RAD 102 - Homework 7a
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Which particles are created/emitted as a result of: Photoelectric Effect
photoelectron
Which particles are created/emitted as a result of: Compton Scattering
compton electron
Which particles are created/emitted as a result of: Pair Production
electron and positron
Which particles are created/emitted as a result of: Photonuclear Interaction
alpha, proton and/or neutron
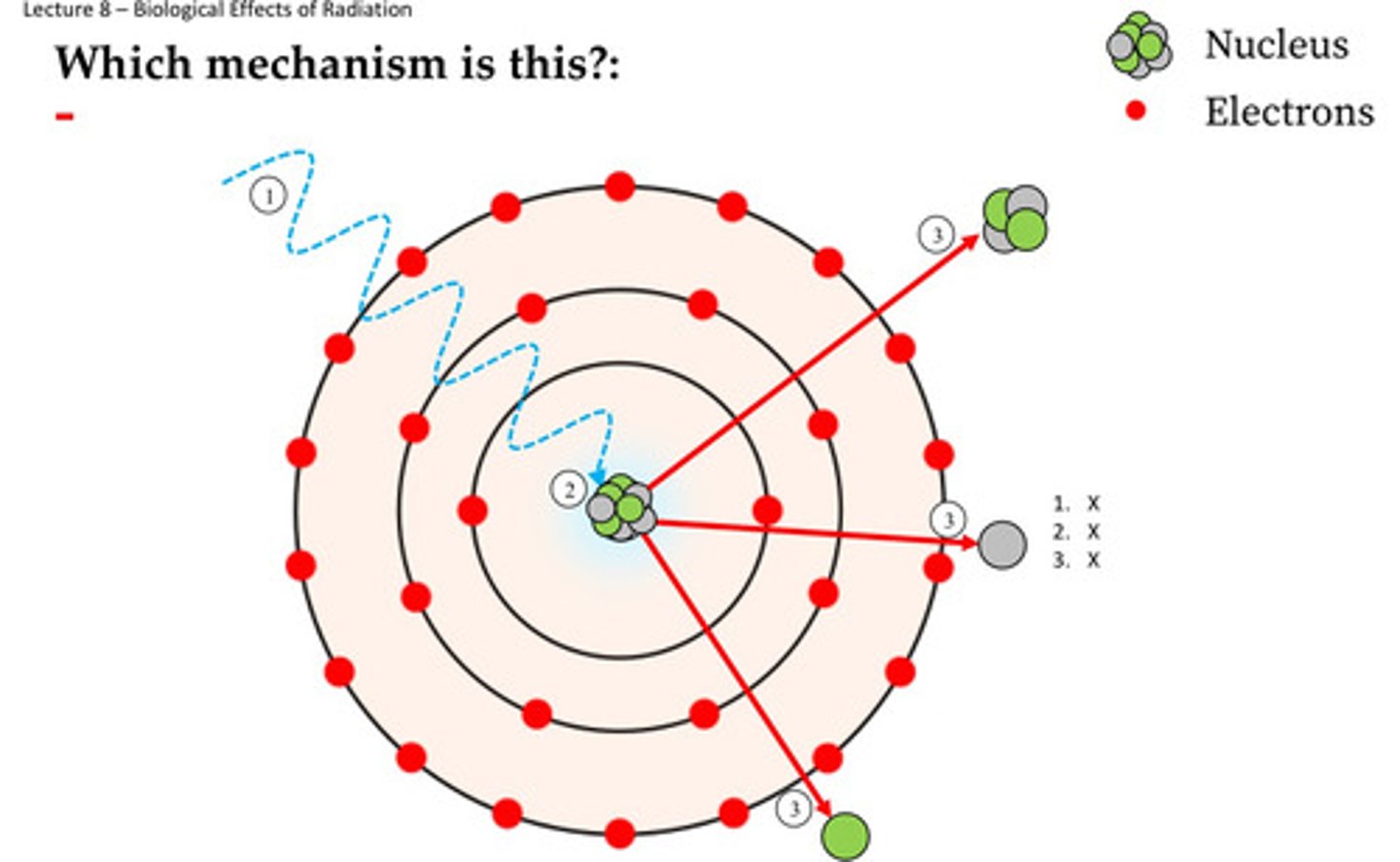
Which answer best describes what happens to the incident photon in the Photon Interaction image below?
A. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed and converted to matter
B. All the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon no longer exists
C. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed by the nucleus, subatomic particle(s) are emitted
D. Some of the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon changes direction with less energy
D. Some of the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon changes direction with less energy
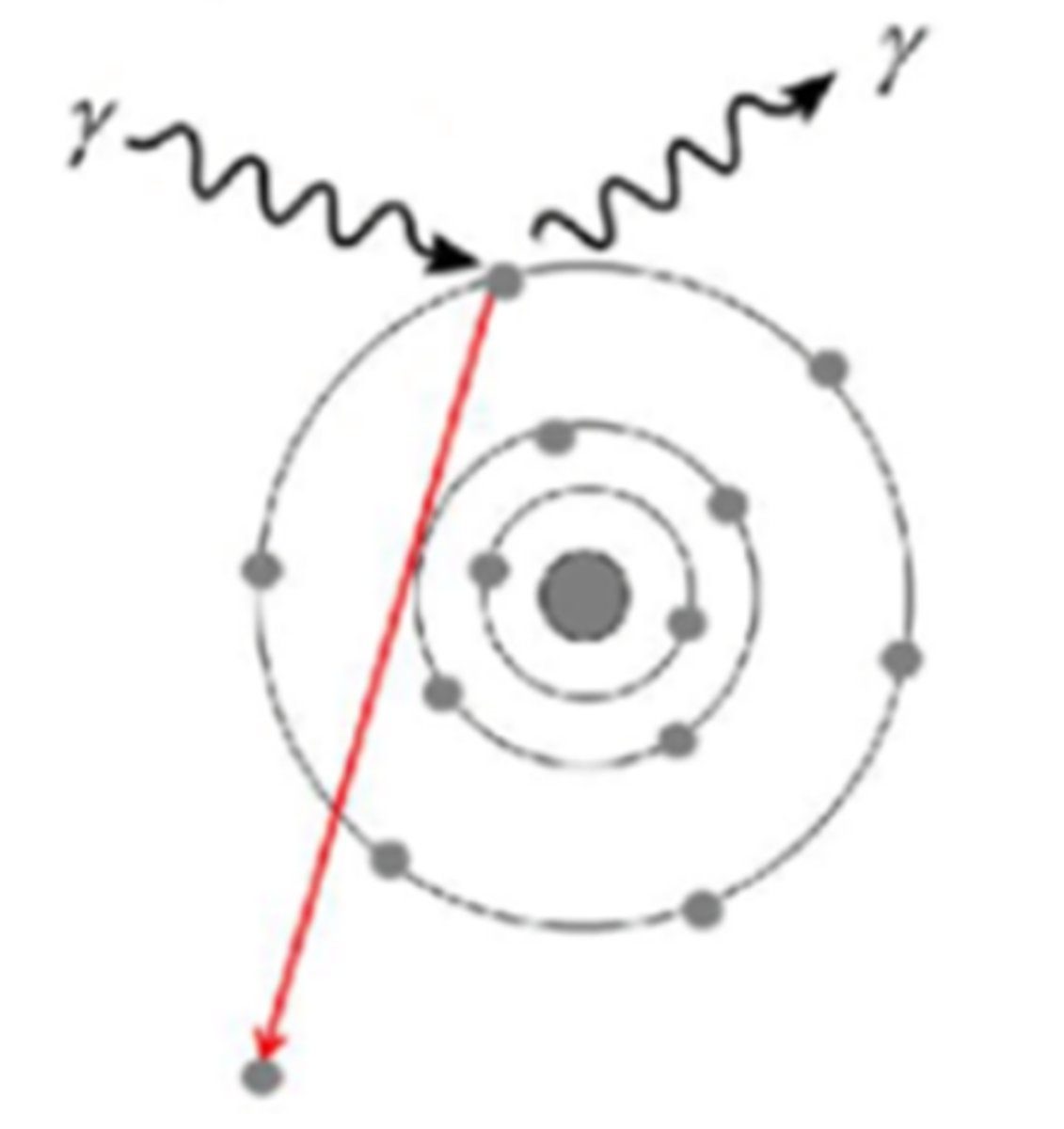
Which answer best describes what happens to the incident photon in the Photon Interaction image below?
A. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed and converted to matter
B. Some of the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon changes direction with less energy
C. All the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon no longer exists
D. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed by the nucleus, subatomic particle(s) are emitted
A. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed and converted to matter
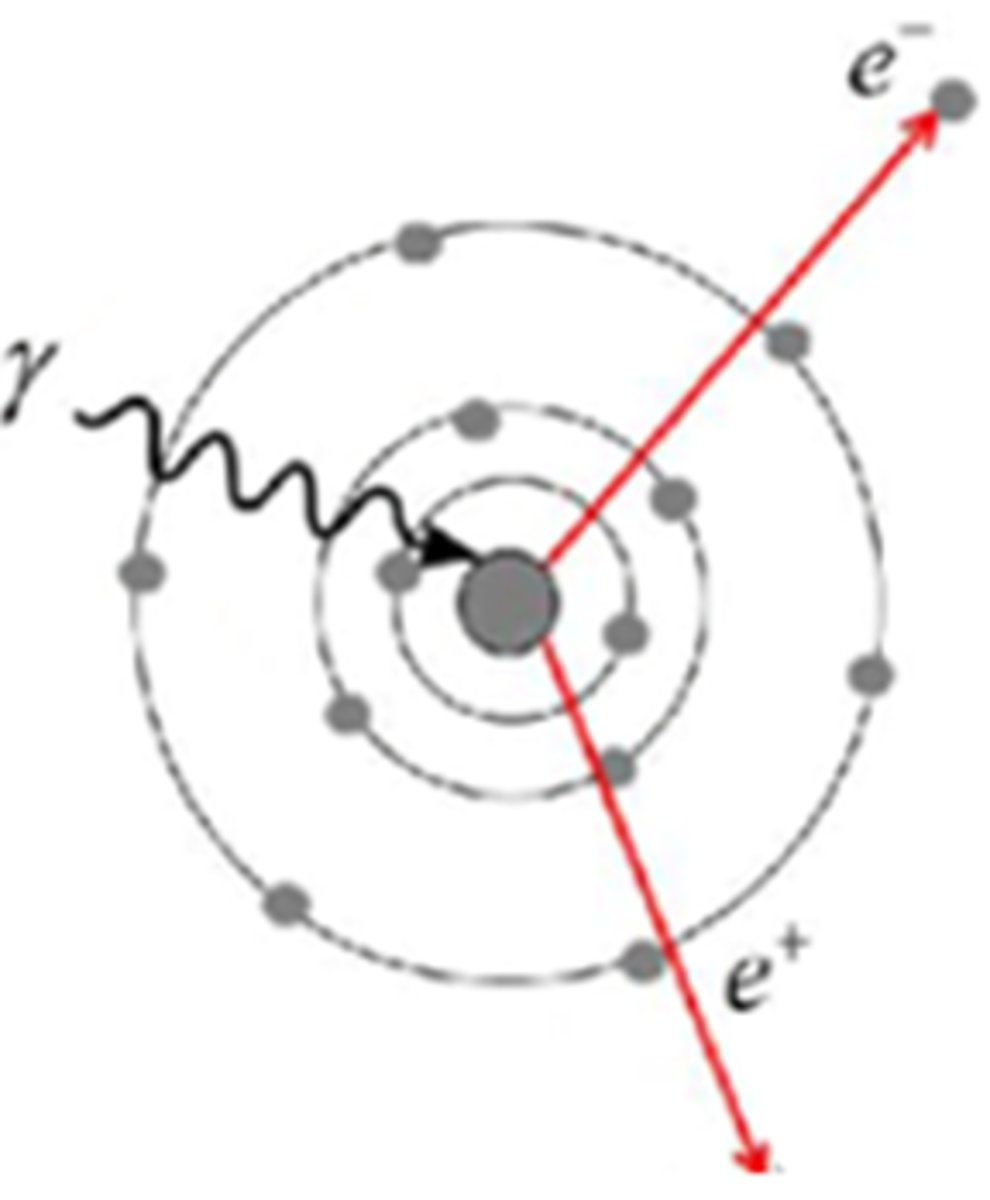
Which answer best describes what happens to the incident photon in the Photon Interaction image below?
A. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed and converted to matter
B. All the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon no longer exists
C. Some of the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon changes direction with less energy
D. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed by the nucleus, subatomic particle(s) are emitted
B. All the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon no longer exists
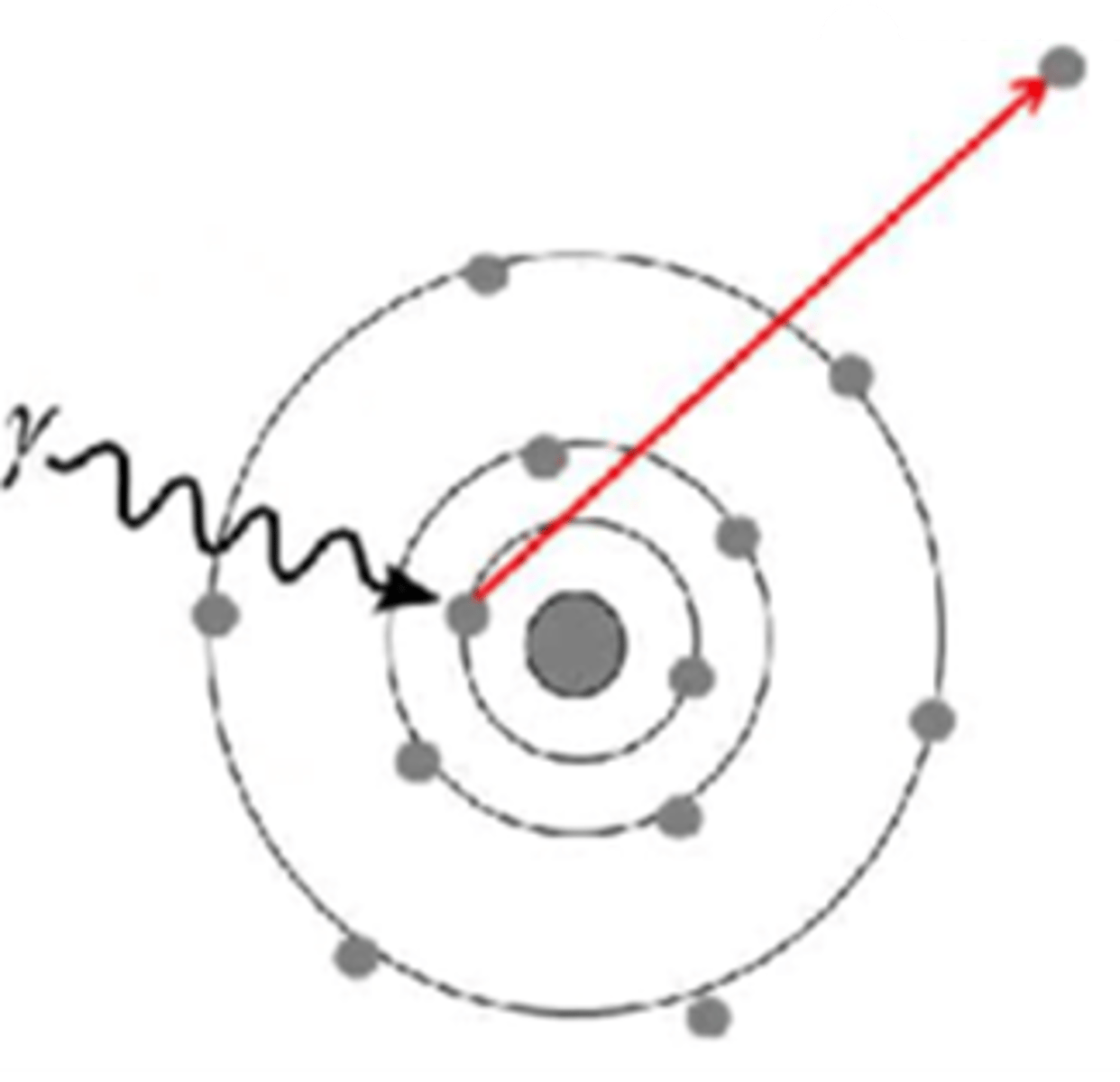
Which answer best describes what happens to the incident photon in the Photon Interaction image below?
A. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed and converted to matter
B. All the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon no longer exists
C. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed by the nucleus, subatomic particle(s) are emitted
D. Some of the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon changes direction with less energy
C. All of the energy of the photon is absorbed by the nucleus, subatomic particle(s) are emitted
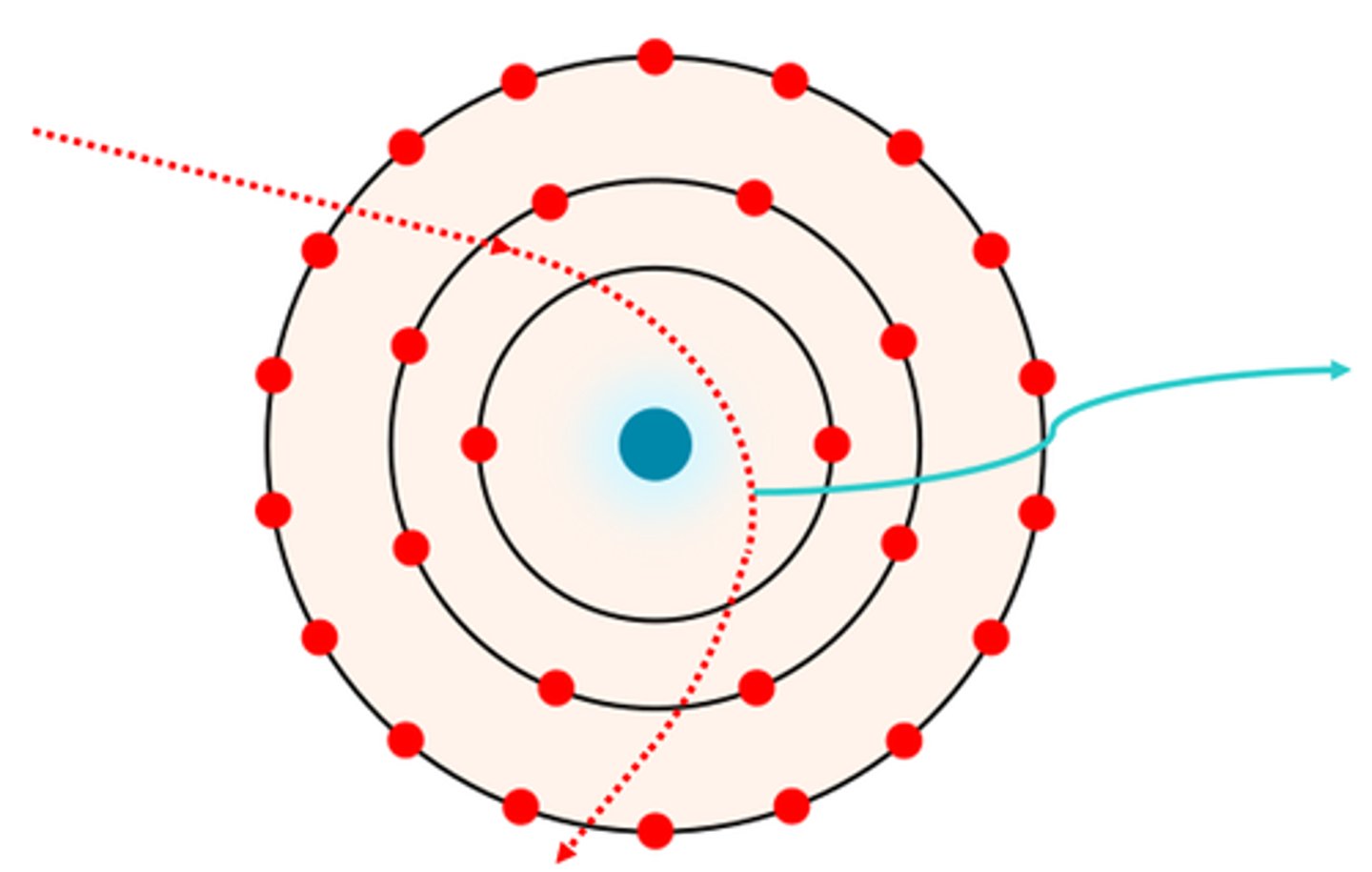
In this diagram, an incident particle comes near the nucleus (red dotted line) and is affected by Coulomb Interaction. The particle then changes direction with less energy and emits _____ (teal arrow) to conserve energy. (fill in the blank)
A. Auger Electron Emission
B. Photoelectron
C. Bremmstrahlung radiation
D. Characteristic X-ray radiation
C. Bremmstrahlung radiation
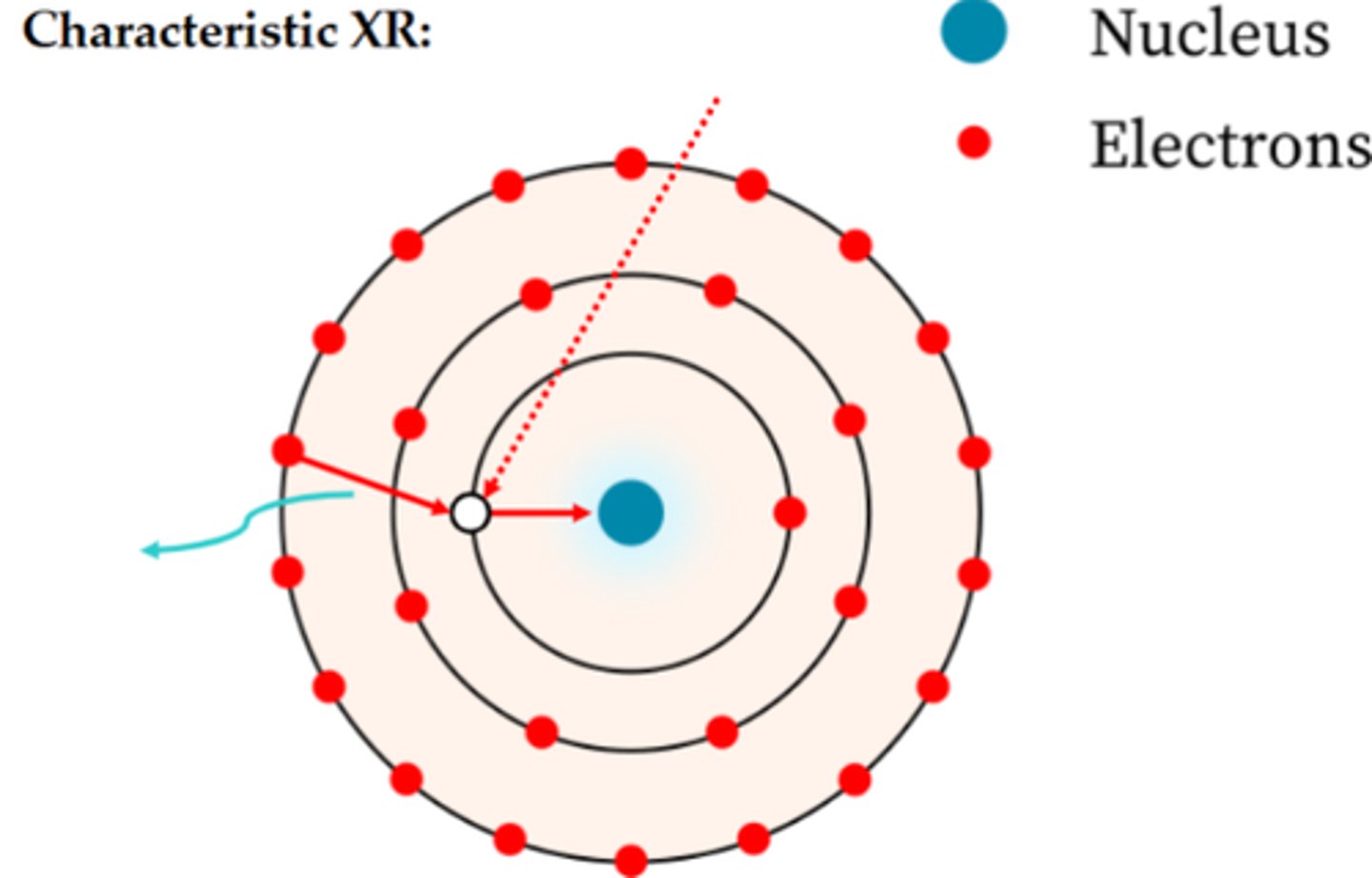
In this diagram, an incident particle comes near the nucleus and has a charged particle interaction (red dotted line) leaving the inner shell empty. The outer shell falls from higher energy to lower energy (red arrow). Conserved energy is emitted in form of ______ (teal arrow). (fill in the blank)
A. Auger Electron Emission
B. Photoelectron
C. Bremmstrahlung radiation
D. Characteristic X-ray radiation
D. Characteristic X-ray radiation
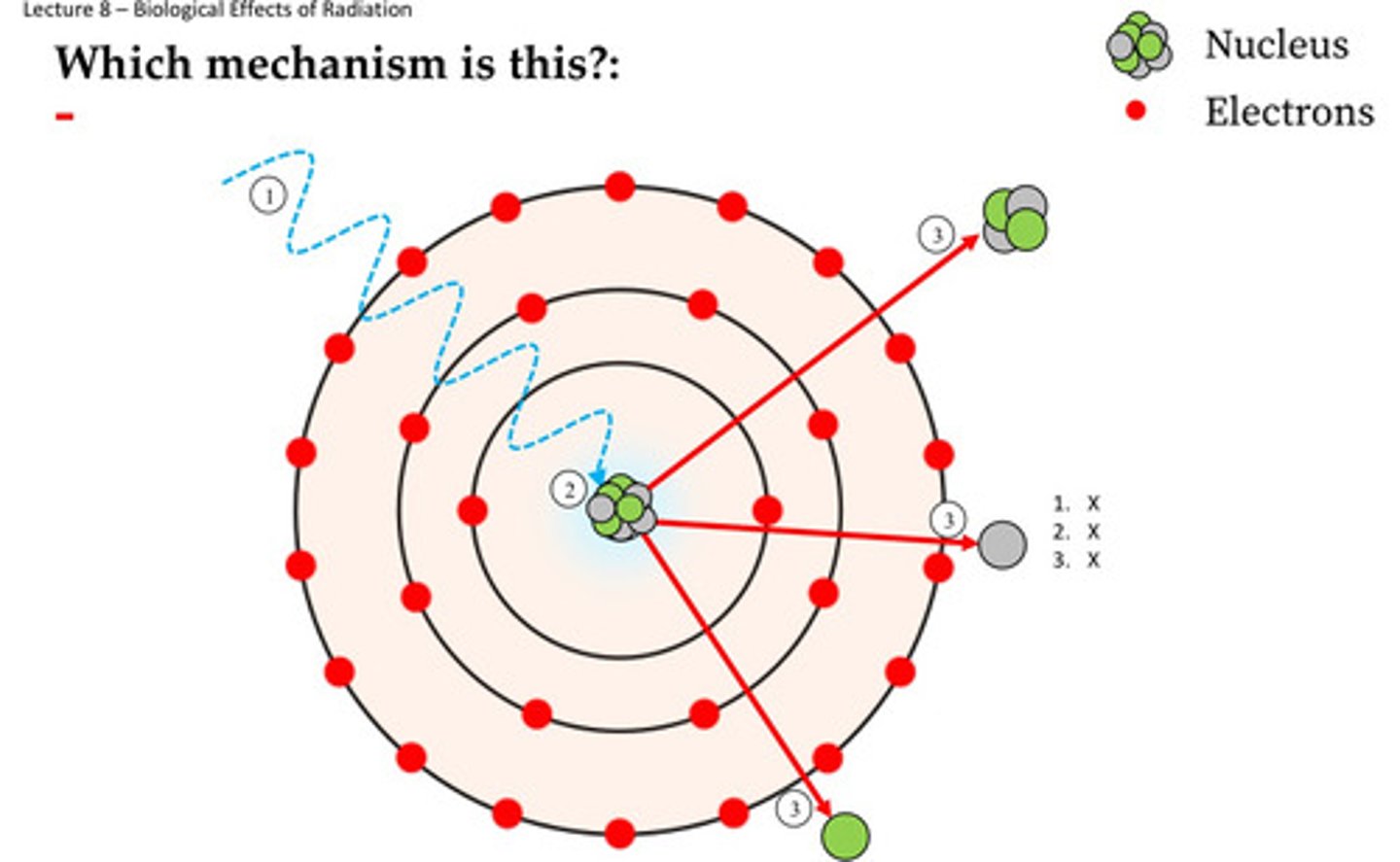
Match diagram below with the correct Photon Interaction:
A. Photoelectric Effect
B. Photonuclear Interaction
C. Compton Scattering
D. Pair Production
A. Photoelectric Effect
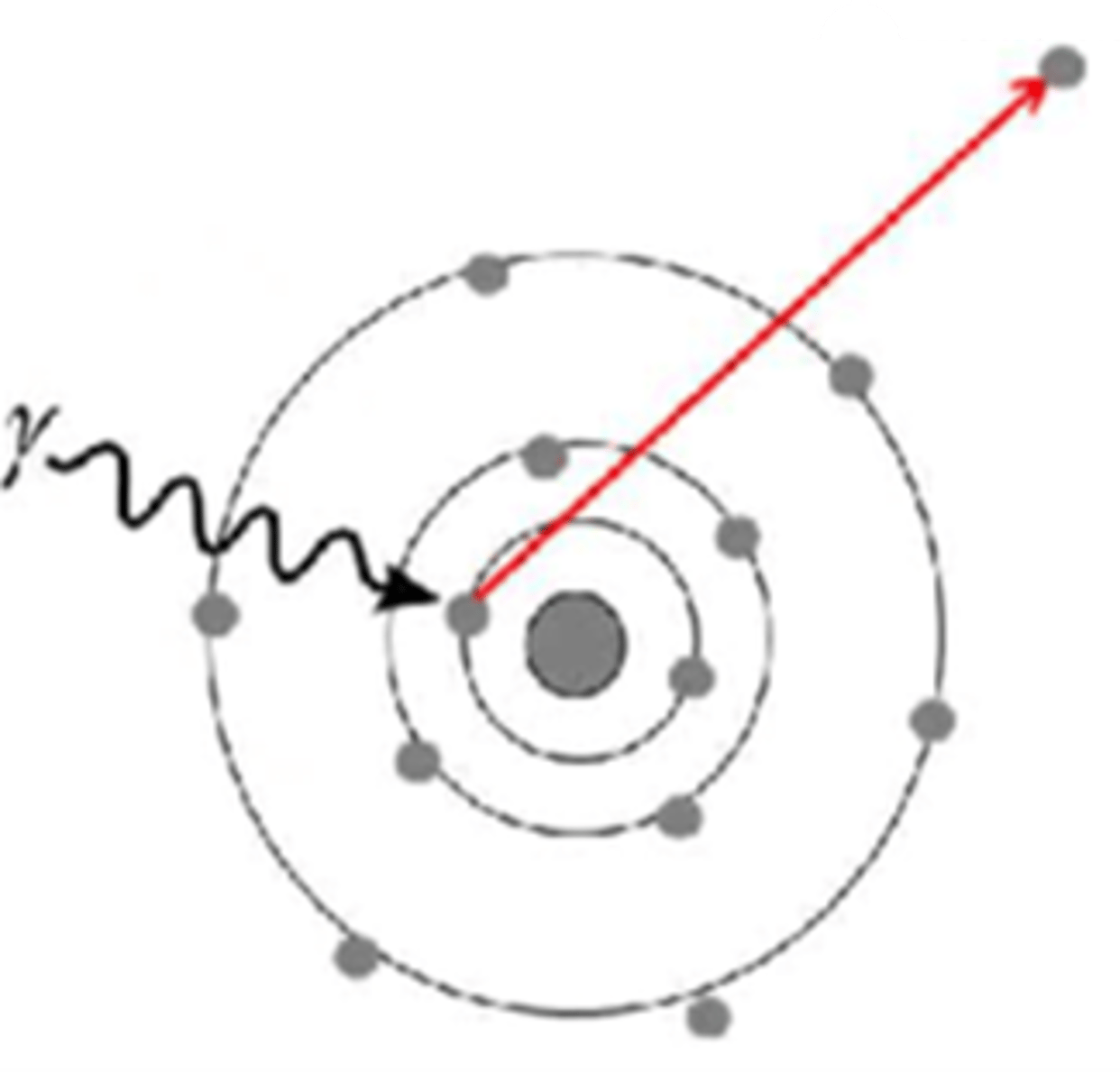
In the diagram below, ALL of the energy of the incident photon is absorbed. The ejected atomic particle is called:
A. Neutron and/or Proton
B. Compton electron
C. Electron and Positron pair
D. Photoelectron
D. Photoelectron
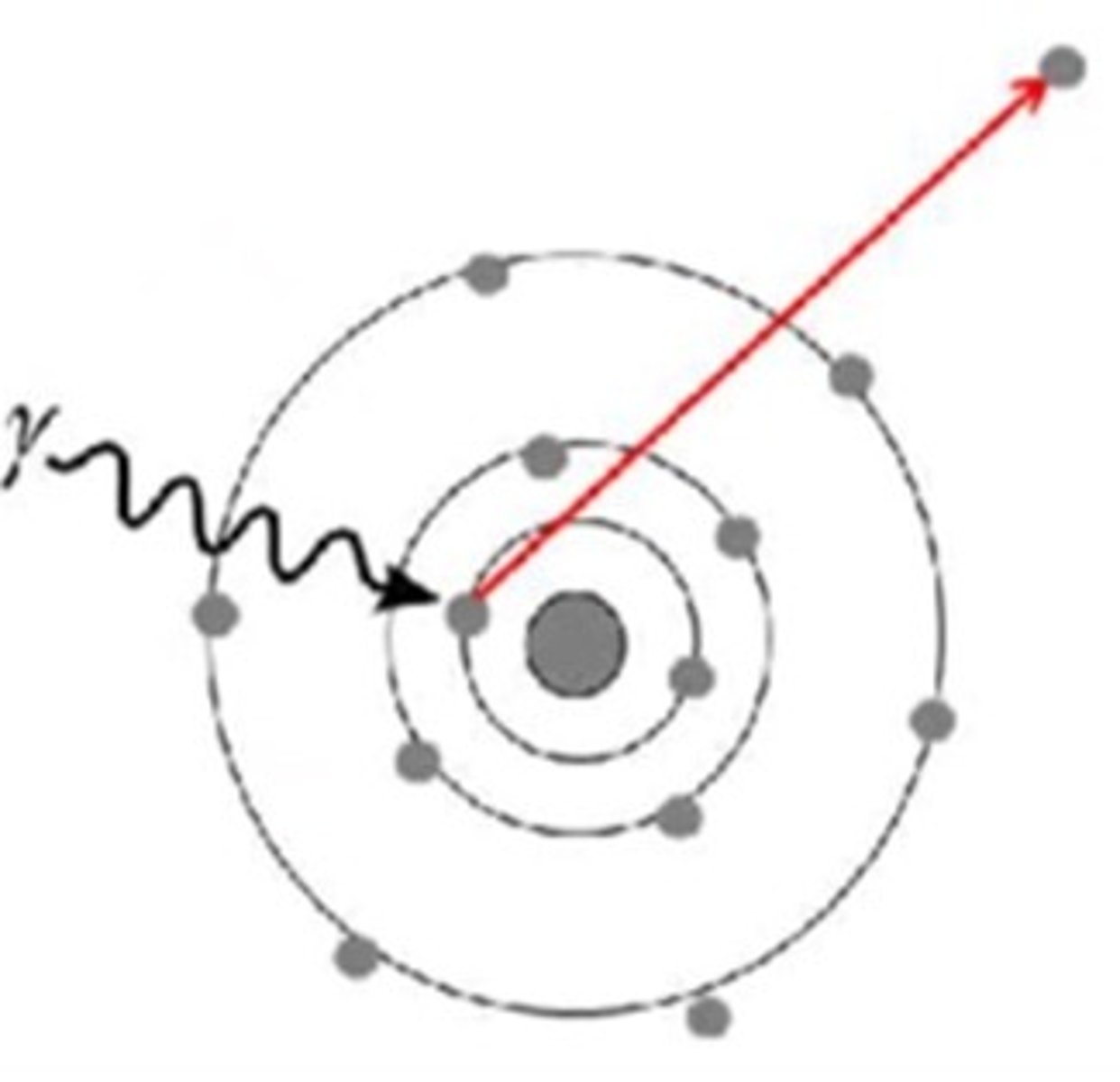
Match diagram below with the correct Photon Interaction:
A. Photoelectric Effect
B. Compton Scattering
C. Photonuclear Interaction
D. Pair Production
D. Pair Production
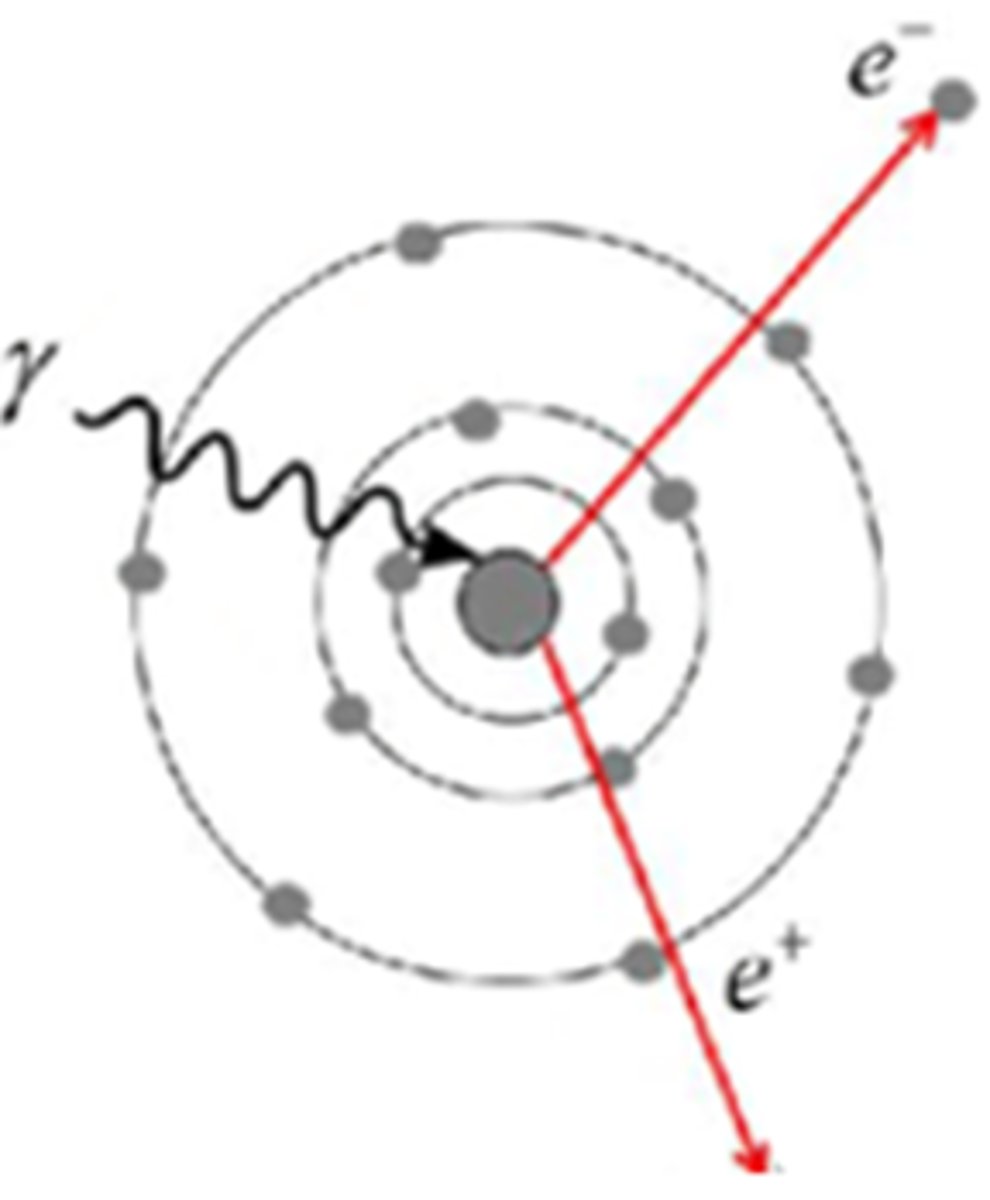
In the diagram below, ALL of the energy of the incident photon is converted to matter. The ejected atomic particles are called:
A. Photoelectron
B. Electron and Positron pair
C. Neutron and/or Proton
D. Compton electron
B. Electron and Positron pair
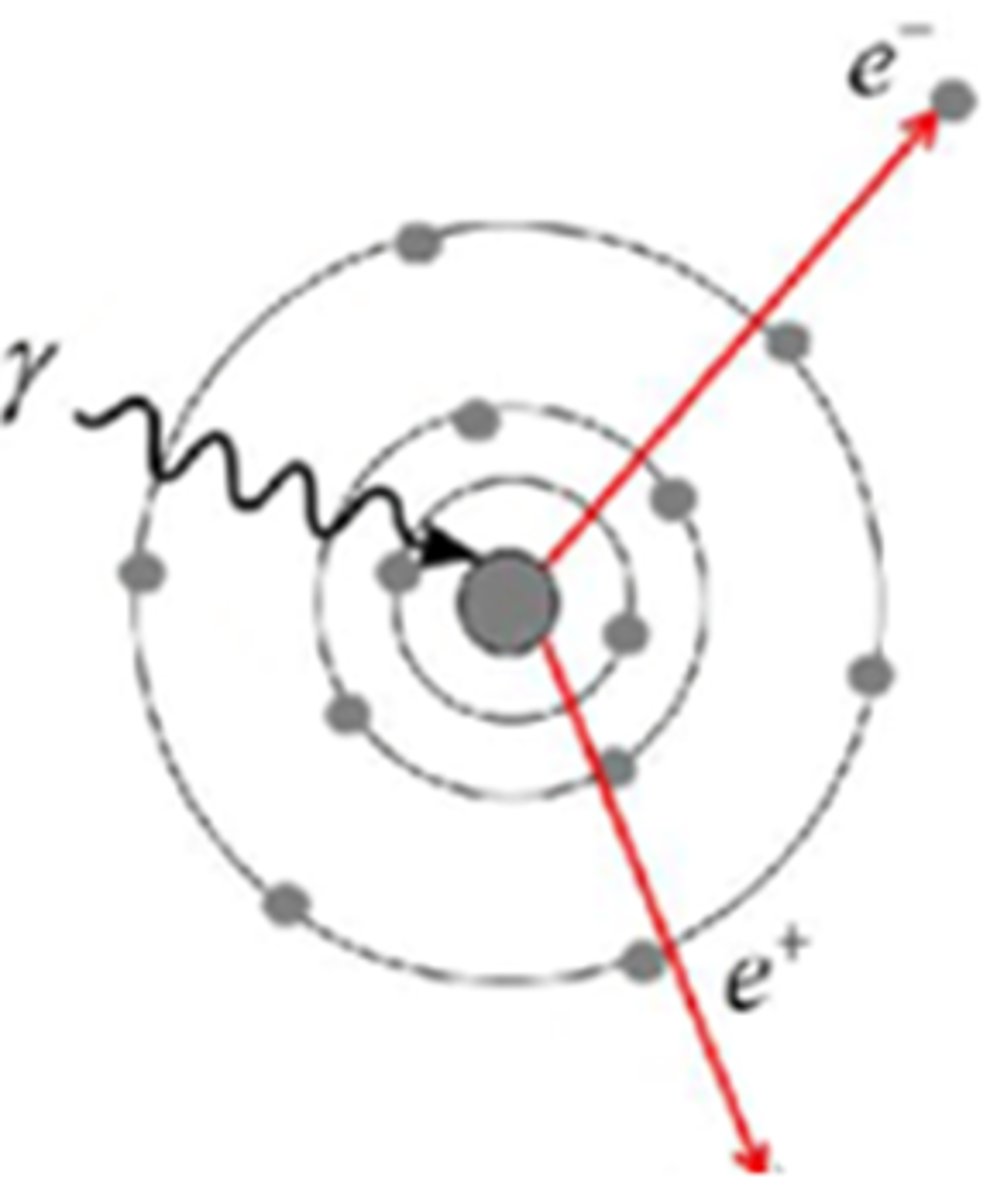
Match diagram below with the correct Photon Interaction:
A. Photoelectric Effect
B. Compton Scattering
C. Photonuclear Interaction
D. Pair Production
B. Compton Scattering
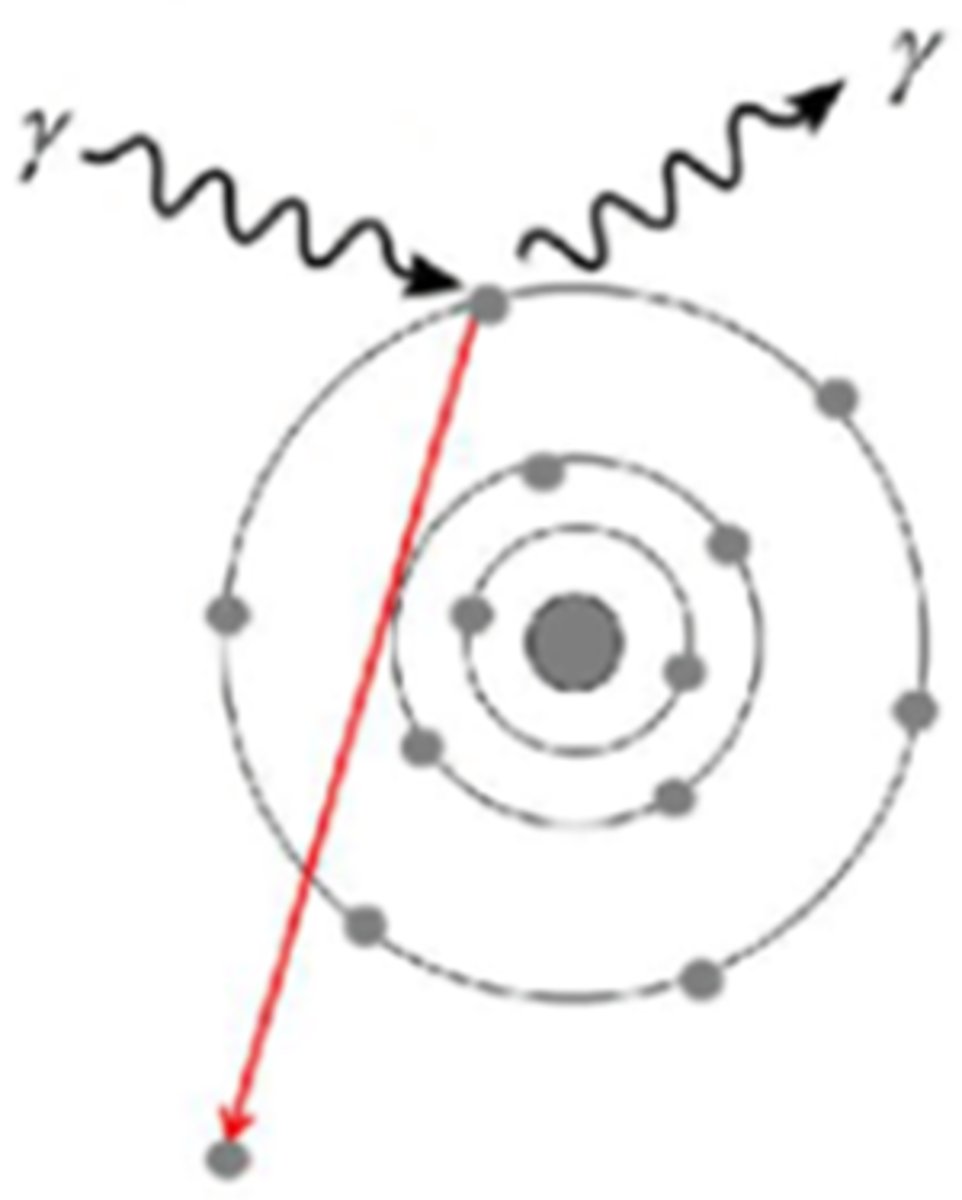
In the diagram below, SOME of the energy of the incident photon is absorbed. The ejected atomic particle is called:
A. Electron and Positron pair
B. Neutron and/or Proton
C. Compton electron
D. Photoelectron
C. Compton electron
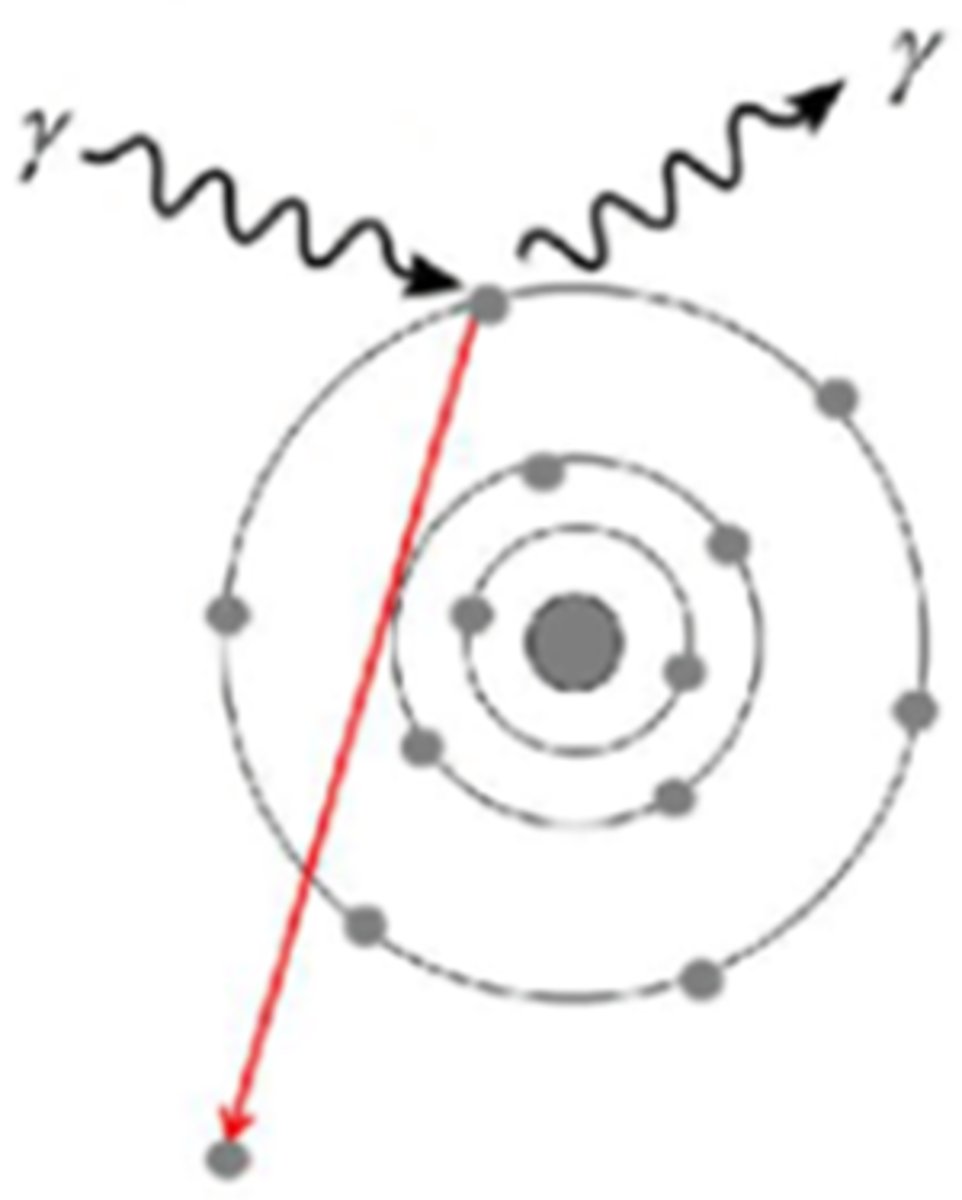
Match diagram below with the correct Photon Interaction:
A. Photoelectric Effect
B. Compton Scattering
C. Photonuclear Interaction
D. Pair Production
C. Photonuclear Interaction
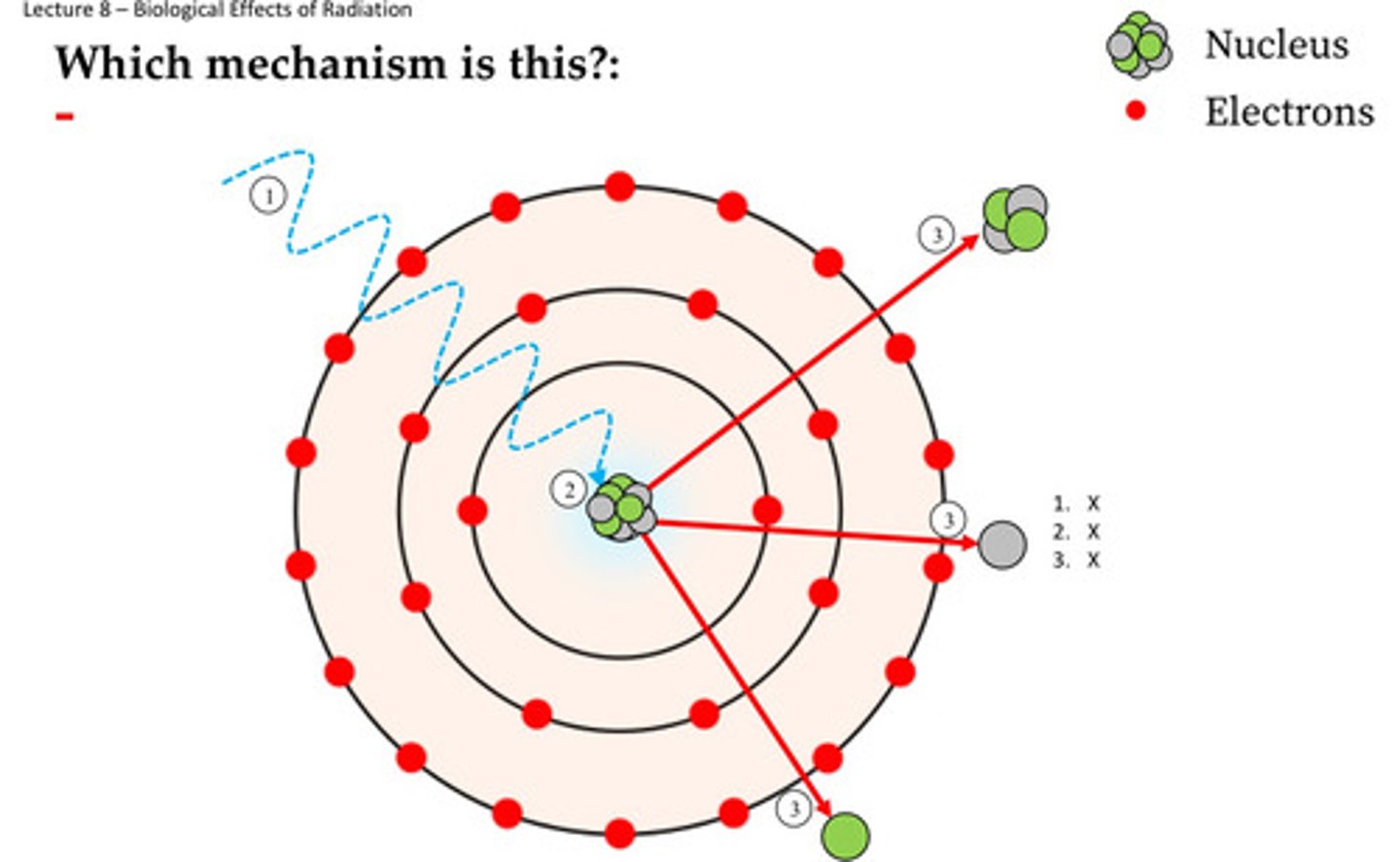
In the diagram below, SOME of the energy is transferred to the electron, the photon changes direction with less energy. The ejected particle is called:
A. Electron and Positron pair
B. Neutron and/or Proton
C. Compton electron
D. Photoelectron
B. Neutron and/or Proton