Lecture 19: Metabolic Regulation II
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Applying Lessons of Lac Operon
microbes have to respond to a changing environment quickly
- they have to compete for their niche or move to another one
- must sense the environment; ex lac operon responds to change in fuel source
- lac operon is inducible
Arginine Operon
repressible operon
- normally expressed but can be turned off/on
- if arginine is present, it acts as a corepressor and physically blocks RNA polymerase from synthesizing genes for arginine biosynthesis
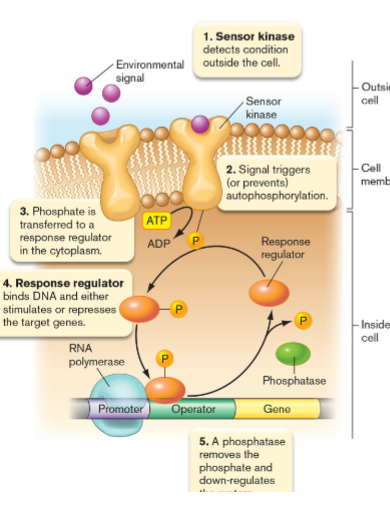
Sensing the Environment
two-component signal transduction
- sensor kinase and response regulator
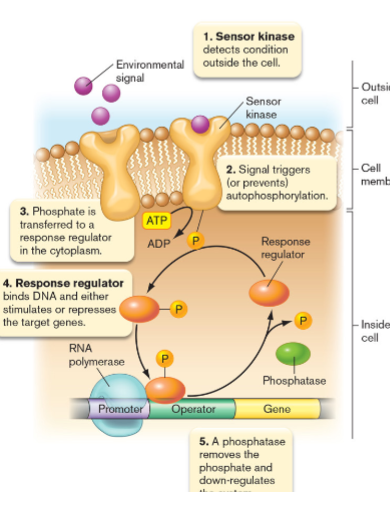
Sensor Kinase
binds to environmental change on the outside of the cell
- causes change on the intracellular side of the cell
- activates itself via phosphorylation
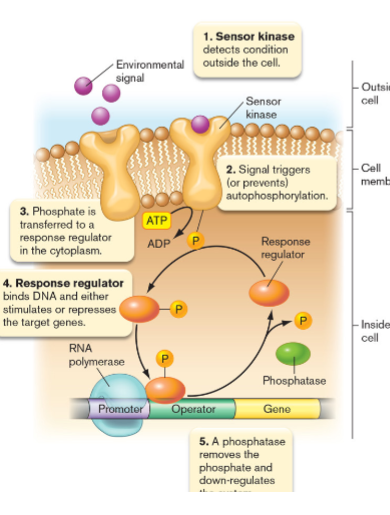
Response Regulator
transcription factor; binds to DNA
- activated via phosphorylation by sensor kinase
- mediates expression by altering transcription; negative/positive
EnvZ-OmpR System
two component system that senses osmotic changes to maintain homeostasis
- sensor histidine kinase autophosphorylates and activates the OmpR response regulator
- when activated, it activates the transcription of ompC and activates ompF in low osmolarity and represses it at high osmolarity
Sigma Factors
regulate transcription of all genes
- s^70 initiates transcription at most genes
- alternative s factors are used for different cases
- controlled by altered transcription and translation
Heat Shock Response of E. coli
regulated by s32 at 30C
- sigma factor is transcribed and stays in cytoplasm by hairpins; where binding site is located
- when microbe is at an increased temperature hairpins melt; ending up as a single stranded RNA and ribosome binding site is available
- allows for translation of sigma factor and regulates the heat shock genes
Anti-Sigma Factors
inhibit sigma factors by binding specific sigma factors and blocking its access from binding to DNA
- release of sigma factors from their anti-sigma factor is important for flagella construction
Secondary Messengers
don’t serve as biosynthetic precursors but have regulatory
function
- they alter activities and regulate proteins and responses inside the cell
- ex. cAMP
Stringent Response
stress response that allows them to adapt to nutrient depravation
- decrease rRNA transcripts made for ribosome assembly
Biofilms
community of microbes
- multi-species communities attached to a surface
- as attachment increases, it attracts other microbes
- anaerobic microbes: grow in the center
- aerobic microbes: grow toward the outside
- ex. cavities, gum disease, ponds, implants, catheter
Quorum Sensing
communication between microbes in biofilms