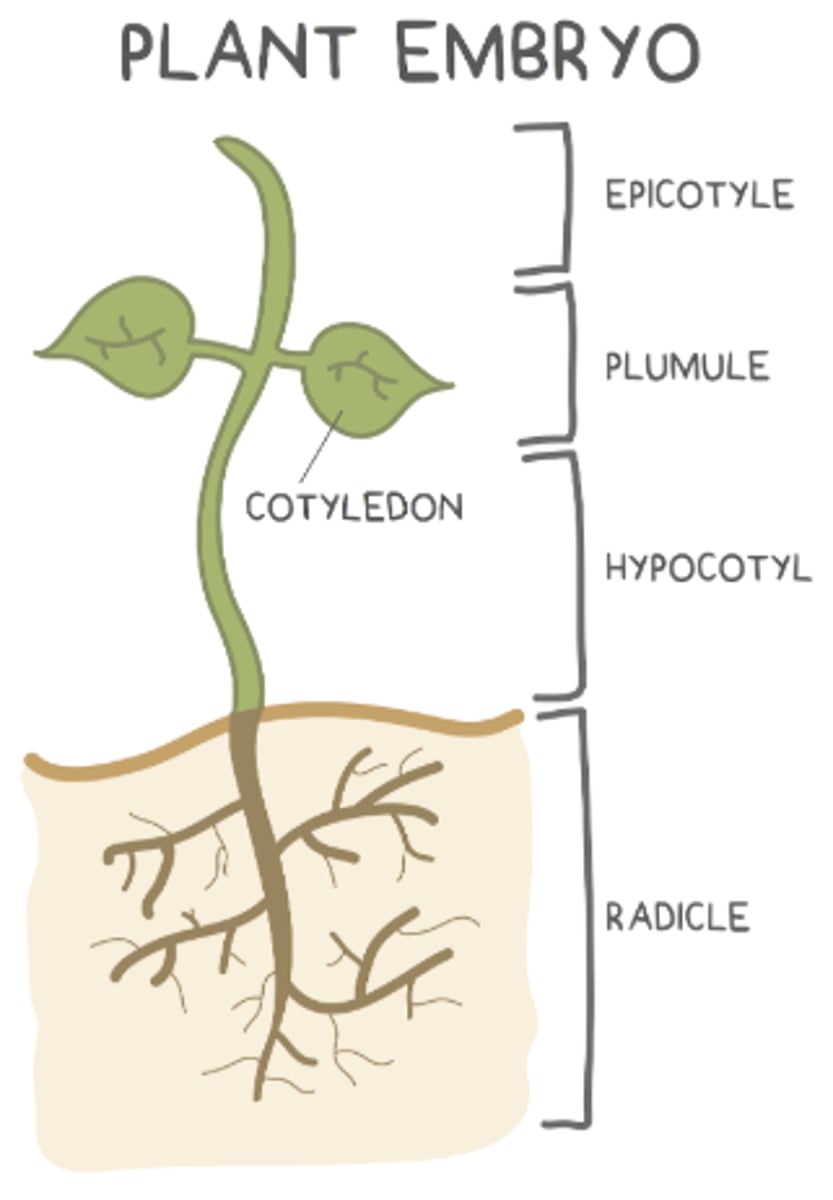
the _____ is the bottom region of the young shoot (above the roots but below the cotyledons)
hypocotyl
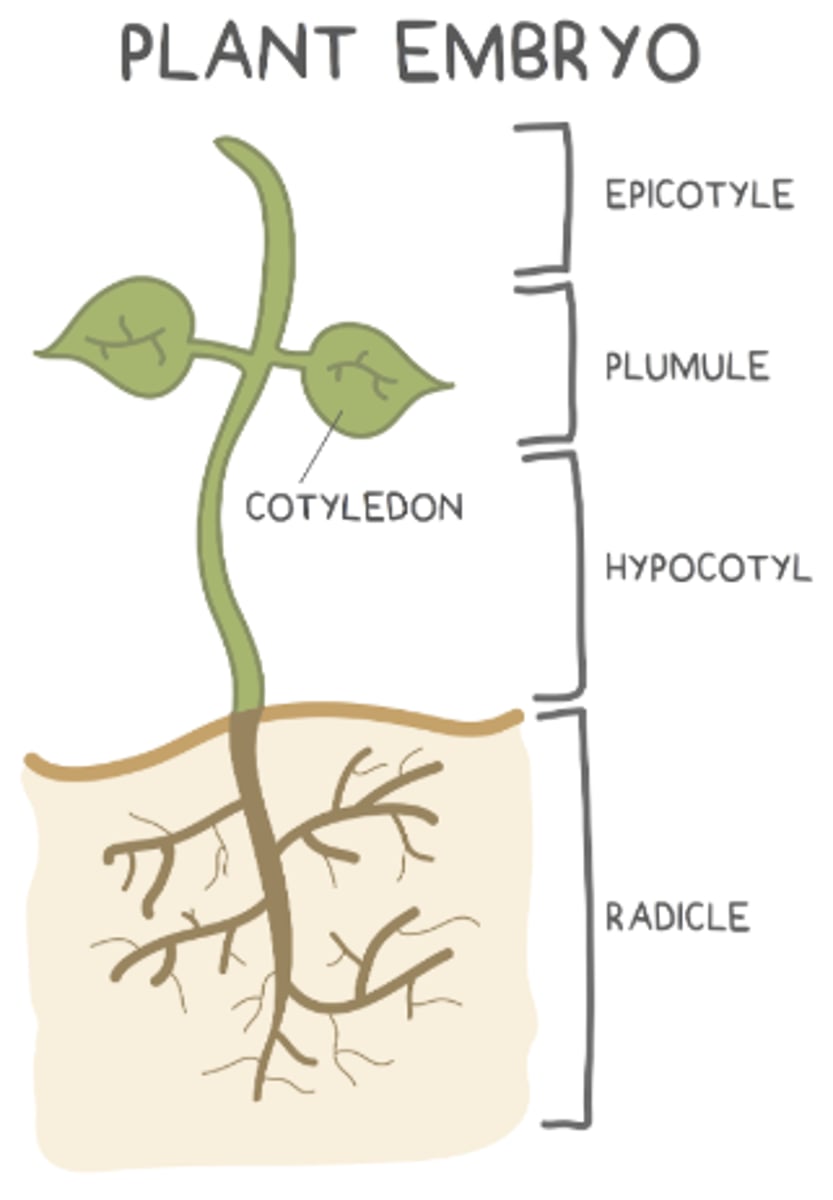
the _____ develops into the very top region of the young shoot (shoot tip)
epicotyl
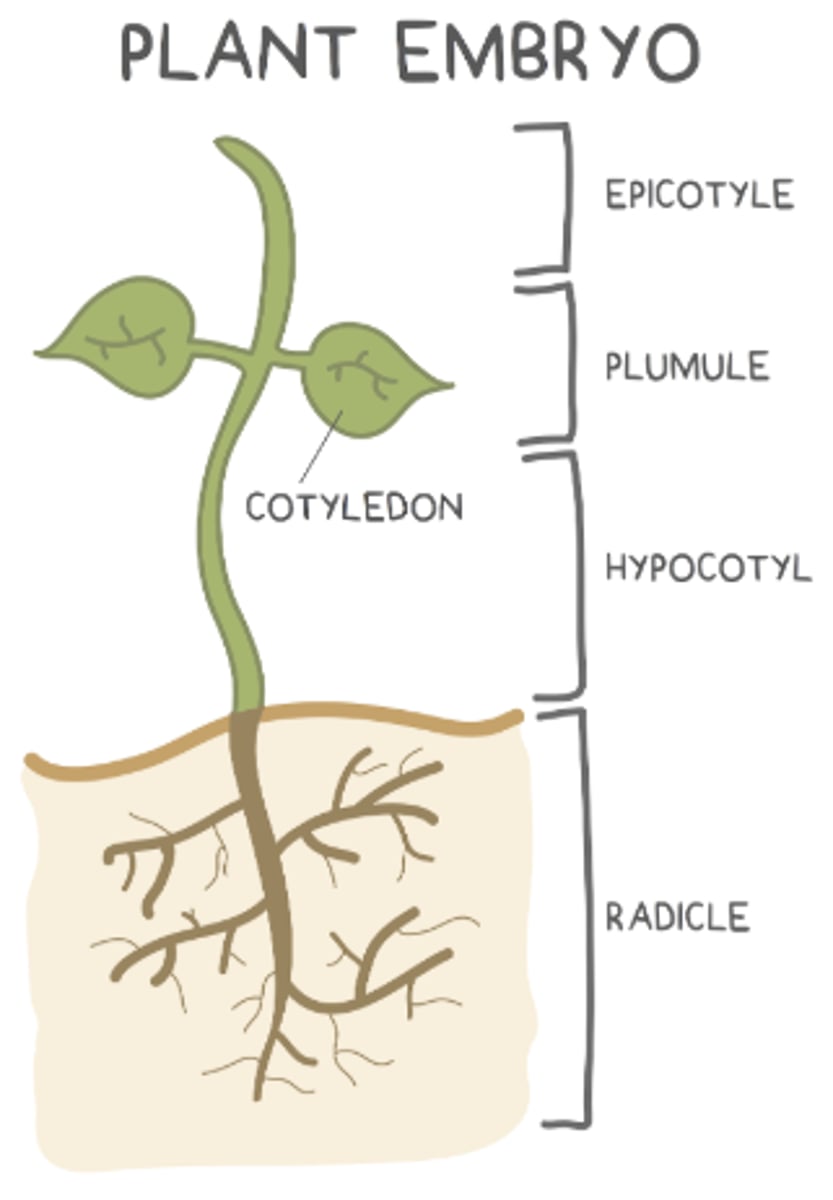
the _____ is found in between the hypocotyl and epicotyl, and it develops into young leaves
plumule
_____ is the sprouting of a seedling from a previously dormant seed
germination
seeds remain in a state of _____ until environmental conditions are suitable for growth
dormancy
which environmental cues are needed to kickstart germination, and which is the most important?
water, temperature, and light; water
what is imbibition?
the absorption of water by the seed
what is the result of imbibition?
the absorption of water by the seed causes it to swell and break its seed coat
in plants, growth takes place via repeated cell division/mitosis at the _____
meristems
what are the two types of meristem?
apical and lateral
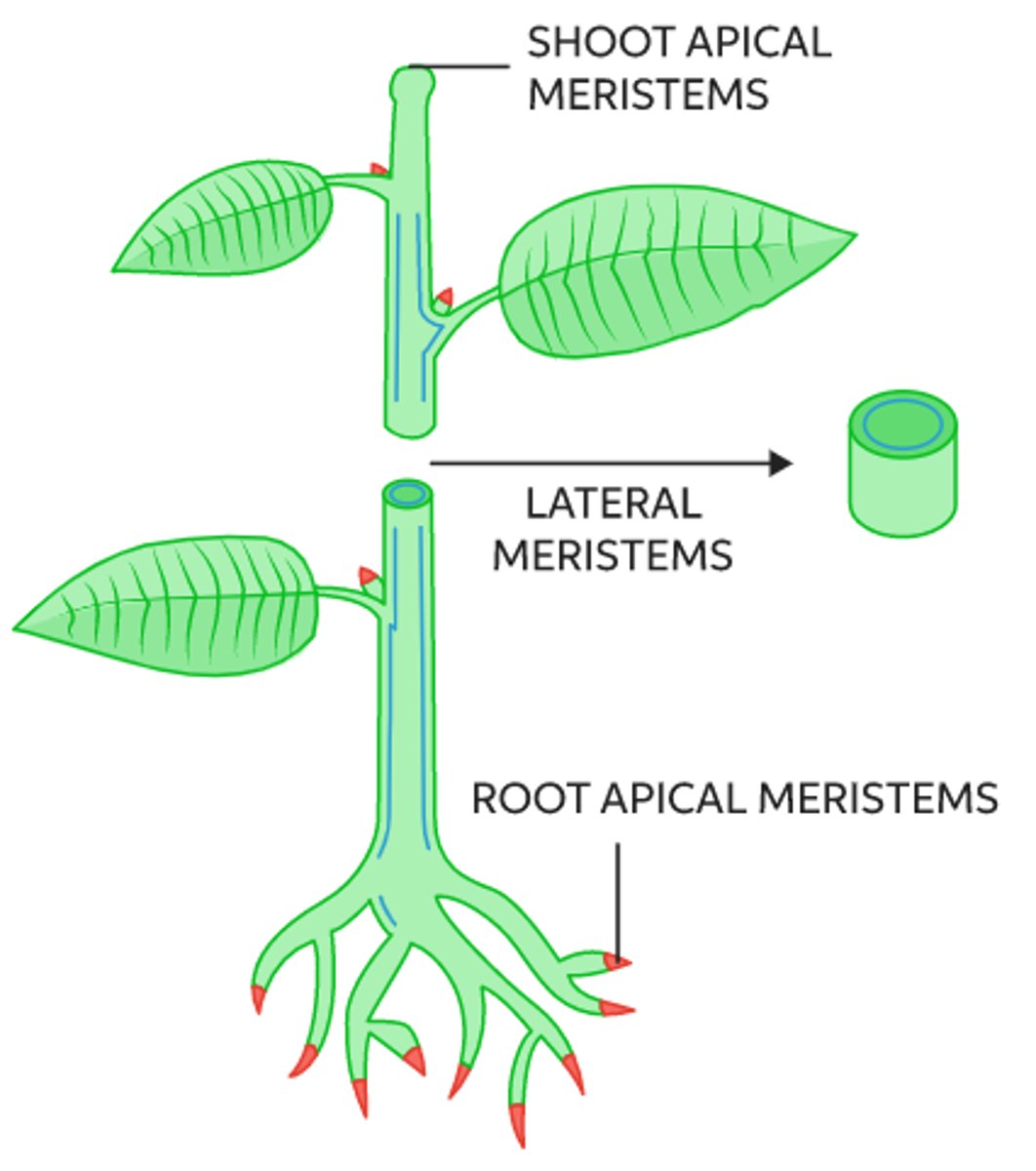
where are apical meristems located?
the very tips of roots and shoots
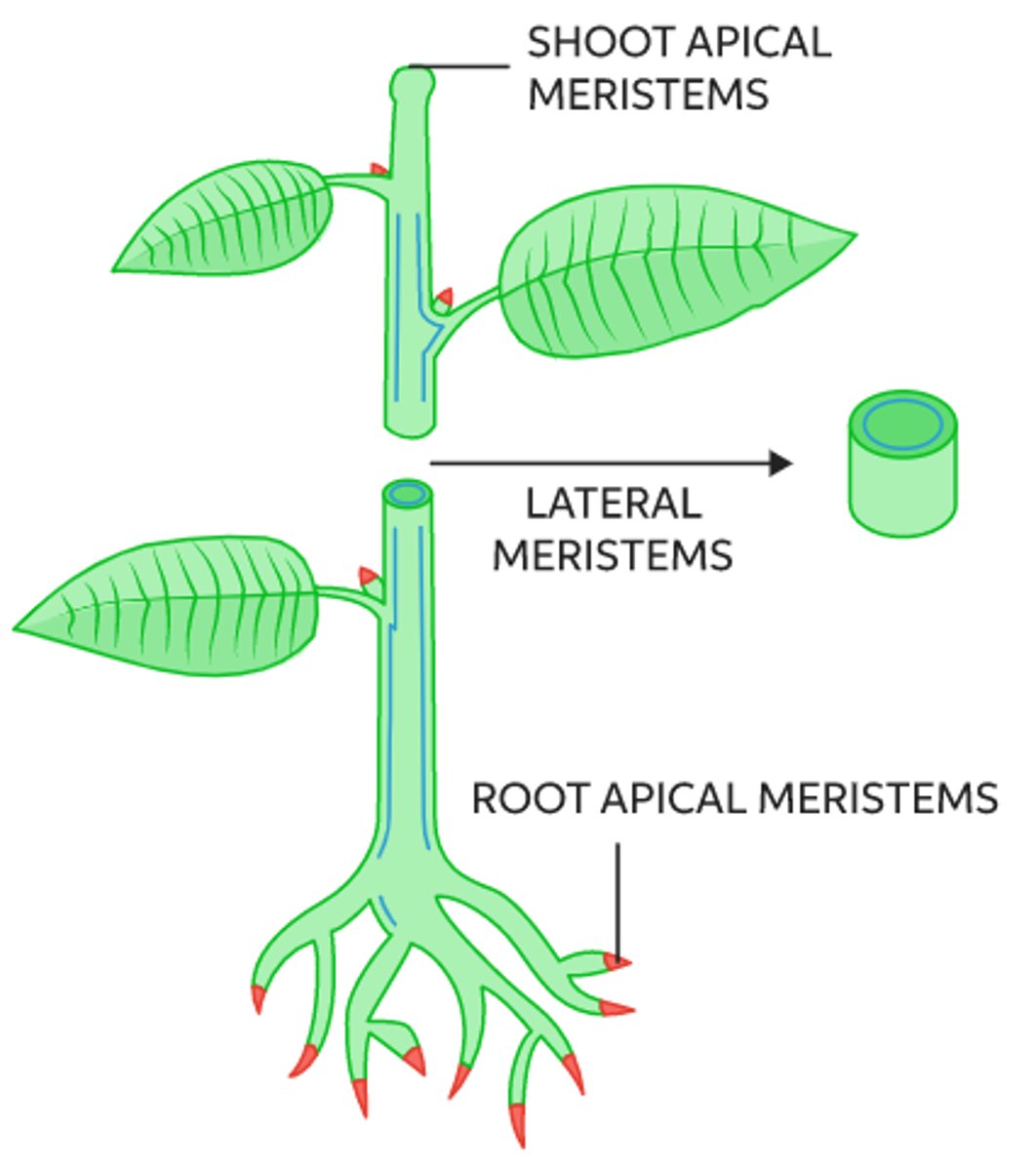
_____ cause the plant to grow vertically
apical meristems
what is the location and function of lateral meristems?
found where horizontal growth can occur
(i.e., lateral meristems function to increase thickness)
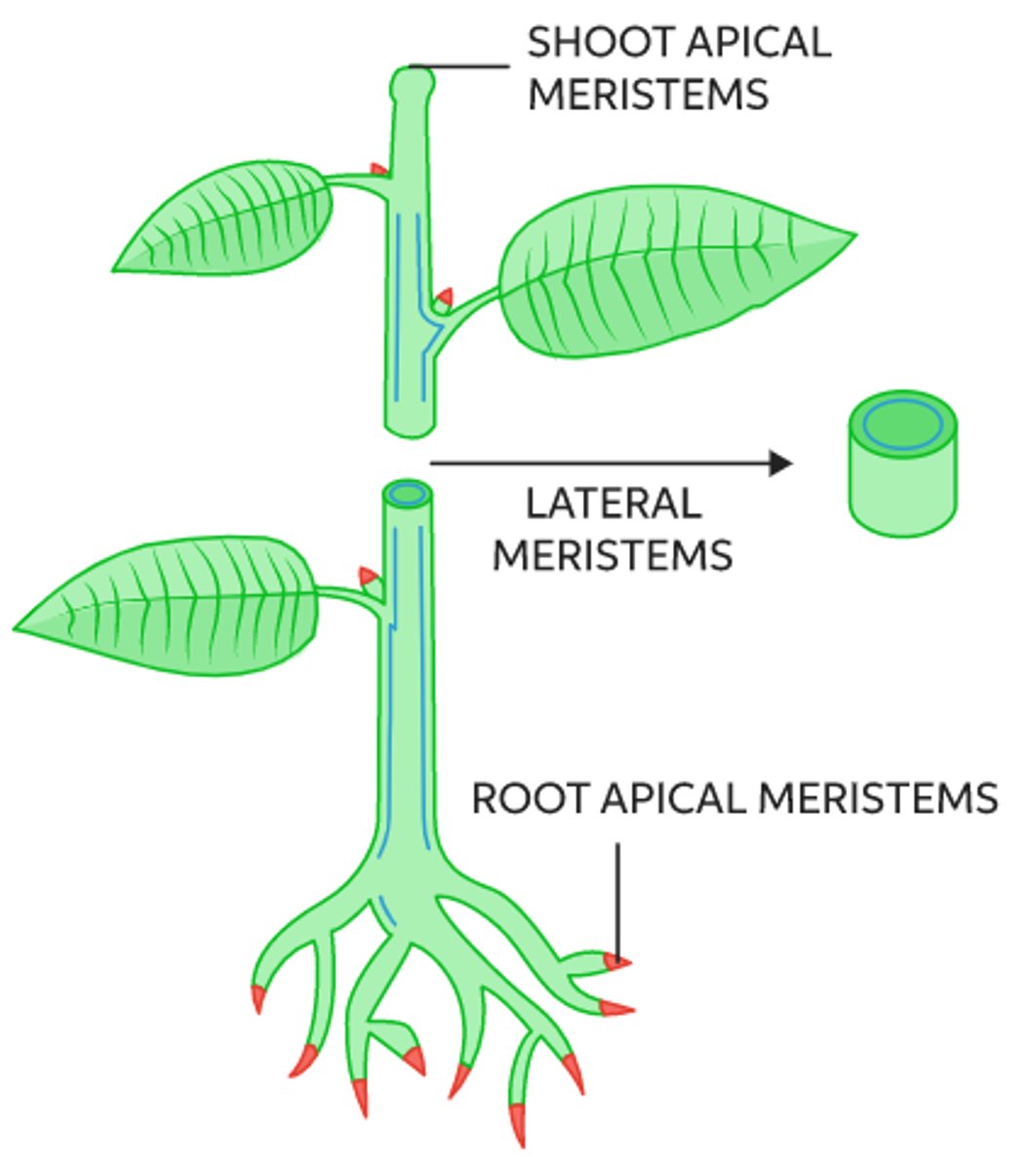
lateral meristems include _____ & _____
vascular cambium; cork cambium
where does primary growth occur in a new hatchling?
apical meristems
_____ cover and protect the apical meristem, so the meristem can further penetrate soil
root caps
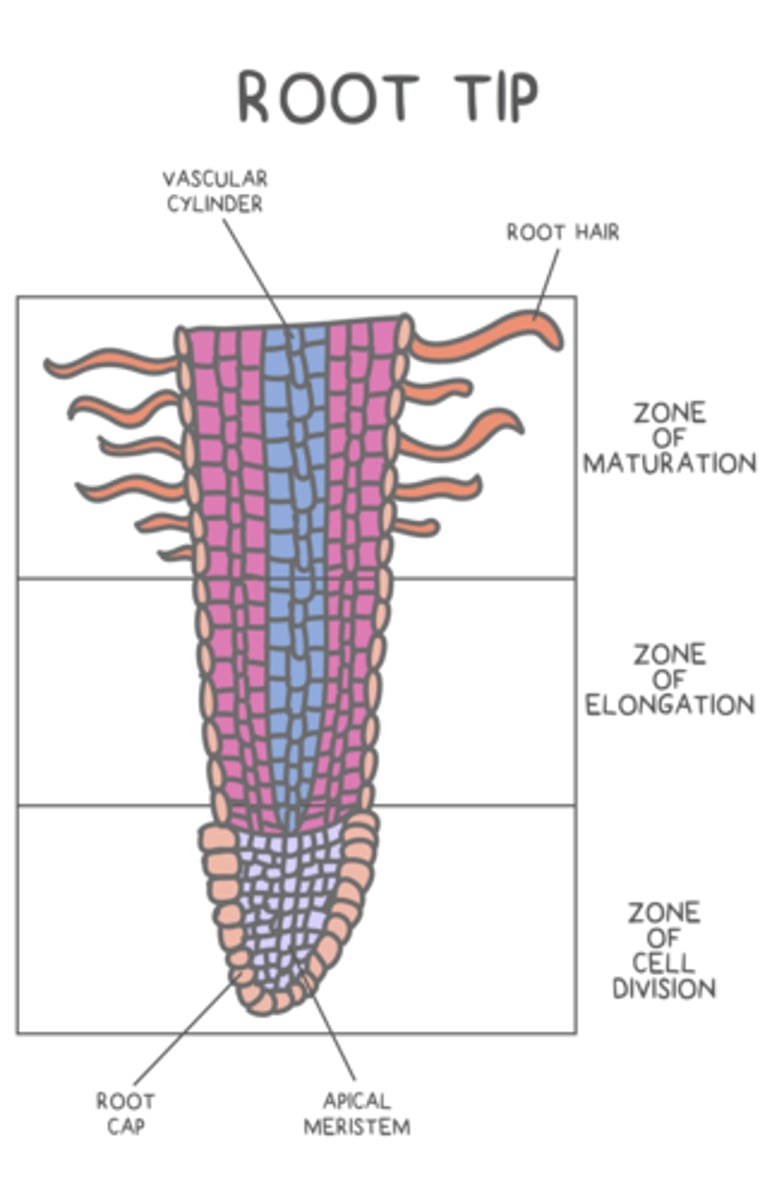
what are the 3 zones created by apical meristem divisions?
zone of division; zone of elongation; zone of maturation
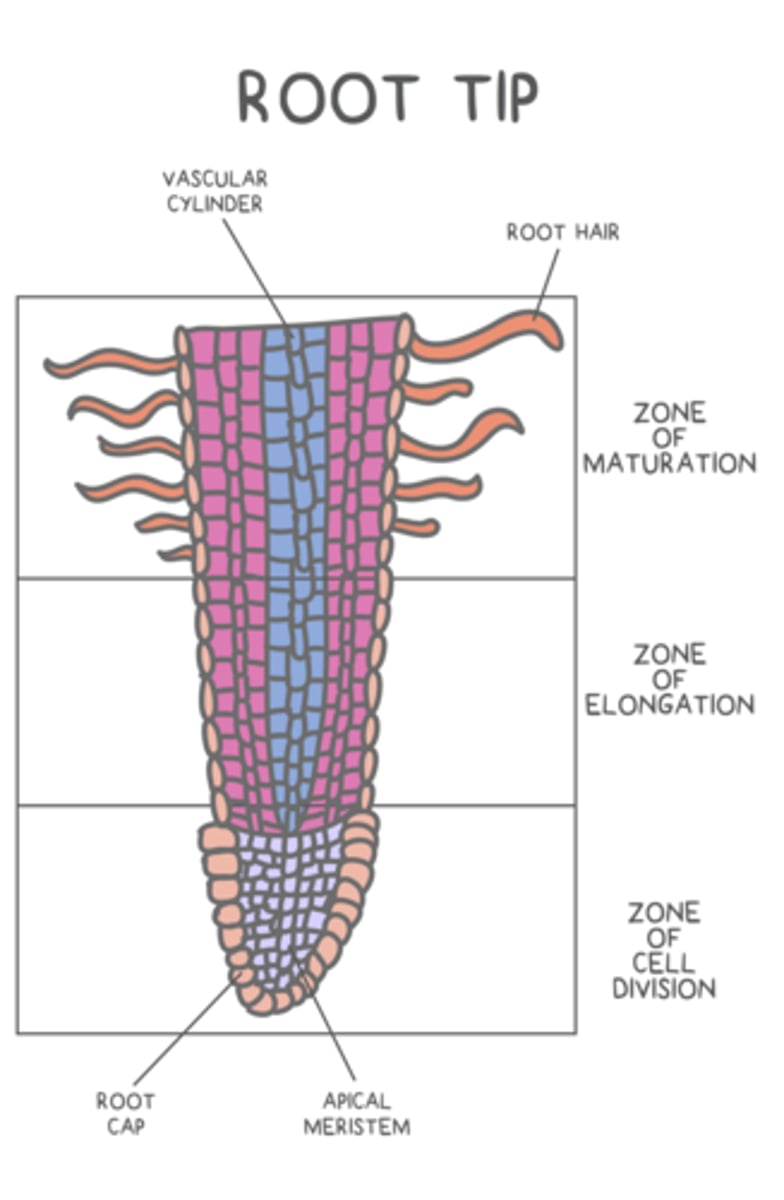
_____ is the vertical growth of a plant at its apical meristems
primary growth
_____ is the horizontal growth of a plant at its lateral meristems
secondary growth
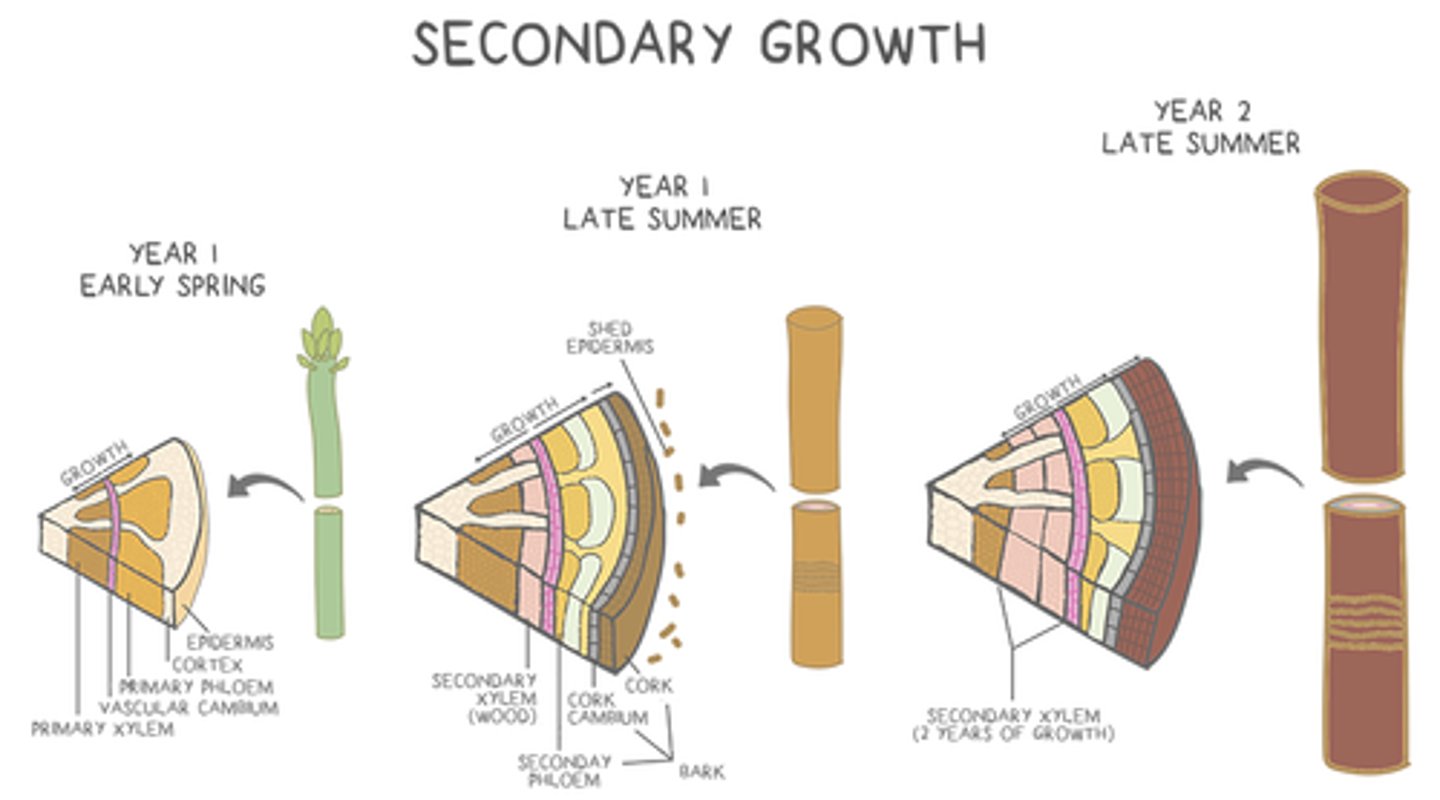
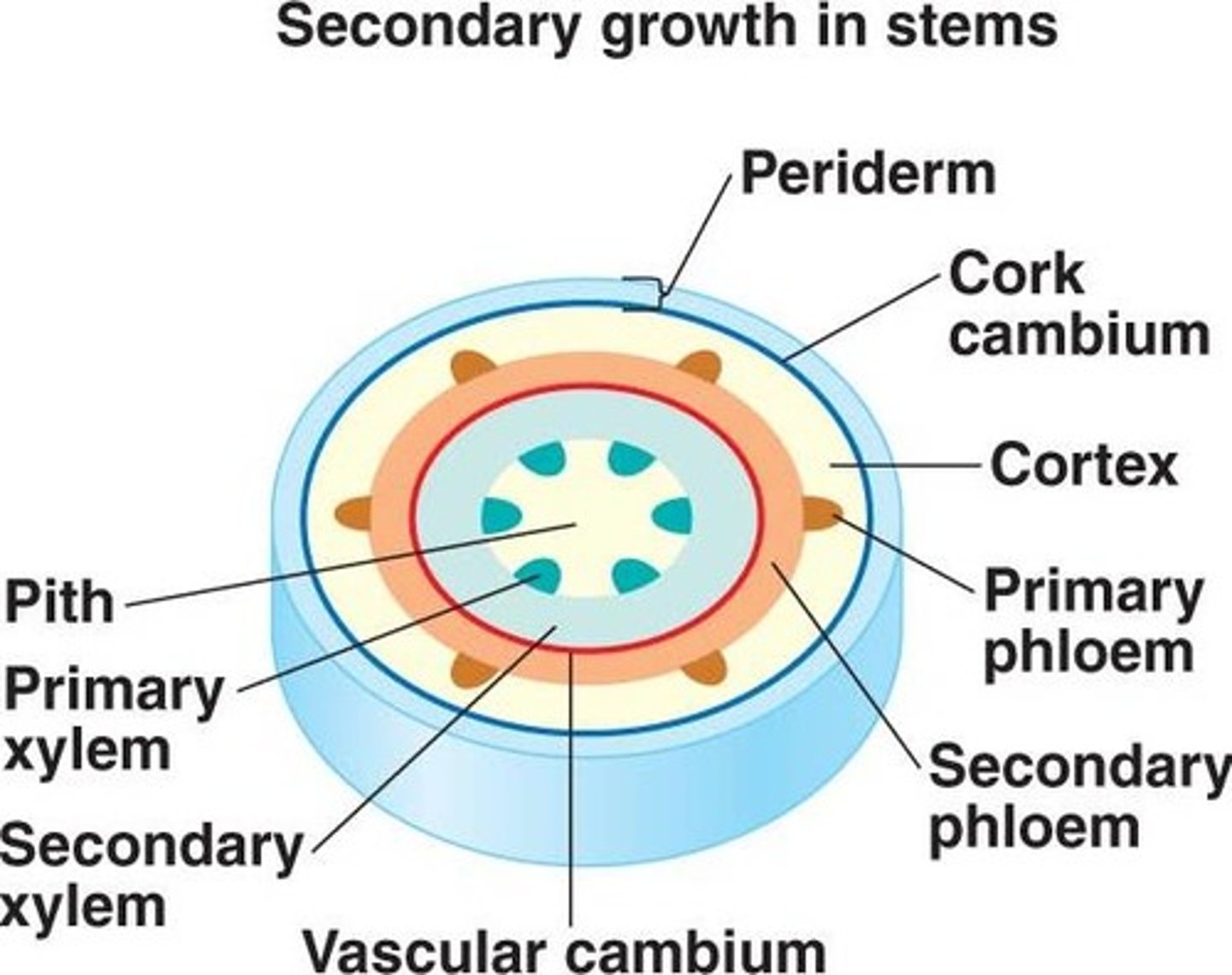
what is the vascular cambium?
a ring of meristematic tissue located between the primary xylem and primary phloem
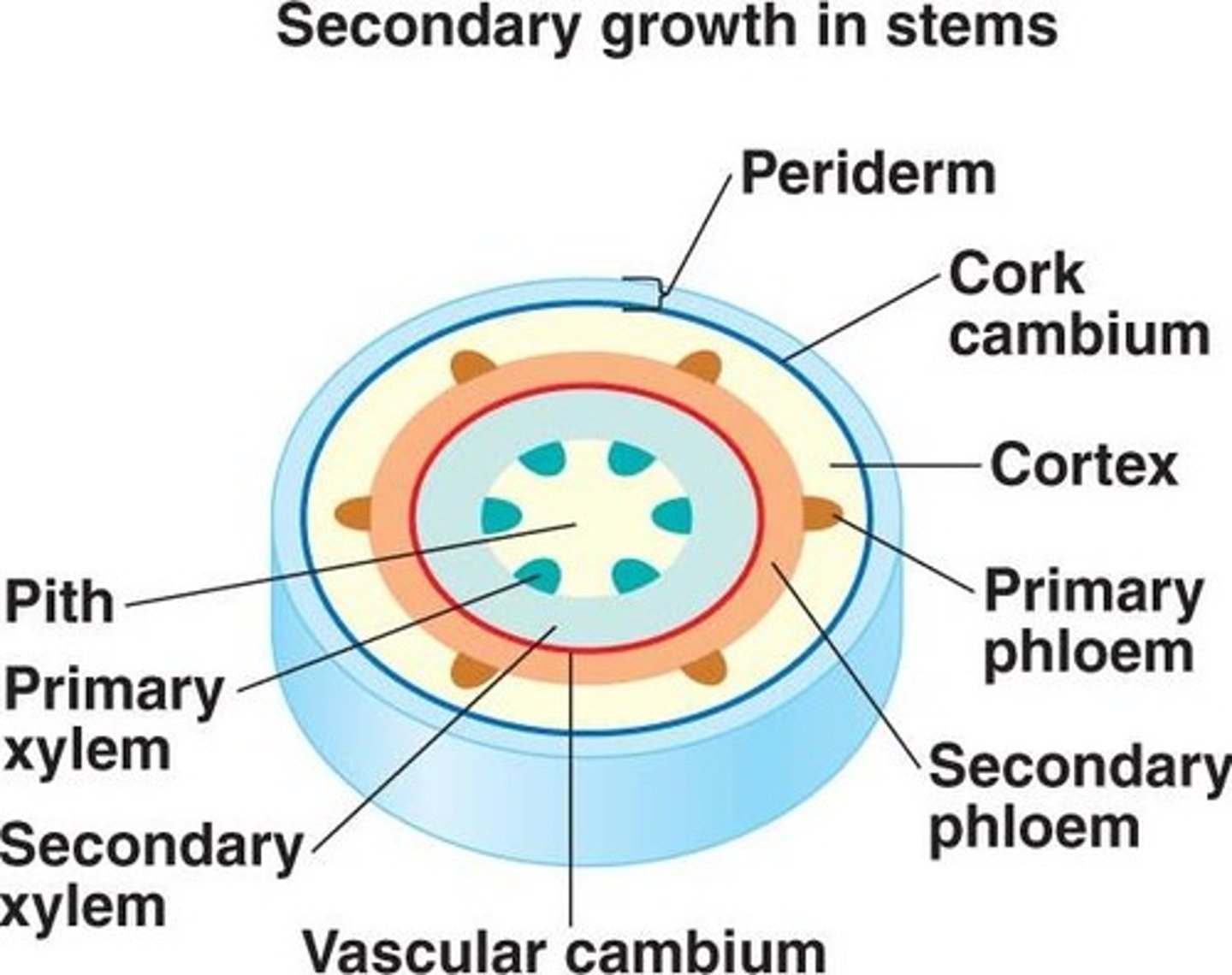
cells that are produced on the _____ (inside/outside) of the vascular cambium ring become the secondary xylem
inside
cells produced on the outside of the vascular cambium ring become the _____
secondary phloem
the _____ forms wood (along with pith)
secondary xylem
(cells inside the vascular cambium = secondary xylem)
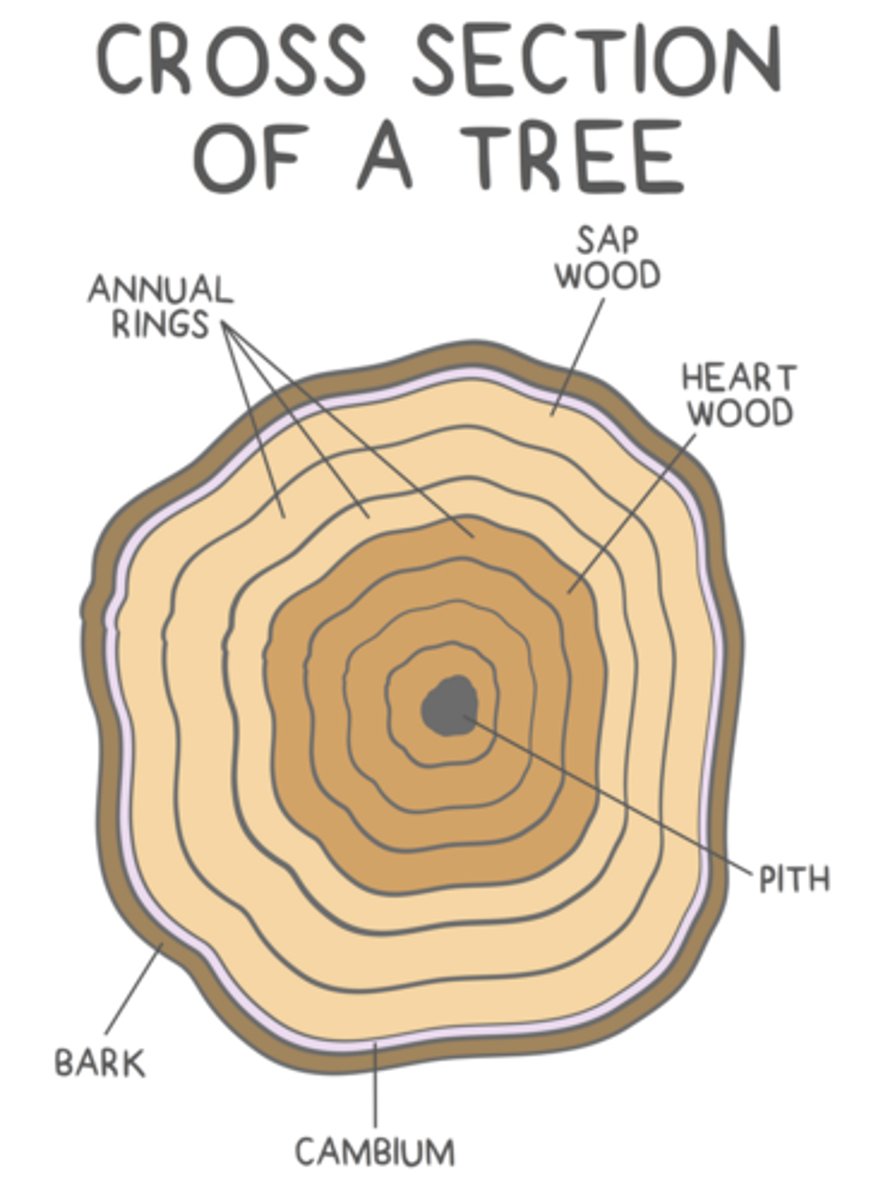
secondary phloem makes _____, which is constantly being shed and replaced
bark
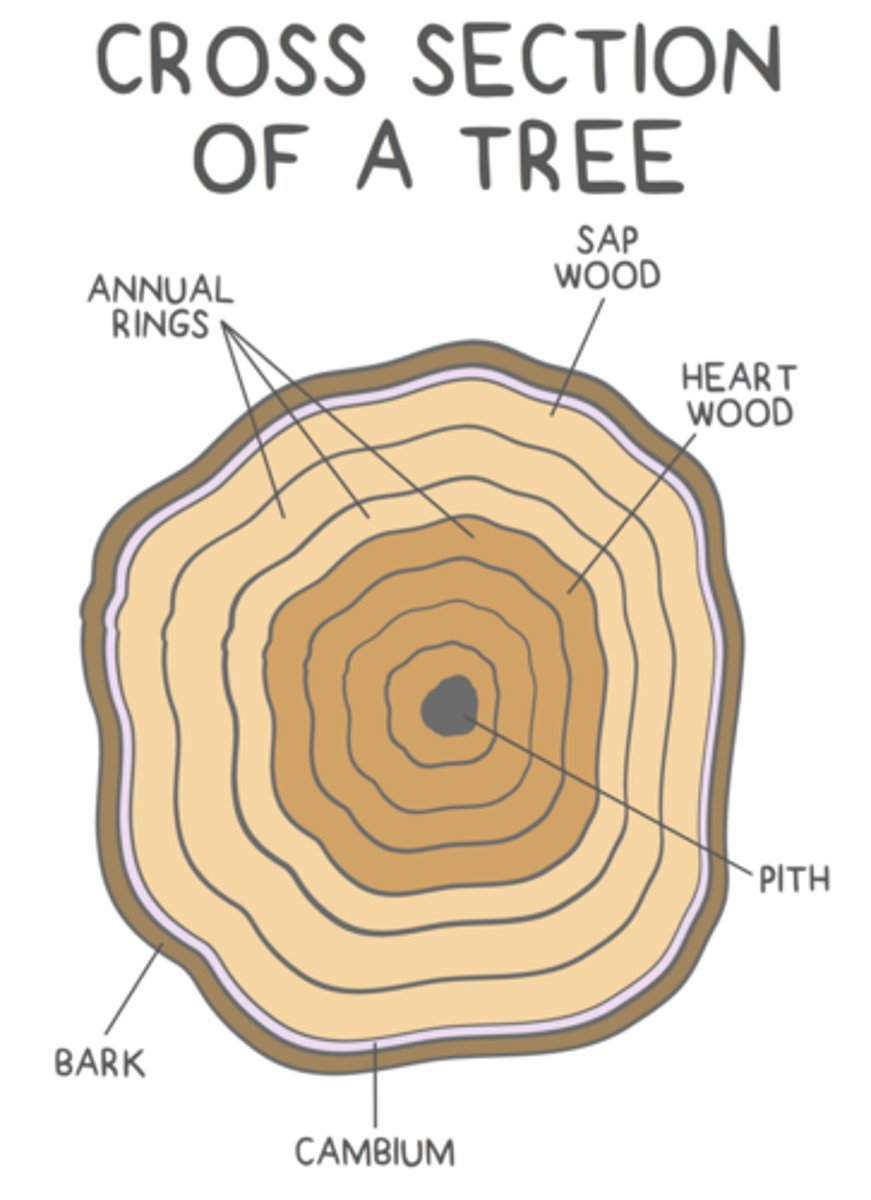
the _____ is a ring of meristematic tissue located beyond the phloem, closer to the periphery of the stem
cork cambium
the cork cambium divides repeatedly to form _____
cork
cork is the _____ layer of bark, which acts as a protective plant layer
outermost
all plants undergo _____ growth but only woody plants undergo _____ growth
primary; secondary
what are the three categories of plant tissue?
ground; vascular; dermal
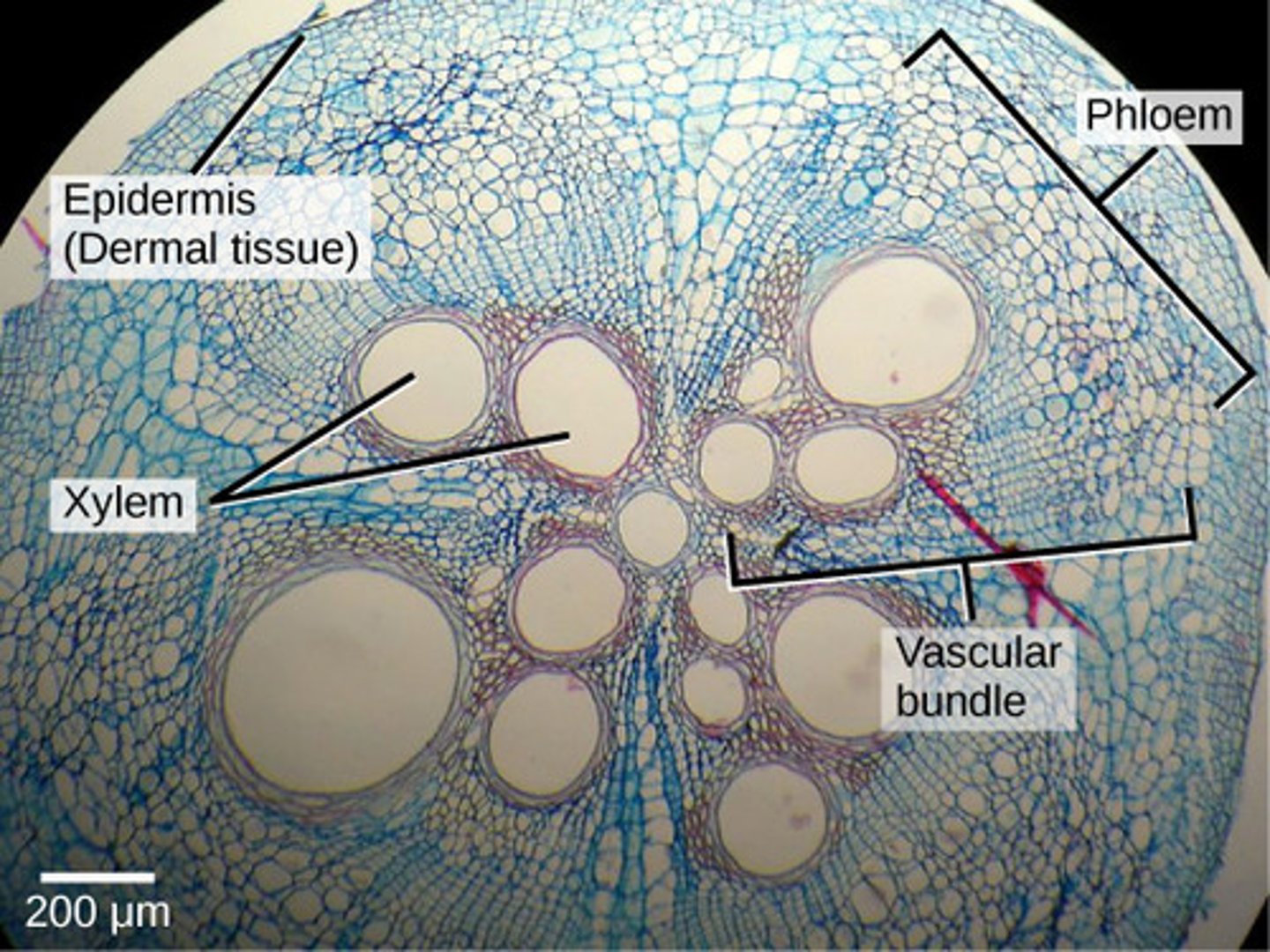
the _____ tissue provides structural support to the plant
ground
the ground tissue makes up the most of a plant's _____
mass
what are the three types of ground tissue?
parenchyma; collenchyma; sclerenchyma
_____ has the thinnest cell walls of the three ground tissue types
parenchyma
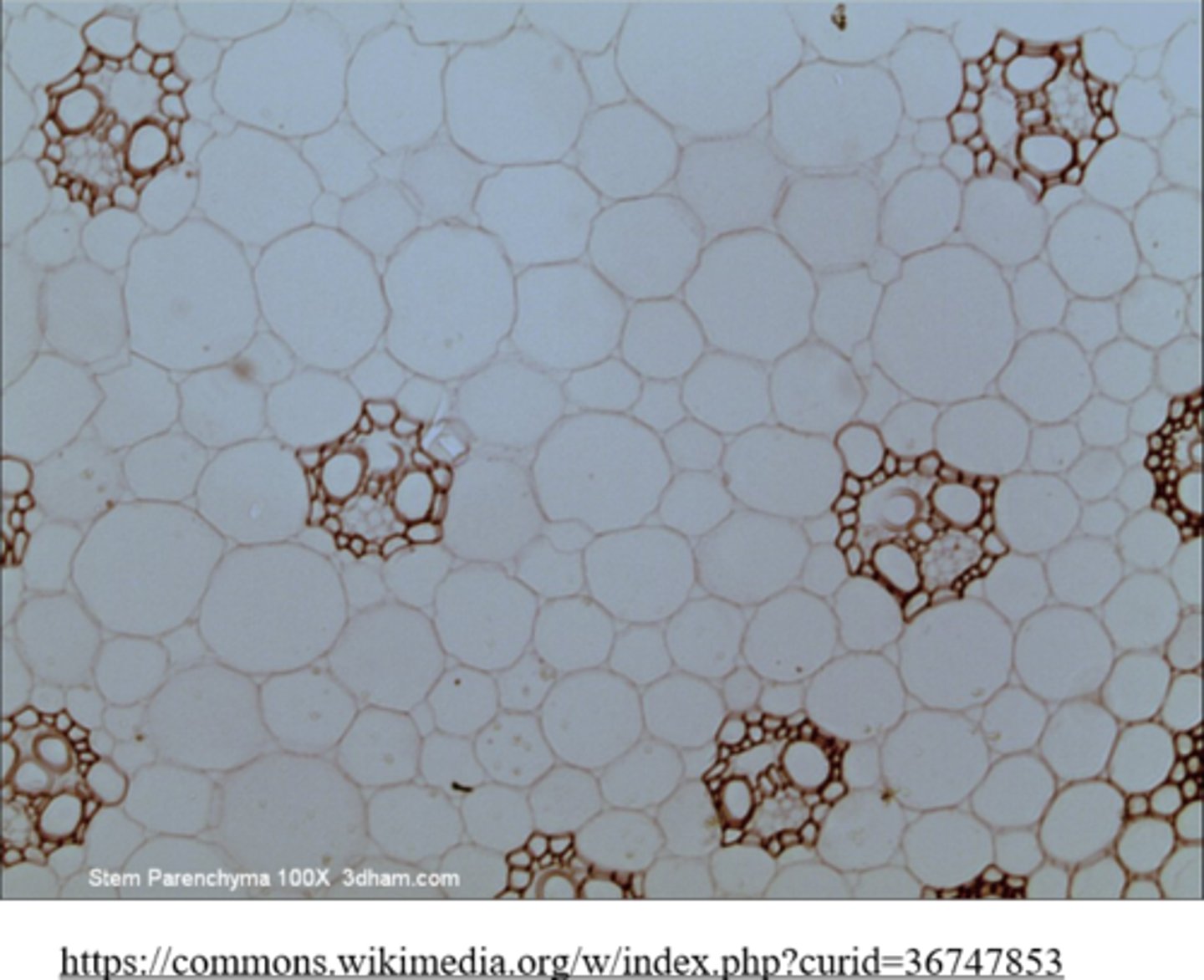
parenchyma is a _____ tissue, which makes up the _____ of the plant
filler; bulk
(parenchyma = ground tissue type)
the _____ ground tissue cells provide extra plant support, especially in areas where the plant is actively growing
collenchyma
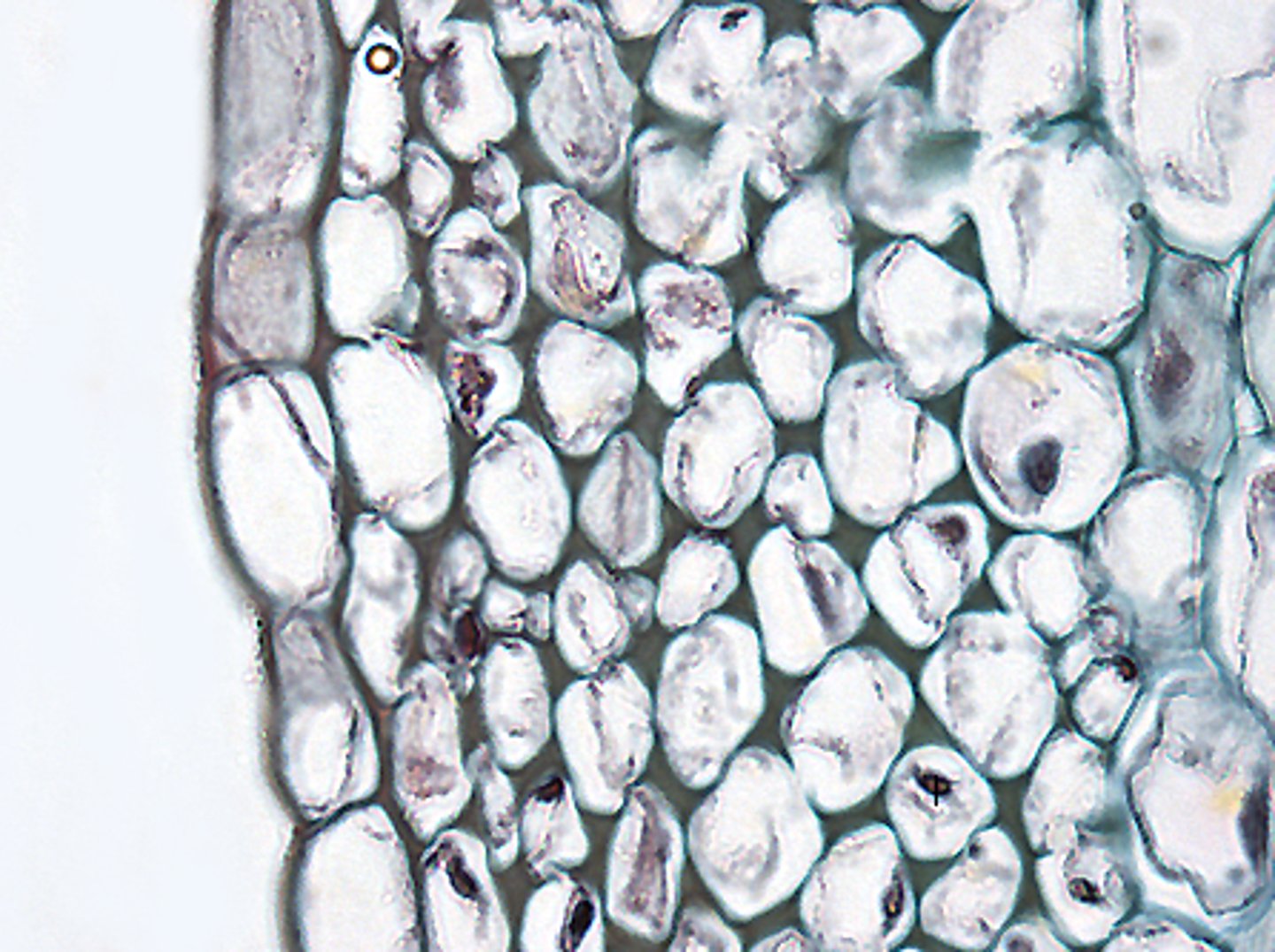
collenchyma ground tissue have _____ cell walls
irregular
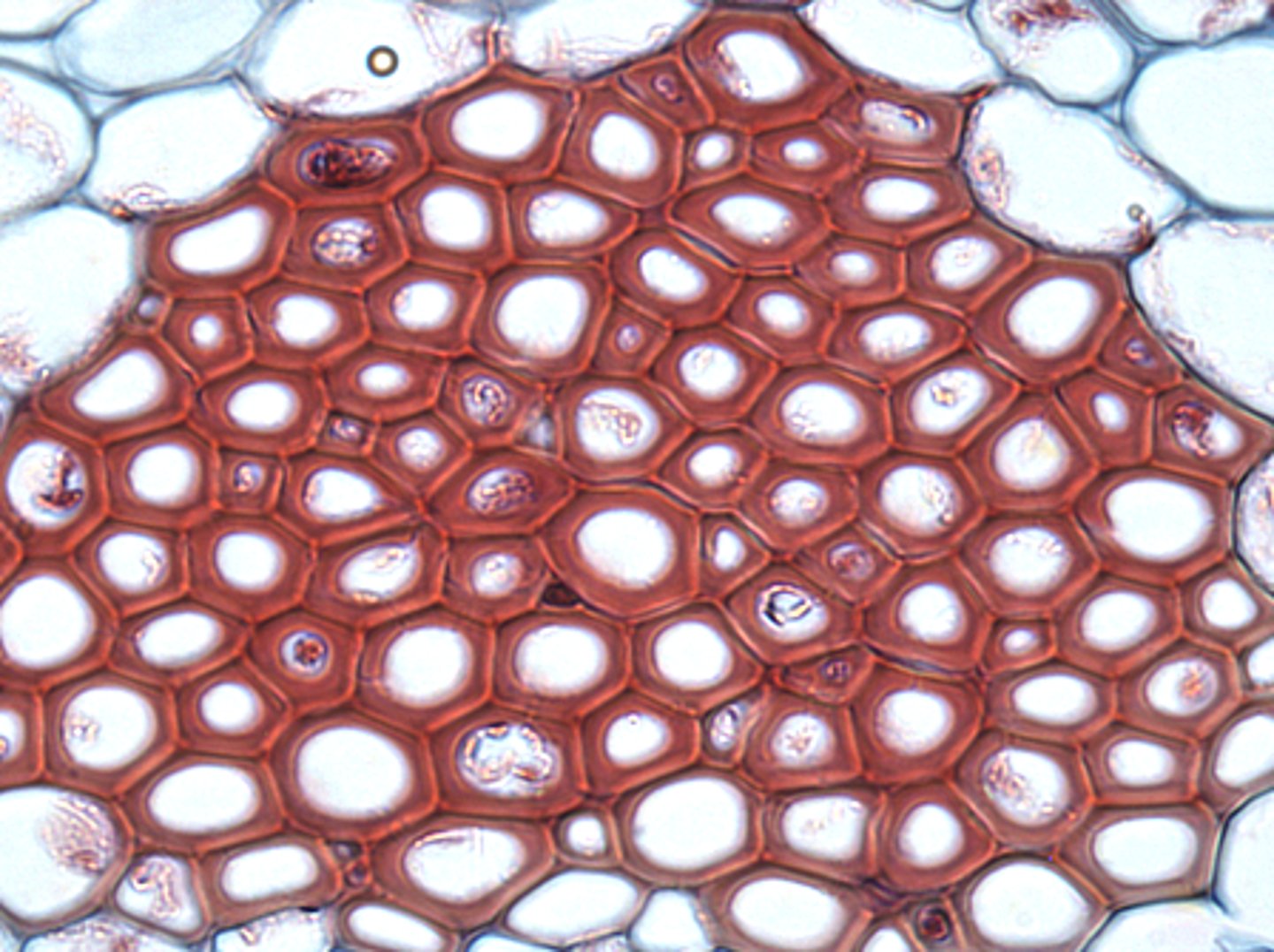
sclerenchyma ground tissue is the main _____ of the plant
structural support
have the thickest cell walls of the three ground tissue types
sclerenchyma
what are the two main components of the vascular tissue?
xylem and phloem
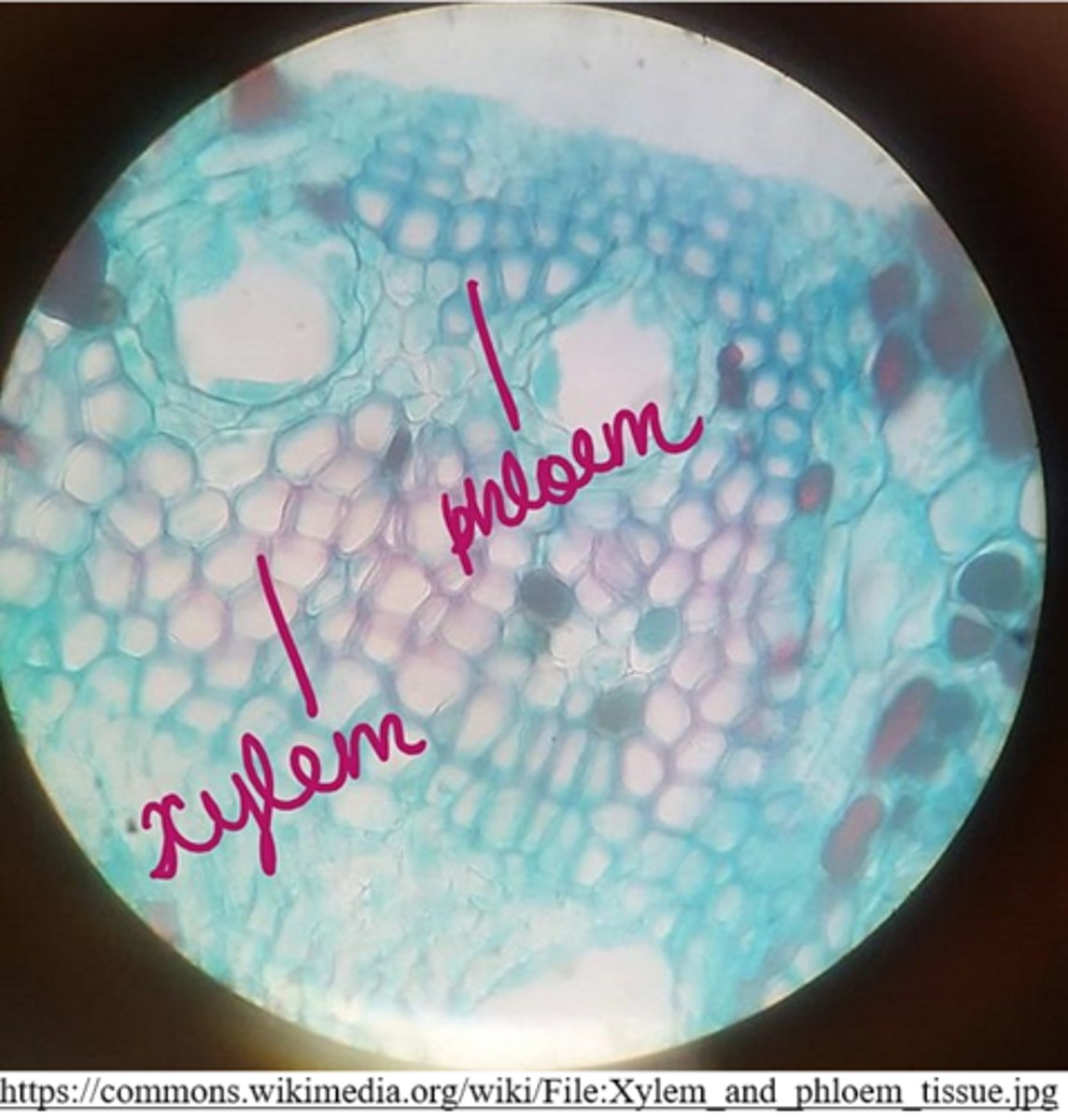
what are the functions of the vascular tissue?
transport material from the source to the sink
the _____ is where plant nutrients are generated
source
the _____ is where plant nutrients are used
sink
the _____ transports sugars from the leaves (source) to the roots (sink)
phloem
(phloem is a sieve tube)
sugars are created in the _____ via photosynthesis
leaves
which cell types are found in phloem?
sieve and companion cells
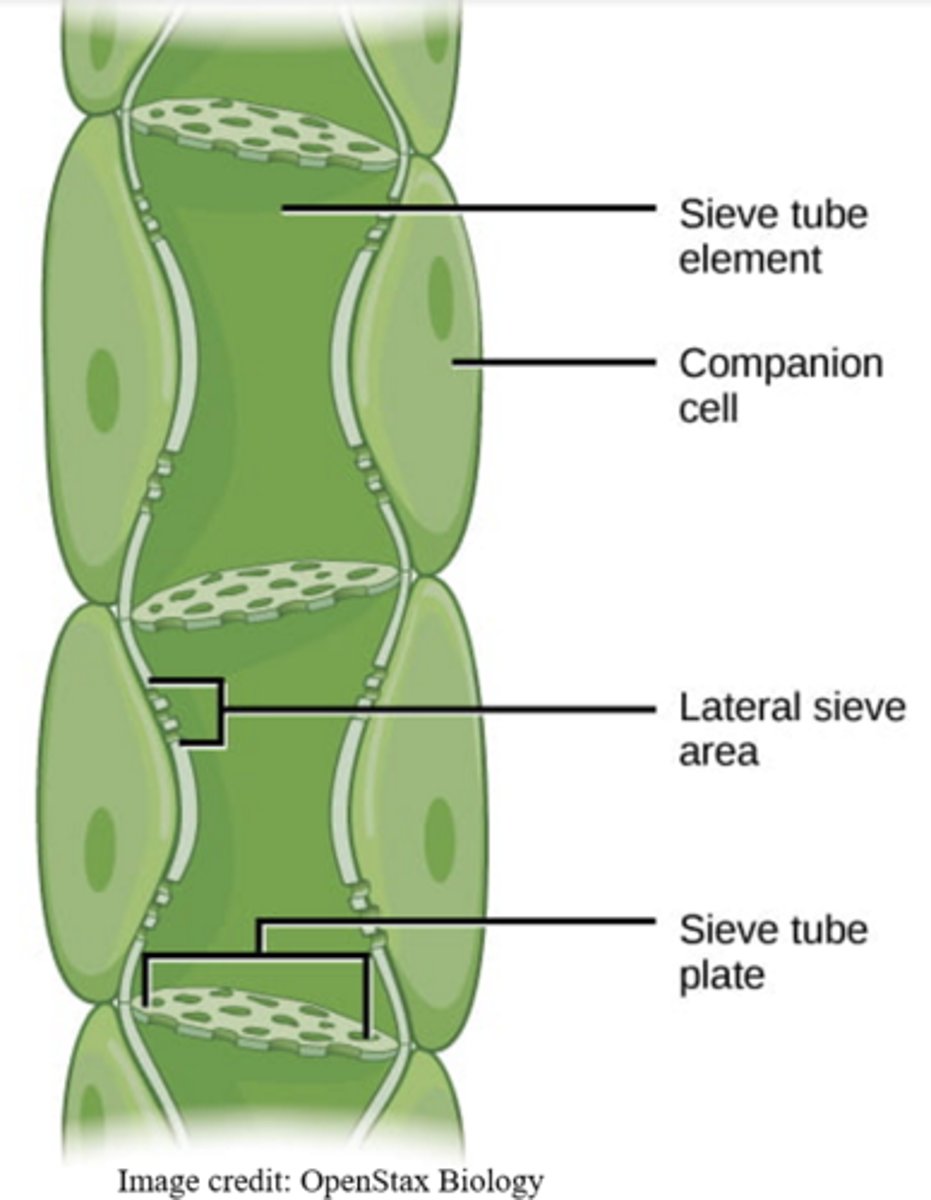
sieve cells are long cells with _____ that allow substances to flow through them
pores
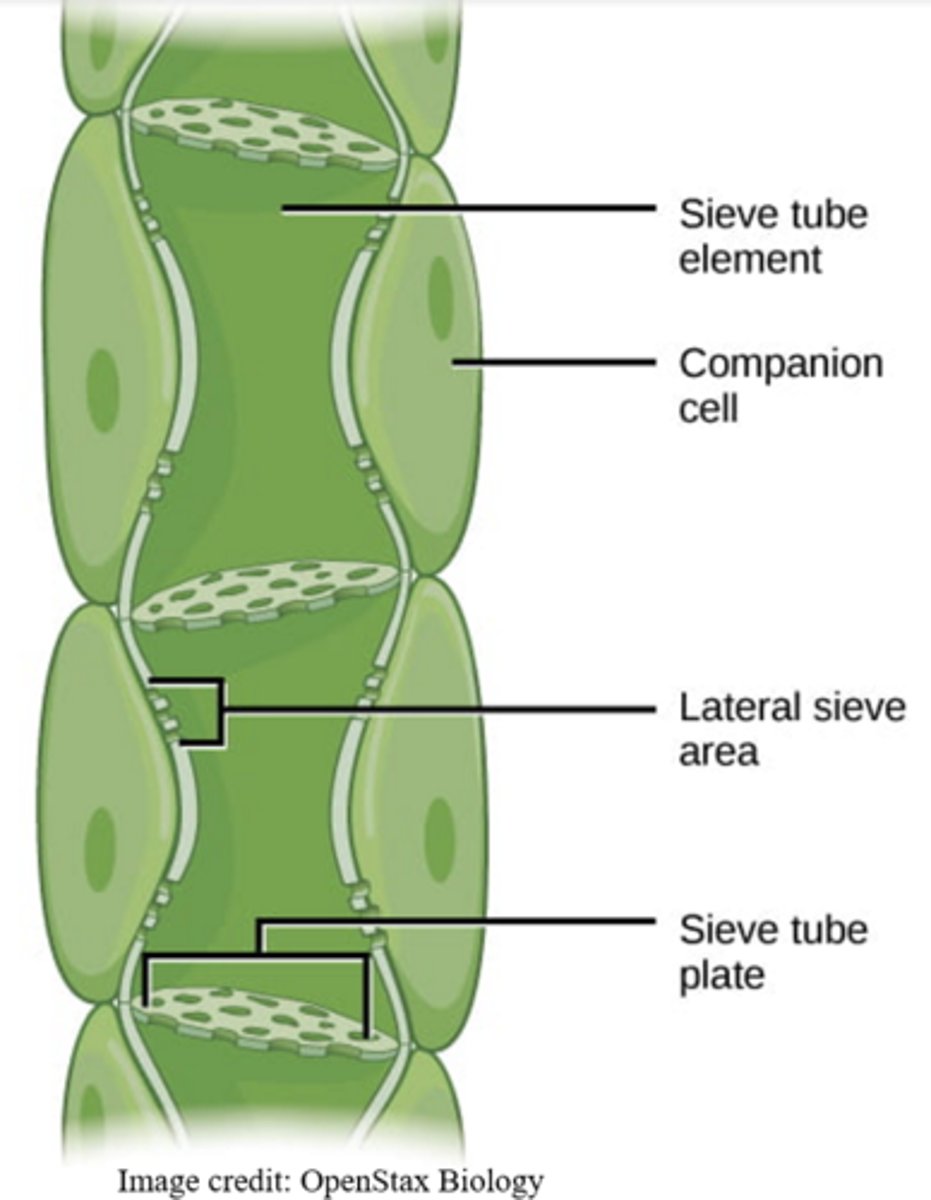
_____ are connected together to form a sort of continuous tunnel
sieve cells
sieve cells lack _____
organelles
_____ cells are connected to sieve cells
companion
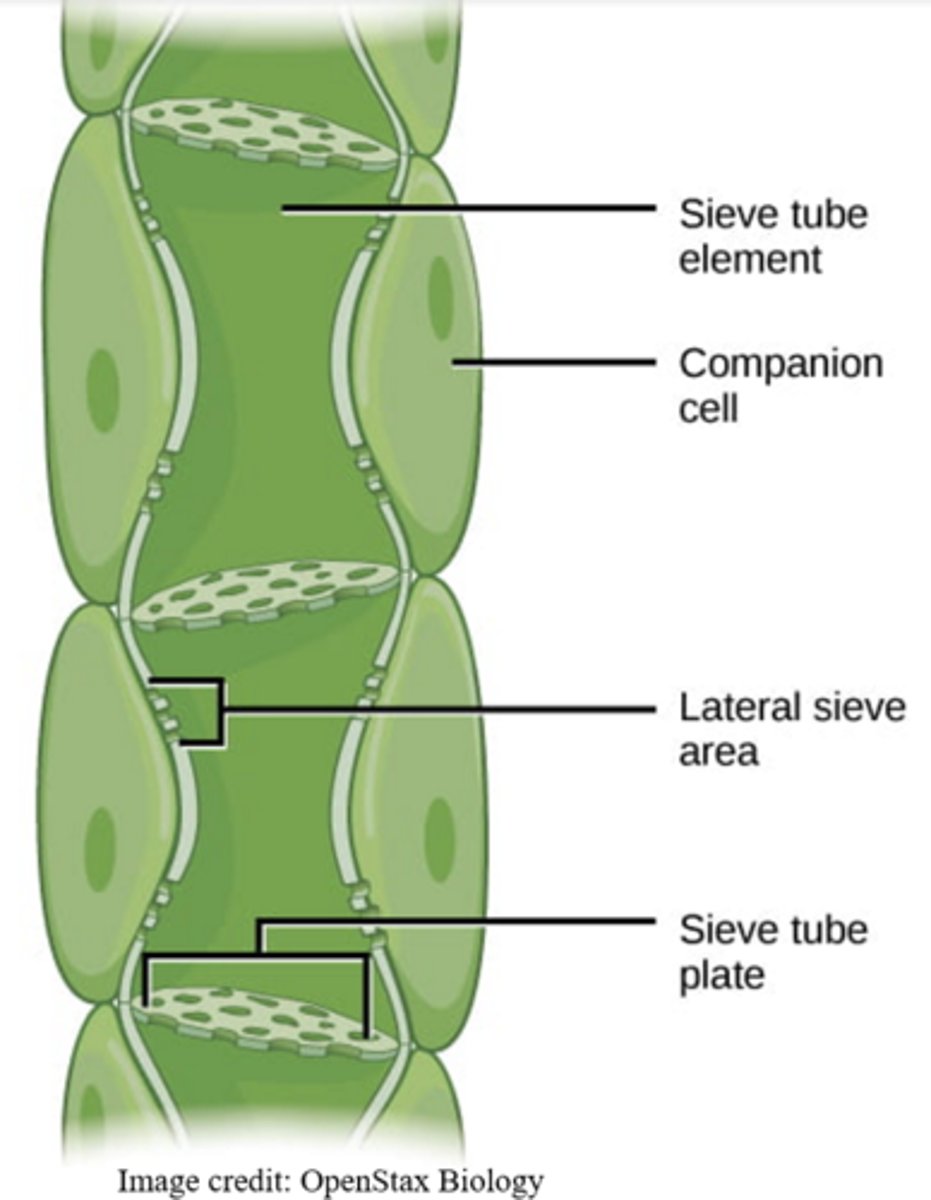
companion cells have the necessary _____ to carry out metabolic functions
organelles
_____ connect sieve and companion cells
plasmodesmata
the _____ transports water from the roots (source) to the leaves (sink)
xylem
(notice roots are acting as a source of water in this case, while leaves are acting as a sink for water)
what are the two cells that make up xylem?
tracheids and vessel elements
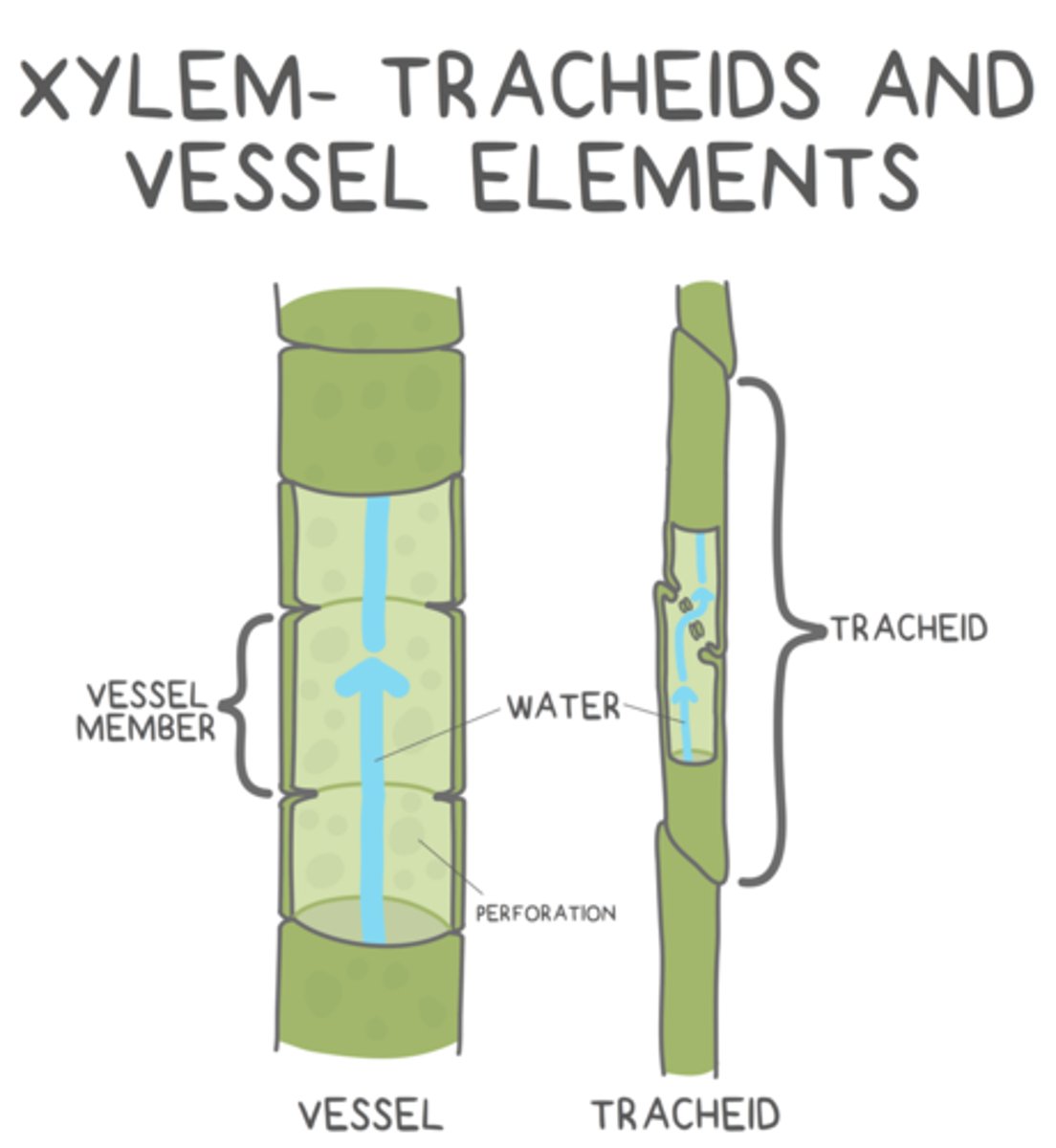
what shape do tracheids have?
long and thin
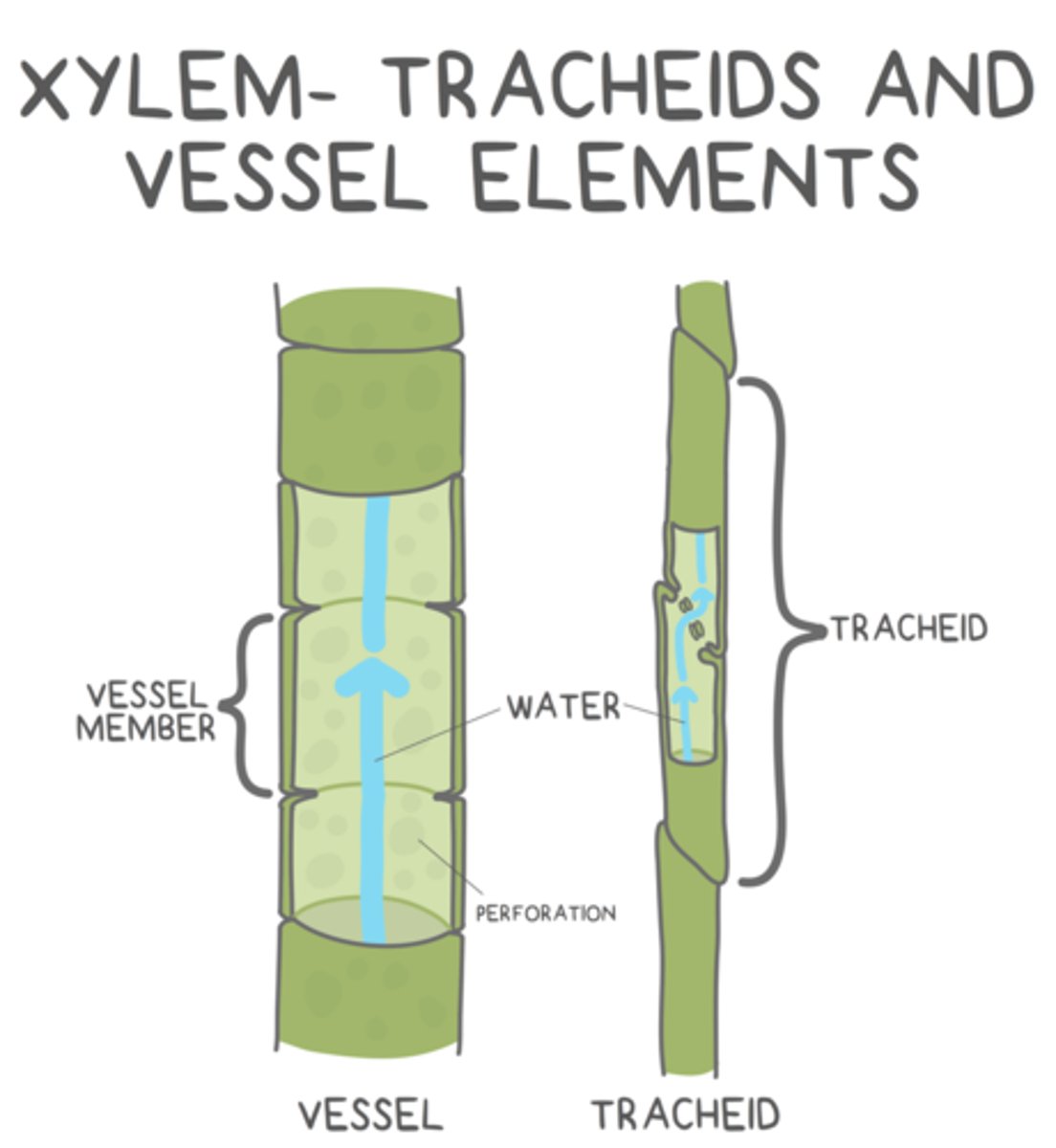
how are tracheids organized?
overlapping tapered ends keeps them in contact with other tracheids
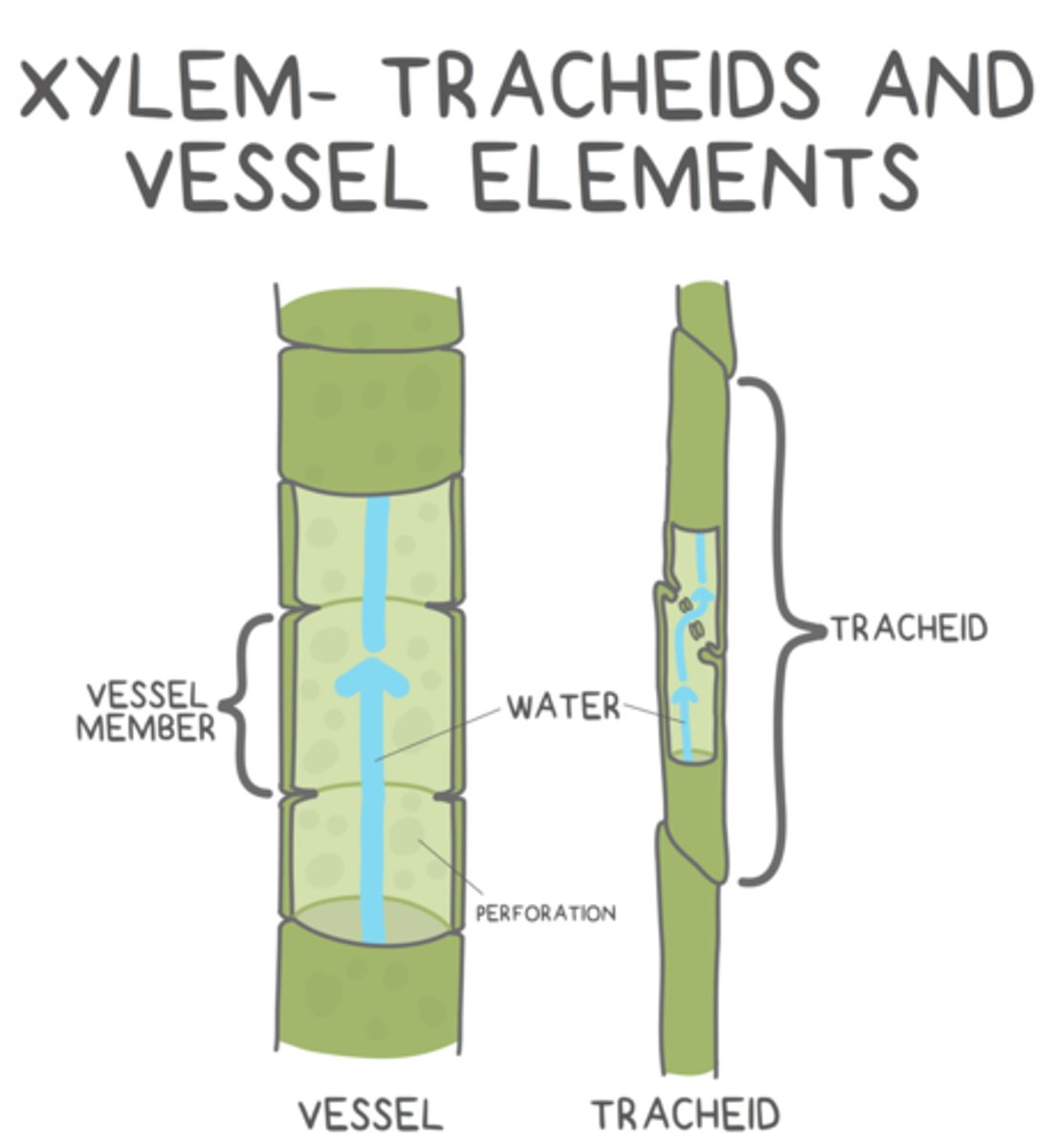
water flows from tracheid to tracheid through _____ found at their overlapping, tapered ends
pits
_____ are shorter and stouter than tracheids, and they are in contact with other _____ (for the most part)
vessel elements; vessel elements
water flows from vessel element to vessel element through _____
perforations
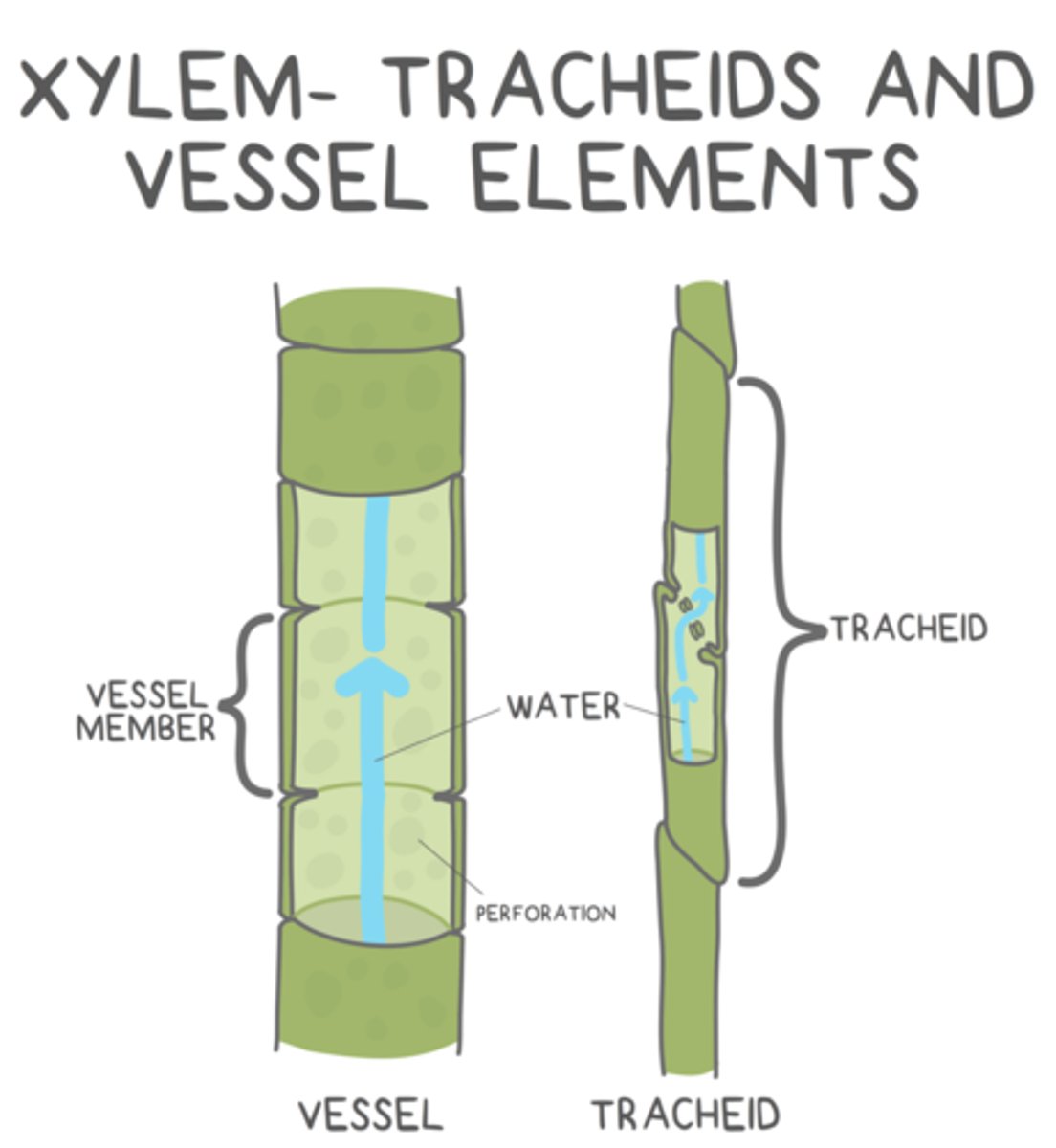
in addition to water conduction, tracheids and vessel elements also provide _____?
structural support
the _____ is the central region of the root or stem, which is formed by the pith, and vascular bundles of xylem and phloem
stele
the _____ is tissue found at the very center of the root or stem
pith
the pith is made of _____ ground tissue
parenchyma
what are the primary functions of the pith?
storage and the transport of materials (like vascular tissues)
_____ is the outer layer that protects the plant interior
dermal tissue
the _____ tissue regulates how the plant is affected by its external environment
dermal
the _____ is the type of dermal tissue that covers the outside of the plant
epidermis
what are the properties of the cuticle and what function does it serve?
it is a waxy layer that covers the epidermis ;

the _____ is especially found in plants found in hot climates
cuticle

root hairs project out of the _____ of root cells
epidermis
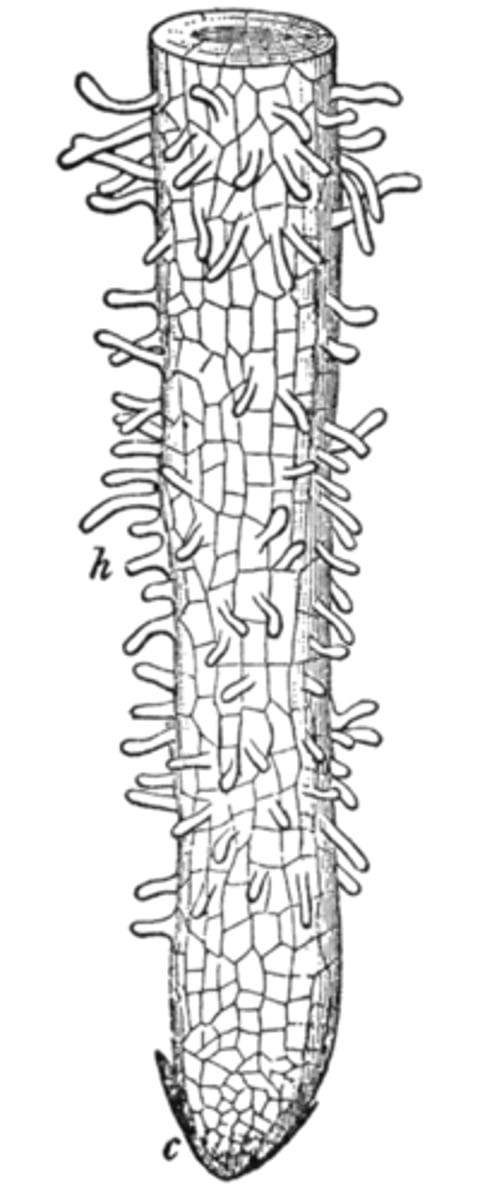
_____ increase the surface area of the epidermis, which allows for greater water and nutrient uptake
root hairs
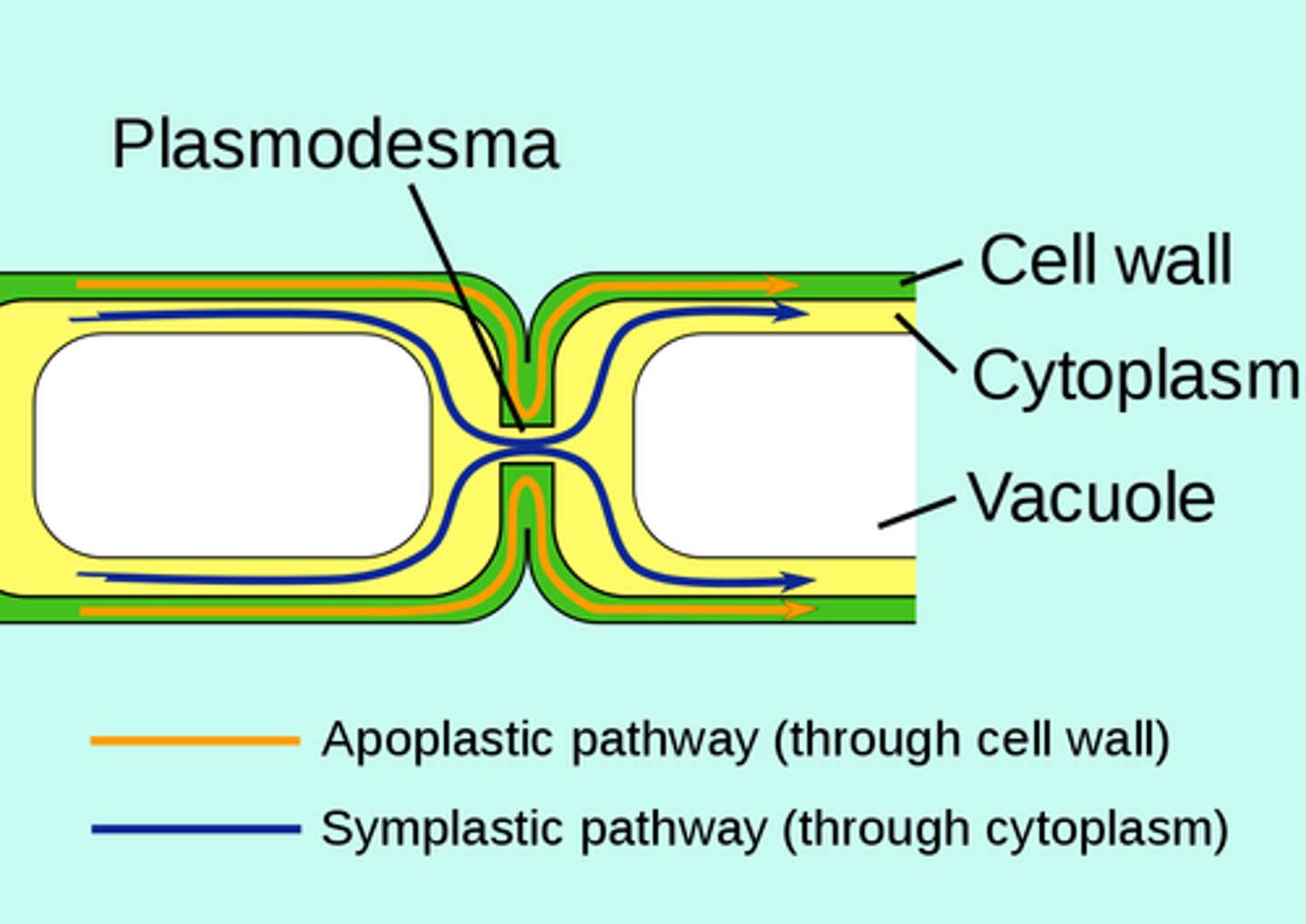
what are the two pathways to move water between plant cells?
symplastic pathway; apoplastic pathway
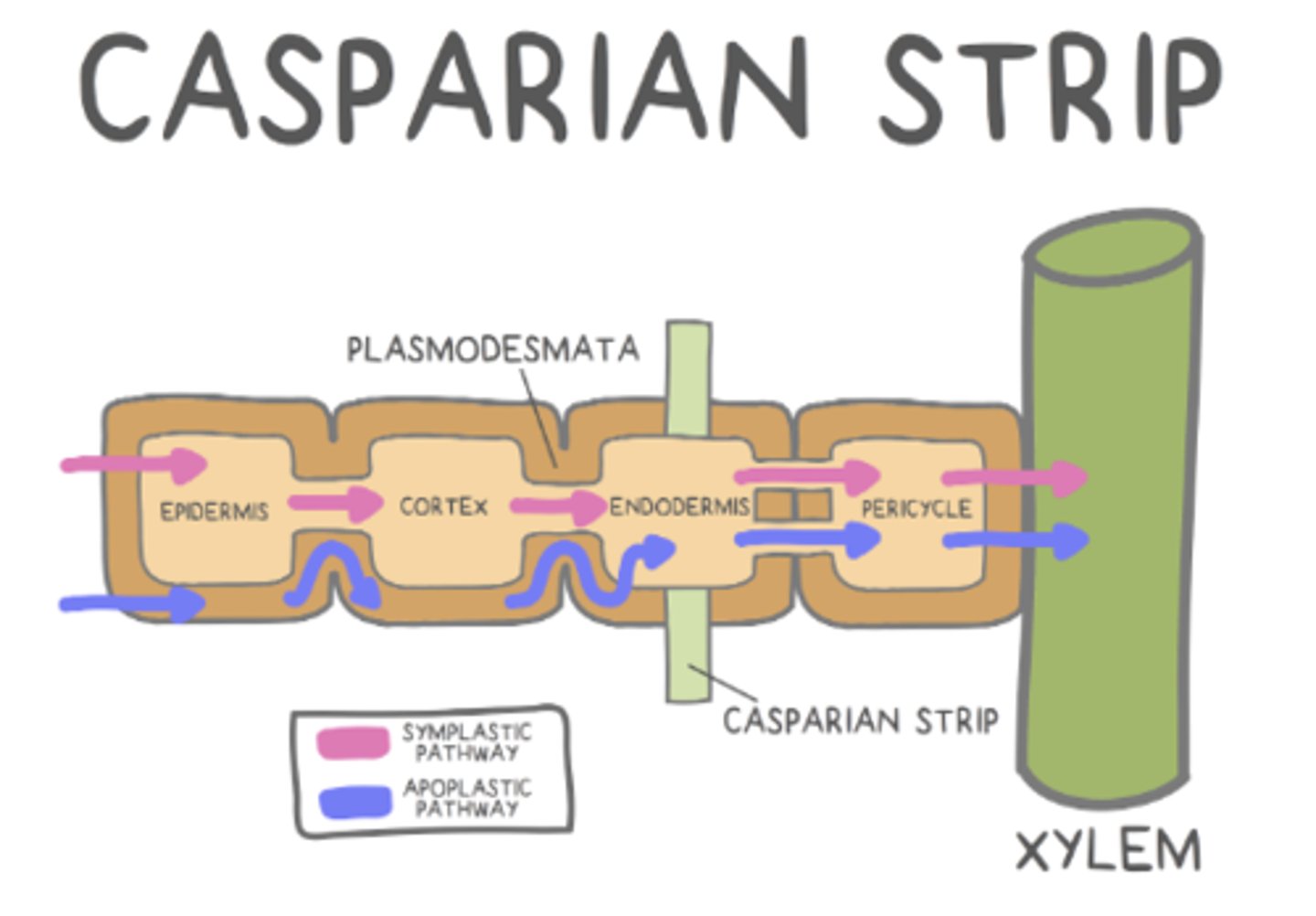
how does water move in the apoplastic pathway?
water movement outside the cell, within the cell wall
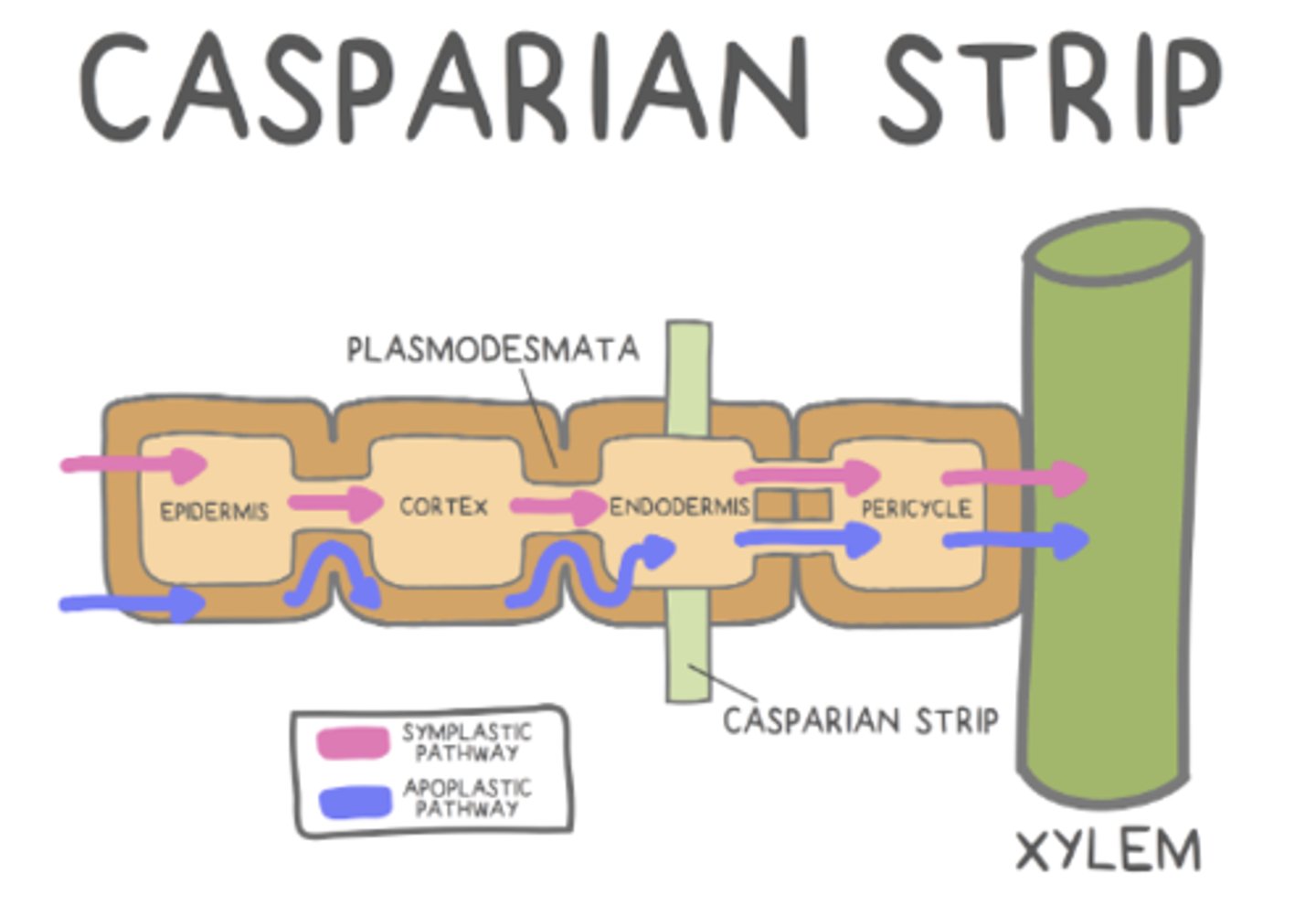
how does water move in the symplastic pathway?
through the cell's cytoplasm
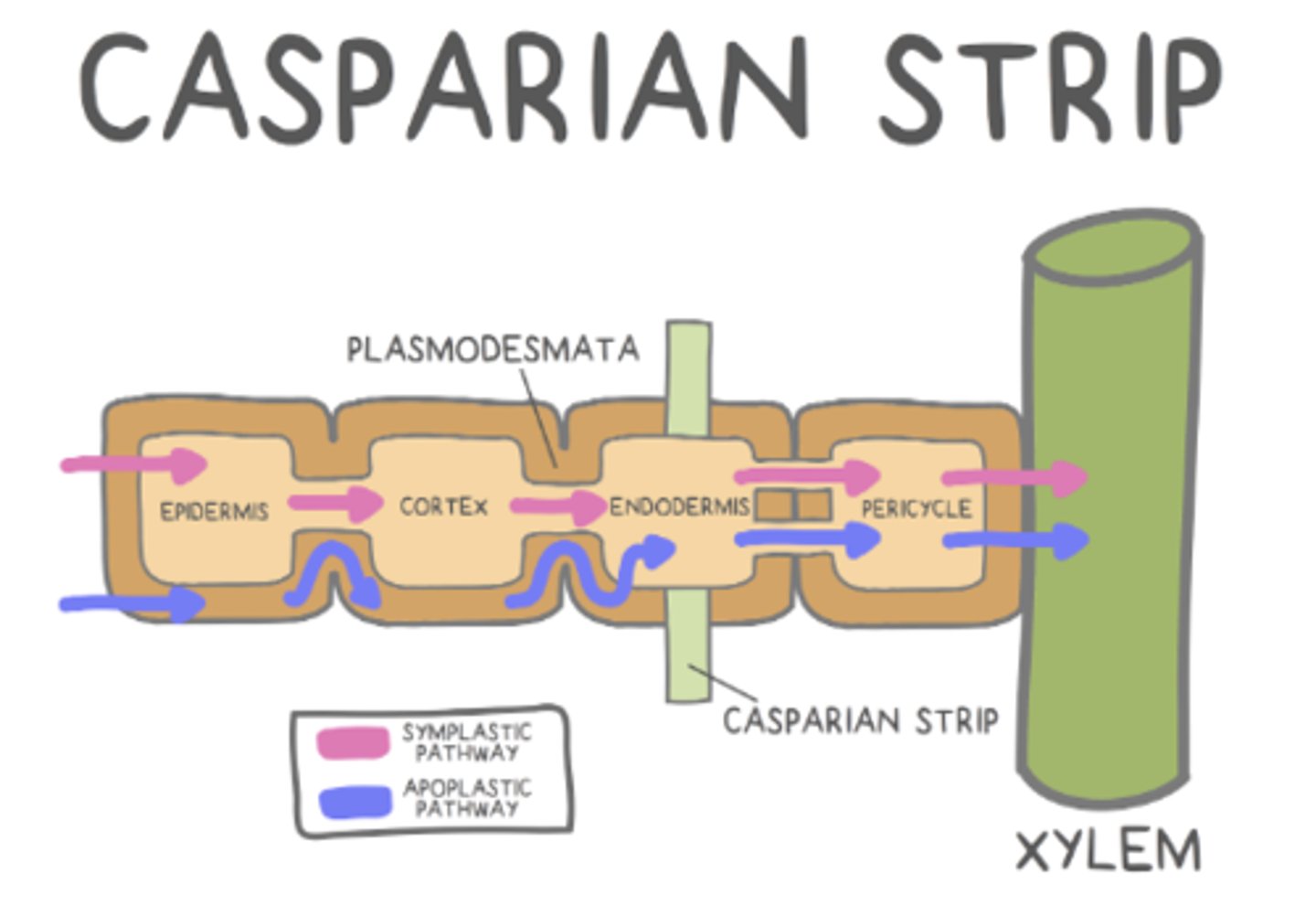
the _____ regulates which substances can enter roots and travel to the rest of the plant
Casparian strip
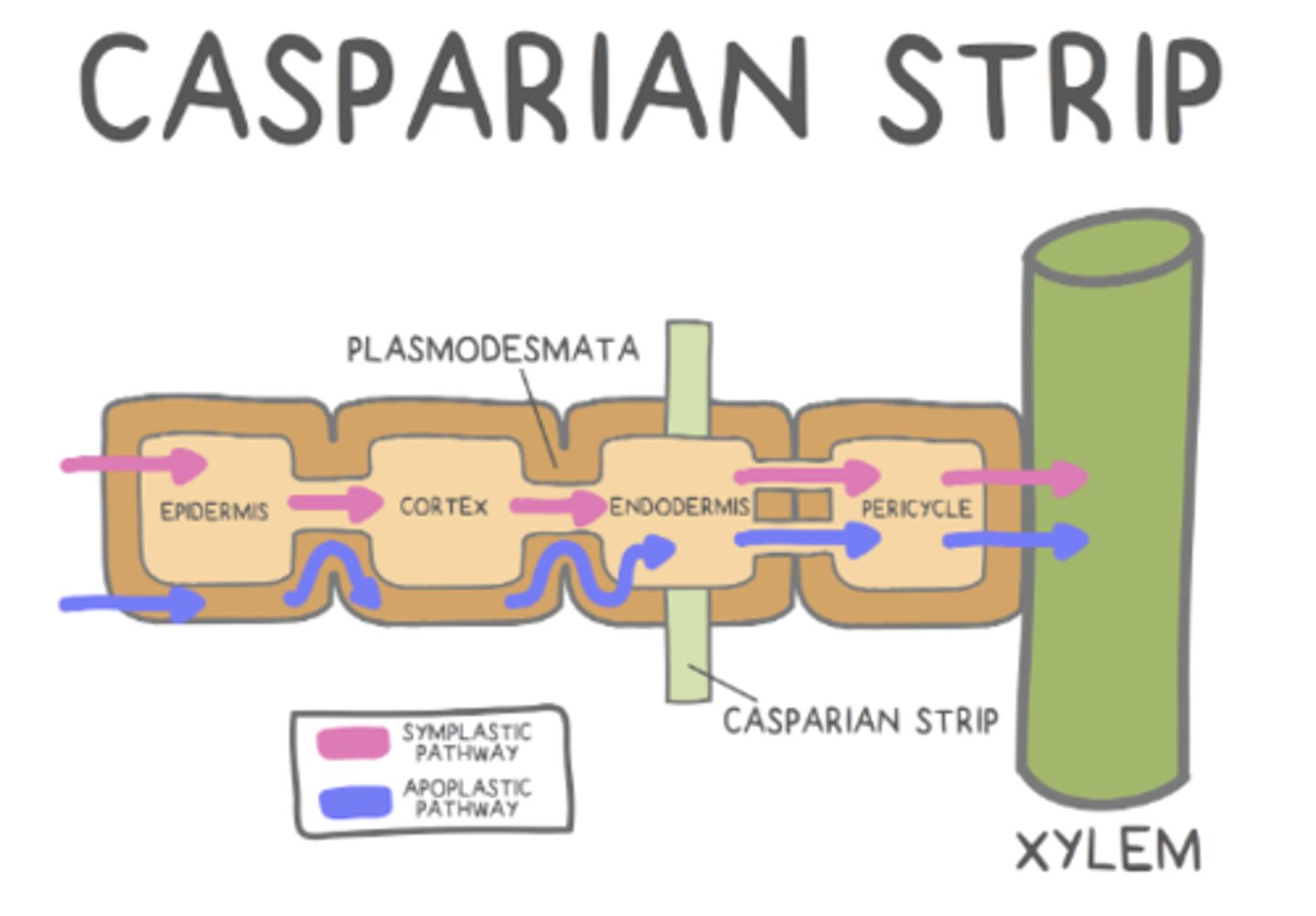
what is the Casparian strip made of?
a fatty, waxy substance that makes it impenetrable
where is the Casparian strip found?
in the cell walls of plant roots
do plant cell walls have a way of filtering substances?
no
do the plasma membranes of root cells have a way of filtering substances?
yes, they are semipermeable membranes
stomata are found on the _____ of leaves
lower epidermis
_____ allow for gas exchange between the external environment and the plant
stomata
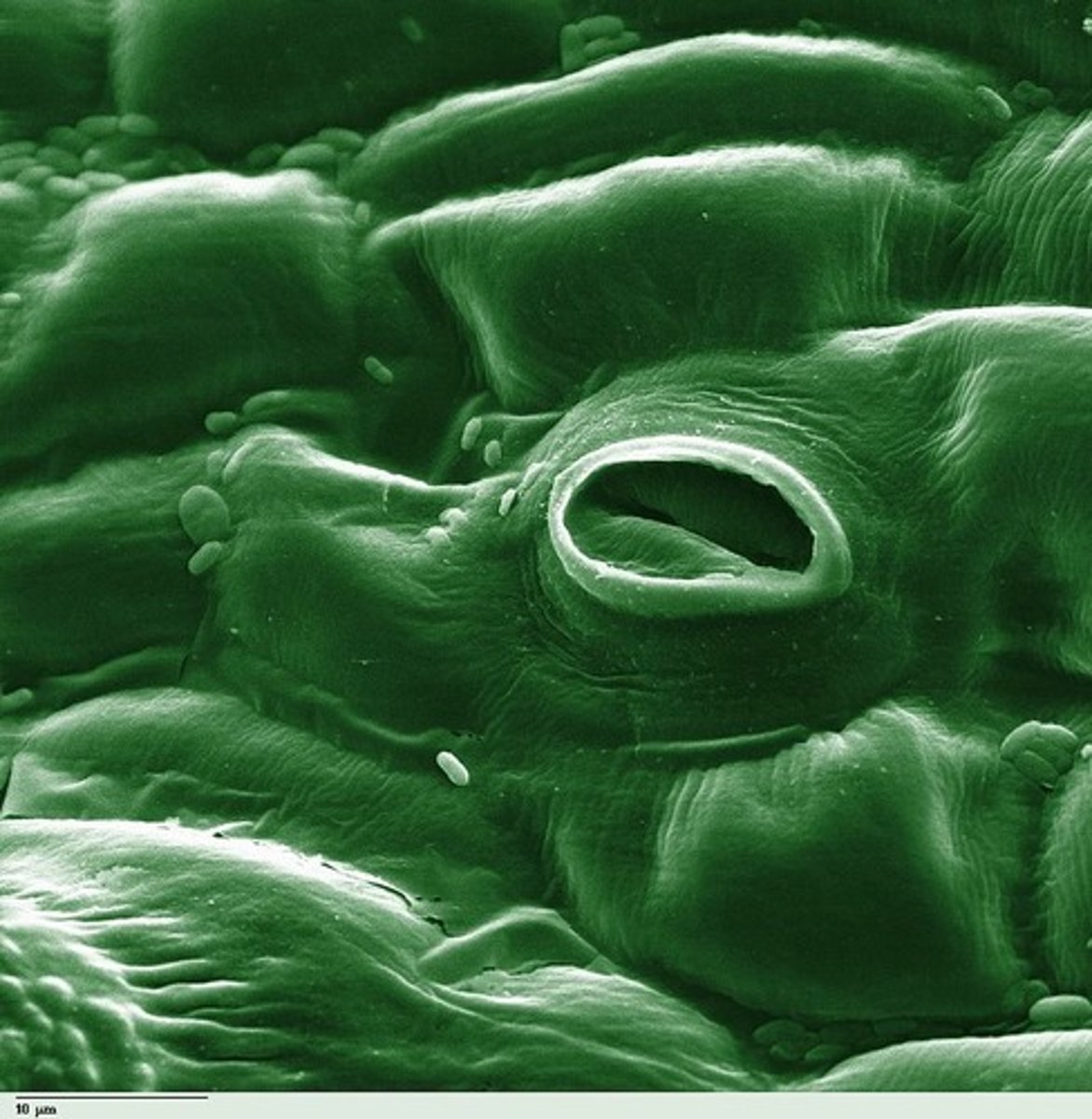
what are the specialized epidermal cells that surround stomata called?
guard cells
what do guard cells do?
control the opening and closing of stomata
how do guard cells open stomata?
K+ ions diffuse in, which causes water to follow by osmosis --> the guard cell becomes turgid
during what period of the day is CO2 low in plants?
during the daytime, when photosynthesis is occurring
when are stomata open, and why?
stomata are usually open during the day to allow for the influx of more CO2 for photosynthesis
(stomata may close during the day to prevent transpiration, or if the plant is a CAM plant)
during what period of the day is CO2 high in plants?
photosynthesis does not occur at night time, so this is when CO2 builds up
when are stomata closed?
during the night, or during high daytime temperatures (to prevent transpiration)
(stomata are open at night in CAM plants)
why do stomata close at night (excluding CAM plants)?
CO2 is high and photosynthesis cannot occur
why do stomata close when temperature is high?
to prevent excessive water loss by transpiration
the _____ cells are found between the upper and lower epidermis (middle of the leaf)
mesophyll
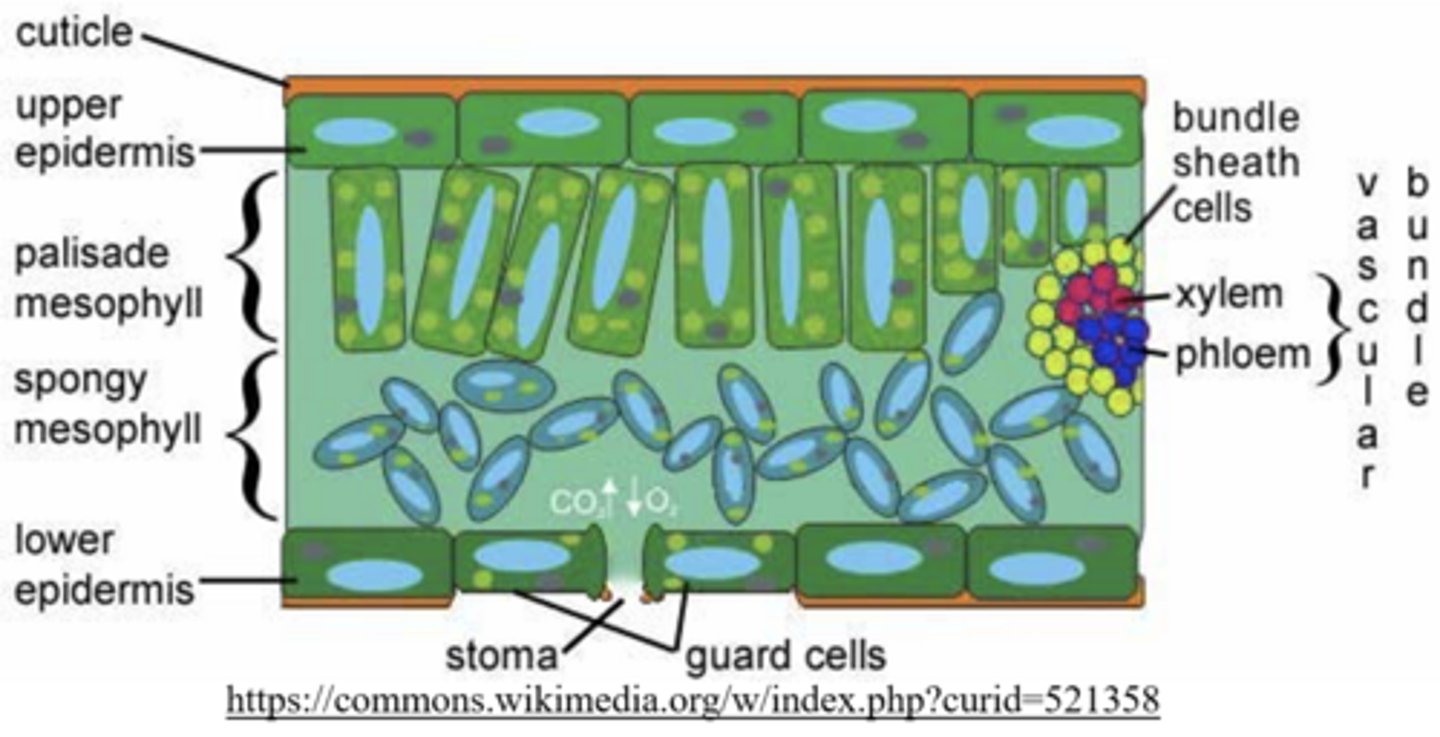
what are the two types of mesophyll?
palisade; spongy
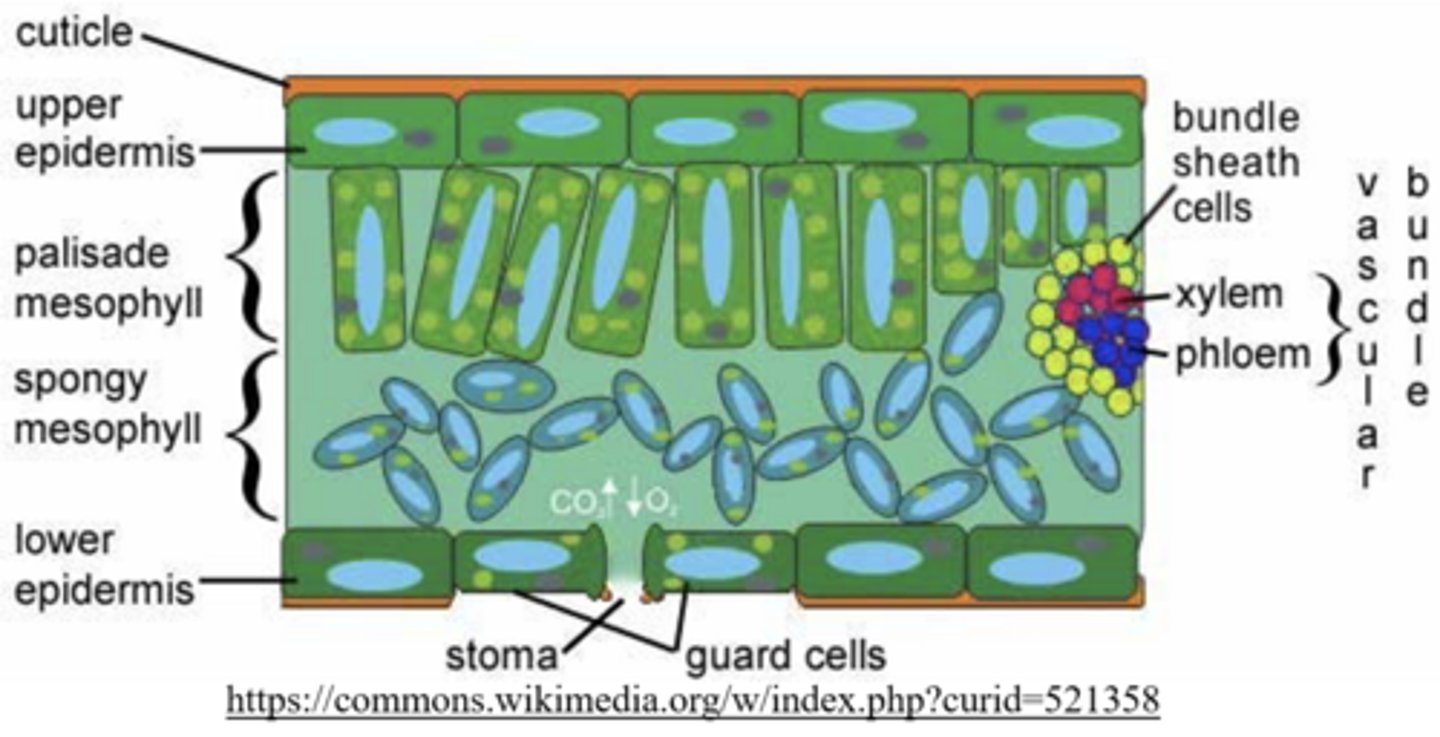
the palisade mesophyll are tightly-packed cells that carry out _____
photosynthesis