psychology 2610 final exam
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Dissociation
a mental process that causes a disconnect between a person's thoughts, feelings, memories, identity, and sense of self. can be a normal process, like daydreaming. However, it can also be a symptom of a mental health condition, often triggered by stress or trauma
Trauma
a mental health condition that occurs when a person experiences an event that overwhelms their ability to process the emotions involved
Dissociative Disorder
mental health conditions that involve a loss of connection between thoughts, memories, feelings, identity, behavior, and surroundings.
Localized Amnesia
a type of dissociative amnesia where a person cannot recall a specific event or period of time, usually related to a traumatic or stressful experienc
selective amnesia
a type of dissociative amnesia where a person forgets specific parts of their memories from a certain period, rather than losing all memory of that time
generalized amnesia
a rare condition where individuals lose memory for their entire life history, including their identity and personal information.
Psychoanalysis therapy
a form of psychotherapy based on Sigmund Freud's theories, which explore unconscious thoughts and feelings to understand their impact on conscious behavior and emotional well-being
Defence Mechanisms
unconscious psychological strategies used to protect the self from anxiety and internal conflict
interpersonality amnesia
the inability of one personality "alter" to recall events experienced by another alter in DID.
Five core components of dissociation disorder
Amnesia: This refers to a gap in memory, either of specific events, periods of time, or even personal identity.
Depersonalization: This involves a feeling of detachment from one's own body or mental processes, as if one is observing oneself from the outside.
Derealization: This is a sense that the external world is unreal, distorted, or dreamlike.
Identity Confusion: This is a state of uncertainty or conflict about one's own identity, including roles, beliefs, and personal history.
Identity Alteration: This involves a shift in one's sense of self, often with the emergence of distinct personality states or alters, sometimes referred to as "switching" in Dissociative Identity Disorder
Depersonalization
This involves a feeling of detachment from one's own body or mental processes, as if one is observing oneself from the outside.
Derealization
This is a sense that the external world is unreal, distorted, or dreamlike.
Identity Confusion
This is a state of uncertainty or conflict about one's own identity, including roles, beliefs, and personal history.
Identity Alteration
This involves a shift in one's sense of self, often with the emergence of distinct personality states or alters, sometimes referred to as "switching" in Dissociative Identity Disorder
dissociative trance disorder (DTD)
a condition where a person experiences a temporary alteration in consciousness and identity, often described as being controlled by an external force.
Traumatic events
experiences that severely threaten an individual's sense of safety or existence, often causing significant emotional and psychological distress. These events can range from single incidents like a car crash to long-term stressors like exposure to war or abuse.
Dissociation amnesia
is a mental health condition that causes abnormal memory loss as a defense mechanism against painful or disturbing events. It's not caused by physical injury or other medical conditions.
Dissociative Fugue
a temporary state where a person has memory loss (amnesia) and ends up in an unexpected place
dissociative identity disorder
a mental health condition characterized by the presence of two or more distinct identities, also known as "alters“
depersonalization-derealization disorder
a mental health condition that causes persistent feelings of detachment from oneself or one's surroundings. The primary symptom is a distorted perception of the body

Resilience
Is the ability to recover from or adjust easily to misfortune or change
post traumatic stress disorder
a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event involving death, injury, or sexual violence
Symptoms
Re-experiencing:
Flashbacks, nightmares, intrusive thoughts or memories, and intense distress when reminded of the trauma.
Avoidance:
Avoiding situations, activities, thoughts, or feelings that remind them of the trauma.
Negative Changes in Thinking and Mood:
Negative thoughts about oneself or the world, feelings of blame, guilt, anger, or shame, difficulty experiencing positive emotions, and detachment from others.
Increased Arousal and Reactivity:
Being easily startled, having trouble sleeping or concentrating, feeling irritable or angry, and engaging in reckless behavior.
4 major area of disturbance (PTSD)
Re-experiencing:
This involves intrusive and distressing memories, flashbacks, or nightmares related to the traumatic event. These can be triggered by reminders of the event and can cause intense emotional and physical reactions.
2. Avoidance:
Individuals with PTSD may actively avoid thoughts, feelings, or conversations associated with the trauma, as well as places, people, or situations that remind them of it. This avoidance can be a way to cope with the distress, but it can also limit their ability to engage in daily life.
3. Negative Alterations in Cognitions and Mood:
This cluster of symptoms includes persistent negative beliefs and feelings about oneself or the world, such as feeling detached or estranged from others, persistent negative emotional states (fear, horror, anger, guilt, or shame), and difficulty experiencing positive emotions.
4. Alterations in Arousal and Reactivity:
This refers to changes in a person's reactivity to stimuli, including being easily startled, having difficulty concentrating, experiencing sleep disturbances (insomnia or nightmares), feeling irritable or having angry outbursts, and engaging in reckless or self-destructive behavior.
Soldier Heart
A term used to describe ptsd symptoms like rapid heart rate, trouble breathing after the war.
complex ptsd
There is no clear definition of it, it not even in the DMS5. It PTSD with three extra elements,
Difficult with emotional regulation
Interpersonal problems
Poor sense of self worth
also known as complex trauma
Post traumatic growth
the positive psychological change that some individuals experience following a traumatic event or life crisis
Example, Individuals may report a deeper appreciation for life, and a greater sense of purpose after experiencing trauma
acute stress disorder
a short-term mental health condition that can develop after a traumatic event, lasting less than one month. Symptoms include anxiety, increased arousal, and dissociative symptoms like disorientation and reduced awareness
Psychosomatic
psychological factors like stress or anxiety affect physical symptoms or conditions
Example: Stress can trigger or worsen headaches, stomach problems, and muscle tension
Somatopsychic
physical illness or condition can cause or exacerbate mental health issue
Example: A person with a chronic illness like cancer might experience increased anxiety or depression due to the physical limitations and emotional distress caused by the illness
franz alexander
key figure in psychosomatic medicine, explored the profound connection between the mind and body, particularly how emotions influence physical health.
Coined the term organ neurosis
The sick role
Some people respond to stressful events by entering the sick role.
Behaviourist explanation: for rewards
Cognitive explanation: interpret bodily sensations
Factitious disorder
rare mental illness where a person intentionally fabricates or exaggerates symptoms of illness or injury
Obsessive compulsive disorder
mental disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and feels the need to perform certain routines repeatedly to relieve the distress caused by the obsession, to the extent where it impairs general function.
Obsessions: thoughts are often disturbing, distressing, and difficult to control
Compulsions: repetitive behaviors or mental acts that individuals feel driven to perform in response to an obsession.
4 types of obsession and compulsion
Hoarding: fear of throwing things away
Cleaning: Obsessed with germs, cleaning
Symmetry/just right: need things to be symmetrical, in the right place
Taboo/forbidden thoughts: fear, urge to harm others and self
thought action fusion ocd
The belief that thinking about something bad will increase the likelihood of that event happening or that actually having the thought is the equivalent to actually committing the action
Tourettic OCD (TOCD)
Also called Pandas
a condition where individuals experience both obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and tic disorder
body dysmorphic disorder
a mental health condition where a person spends a lot of time worrying about flaws in their appearance
hoarding disorder
a mental illness that causes people to accumulate excessive amounts of items, often in a chaotic manner, and have difficulty throwing them away
Difficulty discarding possessions
Excessive acquisition of items
Compromised living spaces
Mood disorder
category of mental illnesses that cause intense and persistent changes in mood, energy, and behavior.
Identity Alteration
persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest in activities.
Bipolar I disorder
a mental health condition characterized by extreme shifts in mood, energy, activity levels, and the ability to think clearly. It is defined by the presence of at least one manic episode, which may or may not be accompanied by depressive or hypomanic episode
Bipolar II disorder
a mental illness that causes unusual shifts in mood, energy, and activity levels, with cycles between depression and hypomania
the "up" moods never reach full-blown mania. The less-intense elevated moods in bipolar II disorder are called hypomanic episodes, or hypomania.
has had at least one hypomanic episode in their life. Most people with _______ have episodes of depression more often.
persistent depressive disorder
a continuous, long-term form of depression. You may feel sad and empty, lose interest in daily activities and have trouble getting things done. Used to be called dysthymia
Anhedonia
the inability to experience pleasure or joy, and is a common symptom of depression and other mental health conditions.
Mania
a psychiatric condition characterized by a drastic change in a person's usual behavior and mood, lasting at least a week
hypomania
psychiatric condition that involves a persistent and abnormal elevation of mood, energy, or activity levels. It's a less severe form of mania
Psychosis
A state where a person experiences a significant loss of contact with reality, symptoms like’s hallucinations, delusions and disorganization thoughts
schizophrenia
Is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and behavior, and flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and rarely resolve. 6months
Prevalence
how common something is within a specific population at a particular point in time or during a specific period
emil kraepelin and dementia precox
Used the term dementia precox to refer to onset of symptoms that occur before adulthood
dementia precox
a group of clinically heterogeneous paranoid and hallucinatory psychoses that tend to become chronic
Catatonic: abnormal movements, withdrawal
Hebephrenia: disorganized behavior and speech
Paranoia: Delusions
Eugen Bleuler
Coined the term schizophrenic. (meaning "split mind") to describe the separation of personality, thinking, memory, and perception
Spilt mind
Is from the Greek words, skizen (spilt) and phren (mind)
Delusion of grandeur
false beliefs that someone has exceptional wealth, power, or identity
delusion of persecution
someone has an irrational belief that they are being targeted or harmed by others.
cotard's syndrome
delusional belief that they are deceased, do not exist, are putrefying, or have lost their blood or internal organs.
capgras syndrome
false belief that a close person has been replaced by an identical imposter.
5 a's of schizophrenia
Affective Flattening:
This refers to a reduction or absence of emotional expression, including facial expressions, eye contact, gestures, and variations in voice tone.
Alogia:
This describes a reduction in the amount and quality of speech, often characterized by impoverished and vague speech.
Anhedonia:
This involves a diminished capacity to experience pleasure and joy, impacting both the ability to anticipate and enjoy pleasurable activities.
Asociality:
This refers to a lack of interest in social interactions and relationships, leading to social withdrawal and difficulties maintaining social connections.
Avolition:
This describes a lack of motivation and initiative, making it difficult to engage in purposeful activities and complete tasks.
Affective Flattening
This refers to a reduction or absence of emotional expression, including facial expressions, eye contact, gestures, and variations in voice tone.
Alogia
This describes a reduction in the amount and quality of speech, often characterized by impoverished and vague speech.
Asociality
This refers to a lack of interest in social interactions and relationships, leading to social withdrawal and difficulties maintaining social connections.
Avolition
This describes a lack of motivation and initiative, making it difficult to engage in purposeful activities and complete tasks
schizophreniform disorder
a mental illness characterized by symptoms similar to schizophrenia, but lasting for a shorter duration, specifically at least one month but less than six month
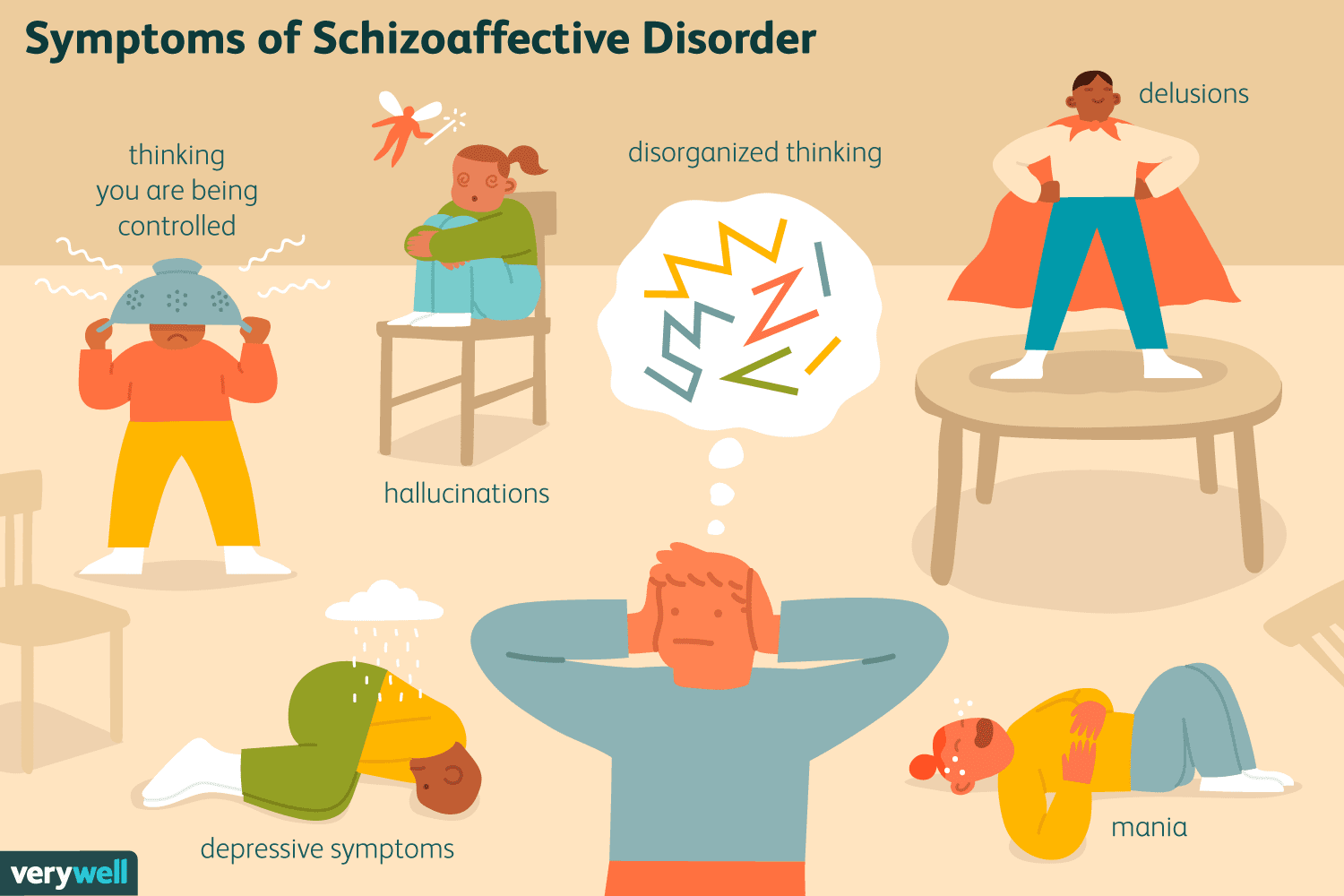
schizoaffective disorder
a chronic mental illness that involves a combination of schizophrenia and mood disorder symptom
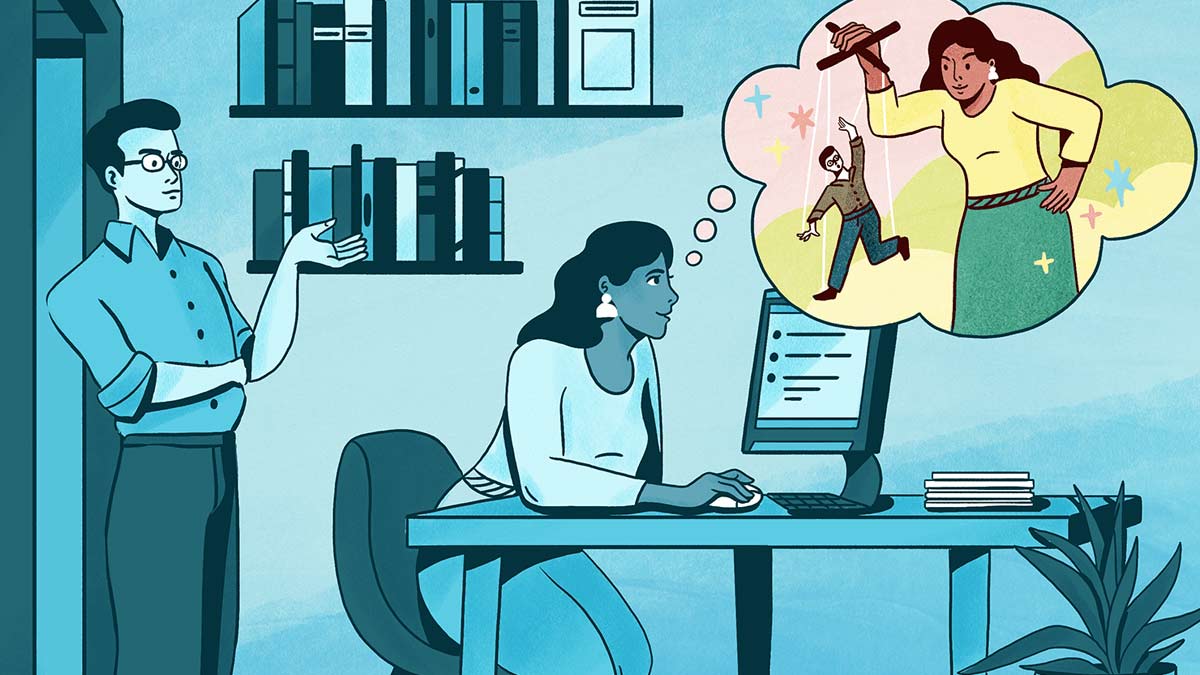

erotomanic (Delusional disorder type)
The individual believes that another person, usually someone of higher status, is in love with them
Grandiose (Delusional disorder)
The individual has an inflated sense of self-worth, power, knowledge, or identity, believing they have a great talent or have made an important discovery.
Jealous (delusional disorder types)
The individual is convinced that their spouse or sexual partner is unfaithful, despite lacking evidenc
Persecutory (delusional disorder types)
The individual believes they are being conspired against, watched, or harassed.
share psychotic disorder
a healthy person starts to take on the delusions of someone who has a psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia.
attenuated psychotic syndrome
hallucinations or delusions, but at a sub-threshold level, meaning they are not severe enough to meet the criteria for a full psychotic disorder.
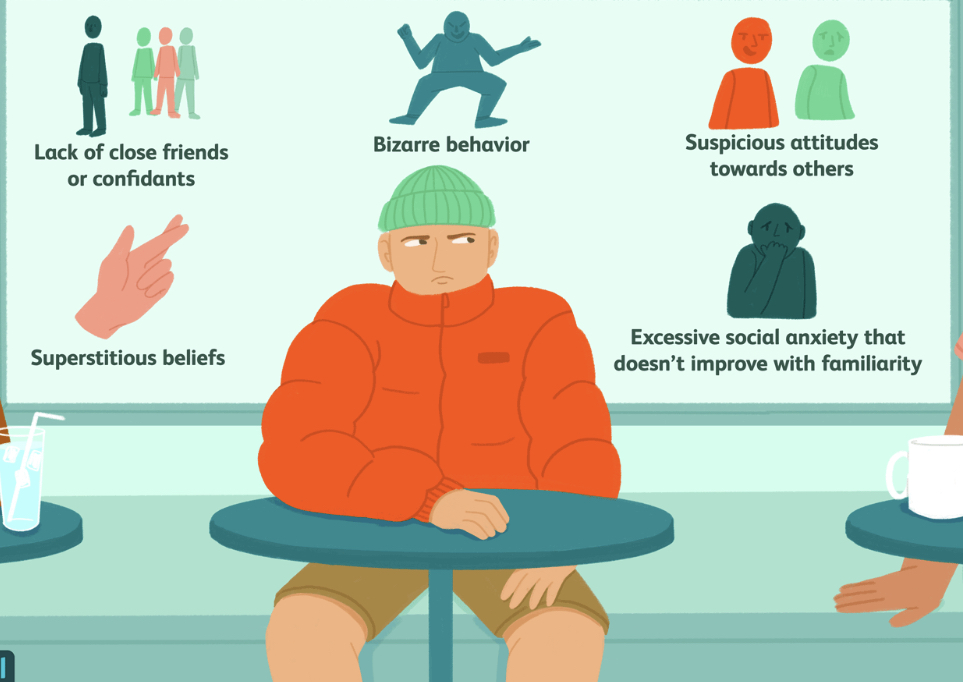
schizotypal personality disorder
Be a loner and lack close friends and other relationships outside of the immediate family. Have flat emotions or have emotional responses that are limited or not proper socially
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
class of antidepressants primarily used to treat depression and anxiety disorders. They work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, which is thought to improve mood and other functions.
They don’t add or give serotonin
Psychosurgery
surgical procedures performed on the brain to alleviate symptoms of mental illness.
Cingulotomy
a type of psychosurgery
targets the anterior cingulate cortex, a region of the brain involved in emotion, learning, and memory
deep brain stimulation
a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes into specific areas of the brain to deliver electrical impulses
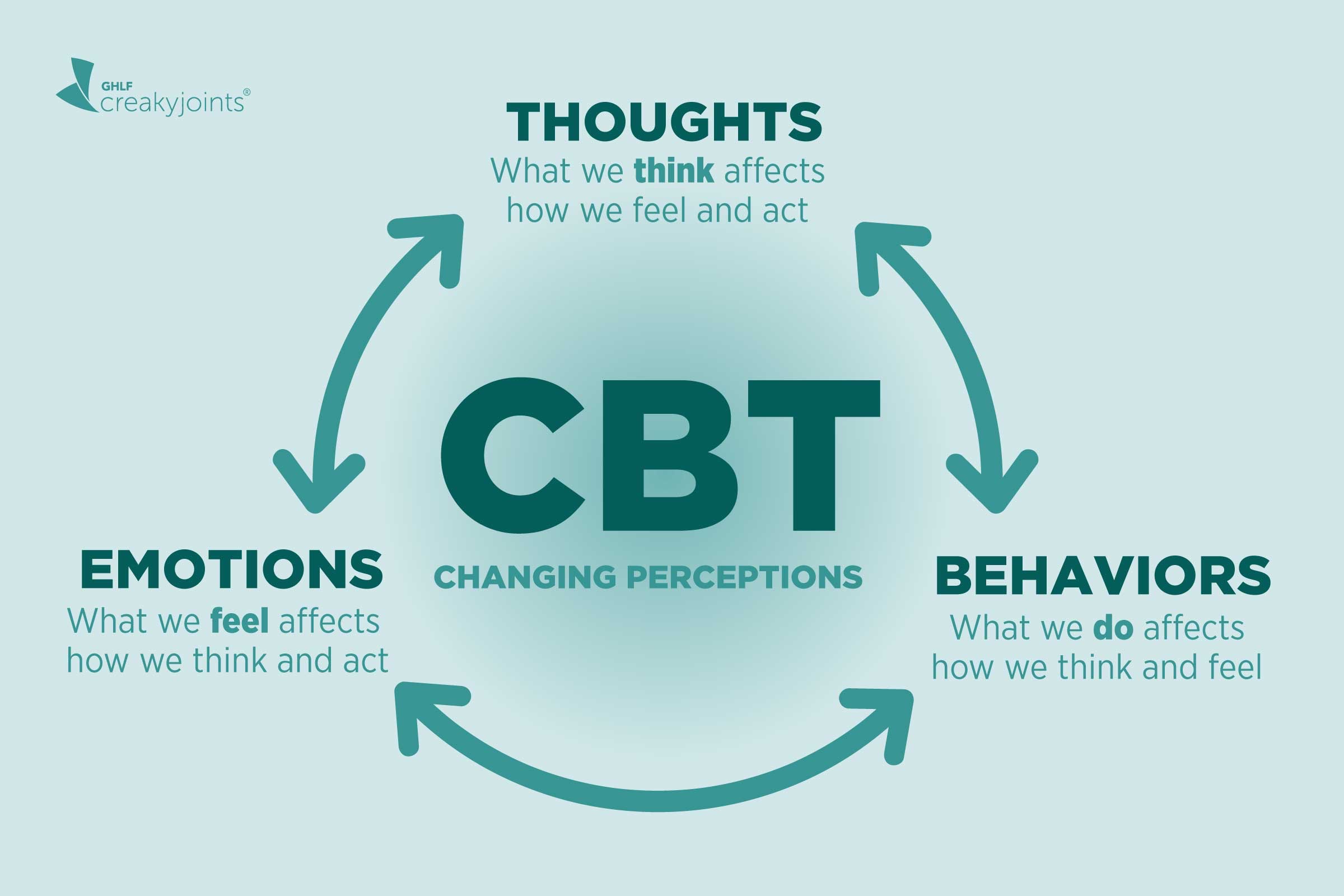
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
This type of talk therapy is also called psychotherapy. helps you become aware of thinking patterns that may be creating issues in your life. Looking at the relationship between your thoughts, feelings and behaviors helps you view challenging situations more clearly and respond to them in a more effective way.
dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
type of talk therapy for people who experience emotions very intensely. It’s a common therapy for people with borderline personality disorder
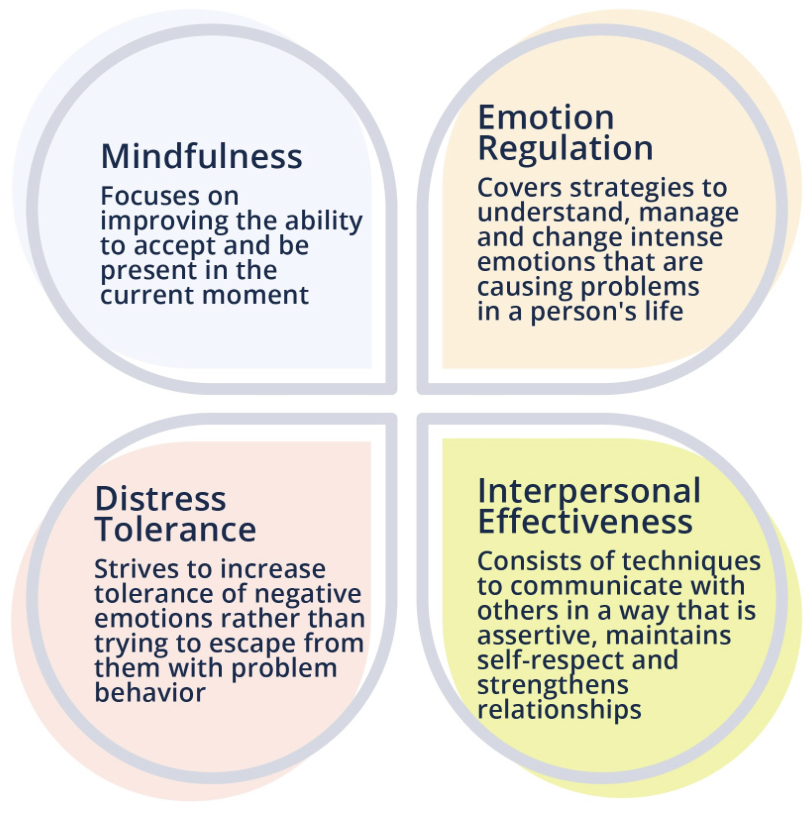
four pillars of dbt
Mindfulness:
This pillar emphasizes being fully present and aware of the current moment without judgment. It's about observing thoughts and feelings as they arise, without getting carried away by them.
Distress Tolerance:
This skill set focuses on coping with intense emotions and painful situations without making them worse through impulsive or destructive behaviors. It involves learning to tolerate and accept difficult moments.
Emotion Regulation:
This pillar teaches individuals how to identify, understand, and manage their emotions effectively. It includes strategies for changing unwanted emotions and increasing positive emotional experiences.
Interpersonal Effectiveness:
This module focuses on improving communication and relationship skills. It teaches individuals how to express their needs and boundaries effectively, while also maintaining respect for themselves and others.
cognitive defusion
a technique used in therapies like Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) to help individuals distance themselves from their thoughts and feelings, rather than being controlled by them
supportive therapy
therapeutic approach that focuses on building a patient's self-esteem, coping skills, and emotional regulation, while addressing immediate needs and concerns
eclectic therapy
a flexible and personalized approach to psychotherapy where therapists integrate techniques from various therapeutic approaches to best suit the unique needs of each client
psychodynamic therapy
a type of talk therapy that explores unconscious processes and past experiences to understand and address current emotional and behavioral patterns
a form of talk therapy rooted in psychoanalytic theory
Types of therapies
Insights therapies
Behaviour therapies
Biomedical therapies
Insight therapies
category of psychotherapies that emphasize a client's gaining awareness and understanding of the underlying causes of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, particularly in relation to past experiences
The goal is to foster self-awareness and facilitate positive changes in thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors by understanding the origins of current problems.
Ego Strength
an individual's capacity to effectively manage their impulses, adapt to challenging situations
transference
psychological phenomenon where individuals redirect feelings and emotions, often from past relationships, onto a present-day person or situation
Example: A patient developing romantic feelings for their therapist, which could be a projection of past romantic feelings or desires.
countertransference
therapist's emotional reaction to a client, which can be influenced by the therapist's own unconscious processes and personal experiences. It's essentially the therapist's version of transference
Example: A therapist might feel overly protective of a client who reminds them of a vulnerable family member
conditions of worth (carl rogers)
Incongruence: there is no overlap in ideal and perceived self
Congruence: there is an overlap in ideal and perceived self
Carl Rogers’ client centered therapy
a humanistic approach to psychotherapy that emphasizes the client's unique experience and potential for growth. It focuses on creating a supportive, non-judgmental environment where clients can explore their thoughts and feelings without fear of evaluation.
Aaron beck’s cognitive therapy
a type of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), is a psychotherapeutic approach that focuses on identifying and changing unhelpful or inaccurate thought patterns. It emphasizes the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, aiming to help individuals develop more adaptive thinking and behavior patterns to overcome difficulties
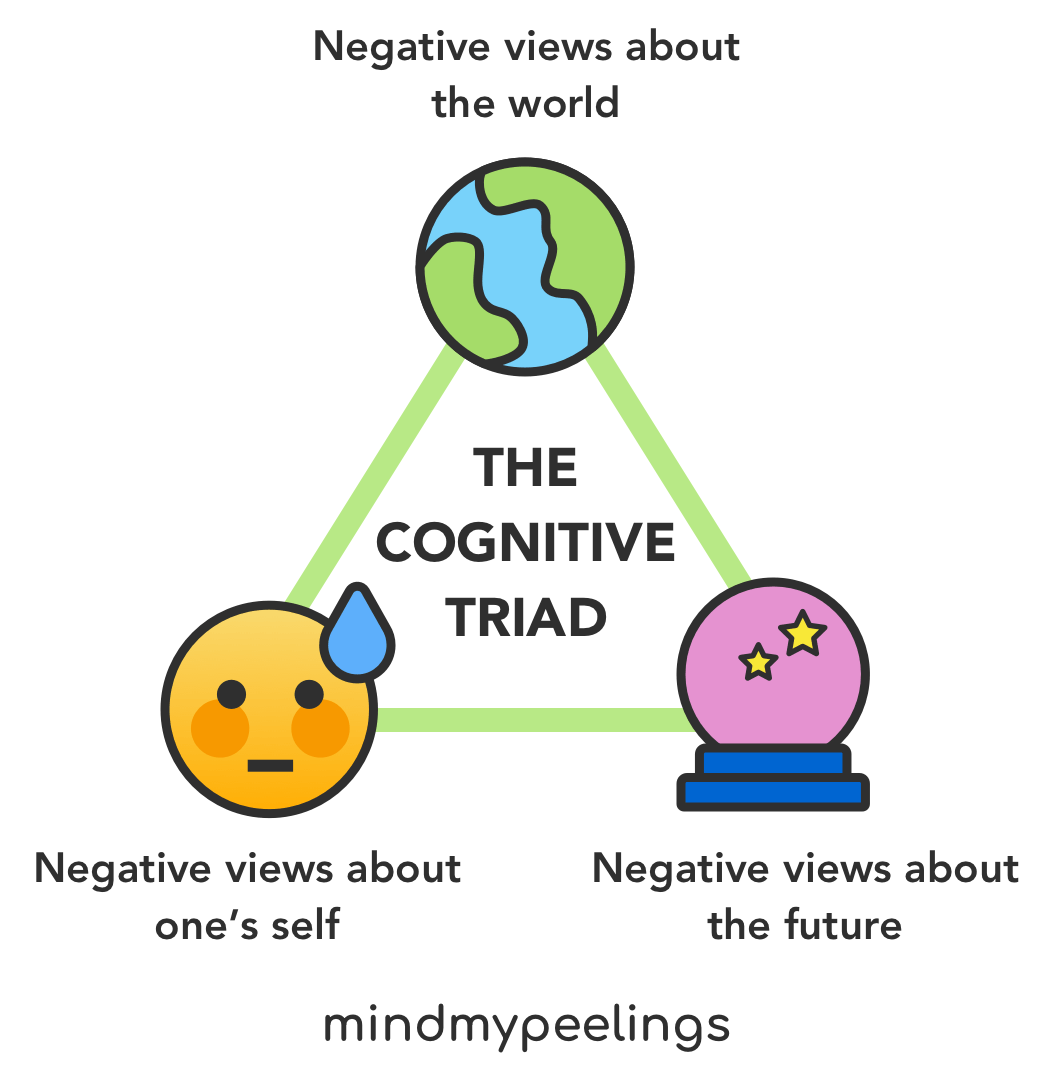
Albert Ellis’ rational emotive therapy (RET)
focuses on identifying and changing irrational beliefs that cause emotional distress and self-defeating behaviors. Uses the ABC model
understand how events (A) lead to beliefs (B), which then influence consequences (C) such as emotions and behaviors. For example, failing a test (A) might lead to the belief that one is a failure (B), resulting in feelings of sadness and discouragement (C)
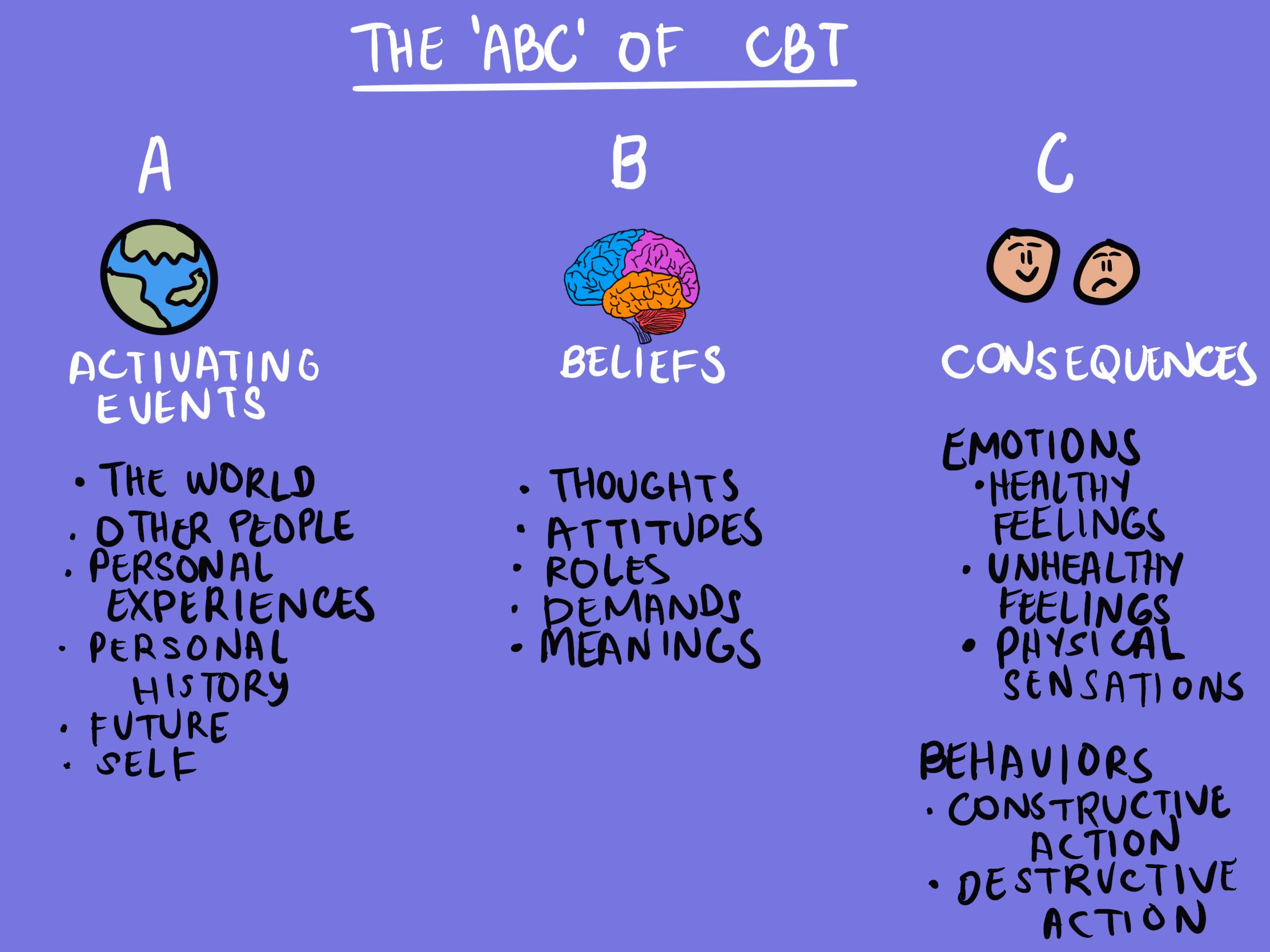
The ABC Model (CBT)
A (Activating Event):
This refers to the situation or event that triggers a thought or feeling. It can be a negative event, a challenging situation, or even a neutral event that you interpret in a specific way.
B (Belief):
This is the thought, attitude, or belief that you have about the activating event. These beliefs can be rational or irrational, and they often influence your emotional and behavioral responses.
C (Consequences):
This refers to the emotional and behavioral responses that result from your belief about the activating event. These consequences can be positive or negative, and they can include feelings, actions, and thoughts.

Inappropriate affect
This refers to an emotional expression that doesn't match the situation (e.g., laughing while talking about something sad). It’s more about emotional expression, not speech or thought processes.
Cognitive slippage
This term describes loose, illogical, or tangential thinking, which can manifest as disorganized speech. It’s an older but relevant term in describing thought disorder, especially in schizophrenia.