Pediatrics
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
feeding volume in the first day of life (DOL) should be _______.
5-10 ml
feeding volume in the second day of life (DOL) should be ___________.
10-20 ml
after the 2nd DOL, what should the feeding volume be?
30+ ml
________ can contribute to overfeeding
bottles
don't change formula in the first ________ of life
2 wks
which milk protein is better:
whey or casein?
whey
nutritive sucking
sucking (& swallowing) to obtain nutrition
non-nutritive sucking
sucking for self-soothing or stimulation of the reflex
- SIDS protection
- helps NAS (neonatal abstinence syndrome) infants
- difficult on mother's nipples
what is neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS)?
a group of problems that occur in a newborn who was exposed to addictive illegal or prescription drugs while in the mother's womb
**don't have to know!
kilocalories (calories) for kilogram (kg) per day [KKD] =

breast milk & standardly mixed formula contains ____ kcal/oz
20 kcal/oz
5 ml =
1 tsp
15 ml =
1 Tbsp
30 ml =
1 oz
recommended KKD for a premie =
120 KKD
recommended KKD for a 0-6 month old infant =
110 KKD
recommended KKD for a 6-12 month old infant =
90 KKD
a mother brings in her 1 month old infant that weighs 3570 gm.
she reports feeding 1.5 oz every 3 hrs.
she is mixing the formula correctly.
is this child getting enough sufficient nutrition?
KKD = (360 ml/3.57 kg)(20/30) = 67 kcal/kg/day
0-6 mo should be getting 110 KKD, so NO!
a mother brings in her 1 month old infant that weighs 3570 gm.
she reports feeding 1.5 oz every 3 hrs.
she is mixing the formula correctly.
how much formula should she offer her baby at each feeding for sufficient nutrition?
110 KKD = (X/3.57 kg)(20/30) = 590 ml/day
2.5 oz/feed
newborns pass meconium stools for the first ______ days
~ 2 to 3
infantile stools
"seedy" orange, yellow
bottle fed babies should pass stool every ______ days
3-5
breast fed babies may pass stool (up to) every ______ days
7-10 days
characteristics of happy babies:
- eat regularly, don't skip meals
- no emesis
- sleep w/o early awakenings
- soft belly
- easily consoled
what is successful stooling dependent on?
relaxation of external sphincter muscles
what patient education can you provide to help a parent tell that their child is NOT constipated?
regardless of how dramatic the baby seems when trying to pass stool
- as long as what is coming out is SOFT, the baby is NOT constipated
milk protein intolerance
loose to watery stools w/ bloody flecks
- poor weight gain
- dehydration
- irritable
- difficult to console
is milk protein intolerance cured by switching to soy?
NO!
- bc it contains the same milk proteins
- use formula w/ partially broken down proteins or exclusively amino acid formula
1 multiple choice option
why should neonatal jaundice be taken so seriously?
can cause kernicterus
what is kernicterus?
brain injury due to high neonatal (unconjugated) bilirubin levels
causes of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns =
- ↑ bilirubin production
- ↓ bilirubin clearance
causes of ↑ bilirubin production in newborns (listed in order from most to least common):
- hemolytic disease (immune mediated or heritable)
- polycythemia
- extravasation of blood (cephalohematoma, intraventricular hemorrhage)
- sepsis w/ DIC
causes of ↓ bilirubin clearance in newborns (listed in order from most to least common):
- prematurity
- increased enterohepatic circulation (breast milk jaundice, pyloric stenosis, small or large bowel obstruction)
- inborn errors of metabolism (Gilbert Syndrome, Crigler-Najjar Syndrome)
- metabolic disorder (hypothyroidism, hypopituitarism)
physiologic jaundice
normal, occurs after 24 hrs old
- never high enough to require phototherapy
pathologic jaundice (hyperbilirubinemia)
can occur before 24 hrs old
- multiple causes
- requires phototherapy
breasting feeding jaundice
can occur during days 2-7 of life
- due to: dehydration, poor feeding, poor output
breast milk jaundice
can occur during days 6-14 of life
- due to: GI tract immaturity or limited enzyme production
is all jaundice the same?
NO
1 multiple choice option
when should you get an immediate biliary tract ultrasound?
if direct bilirubin is > 20% of the total
- concerned for biliary atresia
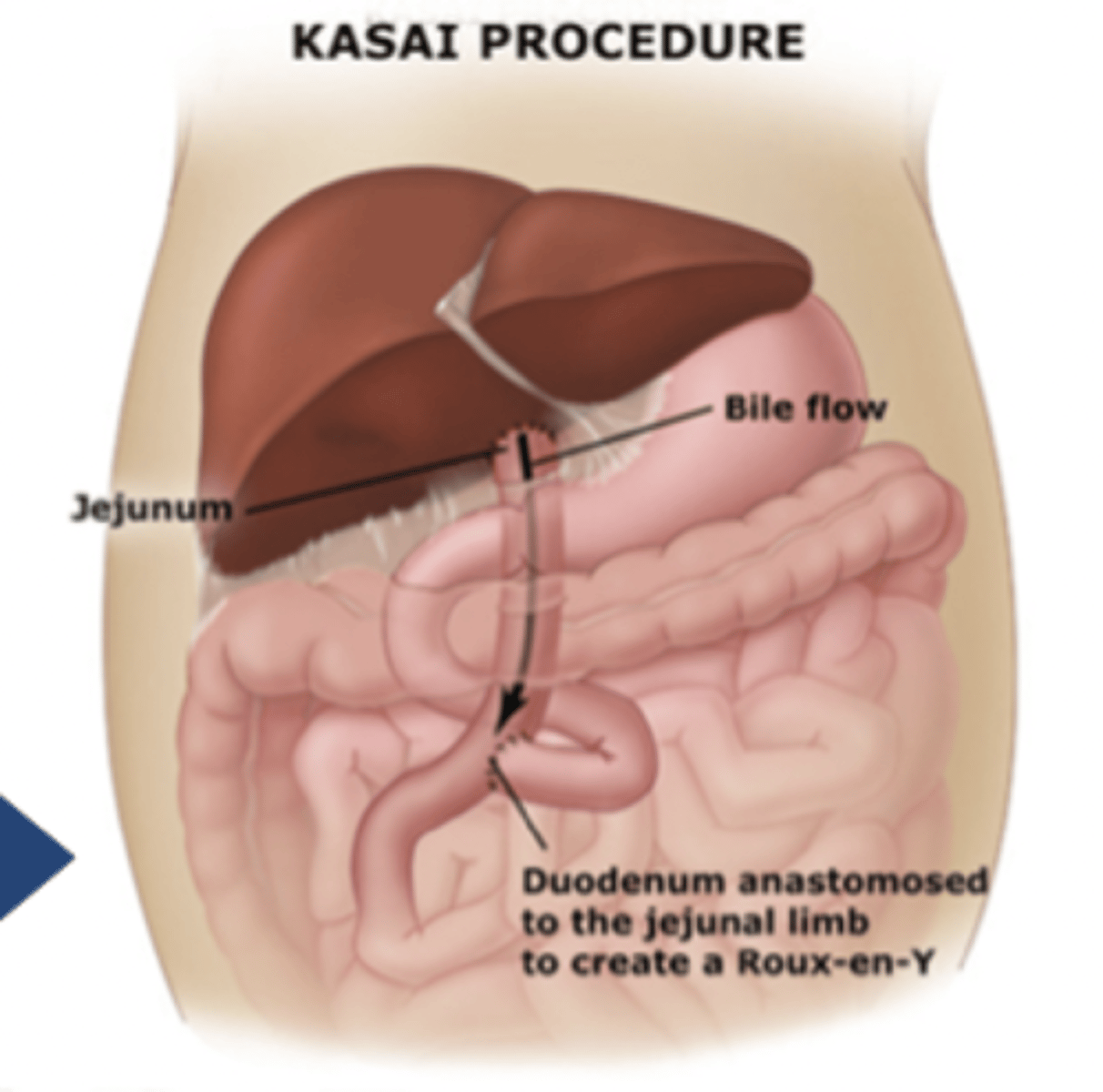
what is biliary atresia?
failure to form or early destruction of extrahepatic biliary tree
- tx: kasai procedure (w/i 6 wks)
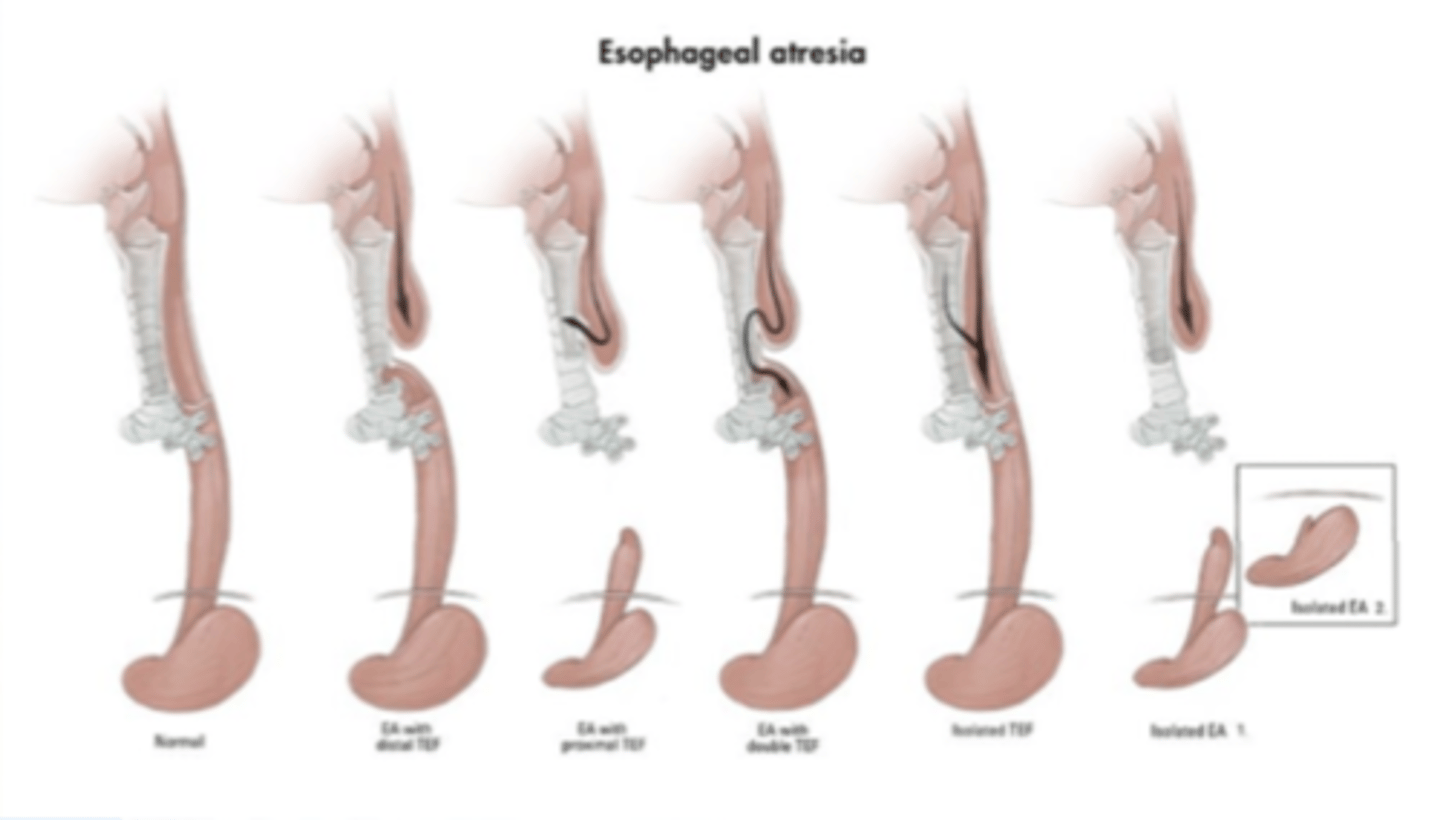
esophageal atresia
congenital absence of part of the esophagus
- tx: foker procedure or colonic transplant
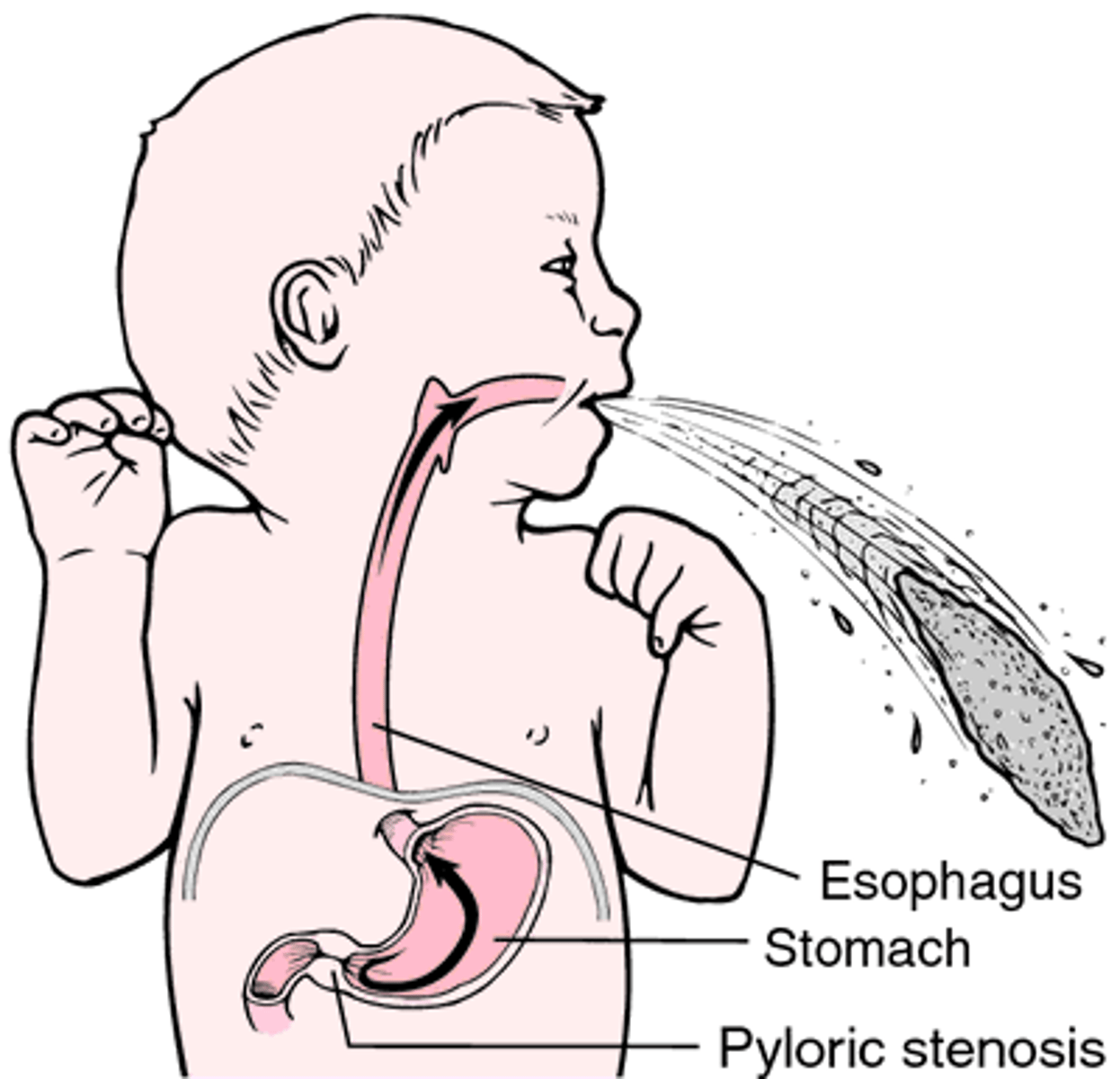
pyloric stenosis
narrowing of the pyloric sphincter
- usually seen in first-born, white males, at 3 wks old
- sx: projectile, non-bilious vomiting, failure to thrive, palpable olive-sized mass (very difficult to do in real life); hypochloremic (↓ Cl-), hypokalemic (↓ K+) metabolic alkalosis w/ dehydration
- tx: myotomy
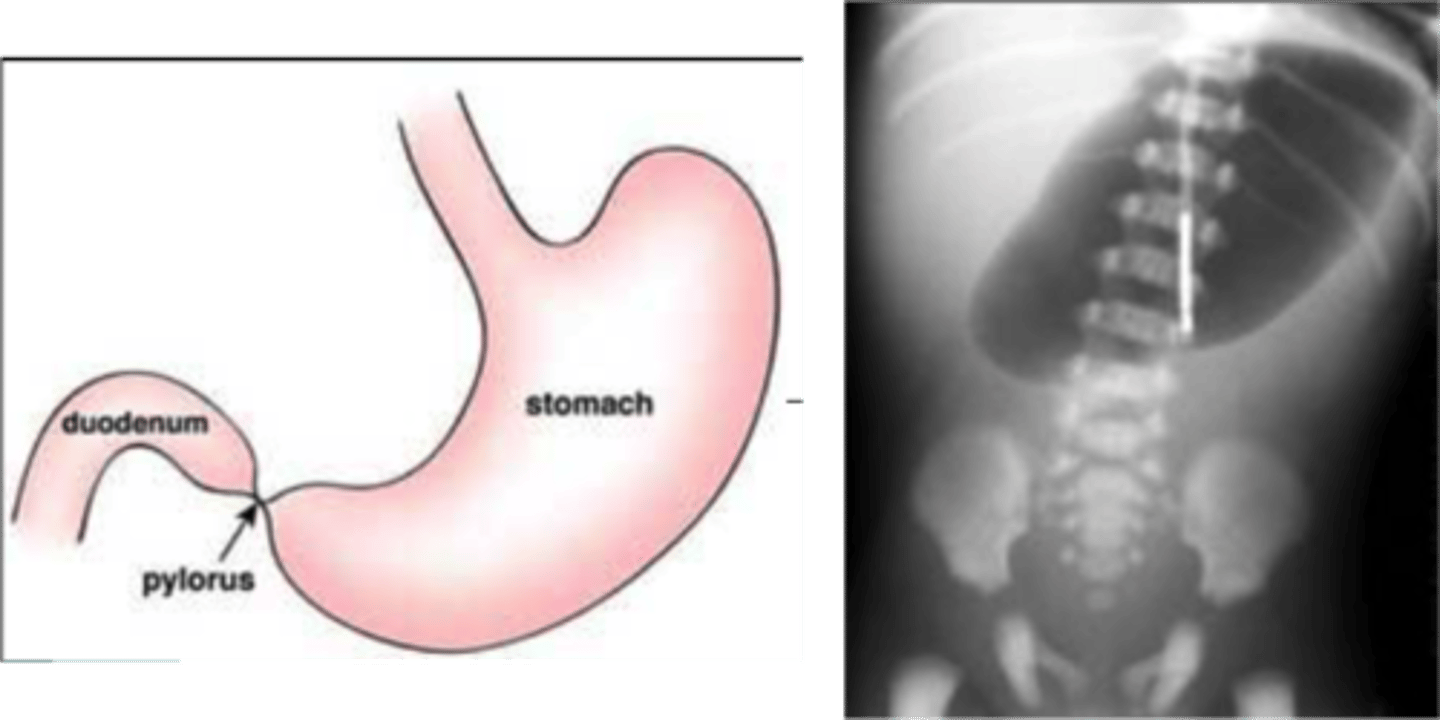
pyloric atresia
a blockage (obstruction) of the lower part of the stomach (the pylorus)
- prevents food from emptying out of the stomach into the intestine
-s/s: vomiting, a swollen (distended) abdomen, absence of stool
tx: survery = gastroduodenostomy or gastrojejunostomy
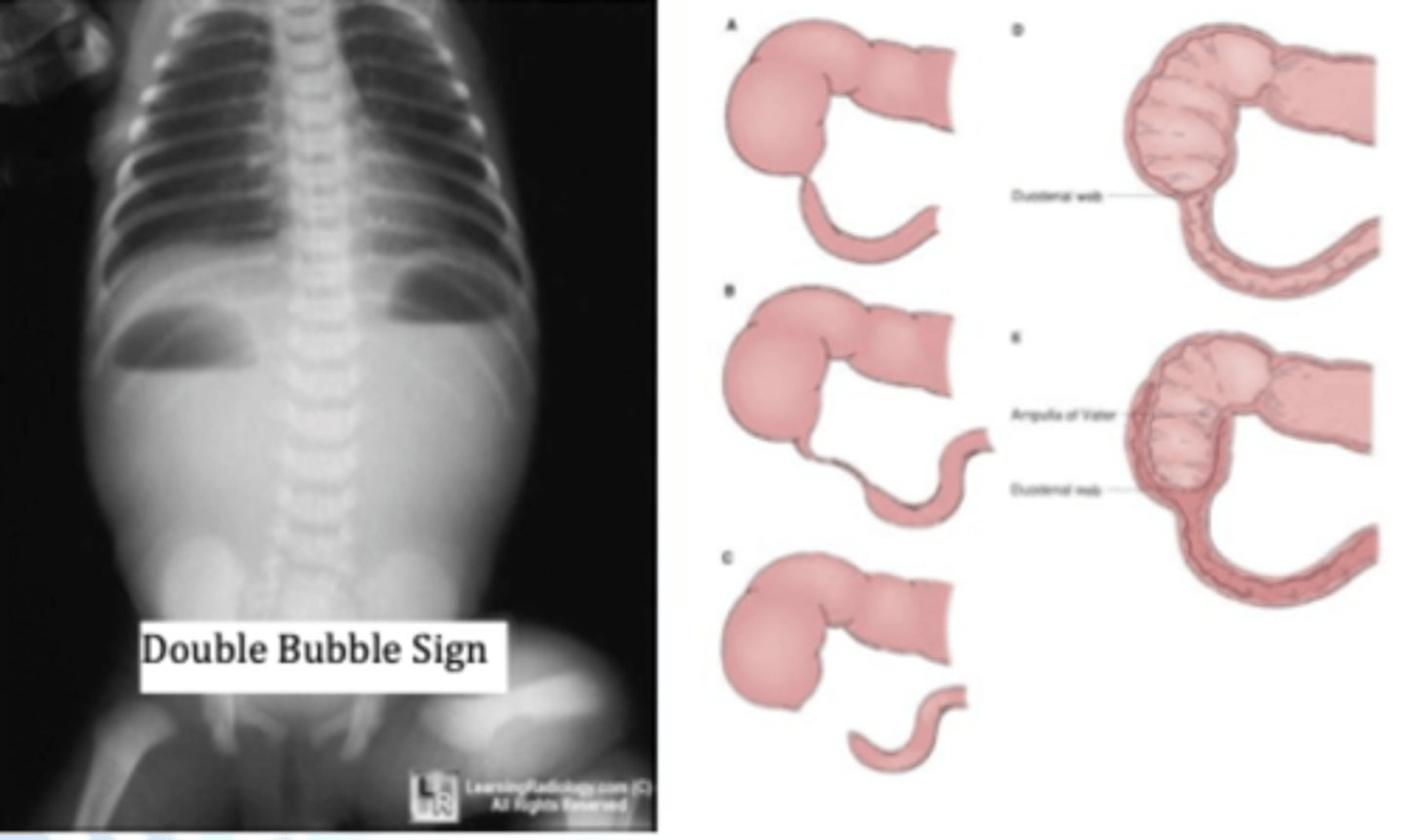
duodenal atresia
duodenum is narrowed or blocked
- keeps liquids and food from passing through the stomach into the rest of the intestine
- up to 1/3 of the patients w/ this will have Down Syndrome
- tx: surgery
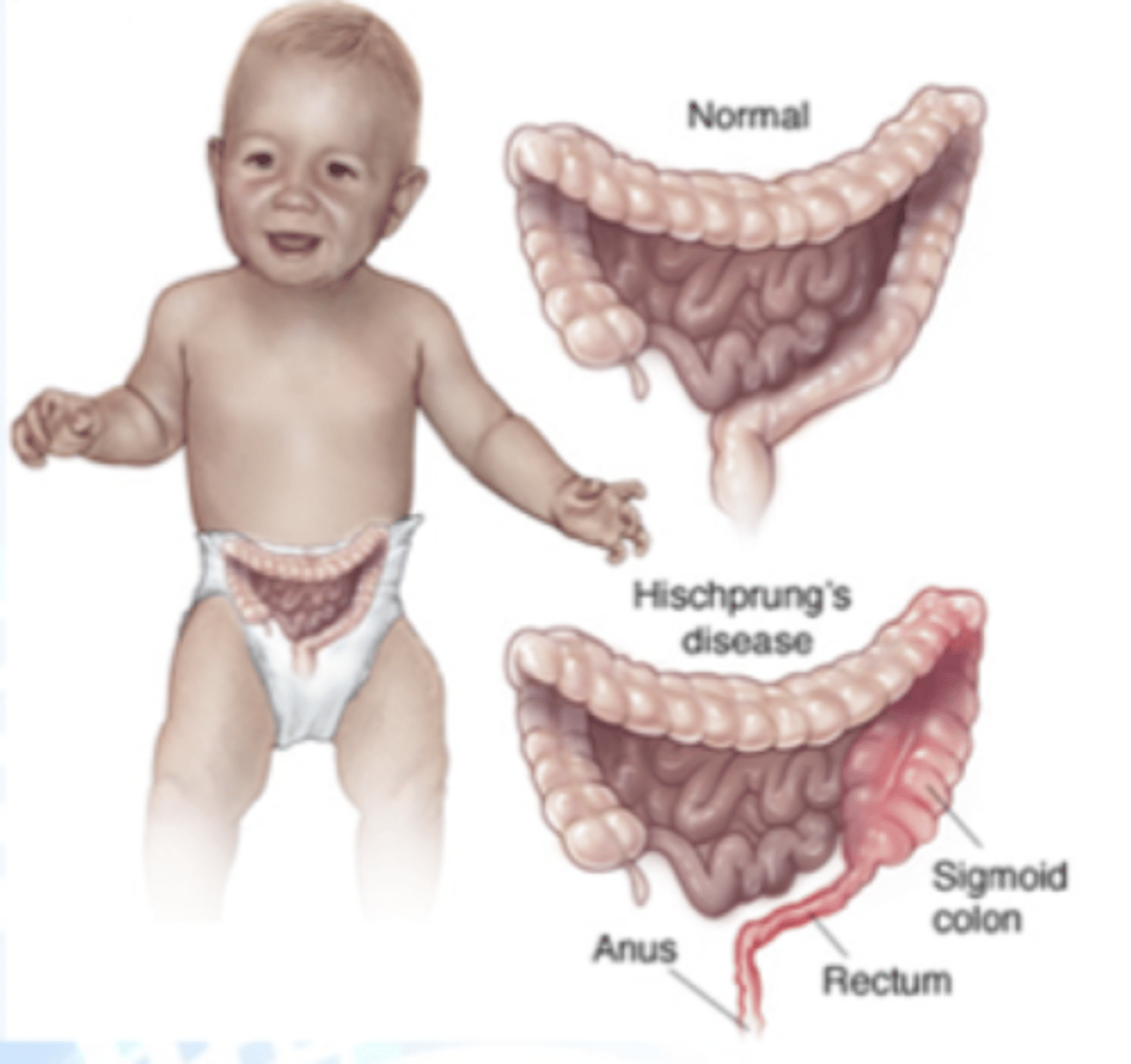
hirschprung's disease
condition of the large intestine (colon) that causes difficulty passing stool
- involves missing nerve cells in the muscles of part or all of the large intestine (aganglionic cells are unable to relax the smooth muscle)
- position is everything during a rectal exam!
- dx: through biopsy
- tx: cecostomy tube (chait tube)
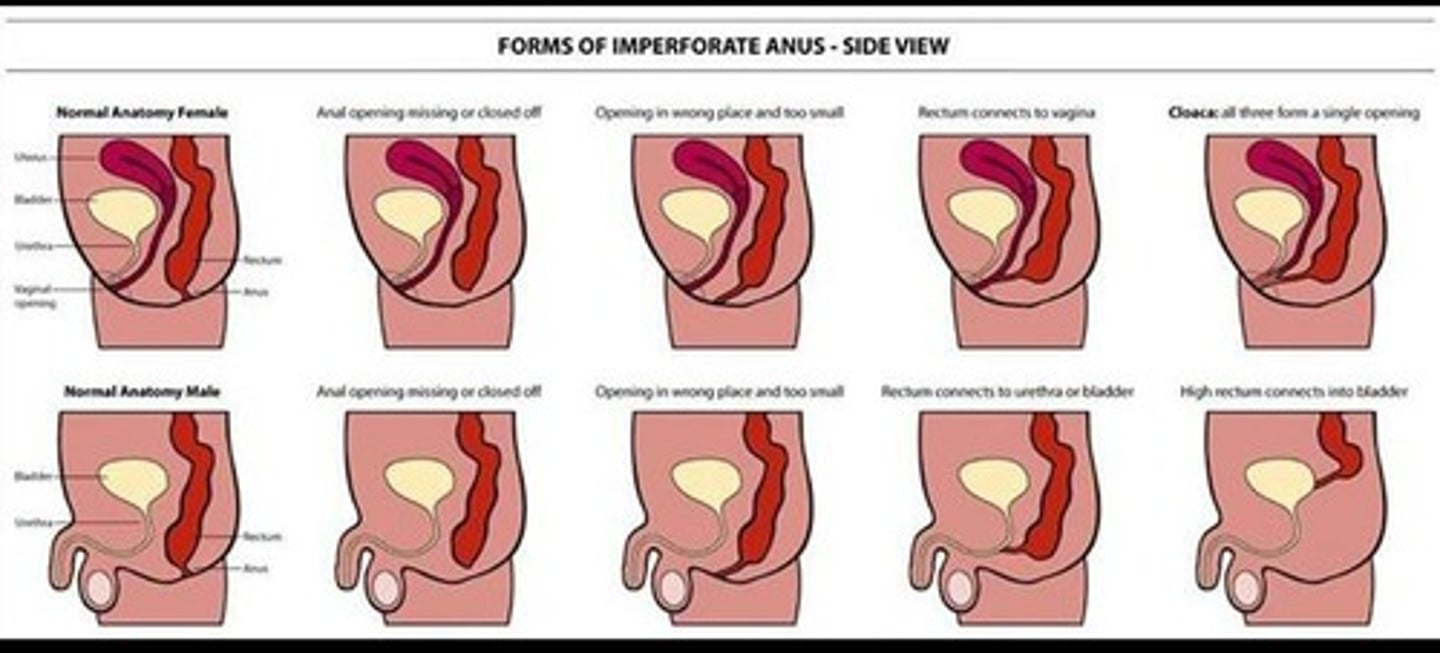
imperforate anus
failure of the anus to connect to the rectum
- tx: colonstomy
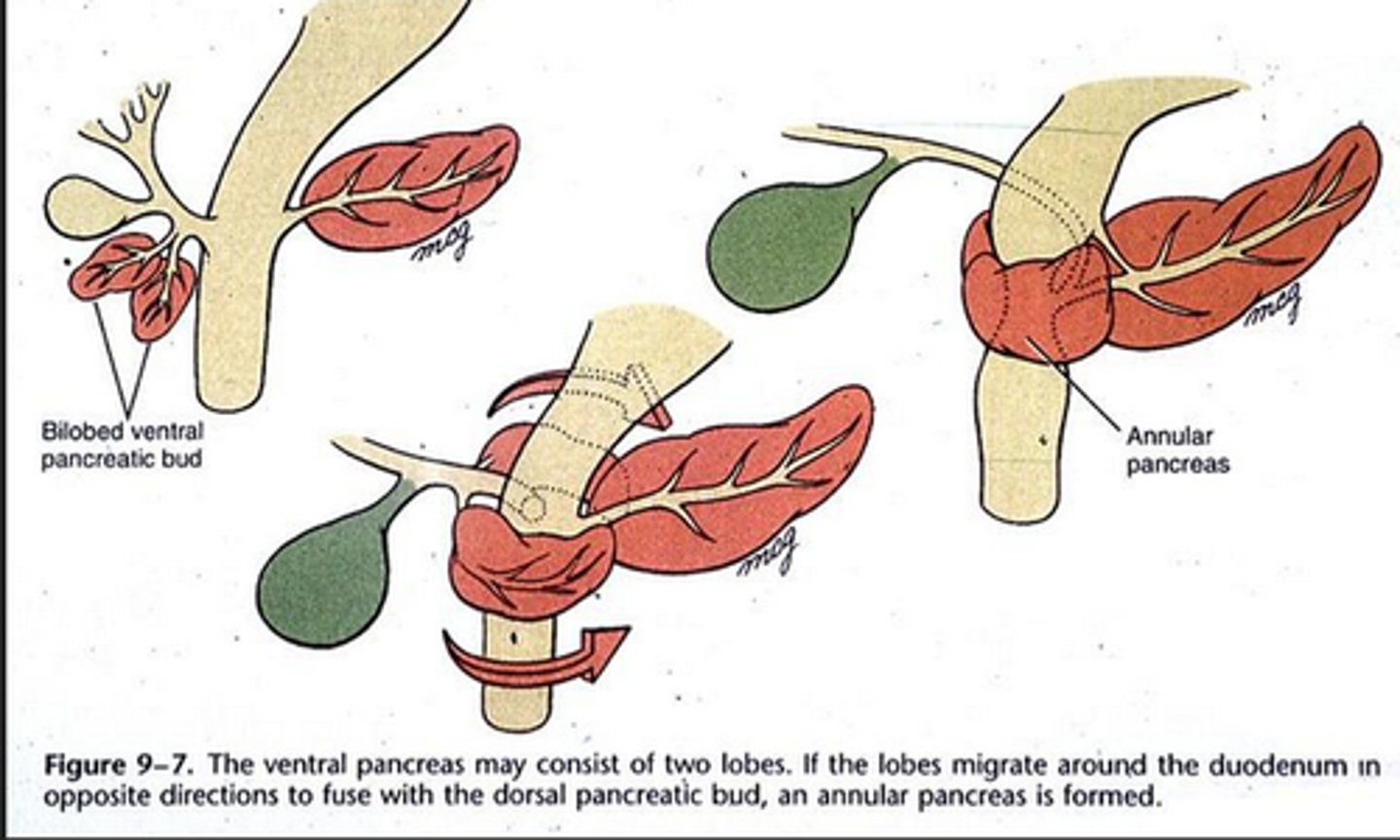
annular pancreas
abnormal migration of the ventral pancreatic bud
- can compress duodenum, causing vomiting
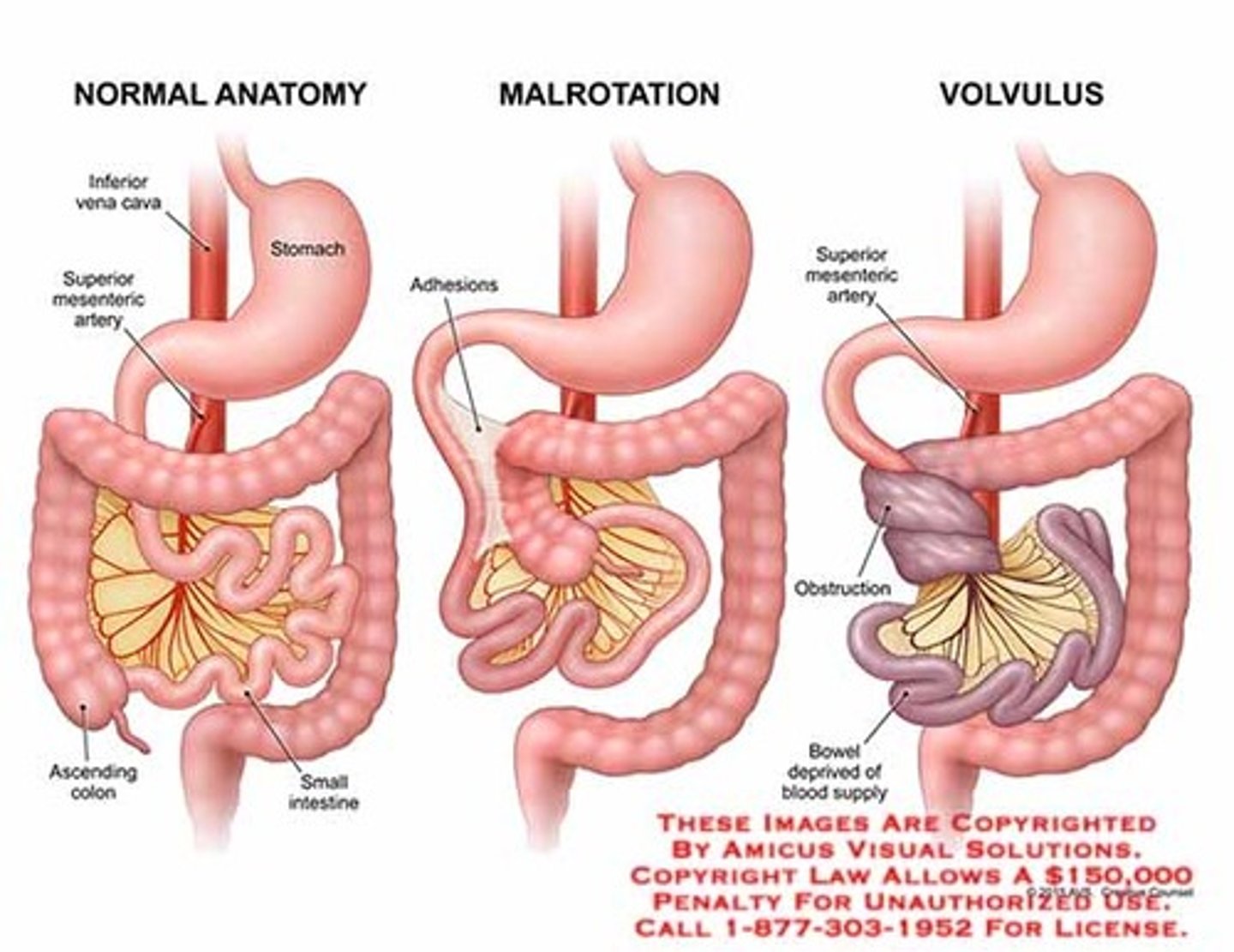
malrotation w/ volvulous
medical emergency!
- decompress, rehydrate, abx
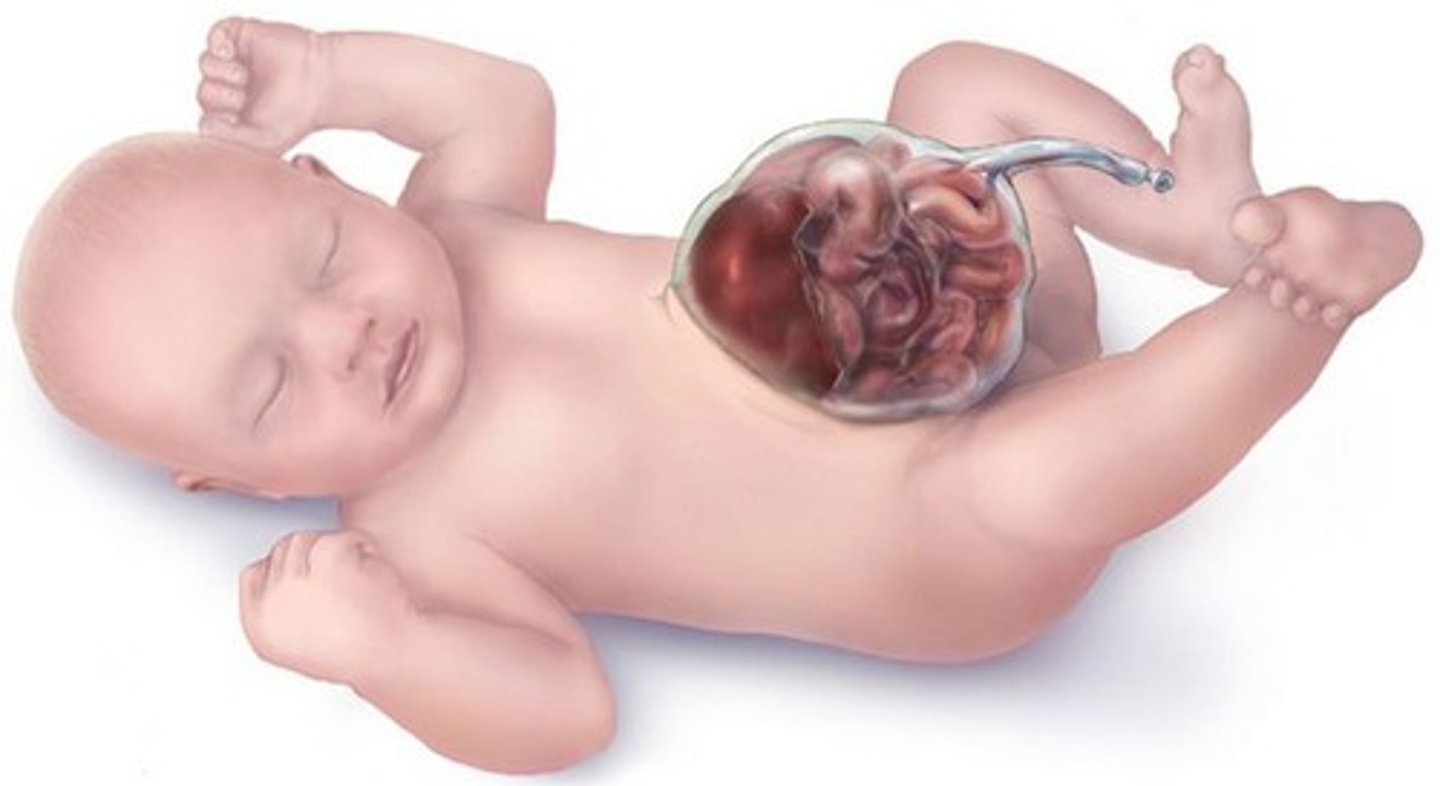
omphalocele
herniation of the intestines through a weakness in the abdominal wall around the navel
- deliver vaginally
- immediately wrap in gauze soaked in warm, sterile water
- cover w/ sterile plastic bag
- if ruptured must immediately go to the OR for silo placement
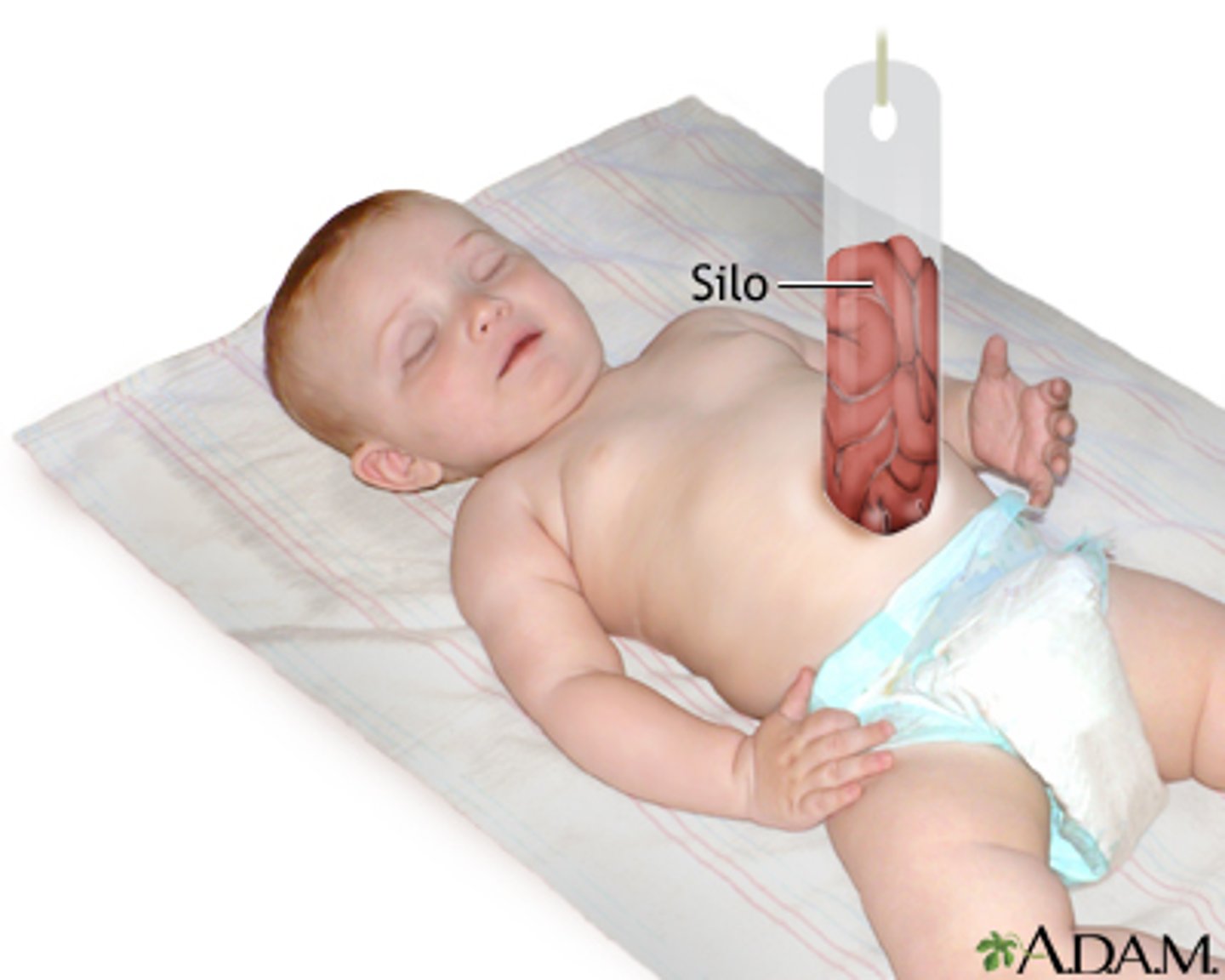
silo for omphalocele
suspended which allows gravity to push contents into peritoneal cavity gradually
- staple lines across the top portion of the bag can speed up this process
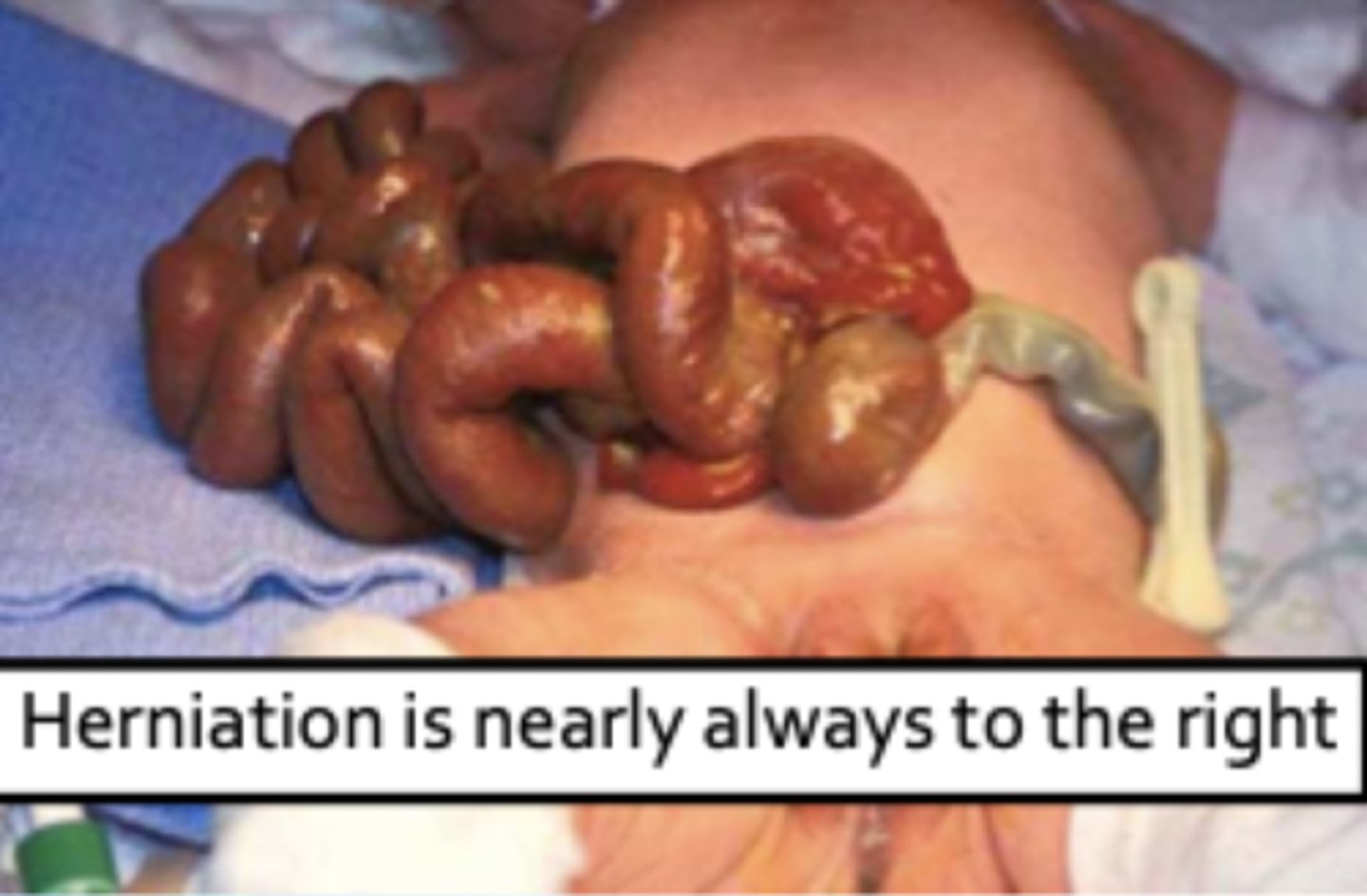
gastroschisis
congenital fissure of the abdominal wall, not at the umbilicus
- often in first born males to young mothers
- associated w/ aspirin use early in pregnancy
- may also be assoc. w/ smoking, drug use, other disruptions to blood flow
omphalocele vs gastroschisis
omphalocele
- cardiac abnormalities
- neural tube defects
- chromosomal defects
gastroschisis
- SGA
- increased malrotation risk

diaphragmatic hernia
abnormal displacement of organs through the diaphragm
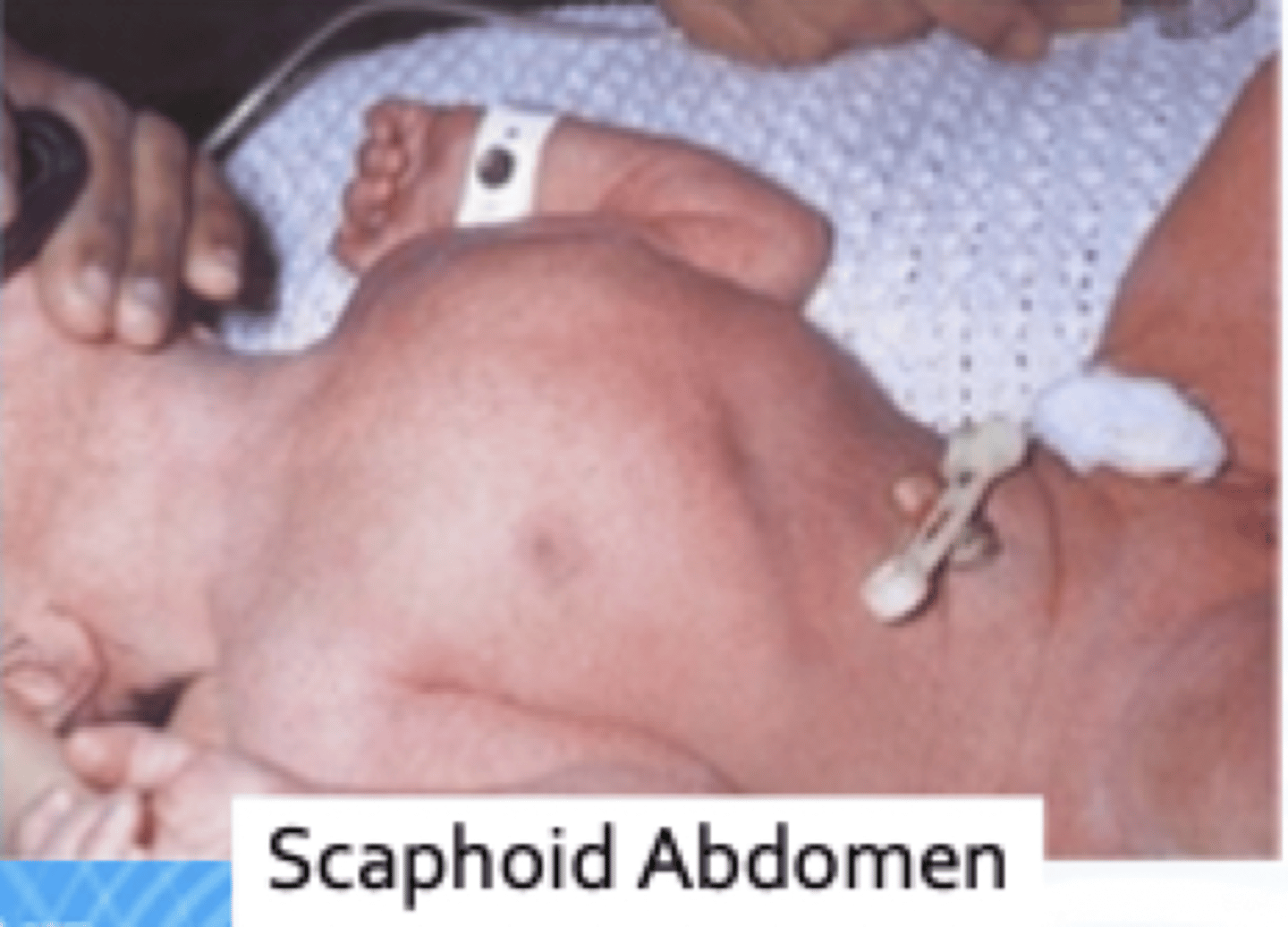
scaphoid abdomen =
diaphragmatic hernia
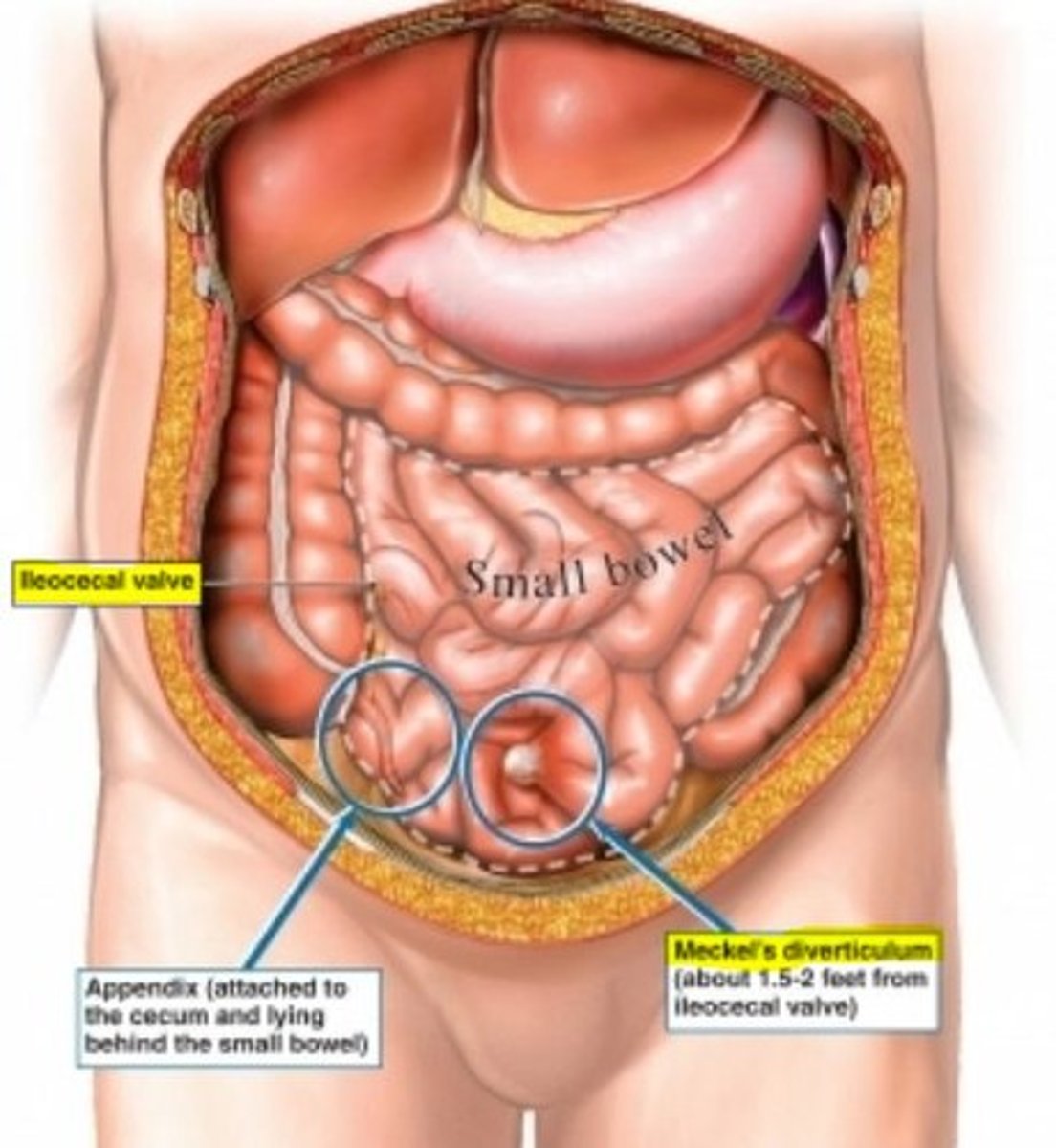
meckel's diverticulum
outpouching of distal ileum (usually w/i 2 ft of the ileocecal valve)
- most commonly seen at 2 y/o
- male > female 2:1
colic
excessive crying at least 3 days/wk for atleast 3 hrs in an otherwise healthy child; DOES NOT CAUSE DAMAGE!
- present in 5-25% of infants
- usually in infants 2 wks to 4 months of age
- no known cause (GI upset, exaggerated moro, persistent crying circuit)
what can be used to treat gastroesophageal reflux (GER; no D bc this is not a disease in children)?
H2 blockers help decrease acidity, but not actual reflux
lower esophageal sphincter (LES) isn't mature until about _________.
4-6 mo
do NOT use PPIs in infants ________.
< 6 mo
red currant jelly stools =
late finding of intussusception
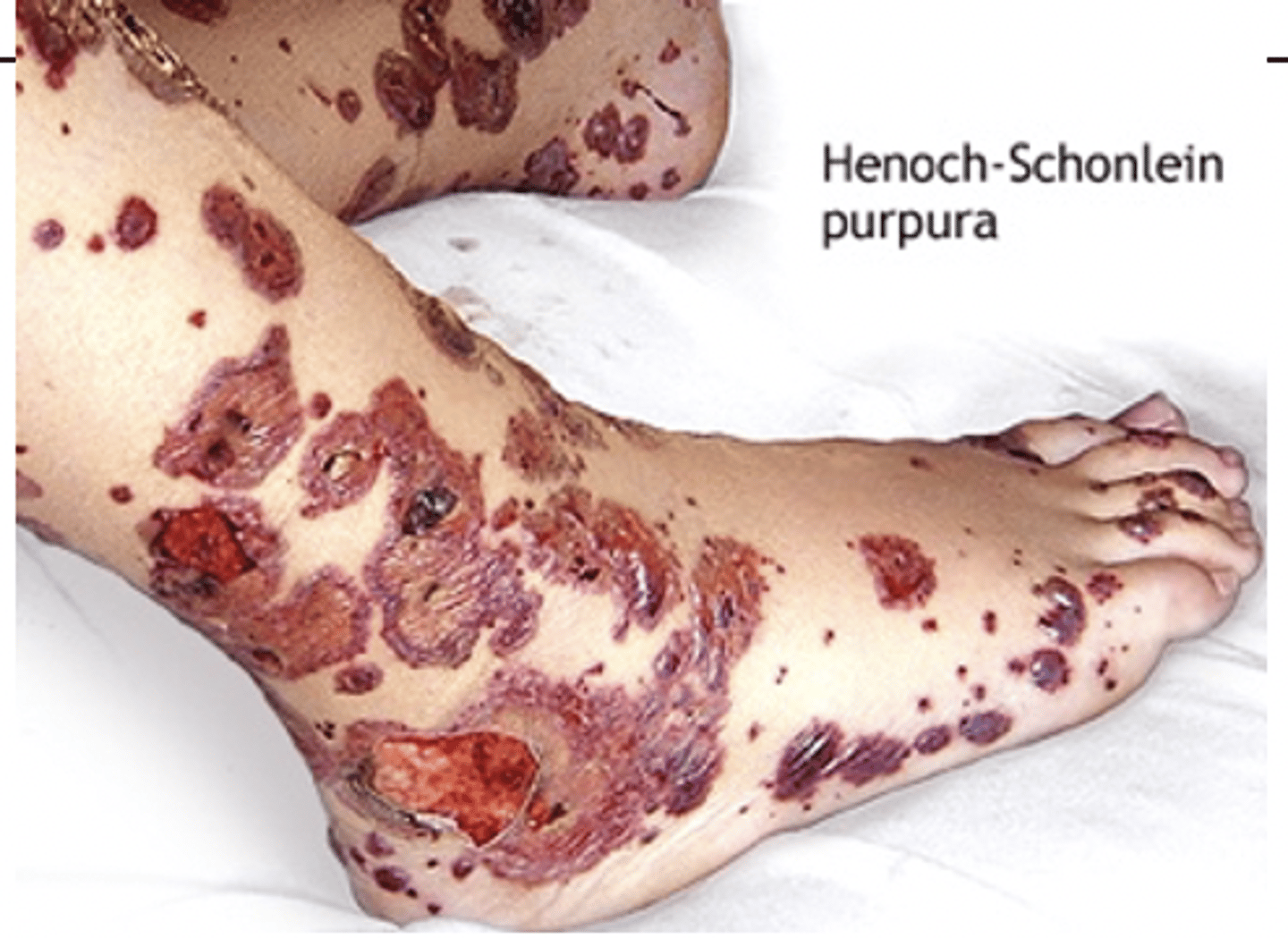
triad of henoch-scholein purpura:
- palpable purpura on legs
- joint pain (no swelling or warmth)
- abdominal pain
*at risk for intussusception (most commonly ileoileal)
what are repeated enemas usually an indication for?
surgery
intussusception
inversion of gut into itself
- most common: ileocecal (next: ileoileal)
- boys > girls
- usually present in first 2 yrs of life
- s/s: colicky pain w/ bilious emesis; late finding = red currant jelly stools
- dx: US; air contrast enema can be both diagnostic & therapeutic
what is both diagnostic & therapeutic for intussuscpetion?
air contrast enema
constipation
difficulty in passing stools
- hard, dry stool
- in children, often presents w/ urinary issues
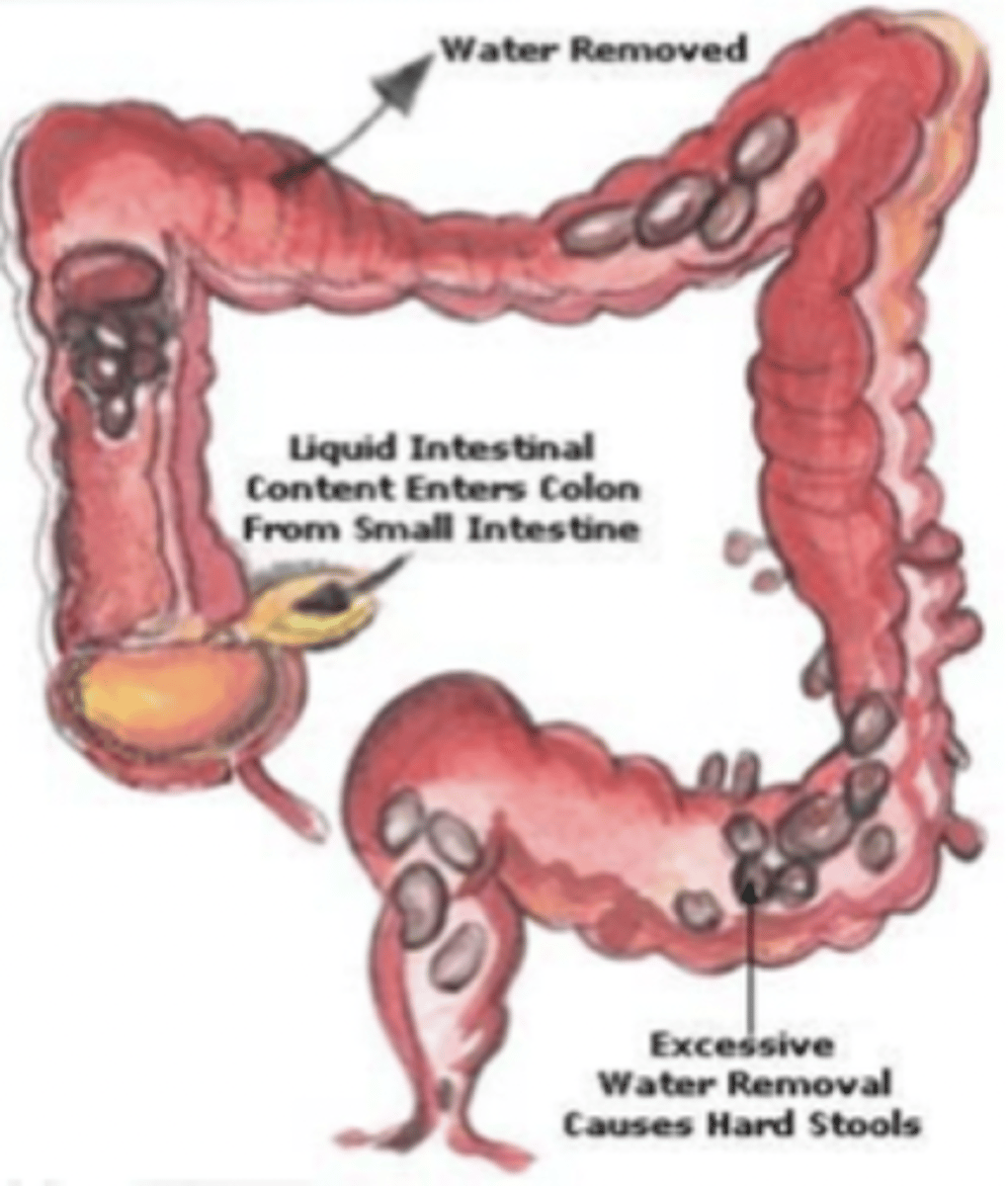
bristol stool chart
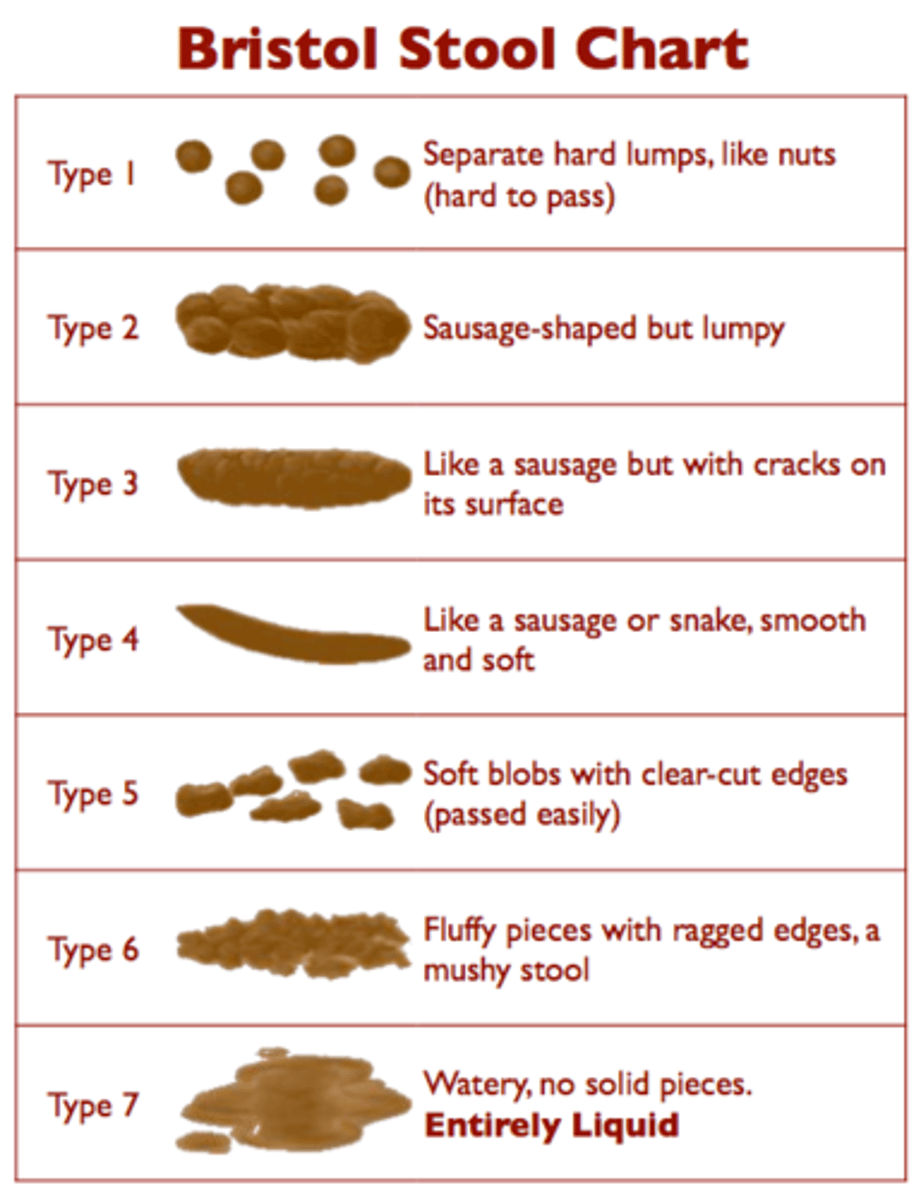
how is constipation treated?
gently (takes twice as long to get UN-constipated)
1. clean out dose = 3 to 5 g/kg over 4 hrs (Miralax)
2. ONLY CHANGE DOSE Q 3 DAYS (taper down)
celiac disease
exposure to gluten & related prolamins in wheat, barley & rye causing an autoimmune inflammation of the small bowel
- most common genetically related food intolerance
- multitude of clinical presentations
- testing: < 3 y/o (anti-endomysial antibodies); > 3 y/o (antitissue transglutamase); total IgA needed to validate
- dx: gold standard = biopsy
esosinophilic esophagitis
inflammatory condition of the esophagus
- often presents w/ hx of food getting stuck
- more common in males
- dx: gold standard = biopsy
risks w/ button battery ingestion:
- electrical burns
- chemical irritation (liquifactive necrosis or acid burns)
- injuries can continue > 2 wks after removal
what do patients whom have previously ingested a battery (if scar tissue develops) usually require for tx?
chronic dilations
trichobezoar
hairball in the digestive tract due to ingestion of hair
- tx: NG tube & Coca-Cola
acid ingestion
coagulation necrosis
- denatured proteins
- eschar/coagulum
**bad, but alkaline is worse
alkaline ingestion
liquefactive necrosis
- saponification of fats
- solubilization of proteins
- cell destruction also produces heat
**worst
what is a modified upper GI study?
performed with a speech therapist and radiologist
- looks at the swallowing mechanisms w/ different liquid and food textures
- examines the esophagus, stomach and upper part of the small intestine (go all the way to ligament of treitz)
pinworms =
e. vermicularis
- use cellophane tape test to diagnose
giardia (Beaver Fever) =
g. lambia
- foamy, green diarrhea
- common in fresh mountain spring water & day care
hookworm =
n. americanus
appendicitis
inflammation of the appendix
- s/s: constant, dull to sharp RLQ pain; + rebound tenderness; not hungry, +/- fever, sterile pyuria (leukocyte esterase in urine, but no bacteria), elevated inflammatory markers
- dx: thin kids = US; or CT
acute gastroenteritis (AGE; stomach flu)
inflammation of the stomach and intestines
- s/s: N/V; +/- fever for 2 to 3 days; diarrhea (loose to watery) for up to 2 wks
- antiemetics & antidiarrheals NOT indicated
- tx: ORT (oral rehydration therapy); avoid spicy, greasy, fatty, dairy type foods, & caffeine
common bacteria in bacterial gastroenteritis
YES3C
- yersinia
- e. coli
- staphylococcus
- shigella
- salmonella
- campylobacter
bacterial gastroenteritis
inflammation of stomach or intestines caused by bacteria
- abx rarely indicated (salmonella in infant < 3 y/o = exception; should treat)
- may mimic appendicitis sx
infantile botulism
a serious illness that results from ingesting clostridium botulinum spores that release a deadly toxin in the gastrointestinal tract
- s/s: floppy, gray baby w/ insidious onset
adult botulism is rapid onset due to ingestion of toxin from..
poorly canned foods
causes of functional abdominal pain (FAP)
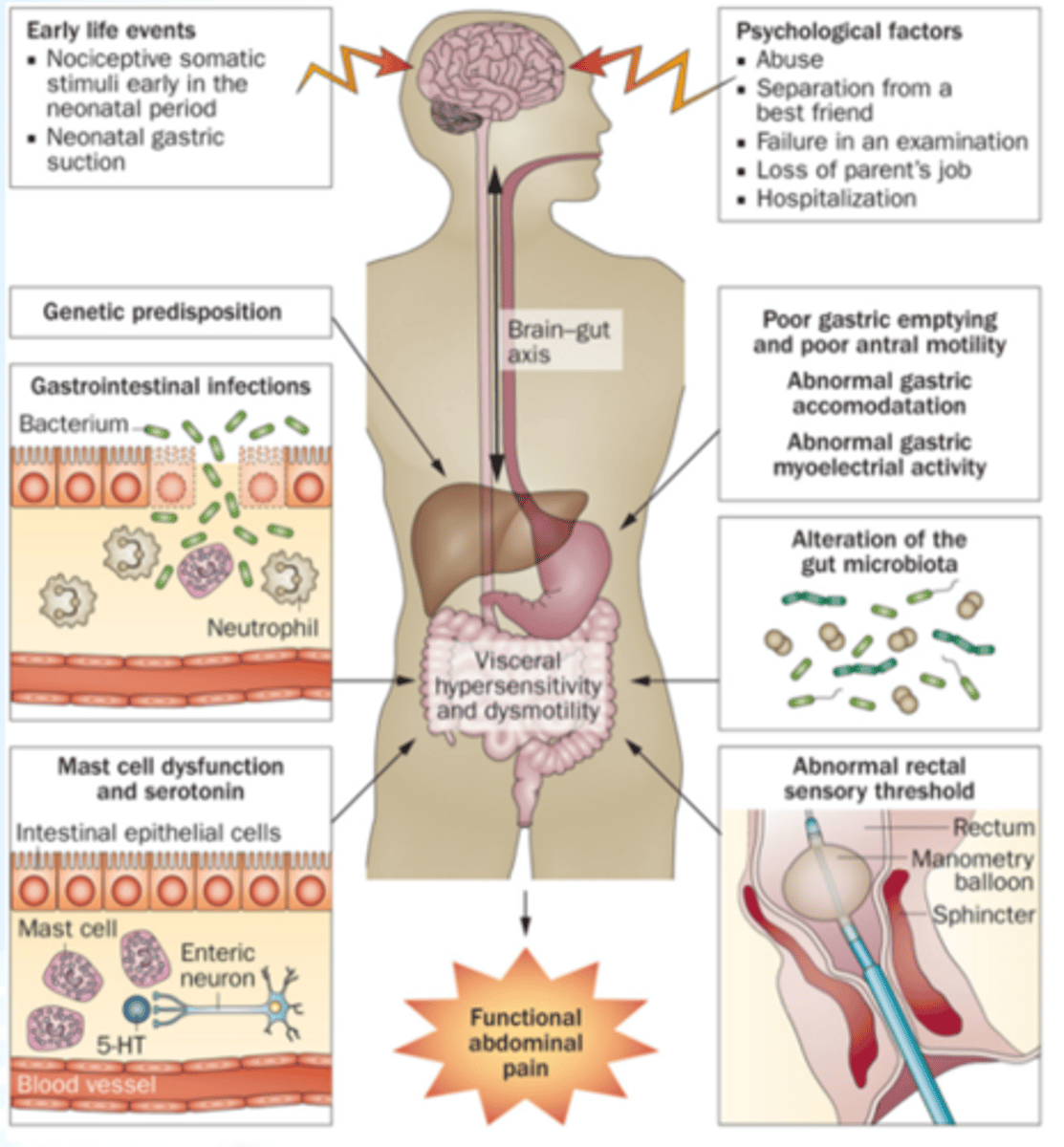
diagnostic criteria for FAP

FAP red flags
how is FAP treated?
- validation
- minimized medical intervention
- distraction
- antispasmodics vs gut motility agents (Bentyl vs Periactin)
- antidepressants
- physical activity (yoga, ti-chi, pilates)
- biofeedback, guided imagery, acupuncture
- probiotics
is serum testing (RAST) helpful in diagnosing food allergies (in children < 5 y/o)?
RARELY (many will test pan-positive for no reason)
what is the best treatment for food allergies?
avoidance/reintroduction
a food allergy test came back positive; however, when the patient eats that food, they have no sx.
should the food be eliminated?
NO!
never eliminate foods that do not produce sx, just bc the test is positive!!
when in doubt (regarding food allergies), what can you prescribe?
epi pen
for children, give peanuts _______.
a. early
b. late
a. early
1 multiple choice option
what does frequent use of antibiotics early in childhood do?
*changes:
- gut microflora
- immune system function
*increased:
- asthma
- food & environmental allergies
- GI dysfunction
*altered metabolism & ↑ risk for obesity