Organizational Behavior Final - Kelley
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Subcultures
Often not a single homogeneous culture. Rather, multiple subcultures that either intensify the existing cultural understanding and practices or diverge from them.
• Subcultures often form around:
• Functional or occupational groups or work roles.
• Divisions or departments.
• Geographical areas.
• Products, markets, technology.
• Levels of management.
Transformational Leaders
Transformational leaders motivate followers to pursue organizational goals over self-interests by using leader behaviors that appeal to followers' self- concepts such as values, motives, and personal identity.
Four key leader behaviors:
1. Inspirational motivation.
2. Idealized influence.
3. Individual consideration.
4. Intellectual stimulation.
Decision-Making Biases
Judgmental heuristics.
• Cognitive shortcuts or biases that are used to simplify the process of making decisions. • Can help managers make decisions but can lead to bad decisions.
Aligning Culture, Structure, and HR Practices to Support Strategy
You can think of an organization's culture, structure, and HR practices as three strands in a single rope. These strands must be tightly woven together to drive successful strategic execution.
Organizational Design
Sets the structures of accountability and responsibility used to develop and implement strategies, and the human resource practices and information and business processes that activate those structures.
Types:
Traditional - Hierarchy, stability, specialization. Clear departments, formal rules, vertical control.
Horizontal - Teams, collaboration, flattening. Project teams, fast decision cycles, less hierarchy.
Open - Networks, outsourcing, external partners. Company as a hub, flexible boundaries, global connections.
Impression Management
Any attempt to control or manipulate the images related to a person, organization, or idea using:
• Speech. • Behavior. • Appearance.
Behavioral Styles Approach to Leadership Effectiveness
Uses four categories of unique behaviors displayed by effective leaders.
1. Task-oriented (TO)
2. Relationship-oriented (RO)
3. Passive (PA)
4. Transformational (TR)
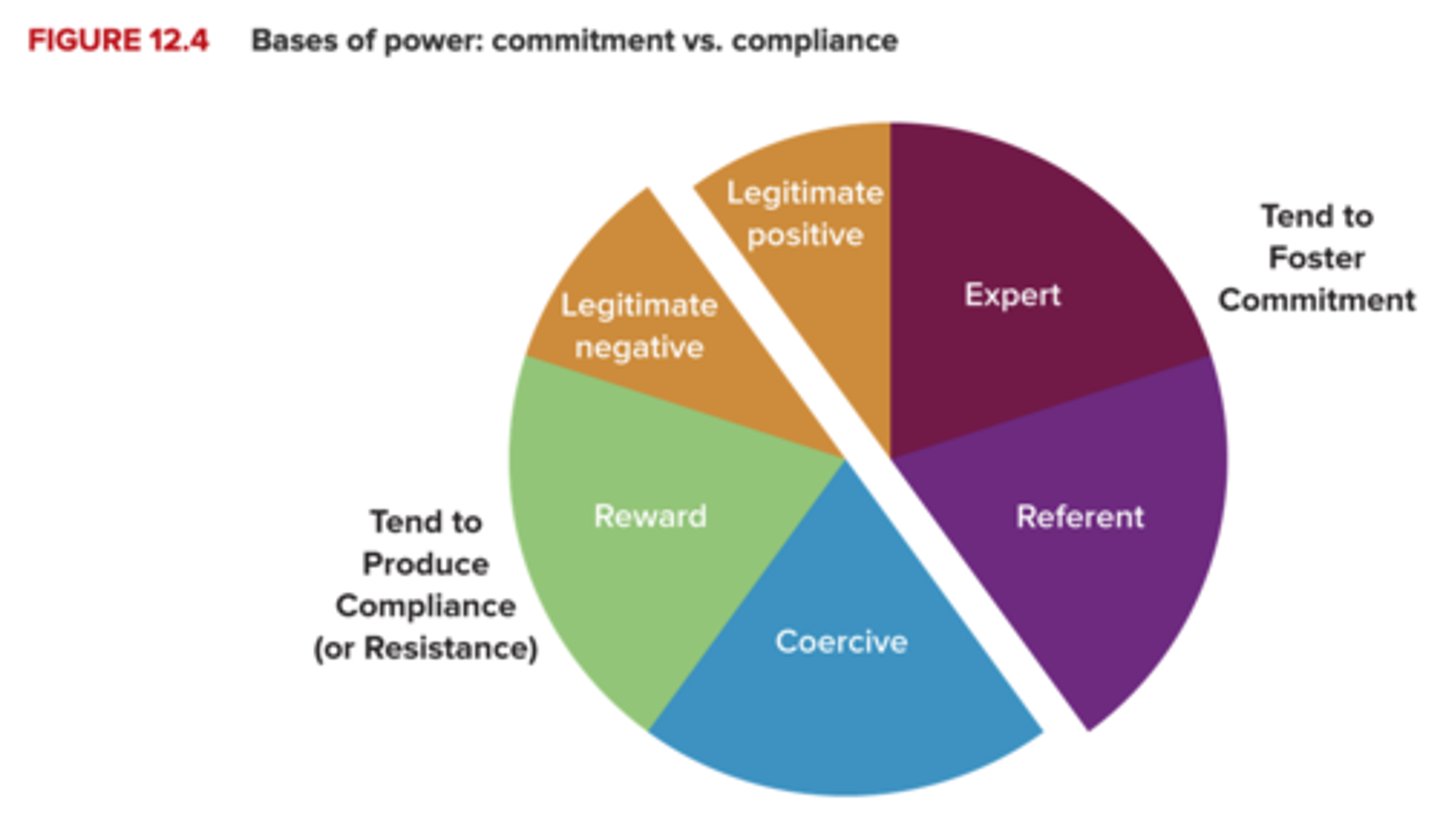
Bases of Power: Commitment versus Compliance
Individuals have three primary responses to power.
• Resistance. • Compliance. • Commitment.
Three Levels of Organizational Culture
Level 1: Observable Artifacts—Physical Manifestations of Culture
• Level 2: Espoused Values—Explicitly Stated Values and Norms
• Level 3: Basic Assumptions—Core Values of the Organization
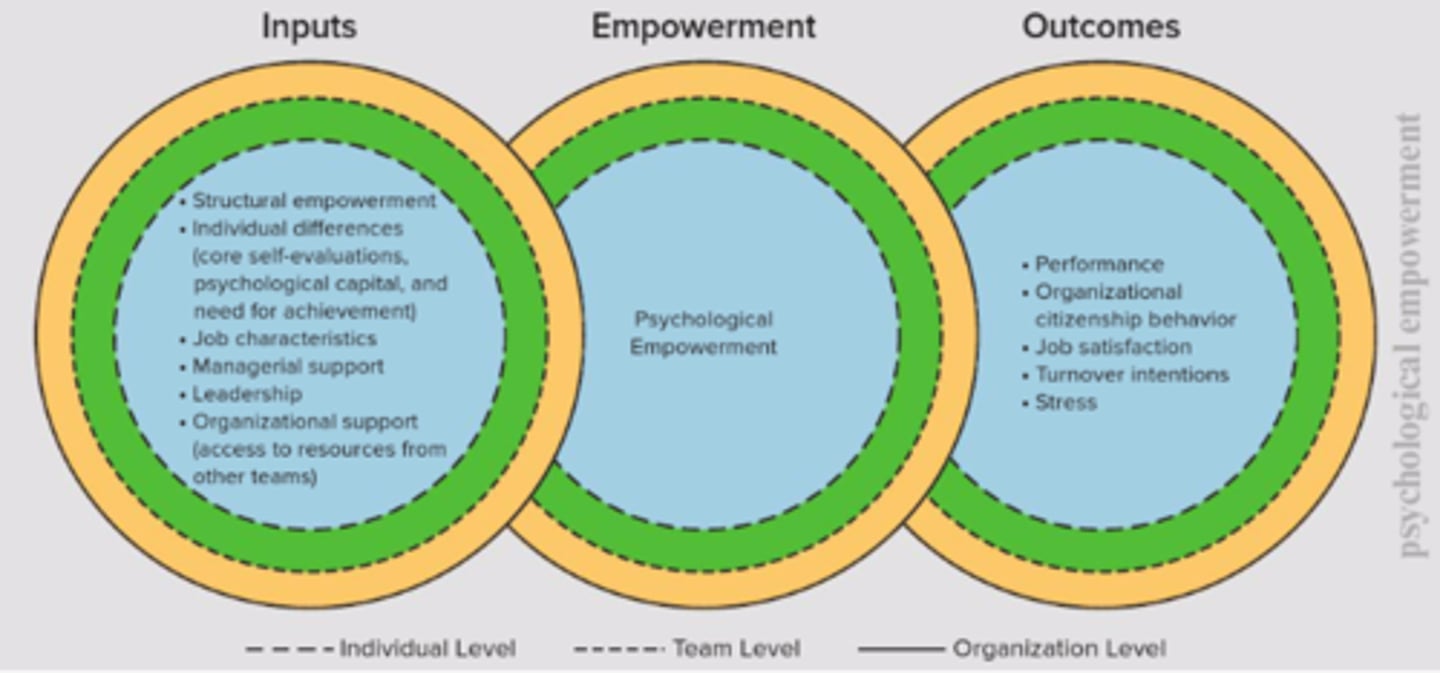
Psychological Empowerment
Occurs when we feel a sense of:
• Meaning from our work.
• Competence in our ability to perform.
• Self-determination: degree of control over how we perform our jobs.
• Impact at work: the difference our efforts make.
Groupthink
Occurs when:
• Members become deeply involved in a cohesive in- group.
• Striving for unanimity overrides motivation to realistically appraise alternative courses of action.
Symptoms: • Invulnerability. • Inherent morality. • Rationalization. • Stereotyped views of opposition. • Self-censorship. • Illusion of unanimity. • Peer pressure. • Mind guards.
Mentoring and Embedding Organizational Culture
Mentoring is the process of forming and maintaining intensive and lasting developmental relationships between a variety of developers and a junior person.
Occurs over four phases: 1. Initiation. 2. Cultivation. 3. Separation. 4. Redefinition.
Effective Leadership - Fielder's Situational Theory
Fiedler's situational theory.
◦ Leaders are thought to have a dominant style: motived by either relationship or task.
◦ Leader effectiveness depends on the extent to which leader style matches the situation.
◦ As situations change, different styles become more appropriate.
◦ Fiedler identified three dimensions of situational control: 1. Leader-member relations. 2. Task structure. 3. Position power.
◦ Leadership effectiveness goes beyond traits and behaviors. ◦ Organizations should attempt to hire or promote people whose leadership styles fit or match the situational demands. ◦ Leaders need to modify their style to fit a situation.
The Organizational Socialization Process
The process by which a person learns the values, norms, and required behaviors which permit them to participate as a member of an organization.
The three-phase model of organizational socialization: 1. Anticipatory socialization. 2. Encounter. 3. Change and acquisition.
Organizational Politics
Intentional acts of influence to enhance or protect the self- interest of individuals or groups that are not endorsed by or aligned with those of the organization. •
Some key causes of political behavior: • Organizational justice. • Trust in co-workers. • Negative affect • Culture • Processes • Perceptions
Uncertainty: may trigger political behaviors
Leadership Effectiveness
What is the trait approach? ◦ Attempts to identify personality characteristics or interpersonal attributes that can be used to differentiate leaders from followers. ◦
Early research identified: ◦ Intelligence. ◦ Dominance. ◦ Self-confidence. ◦ Level of energy and activity. ◦ Task-relevant knowledge.
Leadership traits are linked to leadership emergence.
◦ Positive traits should be cultivated and "dark-side" traits avoided.
◦ It is important to develop a global mind-set.
What is path-goal theory?
Leaders seen as effective when employees view them as a source of satisfaction or as paving the way to future satisfaction.
Leaders do this by: ◦ Reducing roadblocks. ◦ Providing guidance and support. ◦ Linking rewards to goal accomplishment.
Creativity Outcomes
Drivers of creative performance behaviors:
1. Problem formation and definition. 2. Preparation and information gathering. 3. Idea generation. 4. Idea evaluation and validation.
• Drivers of creative outcome effectiveness:
• Person factors:• Motivation.• Personality.• Self-efficacy.• National culture.
• Situation characteristics:• High commitment work practices.• Organizational culture and climate.
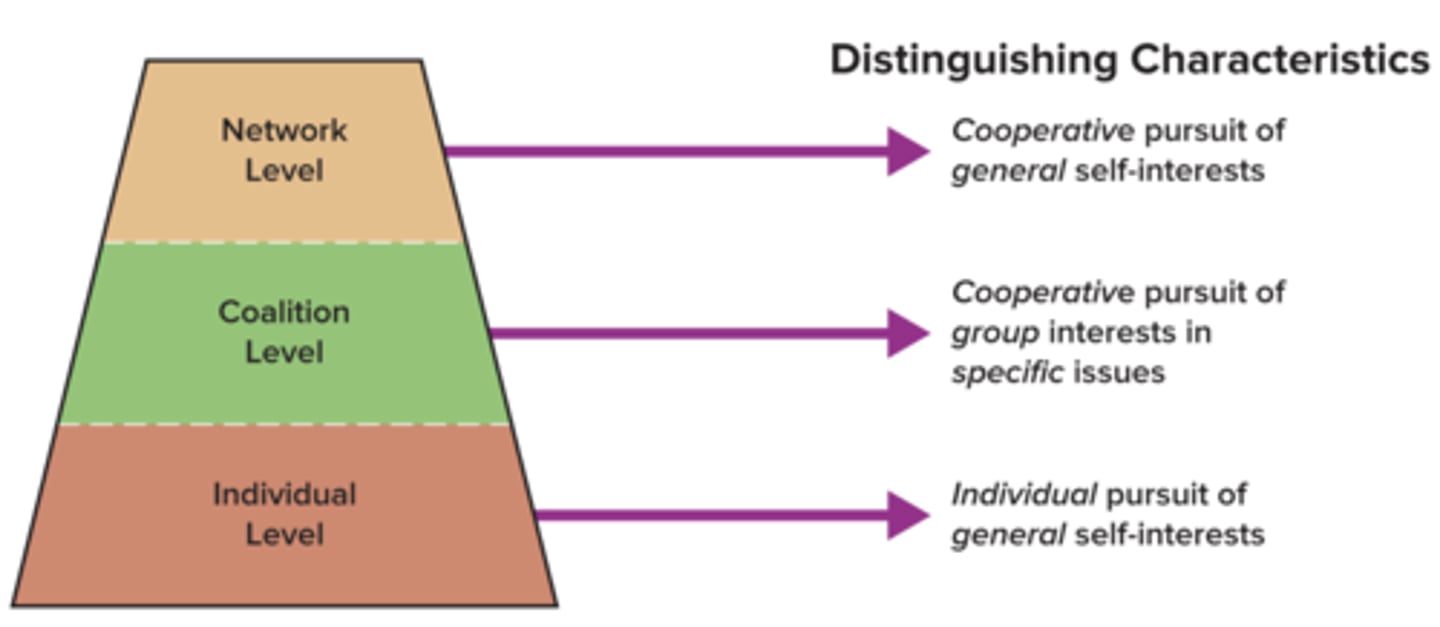
Levels of Political Action
.
Organizational Structures
8 Types:
Functional - Groups people according to the business functions they perform, for example, manufacturing, marketing, and finance.
Divisional - Segregates employees into organization groups based on industries, products or services, customers or clients, or geographic regions.
Matrix - Combines a vertical structure with an equally strong horizontal overlay. Blends functional and divisional.
Horizontal (Team Based) - A structure in which teams or work groups, either temporary or permanent, are created to improve collaboration and work on common projects.
Hollow - Designed around a central core of key functions and outsources other functions to outside companies or individuals who can do them cheaper or faster.
Modular - One in which the company assembles product parts, components, or modules provided by external contractors.
Virtual - One whose members are geographically apart, usually working with e-mail and other forms of technology, but that generally appears to customers as a single, unified organization with a real physical location.
Open - Organization relies heavily on external partners, networks, or independent contractors to deliver services or create value. Boundaries are more flexible than in traditional companies.
Power Sharing and Empowerment
What is empowerment?
• Efforts to enhance employee performance, well-being, and positive attitudes by:
• Giving employees greater influence.
• Use of centralized management practices. -- The sign of a good manager
Empowerment means:
• Structural: Job redesign to transfer of power to employees. • Policies, procedures, job responsibilities, team design
• Psychological: Through enhancing self-efficacy and intrinsic motivation.
Can you have control without fear? Can fear be a good thing?
Evidence Based Decision Making
The process of conscientiously using the best available data and evidence.
• An approach used when making, informing, or supporting a decision.
• Coupled with big data, EBDM can:
• Make information transparent and usable.
• Allow organizations to measure and collect all types of performance information to enhance productivity.
• Allow for more narrow segmentation of customers.
• Be used to develop new products.
Leadership Effectiveness: The Dark-Side Traits
Research has also shown that individuals who possess certain dark traits are more likely to emerge as leaders. These traits, however, are negatively associated with leadership effectiveness.
1. Narcissism. ◦ Self-centered, strong drive for personal power. ◦ More charismatic and passionate yet more likely to promote counterproductive behaviors from others.
2. Machiavellianism. ◦ Entails the use of manipulation, puts results ahead of principles. ◦ Linked to counterproductive behaviors.
3. Psychopathy. ◦ Lack of concern for others. ◦ Lack of remorse or guilt.
Biases
1. Confirmation bias. - Pertains to how we selectively gather information.
2. Overconfidence bias. - Results in overestimating our skills relative to those of others and overestimating the accuracy of our predictions.
3. Availability bias. - Cognitive shortcuts or biases that are used to simplify the process of making decisions
4. Representativeness bias. - Leads us to look for information that supports previously formed stereotypes
5. Anchoring bias. - Occurs when decision makers are influenced by the first information they receive about a decision, even if it is irrelevant.
6. Hindsight bias. - Occurs when knowledge of an outcome influences our belief about the probability that we could have predicted the outcome earlier.
7. Framing bias. - Relates to the manner in which a question is posed or framed. It leads us to change the way we interpret alternatives.
8. Escalation of commitment bias. - The tendency to hold to an ineffective course of action even when it is unlikely the bad situation can be reversed.
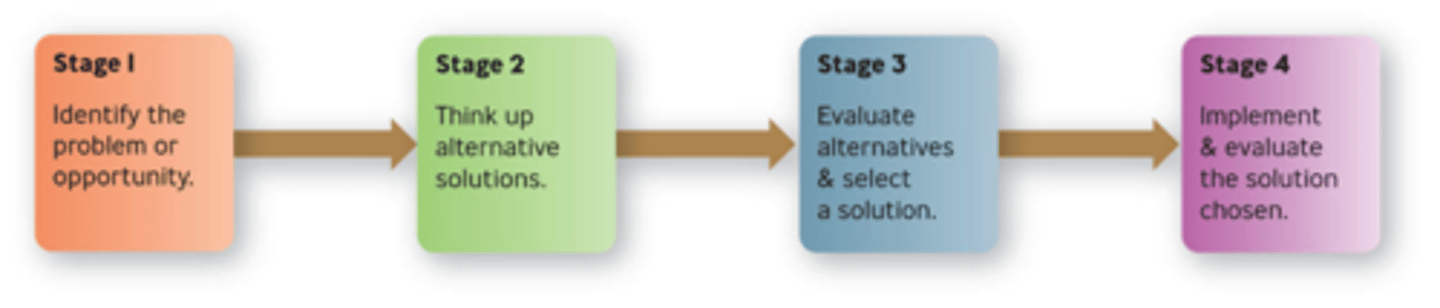
Rational Decision Making Model
Explains how managers should make decisions.
• Assumes managers are completely objective and possess complete information.
• Occurs in four stages.
P-O Fit (person - organization)
Make a list of your personal values, strengths, and weaknesses.
• Spend some time learning about the organization you plan to interview with.
• Compare your list of personal values, strengths, and weaknesses with those of the organization.
• Recruiters • 84% - Culture fit is one of the most important predictors • 90% - Skip over applicants if they don't align with culture
Influencing Others
Common influence tactics to affect changes in others. Soft tactics: • Rational persuasion. • Inspirational appeals. • Consultation. • Ingratiation. • Personal appeals.
• Hard tactics: • Exchange. • Coalition tactics. • Pressure. • Legitimizing tactics.
Relationship-Oriented Behaviors
Primary purpose is to enhance employees' skills and to create positive work relationships.
Empowerment: ◦ Creates perceptions of psychological empowerment in others. ◦ Reflects employees' beliefs that they have control over their work.
Consideration: ◦ Creating mutual respect or trust and focusing on a concern for group members' needs and desires ◦ Promotes social interaction
Task-Oriented Behaviors
Primary purpose—ensure that people, equipment, and other resources are used in an efficient way.
Transactional Leadership: ◦ Focuses on clarifying roles and requirements.◦ Uses contingent rewards and punishments.
Initiating Structure: ◦ Organizes group behavior to maximize productivity◦ Moderately strong positive relationship with leader effectiveness
Four Types of Organizational Culture
• Clan Culture: • An Employee-Focused Culture Valuing Flexibility, Not Stability
• Adhocracy Culture: • A Risk-Taking Culture Valuing Flexibility
• Market Culture: • A Competitive Culture Valuing Profits over Employee Satisfaction
• Hierarchy Culture: • A Structured Culture Valuing Stability and Effectiveness
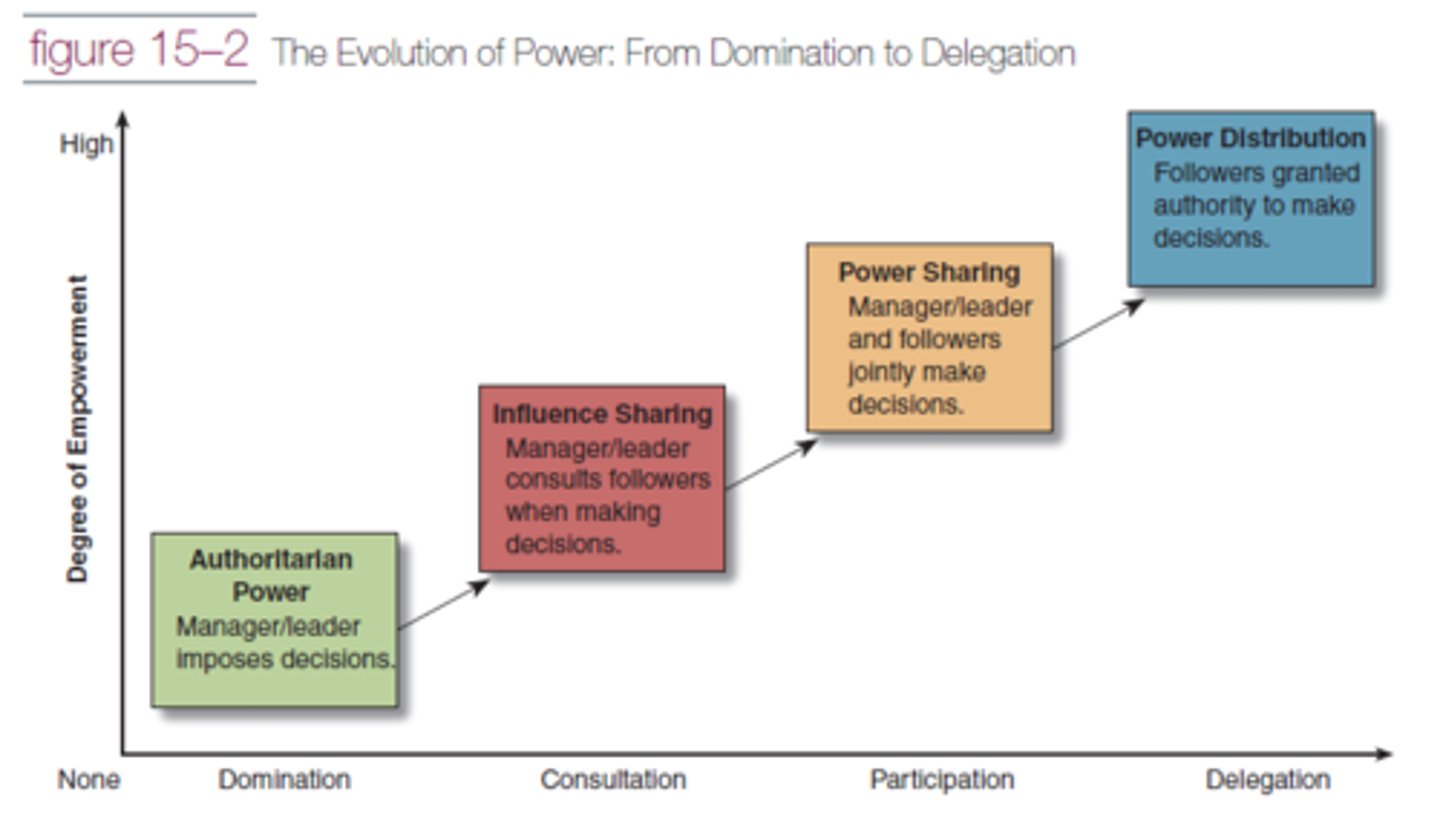
The Evolution of Power from Domination to Delegation
.
Mechanisms of Creating Culture Change
Formal statements:
Using formal statements of: - • Organizational philosophy. • Mission. • Vision. • Values. • Materials used for recruiting.
Represent visible artifacts. - • Design of physical space: • Physical spacing among people and buildings. • Location of office furniture. • For example, open office or flexspace.
Slogans, language, acronyms, and sayings. - • Often powerful forces for cultural change. • Easy to remember.
Role modeling, training, coaching. - • Structure training to provide an in-depth introduction about organizational values and basic underlying assumptions.
Explicit rewards, status symbols. - • Strong impact on employees due to highly visible and meaningful nature. • Strongest way to embed culture.
Stories, legends, or myths. - • Powerful way to send messages about values and behaviors that are desired.
Organizational activities and processes. - • Leaders pay attention to those activities they can measure and control • These can send messages to employees about acceptable norms
• Leader reactions to critical incidents. - • People learn and pay attention to emotions exhibited by leaders. • Positive emotions spread. • Negative emotions travel faster and further.
Leader-Member Exchange and Implications
Based on the assumption that leaders develop unique one-to-one relationships with each of the people reporting to them.
Focus on the quality of the relationship rather than behaviors or traits.
◦ Leaders with positive in-group exchanges (high LMX) get along better, have higher trust, respect, and liking.
◦ Leaders with out-group exchanges (low LMX) tend to have more formal relationships—such as pay for performance—lower levels of trust and respect.
Implications:
Managerial and personal implications:
Expectations. - ◦ Leaders are expected to establish high performance expectations.
Diversity. - ◦ Managers need to be careful that they don't create a homogenous work environment.
Initiative. - ◦ It is important to take positive actions to improve a poor LMX.