Introduction to Cellular Energetics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
air
Where does a dried plant get its mass from?
Solar Energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis Reaction
intermediates, enzymes
In the photosynthesis reaction, what is missing?
flows
What does energy do?
cycles
What does matter do?
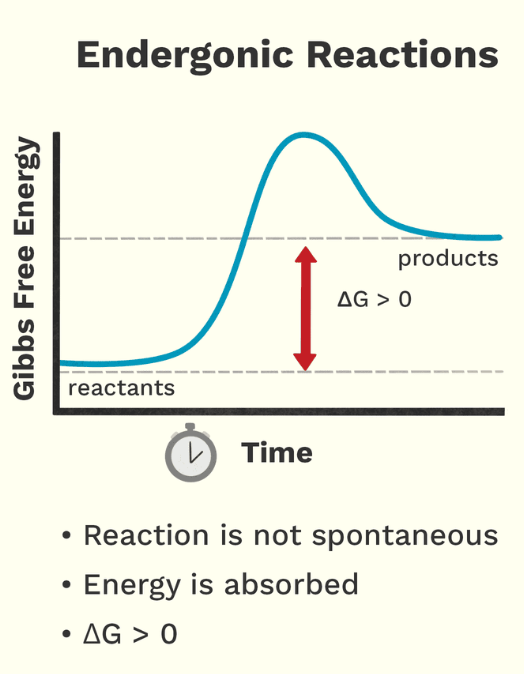
Endergonic
Absorption of energy; products have more free energy than reactants
anabolic
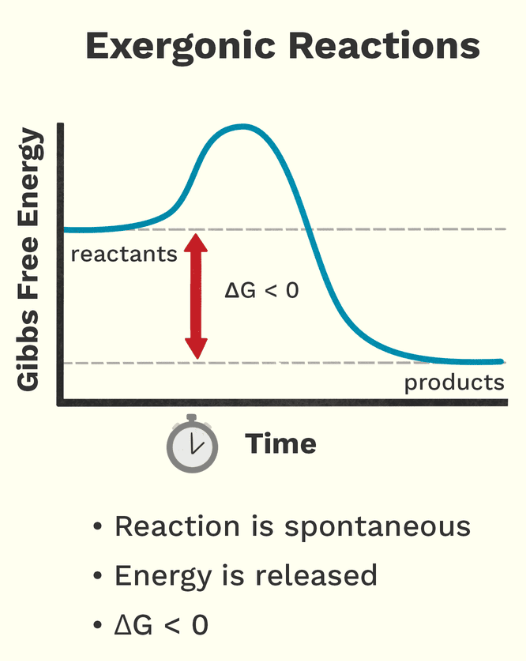
Exergonic
Release of energy; products have less free energy than reactants
catabolic
First Law of Thermodynamics
Matter and energy may be reorganized but not created nor destroyed; it is conserved
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe
Entropy
Measure of disorder or randomness
Synthesis, reproduction, movement, active transport, temperature regulation
What do we need energy for?
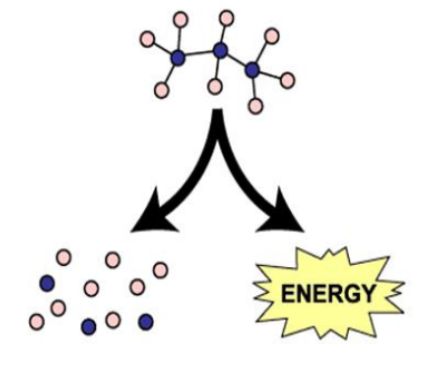
Catabolic Reaction
Break down molecule; release free energy
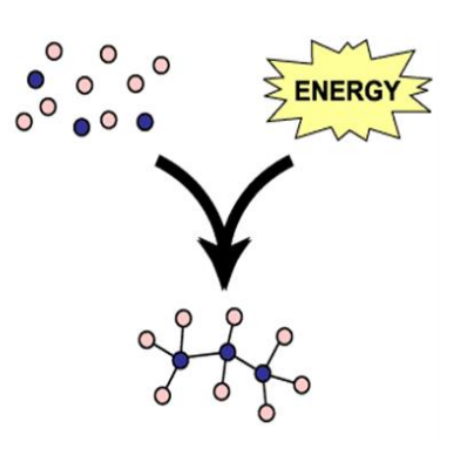
Anabolic Reaction
Build molecule; absorb free energy
Energy storage, growth
What happens with excess free energy?
loss of mass, death
What happens when insufficient free energy is acquired
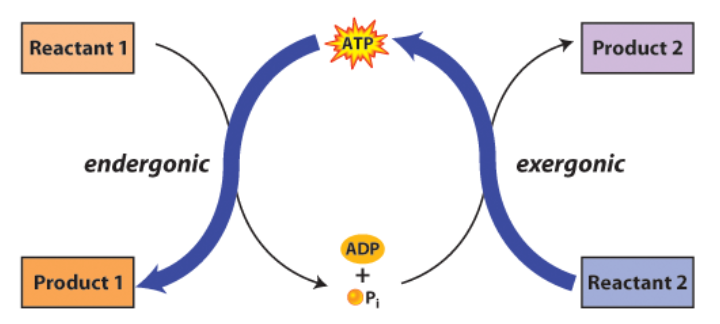
Coupled Reactions
Cellular processes that release energy may be coupled with processes that require energy