EESA06 Topic 4: Convergent Margins
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
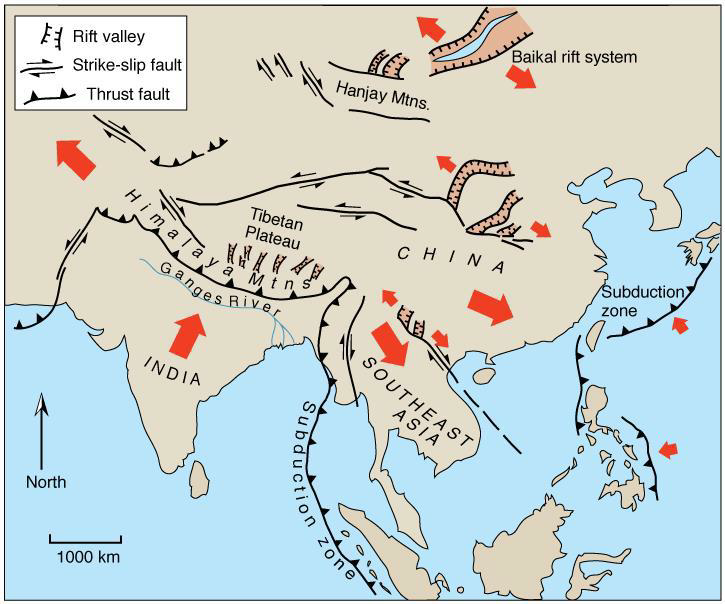
What are the three types of convergent boundaries?
Ocean-ocean
Ocean-continent
Continent-continent
Describe ocean-ocean convergent boundaries.
Denser ocean floor (i.e., older) subducts under less dense (i.e., newer) ocean floor
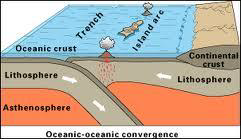
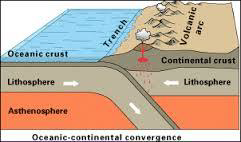
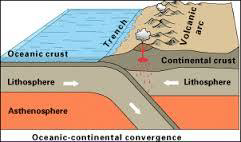
Describe ocean-continent convergent boundaries.
Oceanic crust subducts beneath continental crust
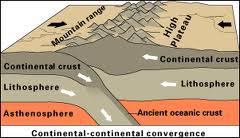
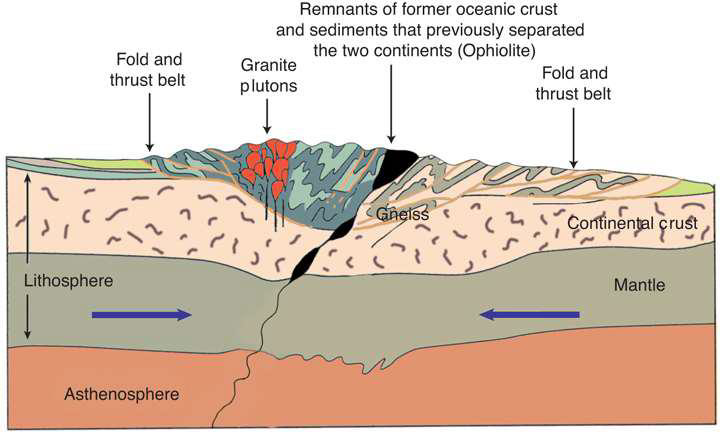
Describe continent-continent convergent boundaries.
Obduction occurs, with only minimal subduction
Subducting slab delaminates (i.e., breaks off)
The end result of oceanic subduction
Describe obduction
Crumpling
Nothing gets pushed into the mantle
Resulting structure tends not to be very volcanic
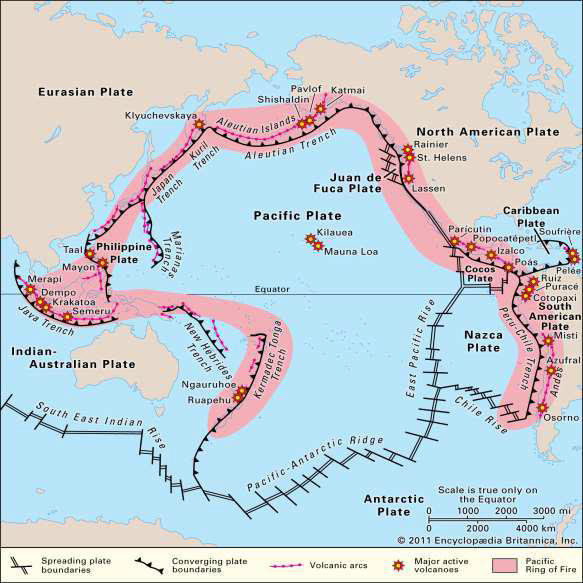
What is the Pacific Ring/Rim of Fire?
Volcanoes lining Pacific subduction zones
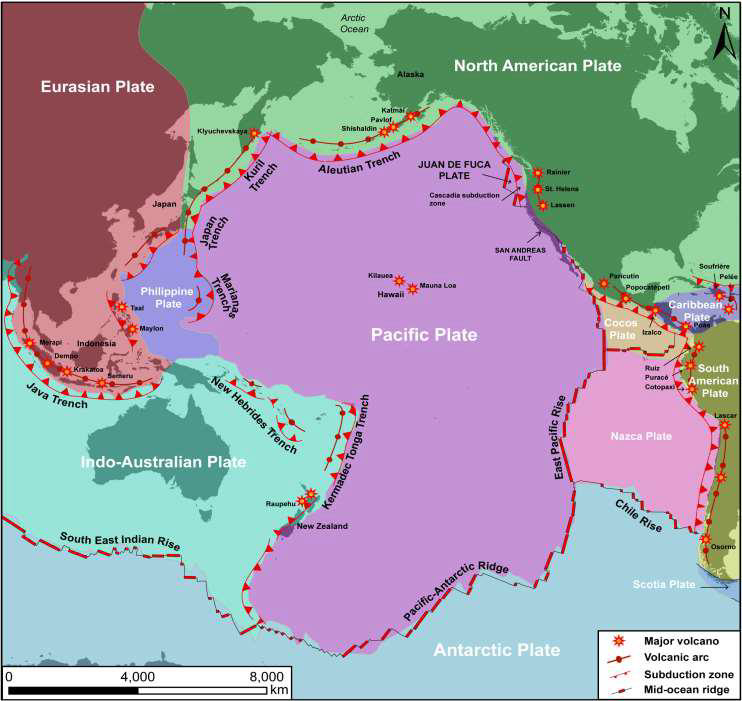
What phase of the Pacific Ocean does the Pacific Rim record?
Its death
i.e., the floor is subducting under converging continents
How is the Pacific Ocean closing?
Zipper-like convergence of Eurasian and Australian plates, closing the Philippine plate
The North American Plate is converging towards these plates as well
What are the 3 ways plates interact around the Pacific Ring?
Ocean crust vs ocean crust - subduction
Ocean crust vs continental crust - subduction
Oceanic or continental crust sliding past each other - transform
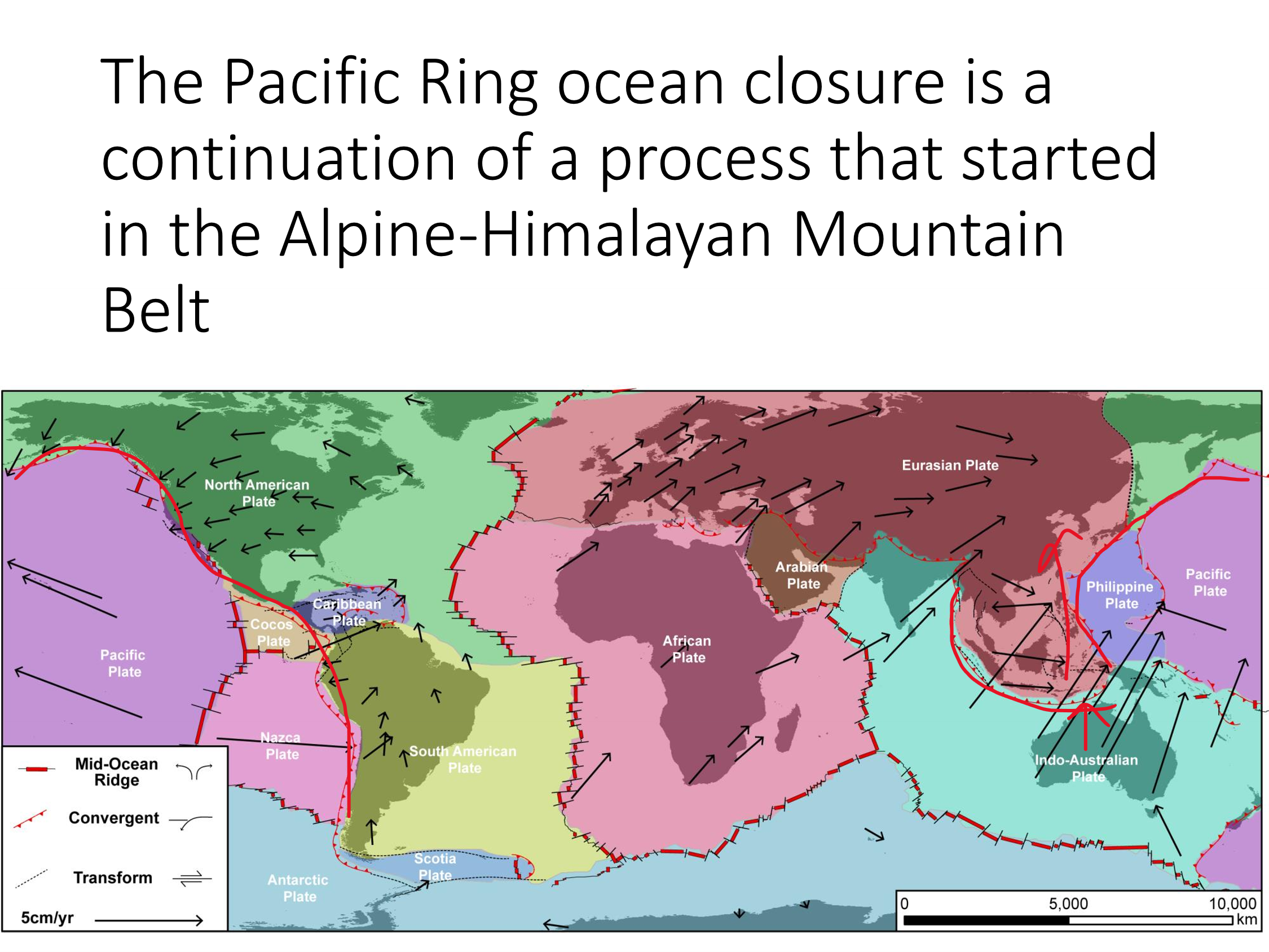
The pacific ring closure is a continuation of a process that started where?
Alpine-Himalayan Mountain Belt
Describe and give an example of ocean crust vs ocean crust (subduction) plate interactions.
e.g., island arcs like Japan and Indonesia
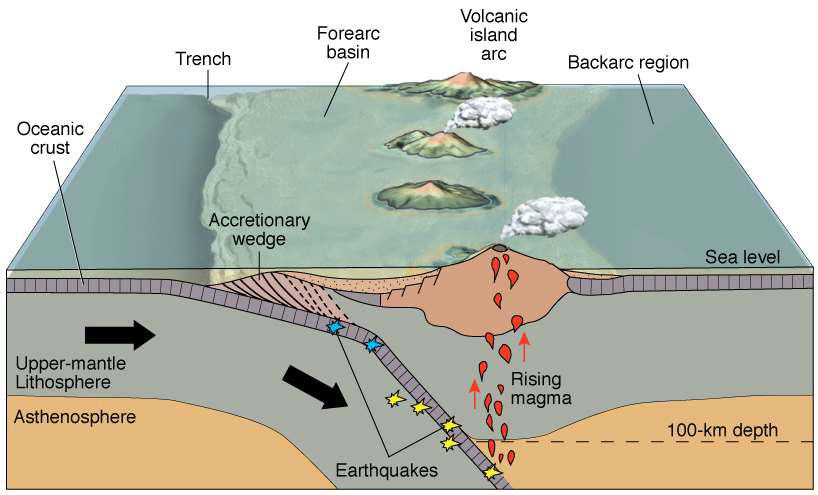
What are volcanic island arcs?
Where oceanic crust is subducted below other oceanic crust
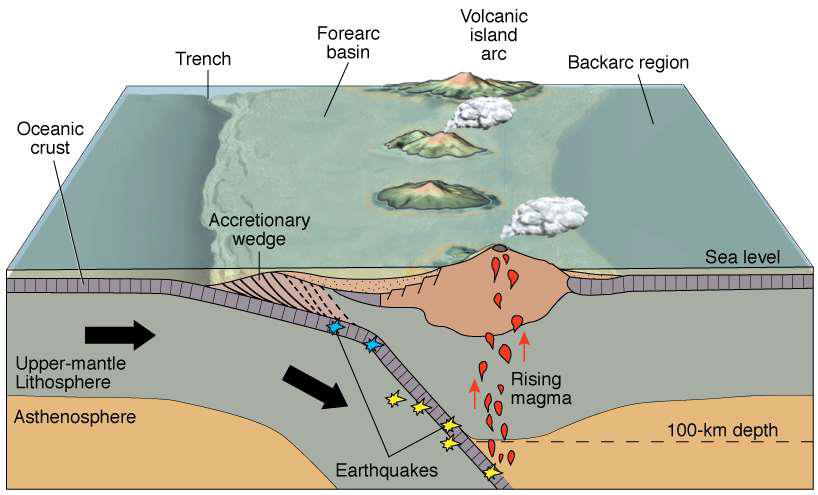
Island arcs mostly contain what type of volcano?
Stratovolcanoes
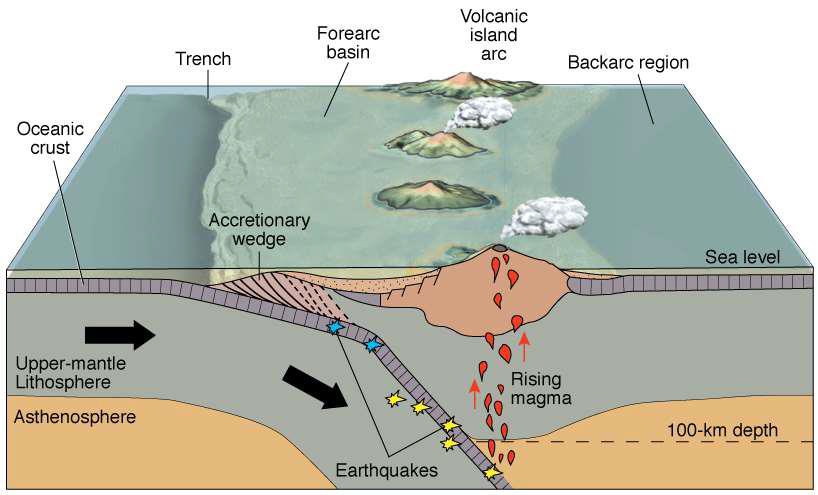
Describe the accretionary wedge
Faulted mounds of sediments
Sediment scraped into mounds rather than washed into the ocean
Susceptible to submarine landslides and collapse, leading to tsunamis, etc.
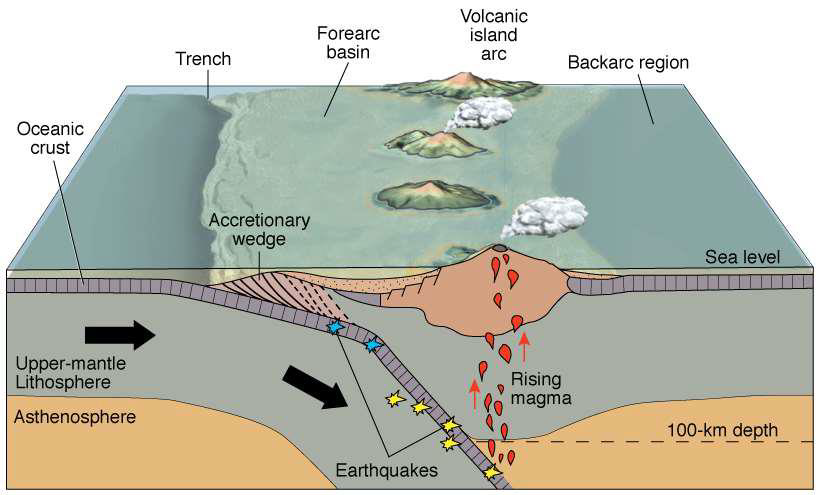
How do volcanic islands contribute to sediment in the ocean?
Erosion of land produces sediment
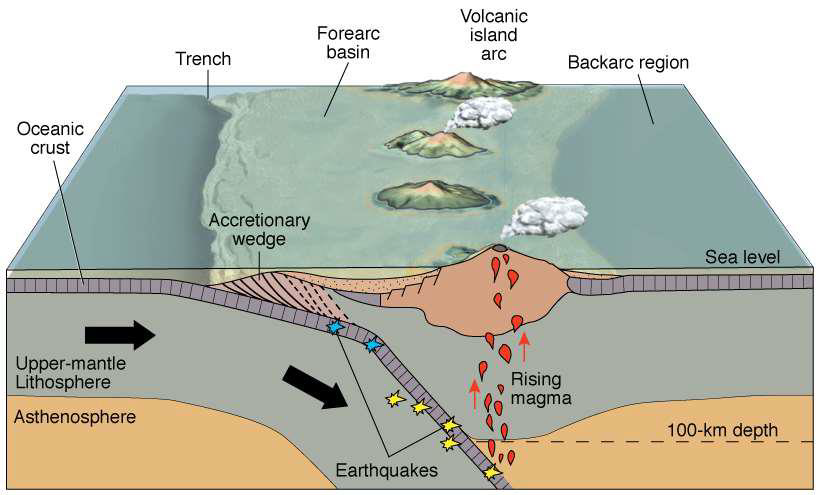
What is the backarc region?
The basin behind the volcanic arc
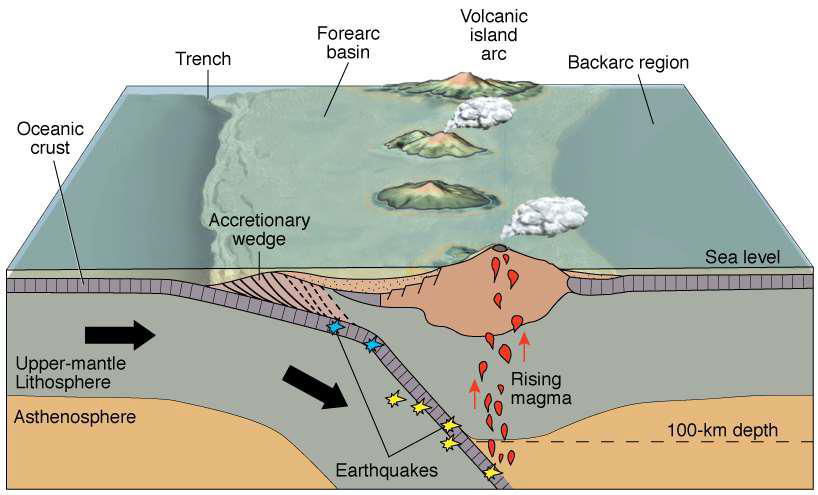
Describe and give an example of ocean crust vs continental crust (subduction) plate interactions.
e.g., magmatic arcs like west coast North and South America
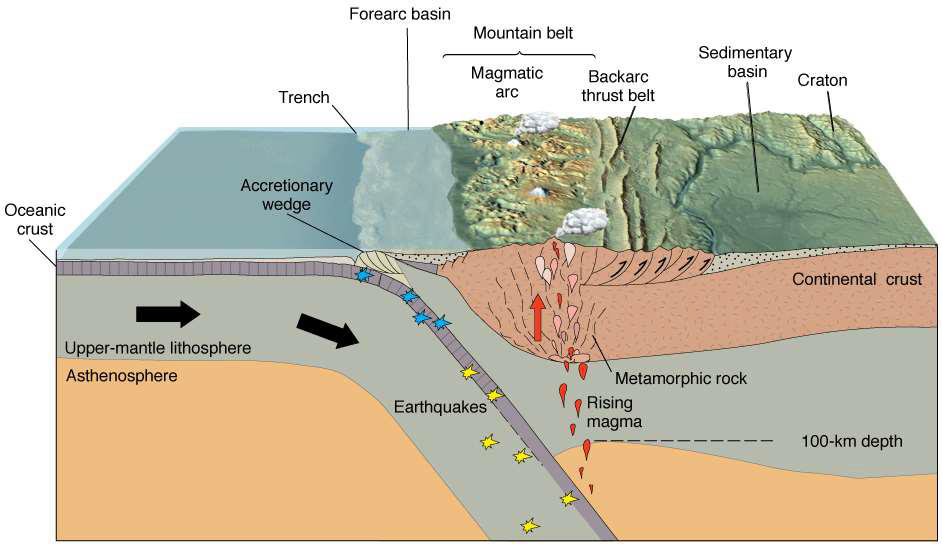
What is a Benioff zone?
Seismically active subduction zones
EQs closest to plate boundary will be shallow
Deeper EQs as you move towards overriding plate
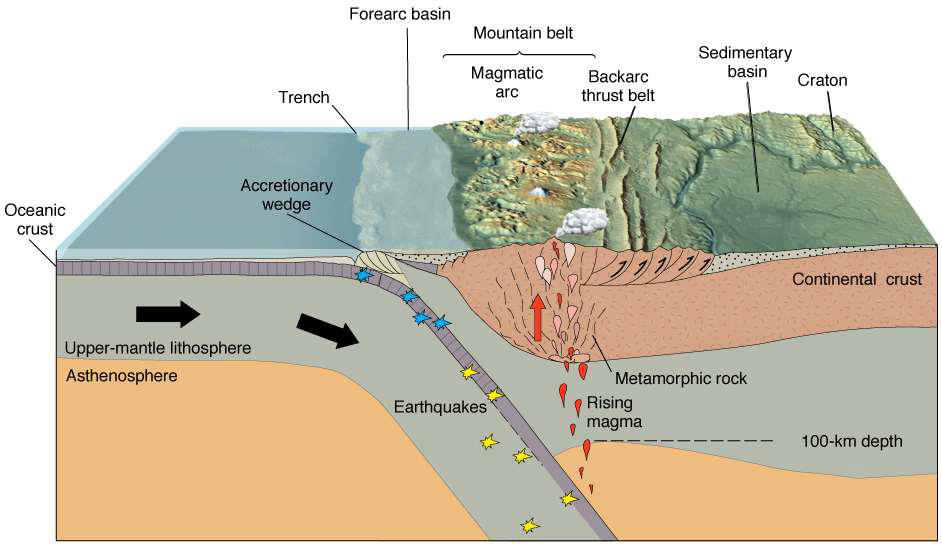
How does magma flow differ in ocean-continent interactions vs. ocean-ocean interactions?
Magma gets stuck in ocean-continent interactions
Describe and give an example of oceanic or continental crust sliding past each other (transform) plate interactions.
e.g., San Andreas Fault
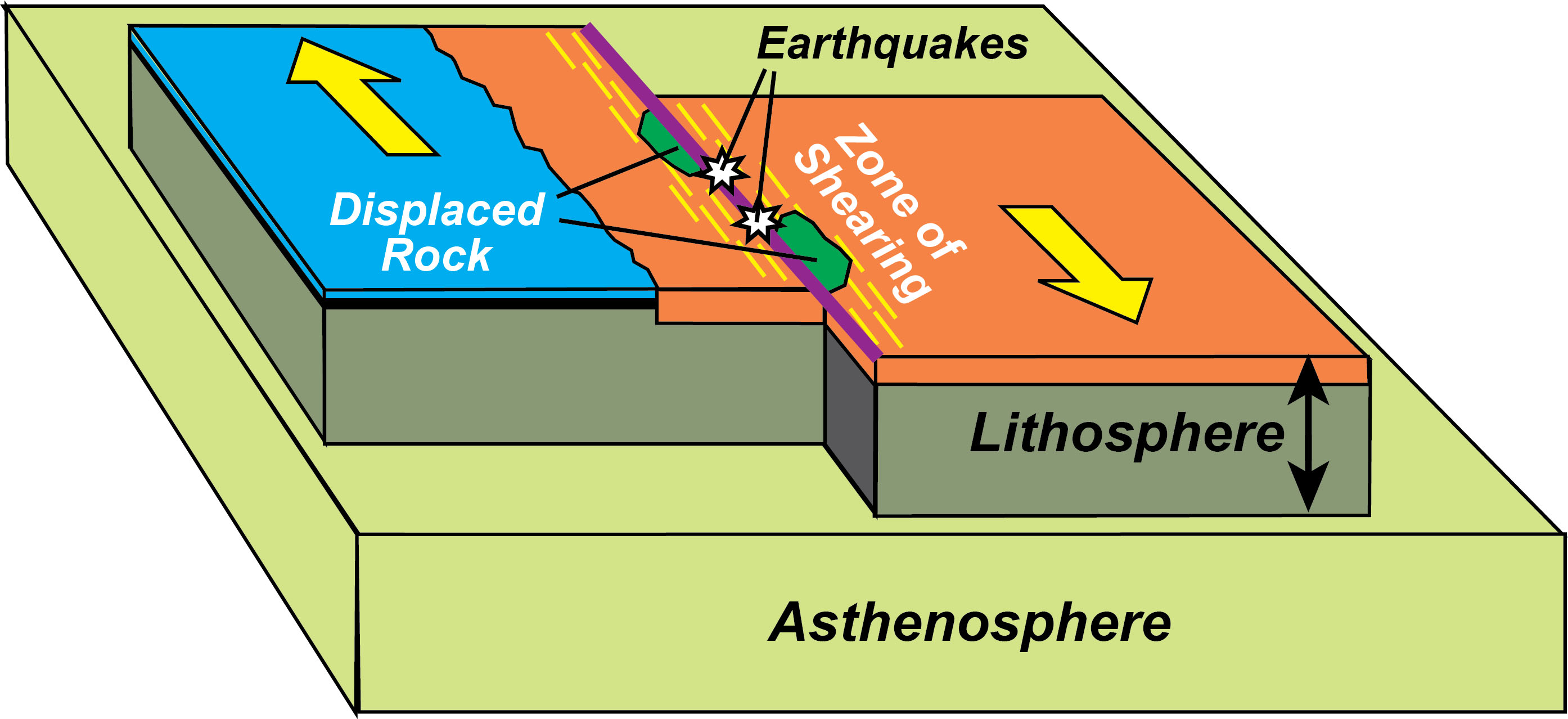
How does ocean floor age impact the steepness of the descending plate (i.e., angle of subduction)?
Younger, thinner, bouyant = shallow angle
Floor rams into overriding crust, deforming overriding crust
i.e., overriding plate pulled down a little
e.g., image a
Older, thicker, denser = steeper angle, since it's primed to subducts
e.g., image b
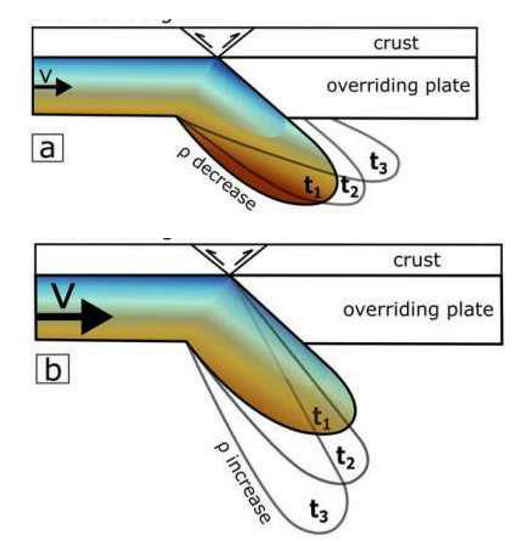
How does angle of subduction influence the result of subduction?
Shallow = production of mountain ranges
Steep = pulls overriding plate
What are example of shallow versus steep angles of subduction
Shallow = East Pacific
Steep = NW Pacific
What are some hazards of Arc Volcanos?
Sector collapse
Lateral blast
Ash clouds
Pyroclastic flows/Nuee Ardente
Ignimbrites
Describe sector collapse
the collapse of a large portion of the volcano
Can lead to landslides
Results in lateral blasts
Magma in underground chamber released due to decompression
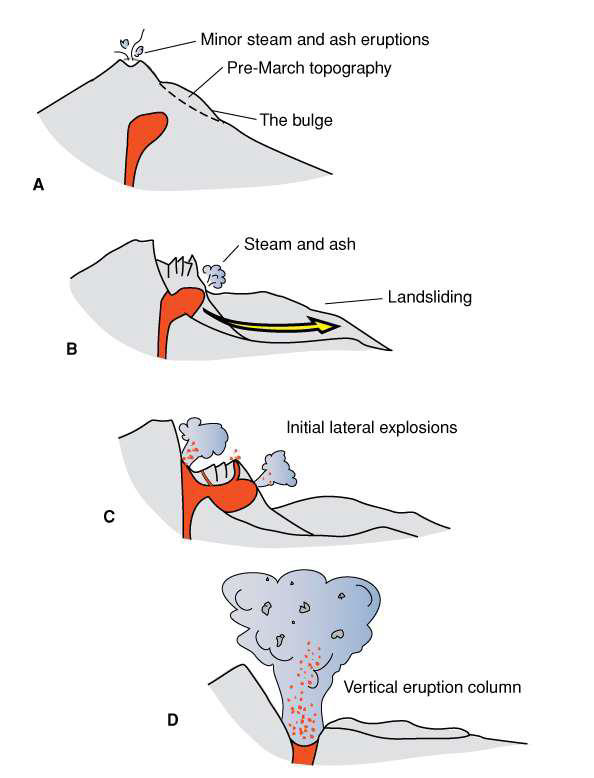
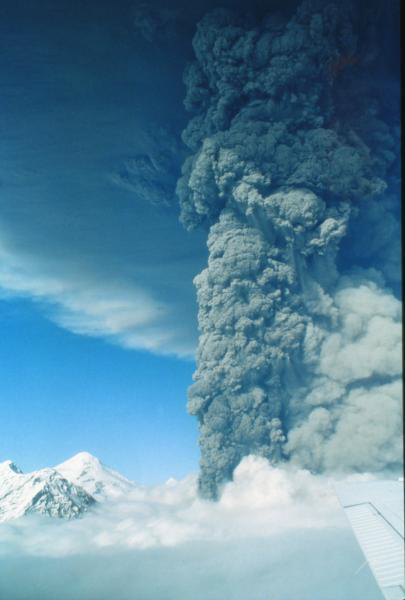
Describe vertical ash clouds
Ash carried into air when viscous lava traps exsolving gas and explodes

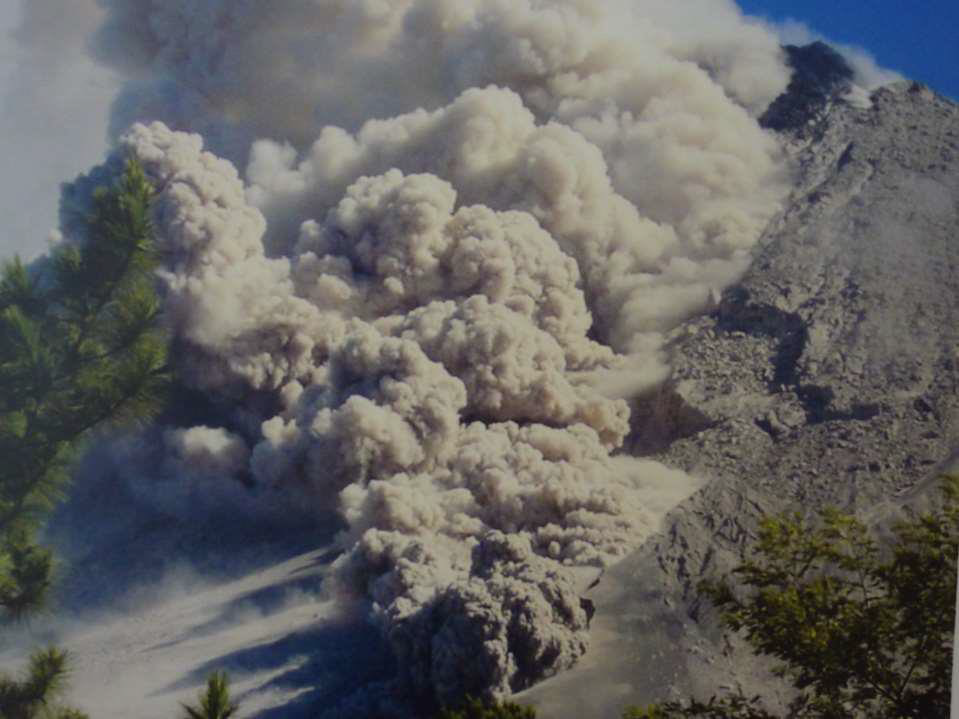
Describe pyroclastic flow (nuee ardente)
fast-moving, extremely hot avalanche of volcanic gas, ash, and rock fragments that rushes down the slopes of a volcano during an explosive eruption
Travel longer distances and in river valleys, etc.
Very hot
Cool into ignimbrite

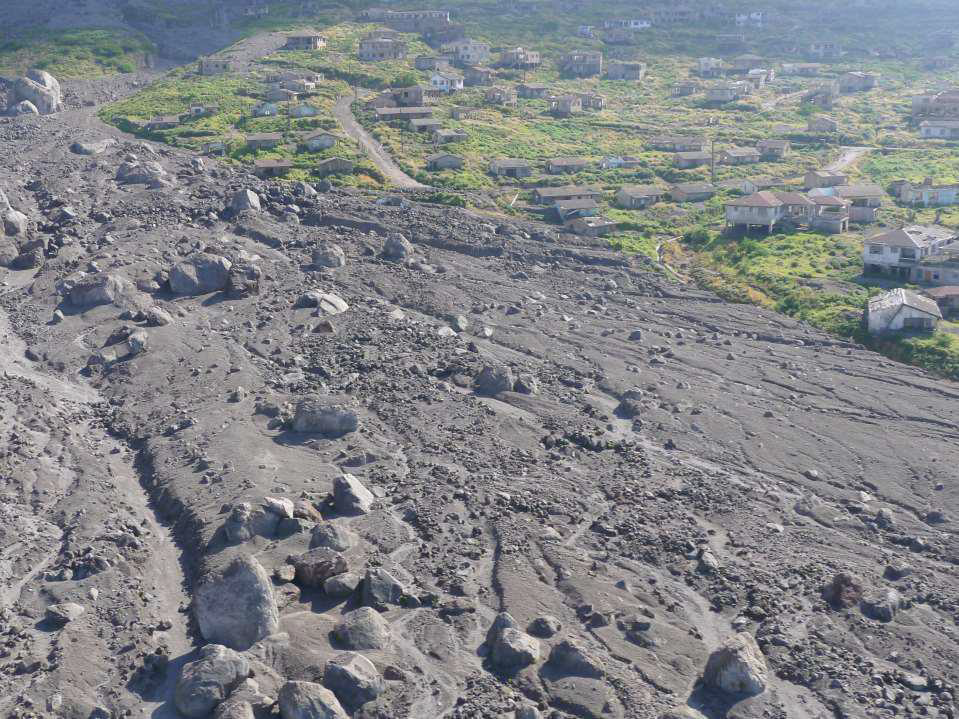
What is ignimbrite?
type of volcanic rock formed from the deposition and solidification of pyroclastic flows
They are very large

Describe volcanic tephra (ash)
Anything blown from a volcano
Short term effects (e.g., air quality) are worse than long term effects (e.g., nutrients in soil)
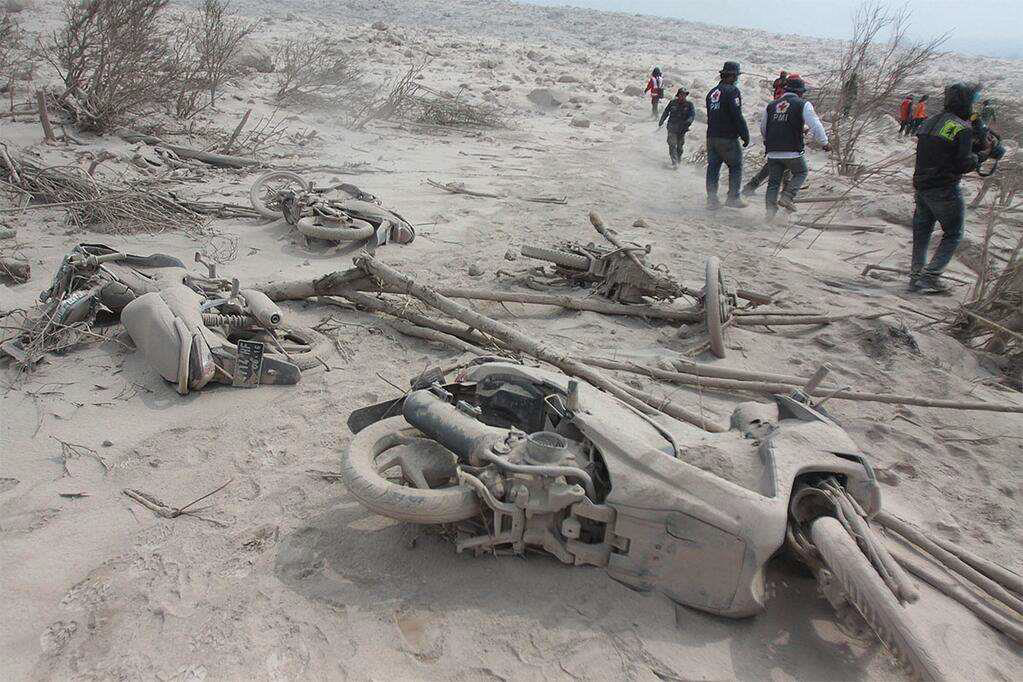

What can volcanic hazard assessments determine?
How active volcanoes are
Especially when looking at earth's history rather than human history
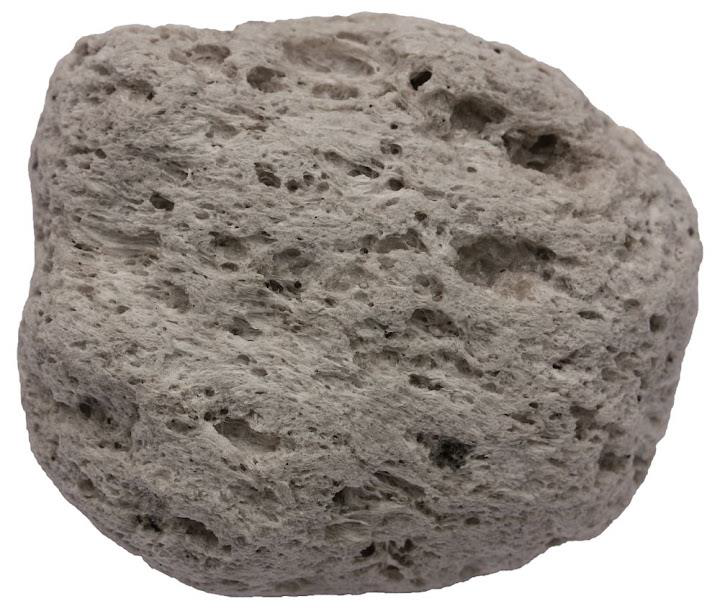
Describe pumice
"frothy magma"
Easy to date, therefore very telling for when eruptions happened

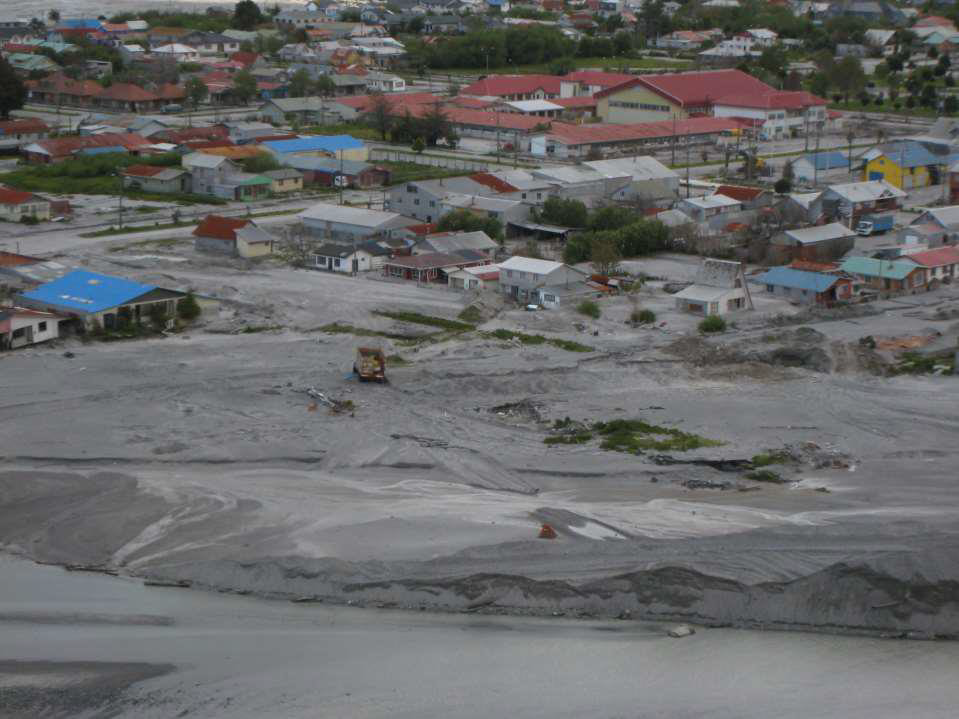
Describe lahars
mudflow made of volcanic ash
Concrete-like substance
Can happen months post-eruption
Travels far

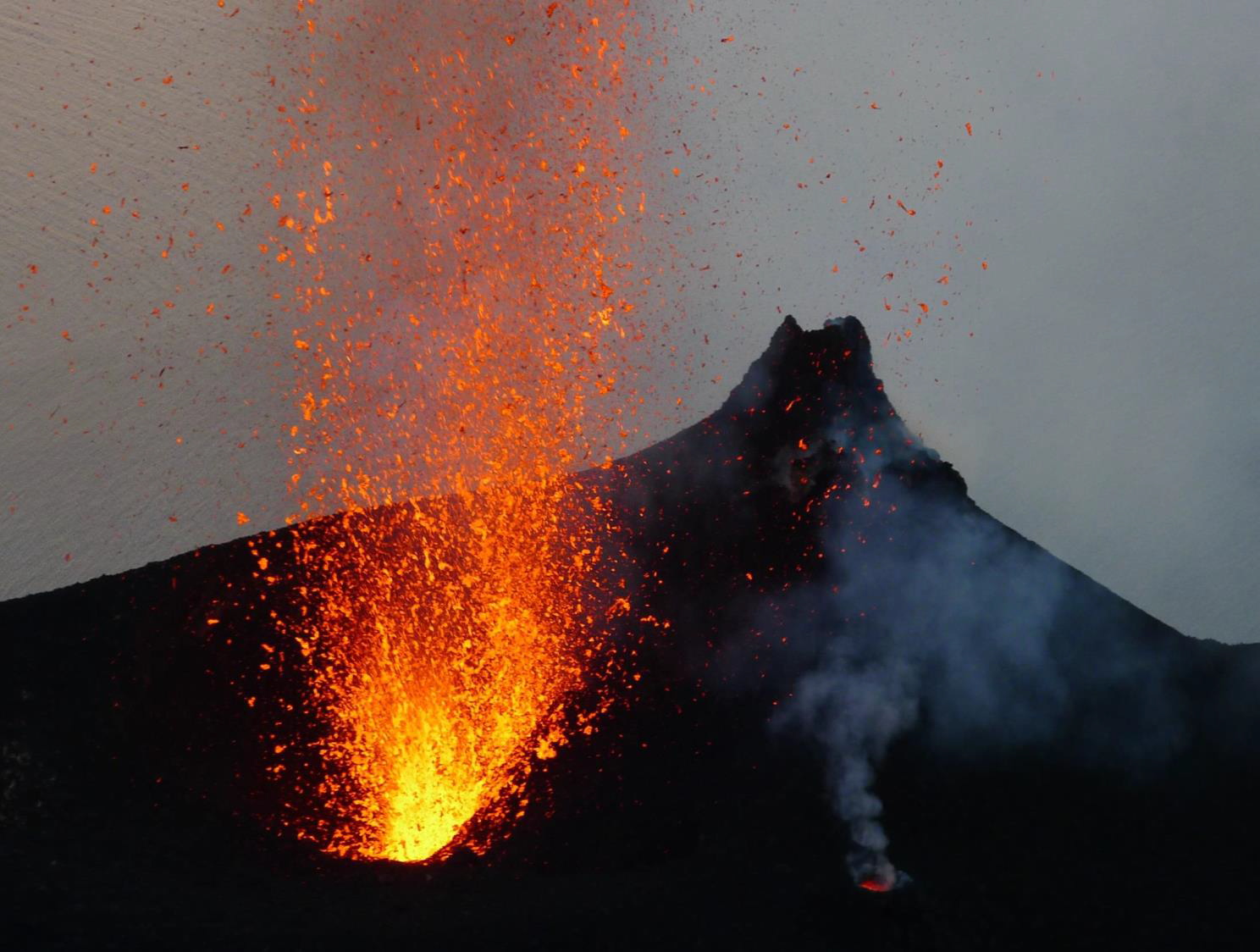
What is a strombolian eruption?
A mild fountaining of lava

What is a Plinian eruption?
A large explosive ashy eruption
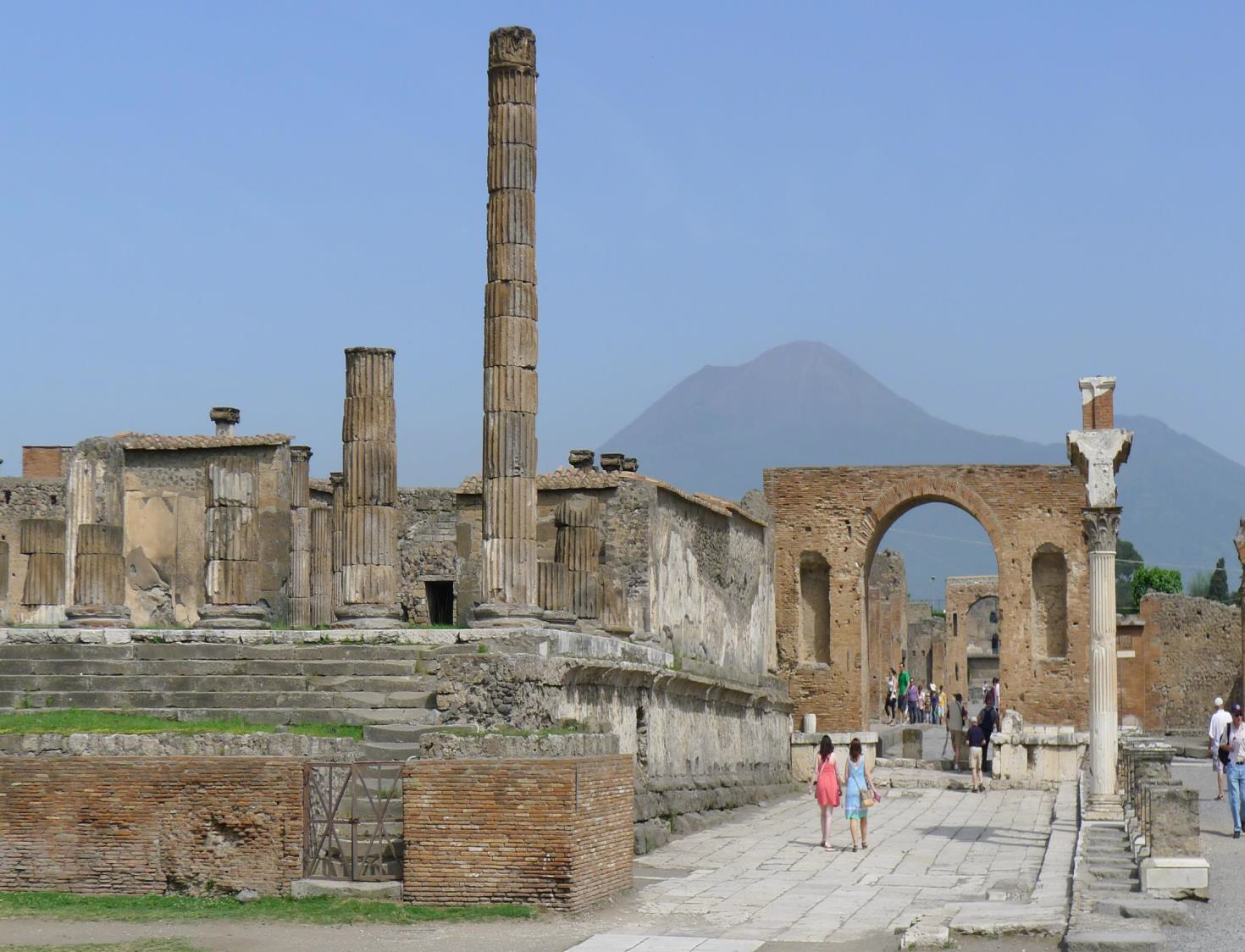

Why did Mount Vesuvius' eruption preserve its destruction?
Pyroclastic flow + Plinian eruption
i.e., ash covered people and object
What are some hazards of megathrust earthquakes?
Tsunamis
Liquefaction
Why were sea defenses not effective in the 2011 Japan earthquake and tsunami?
Seafloor moved eastwards and upwards, meaning the sea level the defenses were built for were lower than the sea levels post EQ
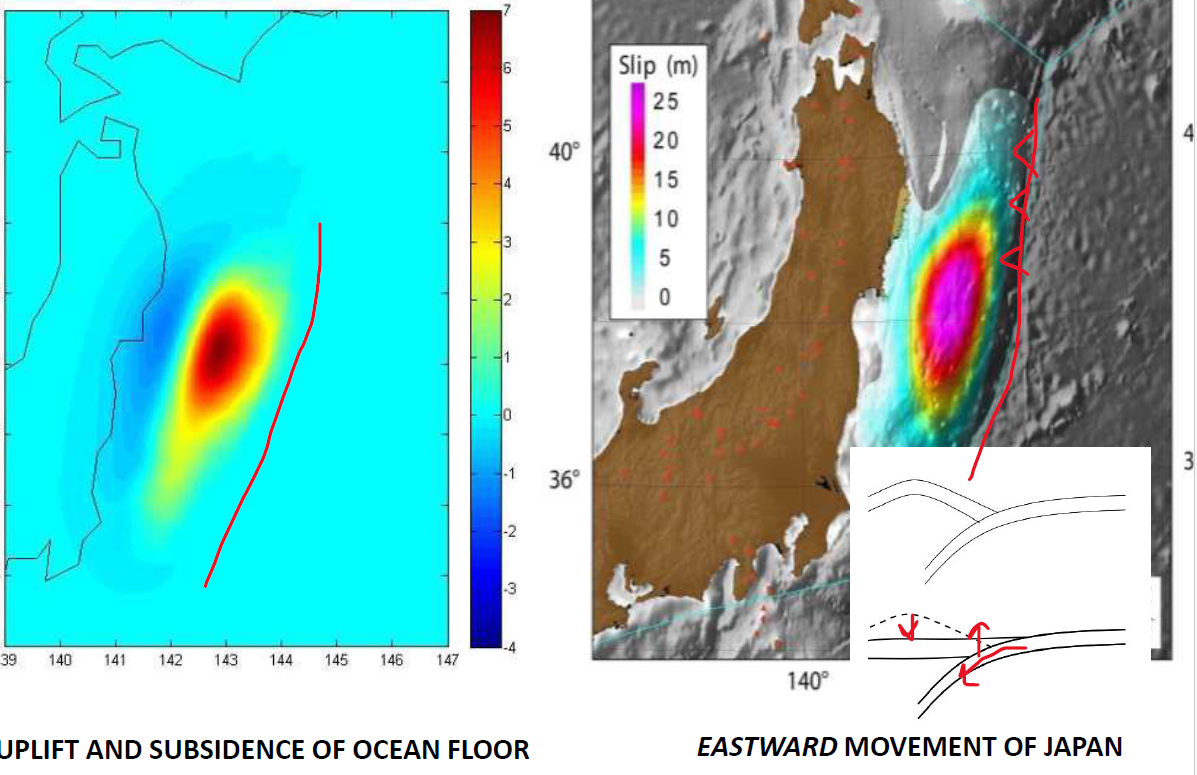
What might trigger tsunamis?
Fault movement/crustal flexure
Collapse of accretionary wedges
Volcanic eruptions
How can major EQs be predicted across the Pacific Rim?
Identification of seismic gaps
i.e., places that have been "stuck" and have had not recent EQs
Result in many megathrust EQs when energy finally releases
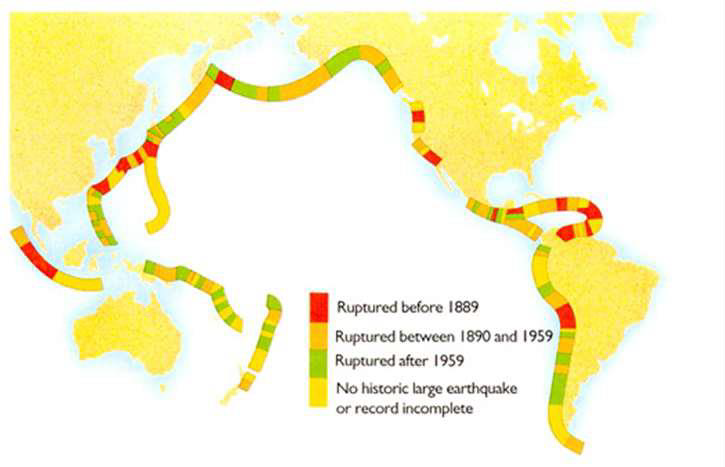
What can trenching faults help identify?
History of movement
Recurrence interval of EQs
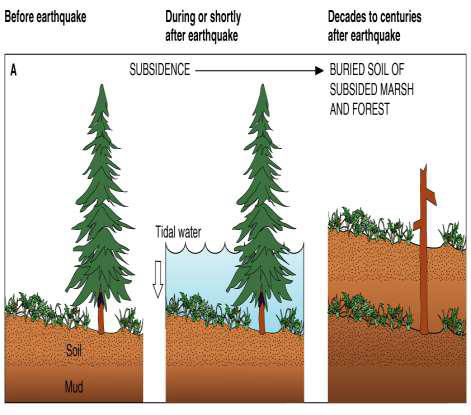
What are ghost forests and what do they measure?
Once forest, but the roots are inundated by sea water due to changing water levels
Record massive EQs and collapse of the crust
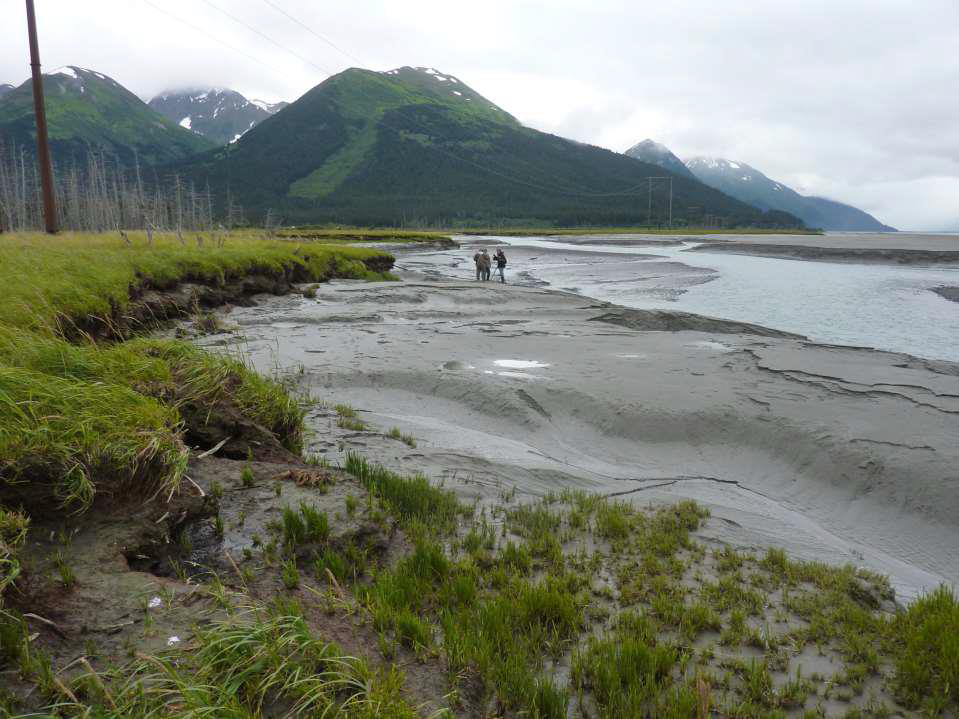

How do you get the reoccurrence interval using ghost forests?
Date each horizon of the ghost forest
Tells frequency of EQs
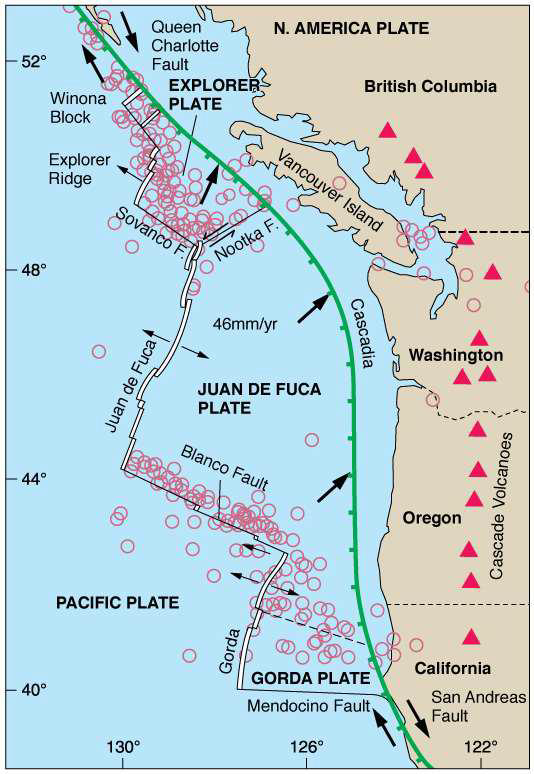
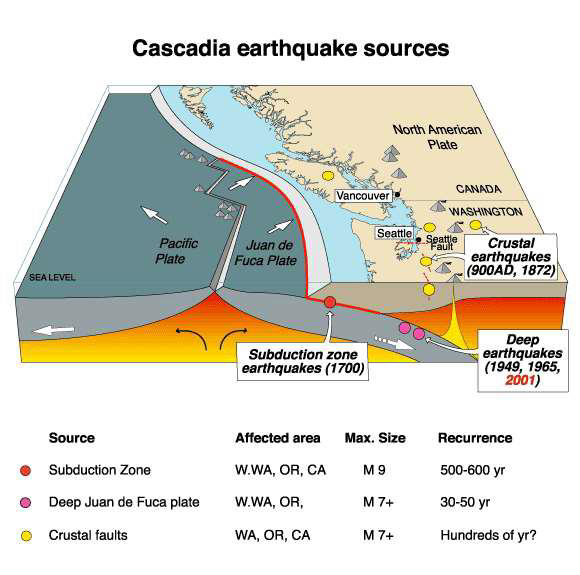
Describe the Cascadia Subduction Zone
Point at which 3 young microplates are forced under North America
What is Project Neptune an example of?
Ocean floor monitors to measure precursor EQ activity
i.e., Web-enables Awareness Research Network (WARN) sensors in BC
What is Mount Rainier an example of and what hazards does it pose?
Cascade range stratovolcano
Due to ice cap, can expect
Floods
Explosion
Etc.
What are the major sources of Cascadia EQs?
Subduction
Deep Juan de Fuca plate movement
Crustal faults
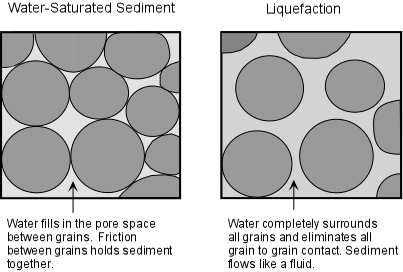
What does the effects of an earthquake depend on?
Local geology
e.g., bedrock vs. soft sediment
When does liquefaction happen?
Soft sediment starts to behave like liquid
Sediment grains become "supported" by water
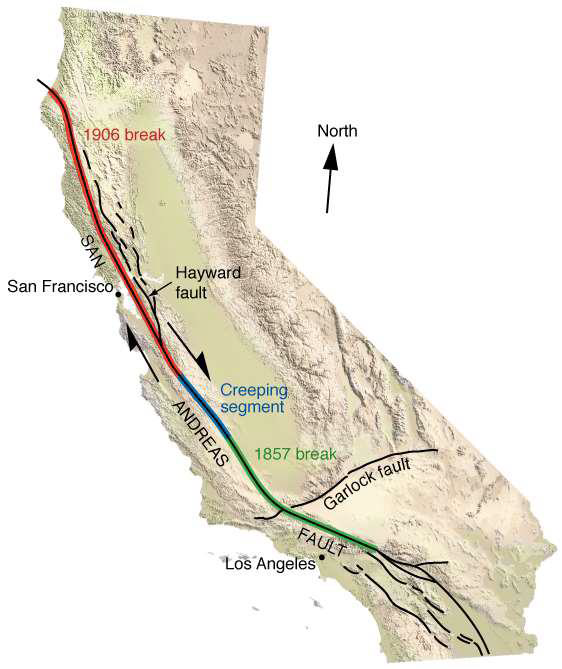
What is a creeping segment?
A fault segment that continuously moves (or "creeps") at a slow, steady rate without significant seismic activity
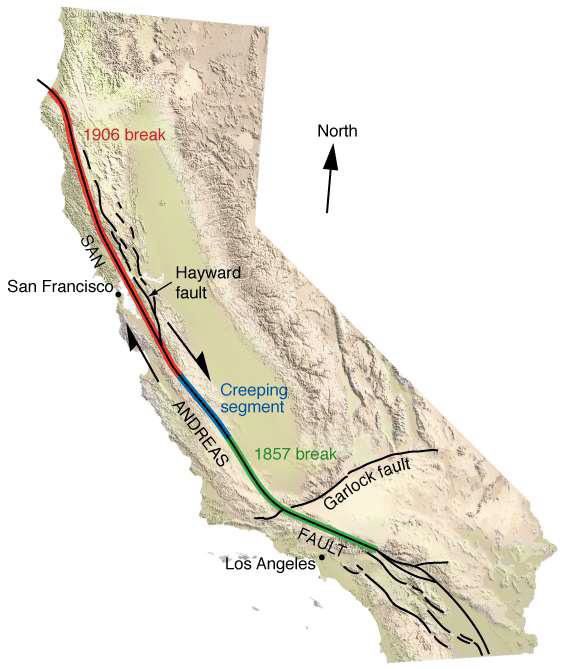
What is a locked segment?
A fault segment that is stuck due to friction
No movement until enough stress builds up to cause a sudden slip, resulting in an earthquake
What is the Mercalli Scale?
Subjective EQ scale
Based on damage survey
What is the main hazard of transform plate boundaries?
EQs
Not volcanoes
What is a magmatic arc volcano?
a volcano that forms above a subduction zone
What is Chile's most active volcano? List its outputs.
Lascar Volcano
30000 tonnes of sulphur dioxide / day
High silica and highly viscous lava

What is the Tethys Ocean?
Dead ocean
Closed during the breakup of Pangea
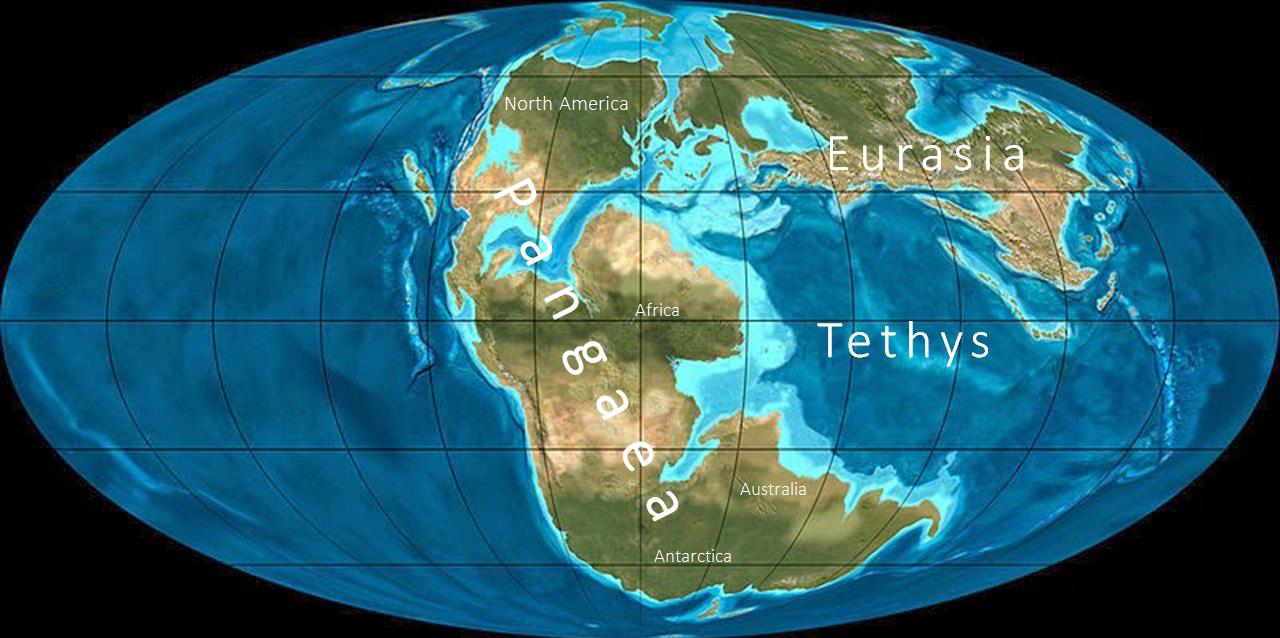
What does the Alpine-Himalayan Orogeny tell us about the Tethys Ocean?
Records the closure of the Tethys
i.e., the collision of African and European plates
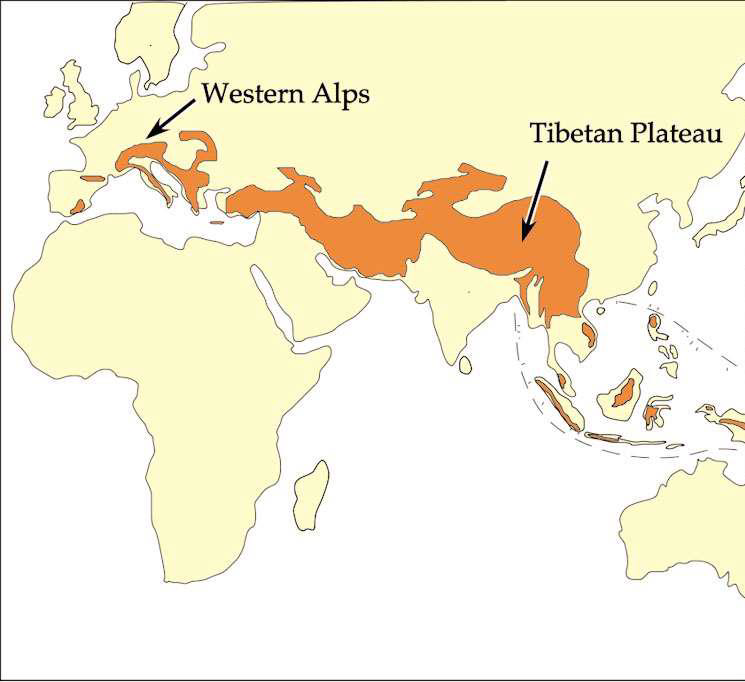
Define orogenesis
Process of building mountains
What is an orogen?
A mountain range
What is a suture zone?
a geological boundary where two distinct tectonic plates or terranes have collided and fused together
i.e., oceans close until continents come together at a suture
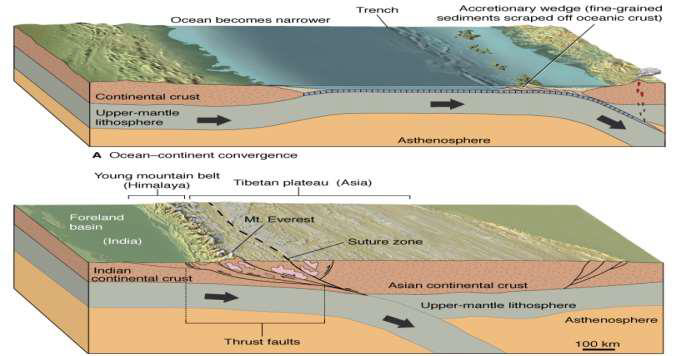
What is a foreland basin?
Land next to the thick part of crust
Lowers beneath the thickest part (elevation)
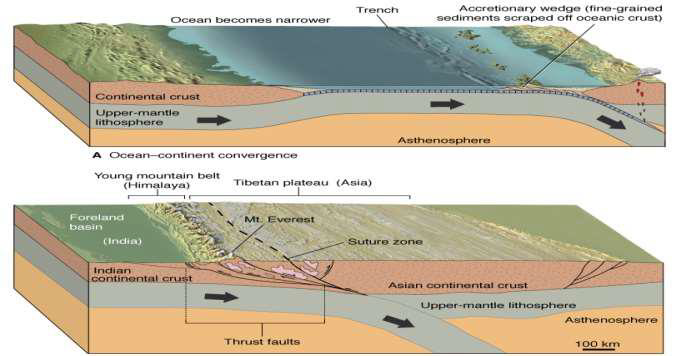
Define obduction
a geological process in which a piece of oceanic lithosphere is thrust onto a continental plate, rather than subducting beneath it
What material are susceptible to obduction (i.e., don't subduct well)?
Island arcs
Continental shelves
Ophiolites
Intraplate volcanoes
Accretionary wedges
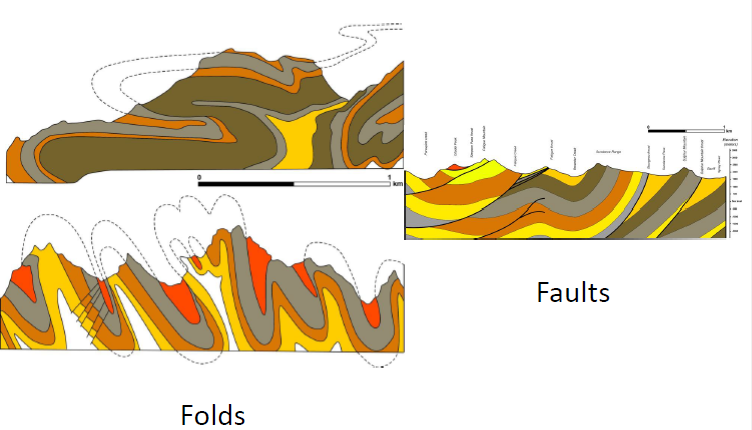
What is crustal shortening?
"crumpling" of the crust
Earth's crust is compressed due to tectonic forces, causing it to thicken, fold, and fault

What is a fold and thrust belt?
a region of the Earth's crust that has been deformed by compressional tectonic forces
Leads to the formation of folds (bent rock layers) and thrust faults (low-angle reverse faults)
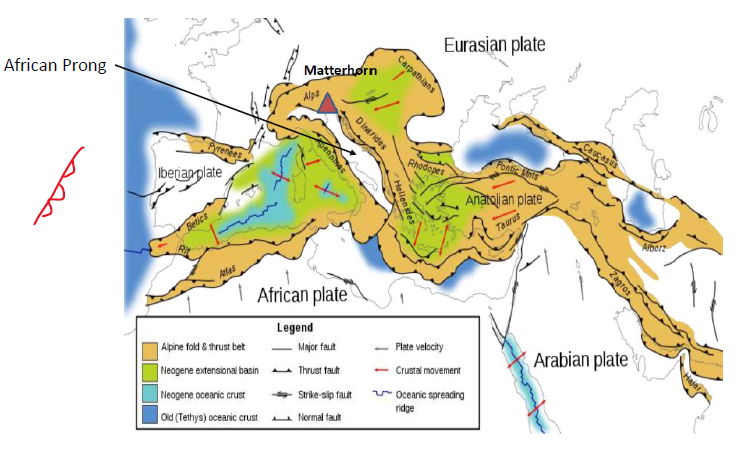
What is the African Prong?
Point where African plate went over the Eurasian plate
How is the subduction of the mediterranean sea influenced by the Anatolian plate?
Subducts as Anatolian plate "escapes" west
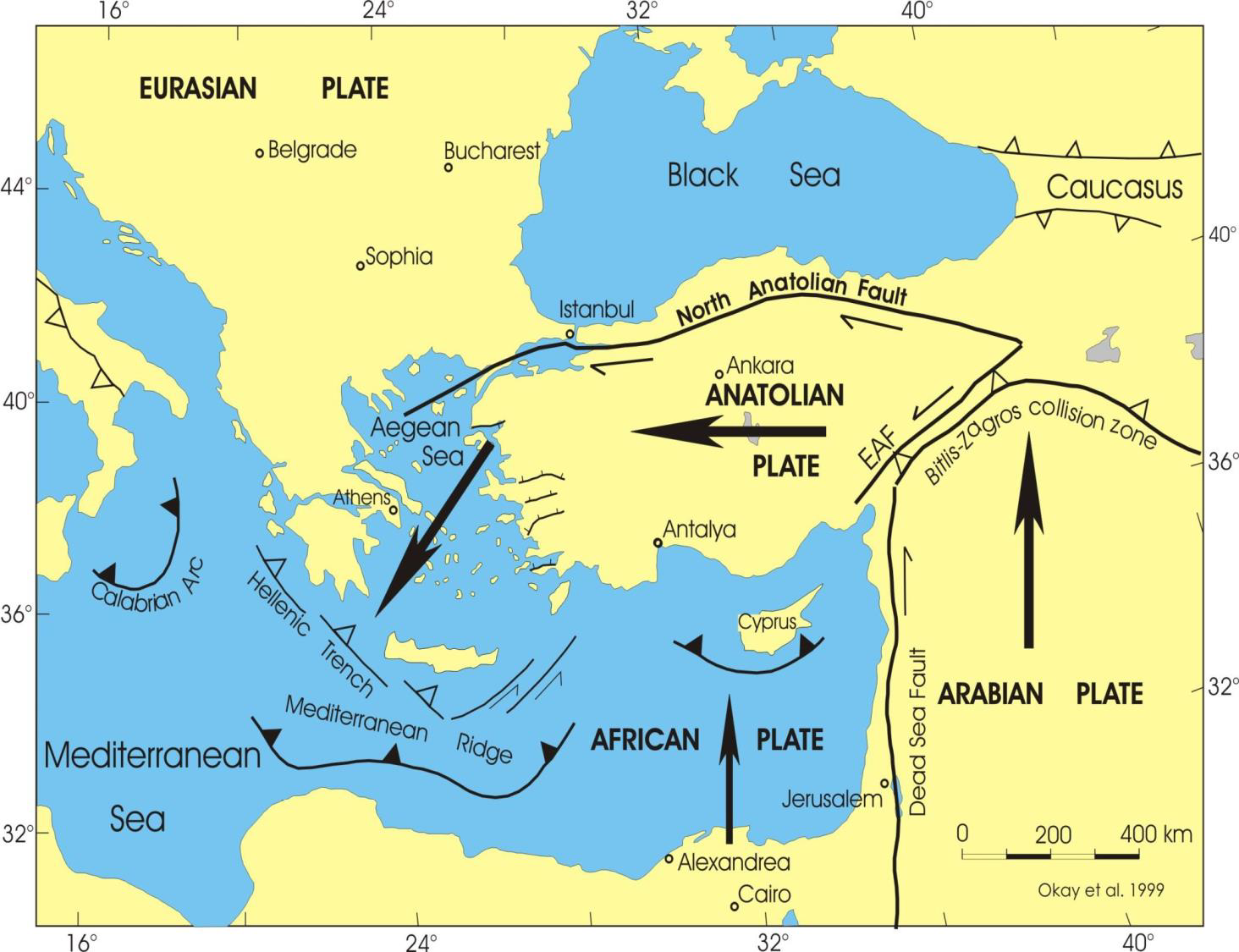
What is an indenter?
a rigid, relatively undeformable landmass or tectonic block that moves into and deforms a surrounding region, typically during a continental collision
What is the Arabian plate an indenter to?
Eurasia
Lifts Zagros and Caucasus mountains
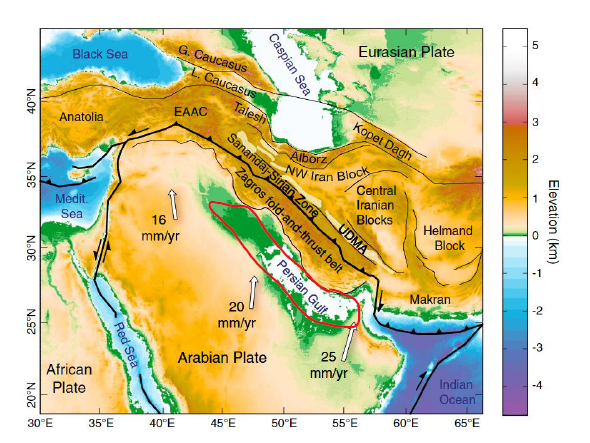
Why does the Persian Gulf exist?
Zagros' substantial crustal thickening is pulling down adjacent crust
Forms foreland basin
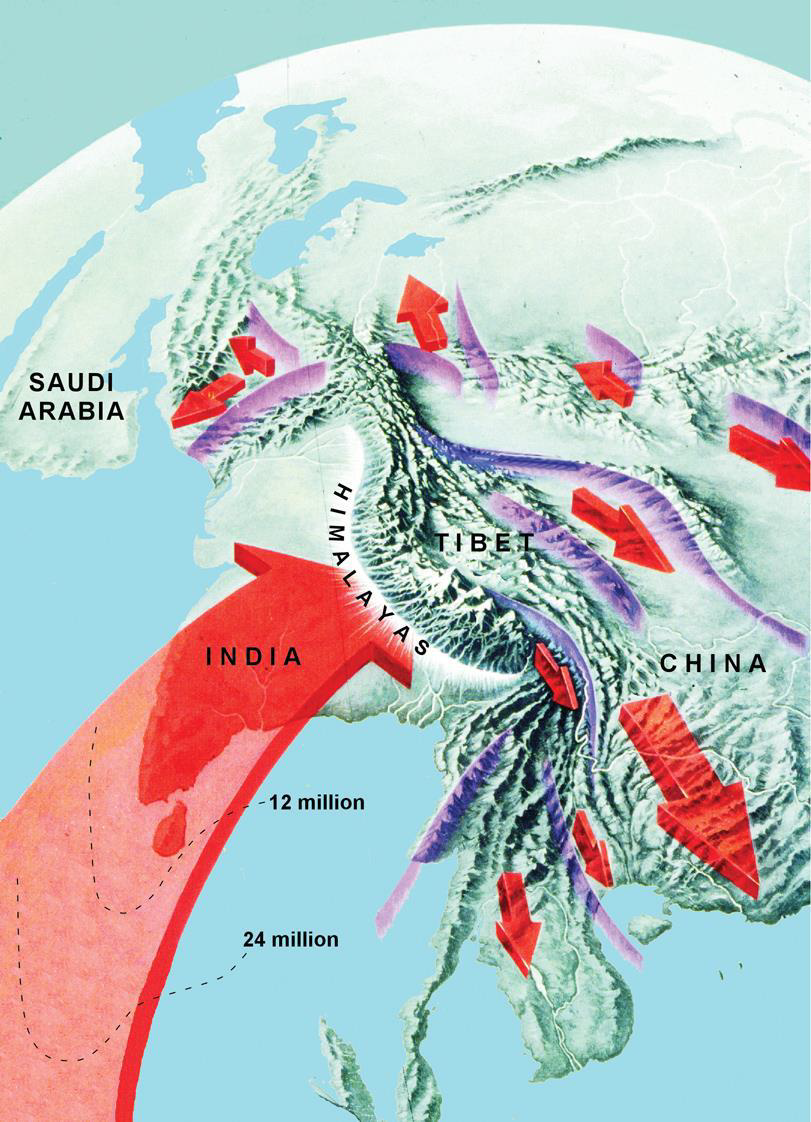
Where has India been indenting and what has this cause?
Into Eurasia for 60million years
Causes obduction and escape tectonics
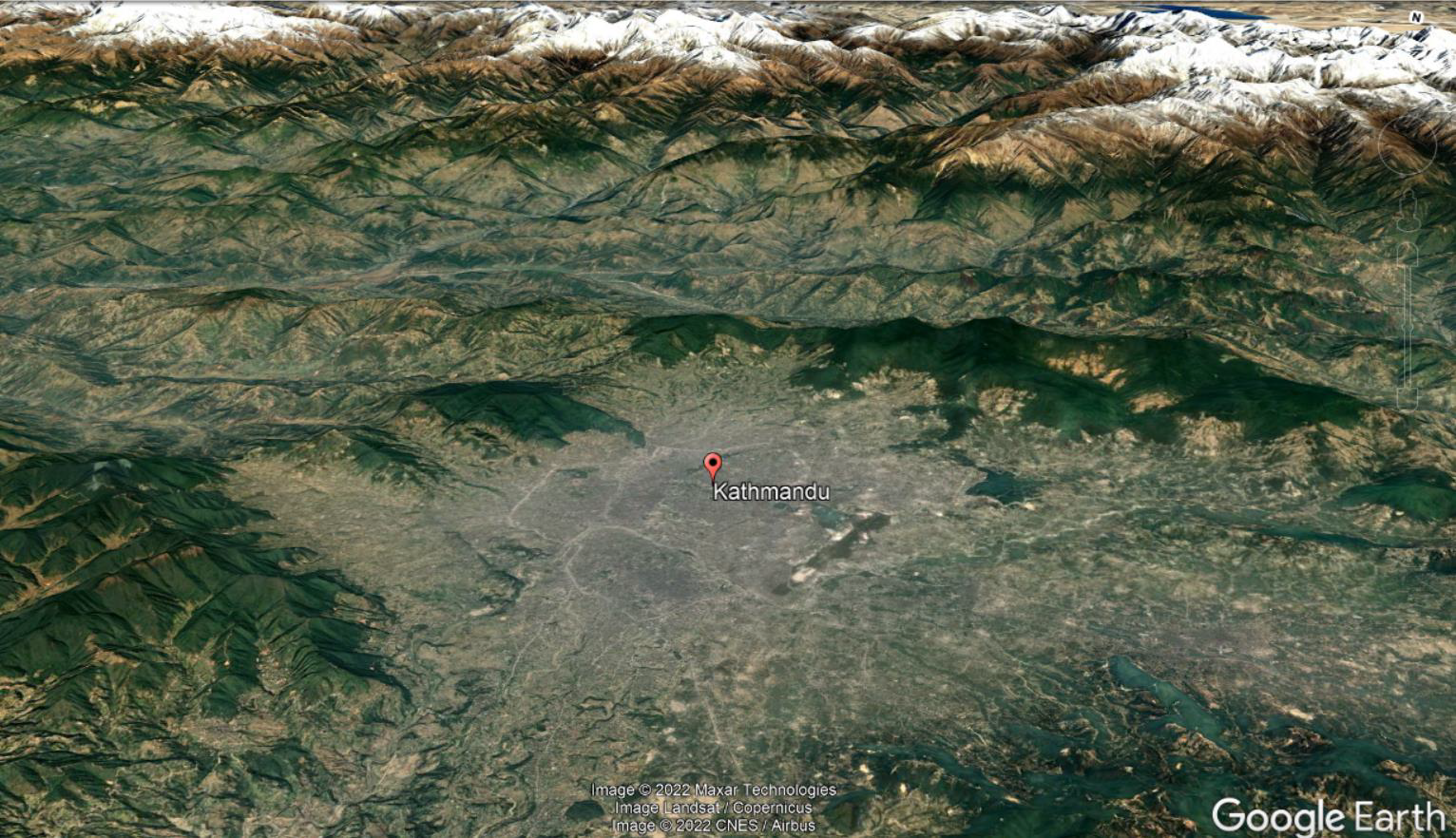
What is the issue with the physiography of Kathmandu?
Bowl-shaped
Collects sediment
EQs will lead to liquefaction
Why may the concept of escape tectonic be especially problematic for China?
They have really high mountains
Too much pressure at the base may cause the mountain to move laterally