H2 Biology - Organelles and Cellular Structures
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Under the Singapore-Cambridge GCE A-Level Syllabus
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are the widths/diameters/lengths of the nucleus, lysosome, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and ribosome?
Nucleus: 5-20 μm in diameter
Lysosome: 0.2-0.5 μm in diameter
Mitochondrion: 0.5-1.5 μm in width, 3-10 μm in length
Chloroplast: 5-10μm in length
Ribosome: 20nm in diameter
State all 3 diagnostic features of the nucleus.
Enclosed by nuclear envelope
Contains chromatin
Contains nucleolus
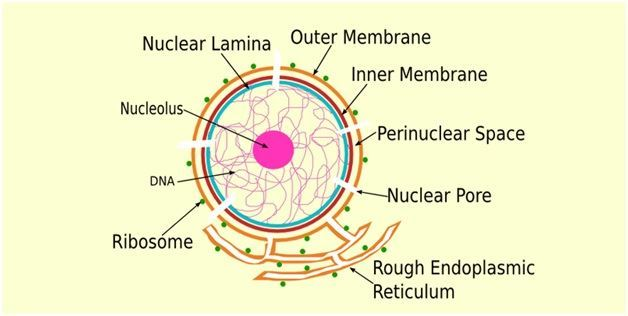
Describe the 5 structures.of the nuclear envelope.
Double membrane separated by perinuclear space
Outer membrane continuous with endoplasmic reticulum
Perforated by nuclear pores
Each nuclear pore is lined with proteins to form nuclear pore complex
Encloses nucleoplasm
Describe the two types of chromatin.
Heterochromatin:
more tightly packed
electron-dense, appears as coarse granules under EM
often transcriptionally inactive
Euchromatin:
less compact
not electron-dense
often transcriptionally active
Describe the 4 structures of the nucleolus.
Dense
Spherical
Made up of large loops of DNA coming from a number of chromosomes
Loops contain genes coding for rRNA
State the 3 functions of the nucleus.
Stores hereditary material (DNA)
Nuclear envelope protects DNA from metabolically active cytoplasm
Site for transcription to synthesise mRNA and rRNA
State the 2 functions of the nucleolus.
Site of rRNA synthesis
Site of assembly of ribosomal subunits from proteins and rRNA
State the function of nuclear pores.
Regulates movement of substances between nucleus and cytoplasm, thus controlling processes in the cell
State the shape of the nucleus.
Spherical to ovoid
Describe the 4 structures of the endoplasmic reticulum.
extensive network of folded membranes forming sheets and tubules called cisternae
ER membrane separates the ER lumen from the cytosol
ER membrane is continuous with outer nuclear envelope
ER lumen is continuous with perinuclear space
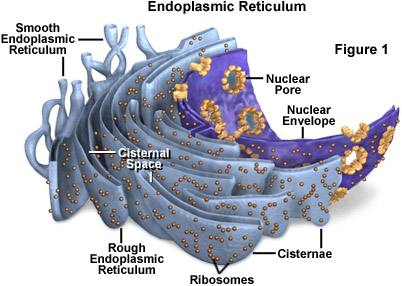
Describe the 2 structures of the RER.
continuous network of membranous sheets (cisternae)
outer surface of membrane studded with ribosomes
State the 2 functions of the RER.
Site for synthesis of proteins destined for secretion or incorporation into membranes
Facilitation of folding of polypeptide chain
Describe the function of the RER as a site for protein synthesis.
RER is the site for synthesis of proteins destined for secretion or incorporation into membranes
these proteins are transported to other compartments in the cell via transport vesicles that bud off from RER membrane
Describe the function of the RER in facilitating the folding of polypeptide chain.
polypeptide chain grows from bound ribosome
it enters ER lumen through a pore in ER membrane
it folds into its specific 3-dimensional shape as it enters, guided by ER proteins and enzymes
Describe the 2 structures of the SER.
network of membranous tubules (cisternae)
lacks ribosomes
State the 2 functions of the SER.
synthesis of lipids
detoxification of drugs and poisons
Describe how detoxification is carried out in SER.
hydroxyl groups are added to drugs and poisons
Describe the 5 structures of the Golgi Apparatus.
consists of stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs (cisternae)
has distinct structural polarity
cis face, nearest to the ER receives transport vesicles containing newly synthesised proteins and lipids from the ER
trans face, nearest to the plasma membrane ships vesicles containing mature proteins and lipids to other parts of the cell
contains golgi vesicles that transfer material between cisternae as well as between GA and other parts of the cell
State and describe the 6 functions of the GA.
further modifies, sorts and packages products of the ER into vesicles
vesicles transport products to other parts of the cell or releases them out of the cell.
synthesis of secretory polysaccharides
synthesis of lysosomes via budding from trans face
glycosylation of proteins
phosphorylation of proteins
Compare Golgi vesicles to transport vesicles to secretory vesicles.
Golgi vesicles transport products between GA cisternae, transport vesicles transport products from one cellular compartment to another, secretory vesicles transport products to the cell surface membrane.
State the 4 diagnostic features of lysosomes.
Spherical sac bound by single membrane
Uniformly granular electron-dense appearance under EM
Contains lysosomal enzymes that digest various macromolecules
Acidic internal pH of 4-5 at optimum acidic pH of lysosomal enzymes
State the 3 functions of lysosomes.
Digestion by endocytosis
Autophagy
Autolysis
Describe the function of lysosomes which is digestion by endocytosis.
lysosomes fuse with vacuoles formed from endocytosis
lysosomal enzymes release into vacuole and digest its material inside, which could be food or harmful substances/organisms
Describe the function of lysosomes which is autophagy.
unwanted structures are enclosed by membrane from the ER
structure fuses with lysosome to form autophagic vacuole
lysosomal enzymes hydrolyse ingested material and return products to cytosol for reuse
Describe the function of lysosomes which is autolysis.
many lysosomes in the cell release their contents together, destroying the cell
State the shape of mitochondria.
Cylindrical or rod shaped
Describe the 3 diagnostic features of the mitochondria.
Wall comprises 2 membranes separated by intermembrane space. Outer membrane is smooth, inner membrane is highly convoluted with numerous infoldings called cristae
Mitochondrial matrix, interior of mitochondria, contains 70S ribosomes, circular DNA and various enzymes
Mitochondrial space divided into intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
Explain the function of the mitochondria.
Function: Main site of ATP production during aerobic respiration.
Explanation:
Matrix contains enzymes of Krebs cycle.
Cristae maximise surface area to accommodate the proteins and enzymes responsible for ATP synthesis.
State the shape of chloroplasts.
Disc-shaped
Describe the 3 diagnostic features of chloroplasts.
Enclosed by double membrane called the chloroplast envelope, where the two membranes are separated by intermembrane space.
In stroma is another membranous system in the form of flattened, interconnected disc-like sacs called thylakoids.
Membranes divide chloroplast space into intermembrane space, stroma and thylakoid space.
State the function of chloroplasts.
Site of photosynthesis
State the shape of ribosomes.
Small, spherical and dense.
Describe the 3 diagnostic features of ribosomes.
Comprises rRNA and proteins.
80S eukaryotic ribosome consists of small 40S and large 60s ribosomal subunits.
Located in the RER as bound ribosomes, cytosol as free ribosomes, mitochondrial matrix and chloroplast stroma.
State the 2 functions of ribosomes.
Site of polypeptide synthesis.
Facilitates translation of mRNA base sequence into specific amino acid sequence of polypeptide chain.
Define the cytoskeleton.
Cytoskeleton is a dynamic network of fibrous protein structures throughout the cytoplasm.
Describe the diagnostic feature of microtubules.
Walls are composed of globular proteins called tubulin.
Describe the 5 functions of microtubules.
Maintain cell shape.
Serve as tracks along which organelles and materials move within cells.
Forms spindle fibres which separate chromosomes during cell division.
Makes up centrioles which function as MTOCs in lower plants and animals.
Major structural components of cilia and flagella.
Describe the 3 diagnostic features of centrioles.
Centrosome, near the nucleus, comprises 2 centrioles
Exist as pair of rod-like structure at right angles to each other.
Comprises 9 triplets of microtubules arranged in a ring.
Explain the function of centrioles.
During prometaphase, centrioles produce system of microtubules called spindle fibres that radiate towards metaphase plate of cell.
Spindle fibres attach to kinetochore proteins found in centromere of chromosomes.
What components of the cell does the endomembrane system comprise? State in order of flow from nucleus to CSM.
Outer nuclear membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome and vacuoles, cell surface membrane.