Unit 1: chemical components of cells
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
mole
represents the # of molecules available to participate in chemical rxns
covalent bond
sharing of electrons
stronger & more stable than ionic bonds
lots of energy needed to break
can share one or more pairs of electrons
polar covalent bond
one atom is larger than the other atom in a covalent bond
forms a dipole; one end has partial + charge, the other has partial - charge
ionic bond
form from gain & loss of electrons
electrostatic interactions
attraction between negative and positive charges
allow molecules to interact via complementary charges
weak non-covalent bonds that are stronger in numbers
van der waal forces
attraction between atoms w/ uneven charge distribution
weak, non-covalent bonds
polarized atoms are attracted to eachother
hydrogen bonds
H—X, where X is an electronegative atom
stronger in numbers
how water is held together; can form spheres of hydration around ions
organic molecules
anything w/ carbon in it
UV can break carbon covalent bonds
cells are formed from carbon compounds
monosaccharides (sugars) →
→ polysaccharides
fatty acids →
→ fats, lipids, membranes
amino acids (form peptide bonds) →
→ proteins
nucleotides →
→ nucleic acids
macromolecules
essential biological molecules
abundant in cells
grow by adding monomers to one end of the polymer chain
most ___ have polarity
ATP cycle
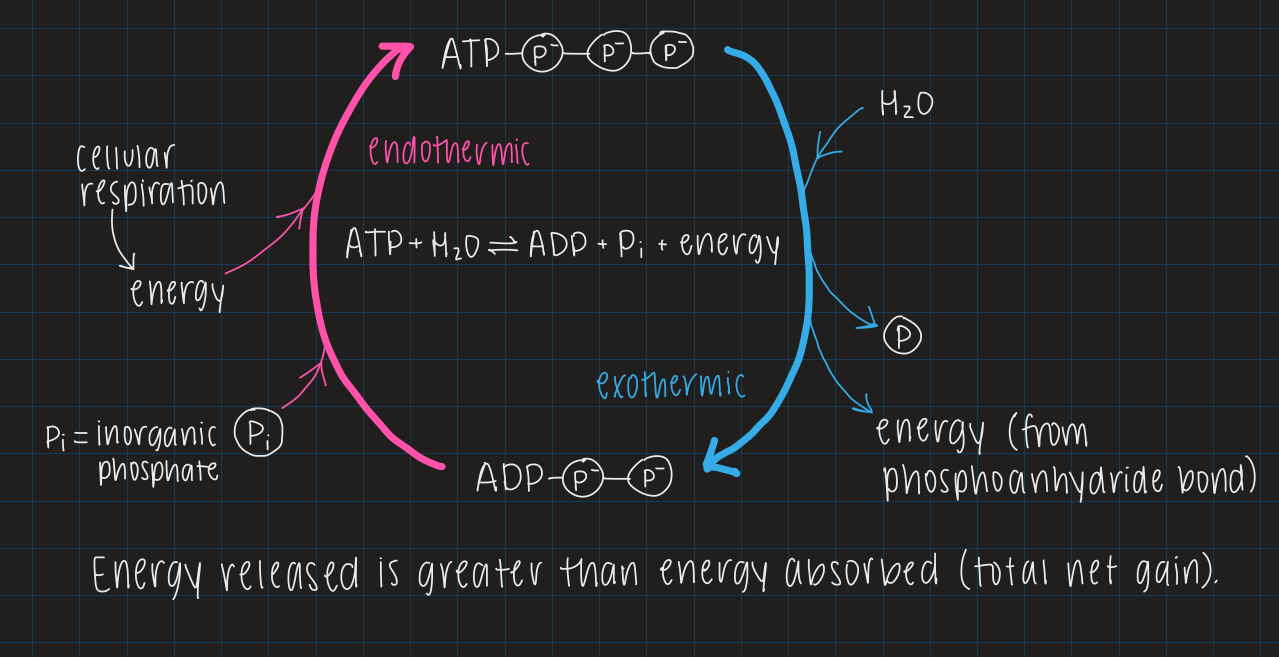
condensation
water expelled
hydrolysis
water consumed
polysaccharide
energy source comprised of monosaccharides
joined by glycosidic bonds and condensation rxns
hydrolysis rxn breaks monosaccharides apart
two main functions in cells: storage & structure
storage: held in reserve for energy production
glycogen (animals)
starch (plants)
structure: provides mechanical support for cells
cellulose (plant cell walls)
chitin (insect exoskeleton & fungal cell walls)
oligosaccharides
help protect the cell & allow cells to interact w/ one another
small oligosaccharides can be linked to other macromolecules
glycoprotein
sugar covalently linked to a protein
glycolipid
sugar covalently linked to a lipid
fatty acid
components of cell membranes
more efficient at storing anergy than carbohydrates
amphipathic: has both hydrophilic & hydrophobic regions
hydrophilic carboxylic acid head
hydrophobic hydrocarbon tail
saturated vs unsaturated
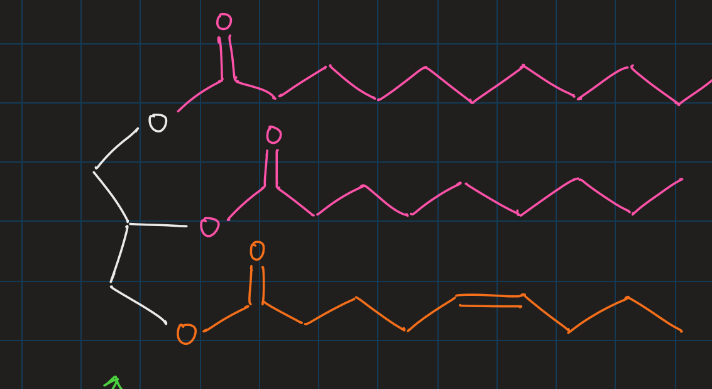
triacylglycerol
three fatty acids held together by a glycerol molecule
ester linkage
storage lipids
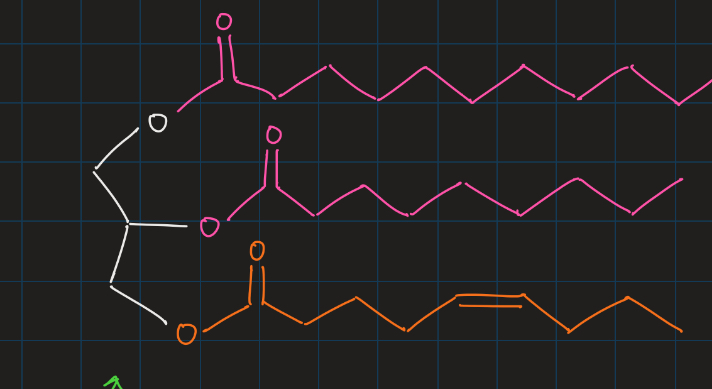
phospholipid
hydrophilic phosphate head & hydrophobic fatty acid tails
aggregate to form cell membranes
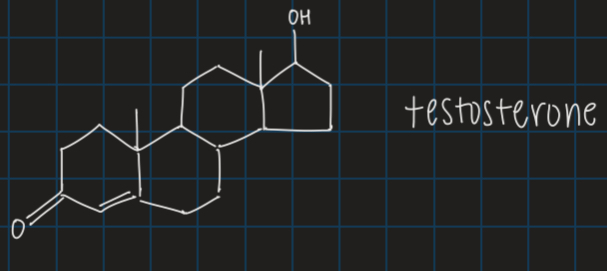
steroids
common multiple-ring structure
amino acid
subunits of proteins
peptide bonds
alpha carbon, amino group, carboxylic acid group, variable side chain
polypeptide
string of amino acids
may or may not have a function
N-terminus (amino terminus): has amino group (NH2), starting point
C-terminus (carboxyl terminus): has carboxyl group (COOH, ending point (where peptides are added)
proteins
comprised of one or more polypeptides
ALWAYS has a function
nucleoside
nitrogenous base linked to a pentose sugar
adenosine
nucleoside made of adenine attached to a ribose sugar
nucleotide
nucleoside w/ one or more phosphate (PO4) groups attached
add to 3’ end (DNA synthesis & replication)
subunits of DNA and RNA
RNA has many functions because it is single stranded & can take on many shapes
sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base
can be short-term carriers of chemical energy
held together by phosphodiester bonds in DNA and RNA
pyrimidine
six membered ring nucleotide
thymine, cytosine, uracil
purine
5 and 6 membered rings together nucleotide
adenine, guanine