NURS 203: Unit 3 - Cardiovascular System II: Peripheral Vascular System and Lymphatics (Lab 3 Review)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Major Arteries
- Temporal
- Carotid
- Arteries in the arm
- Arteries in the leg
Temporal Artery
The artery that lies superior to the temporalis muscle, and its pulsation is palpable anterior to the ear
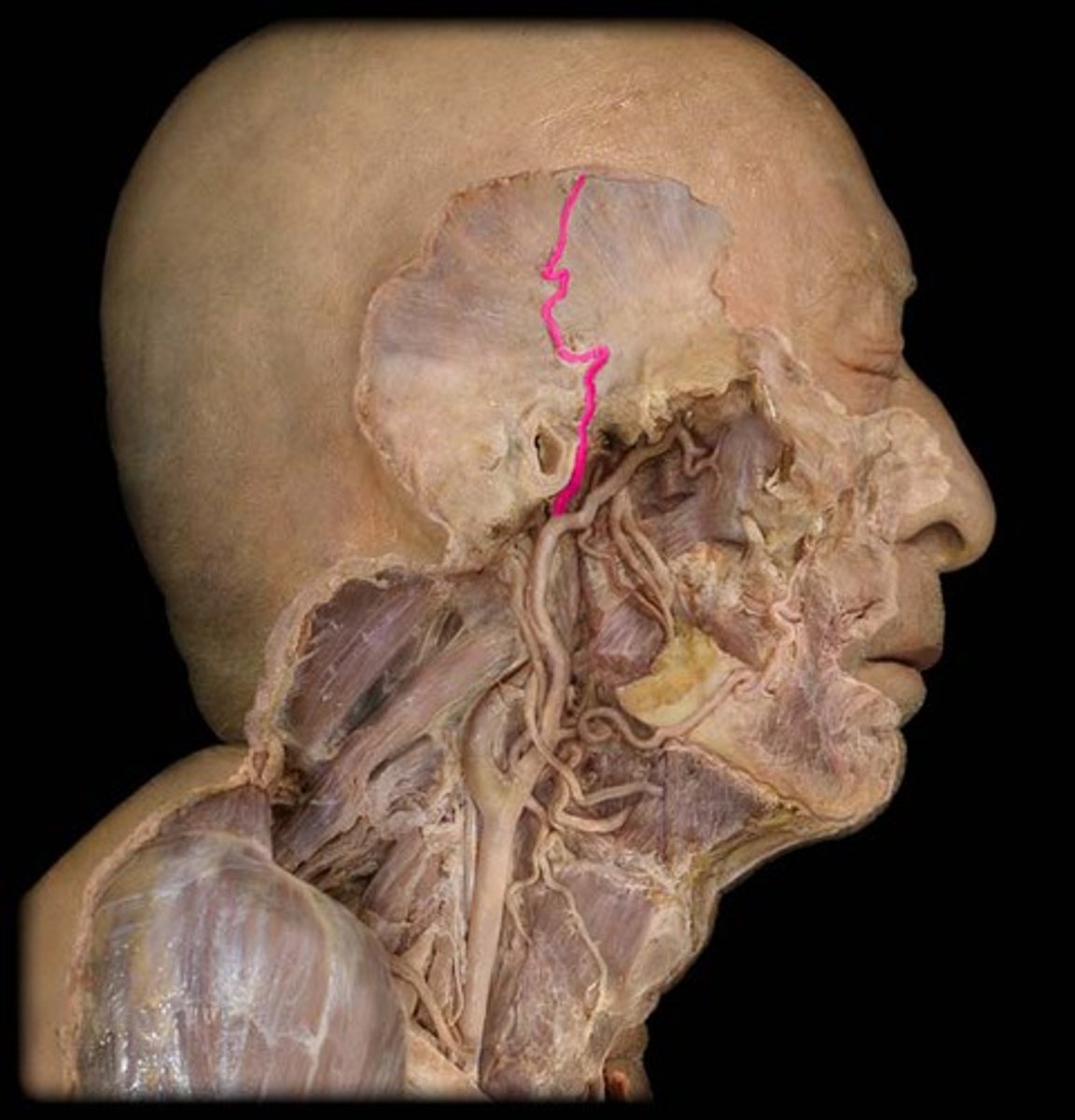
Carotid Artery
The major neck vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the head
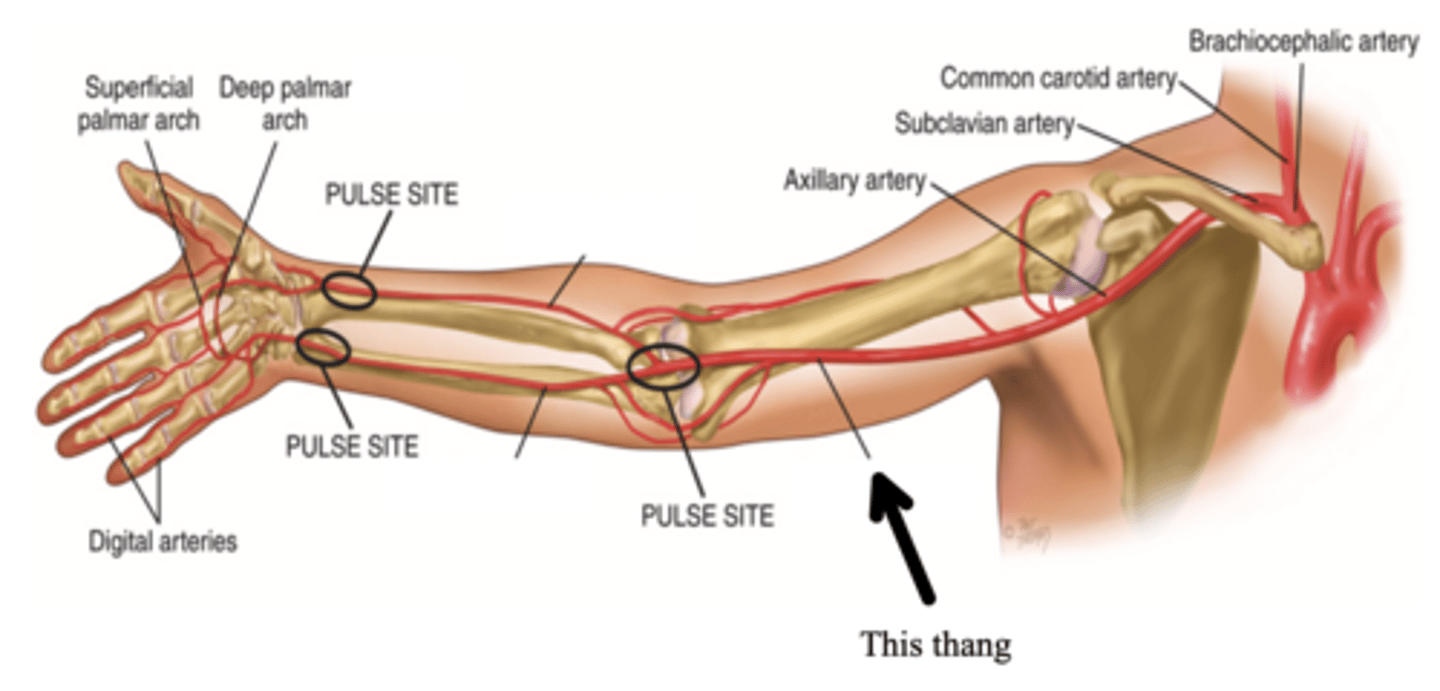
Major Arteries in the Arm
- Brachial
- Ulnar
- Radial
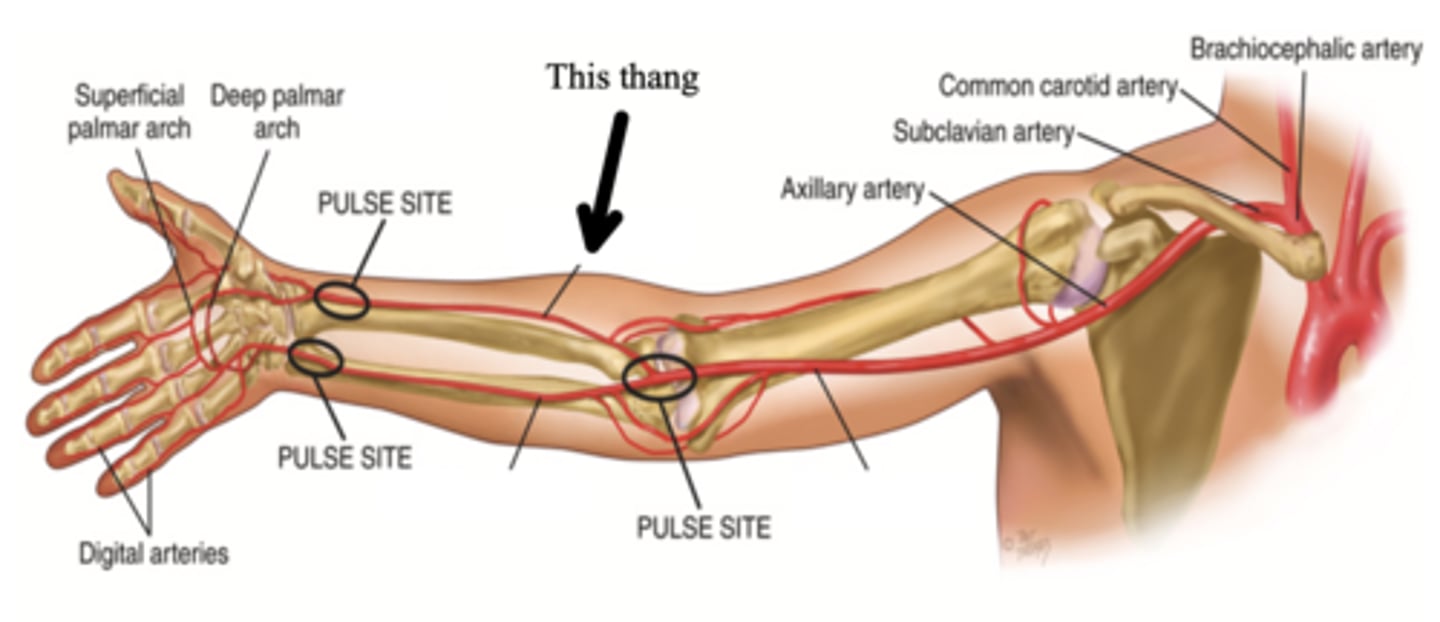
Brachial Artery
The major artery that supplies the arm with blood
Ulnar Artery
One of the two arteries that supply the hand with blood; can be palpated medial to the ulna and is usually deeper
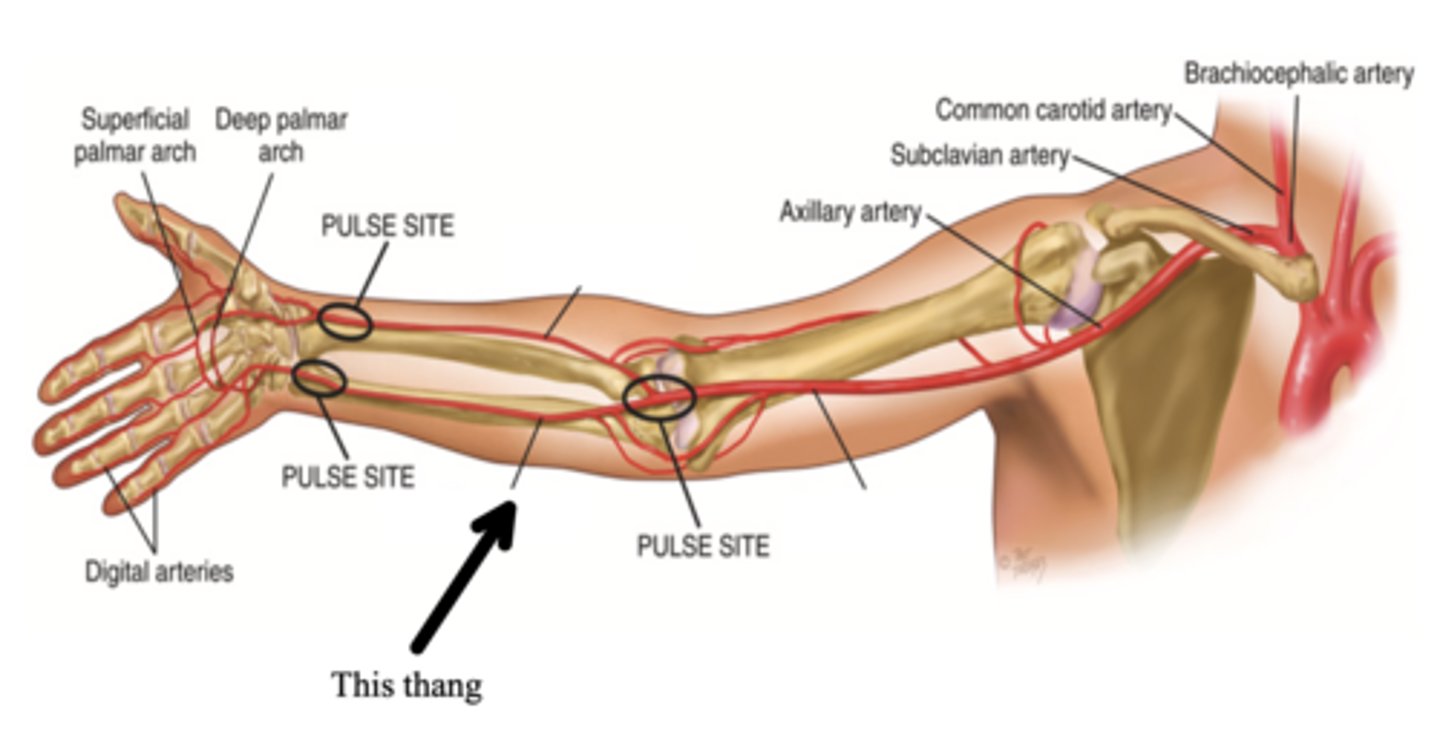
Radial Artery
One of the two arteries that supply the hand with blood; can be palpated medial to the radius and is usually more superficial
Major Arteries in the Legs
- Femoral
- Popliteal
- Dorsalis pedis
- Posterior tibial
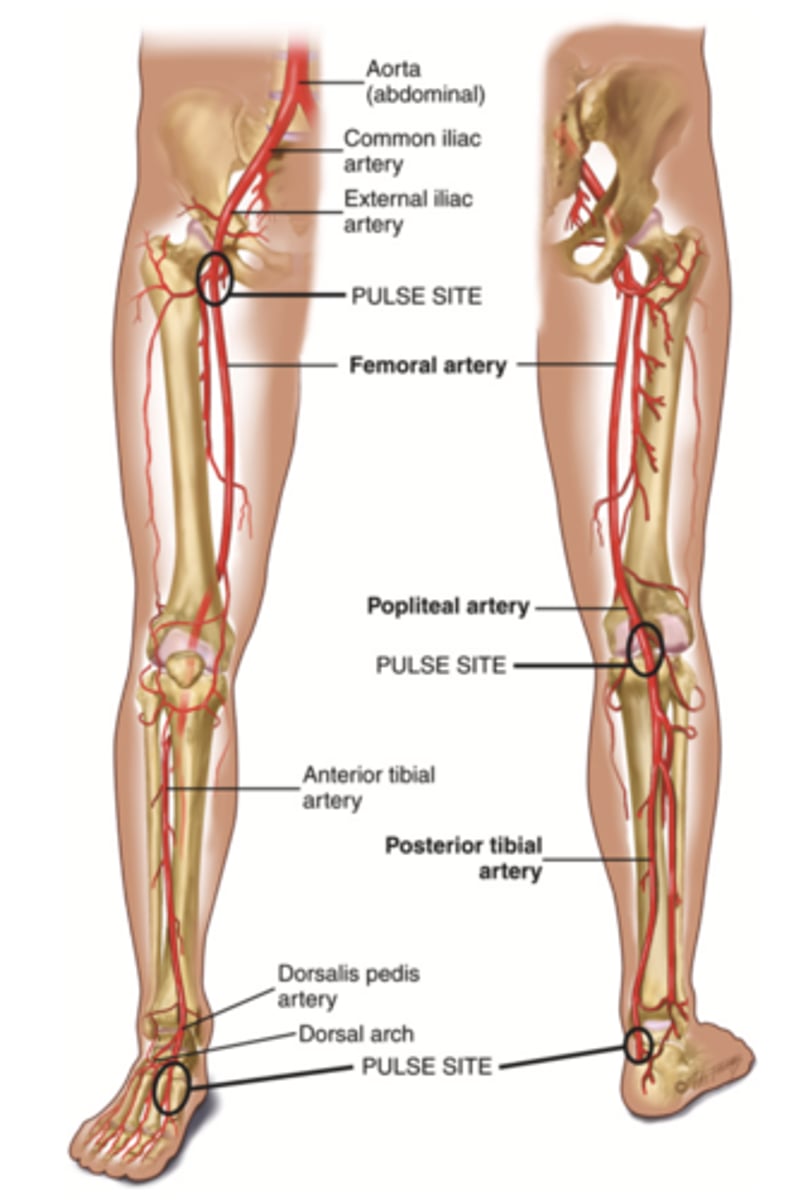
Femoral Artery
The major artery that supplies the leg with blood; found in the thigh
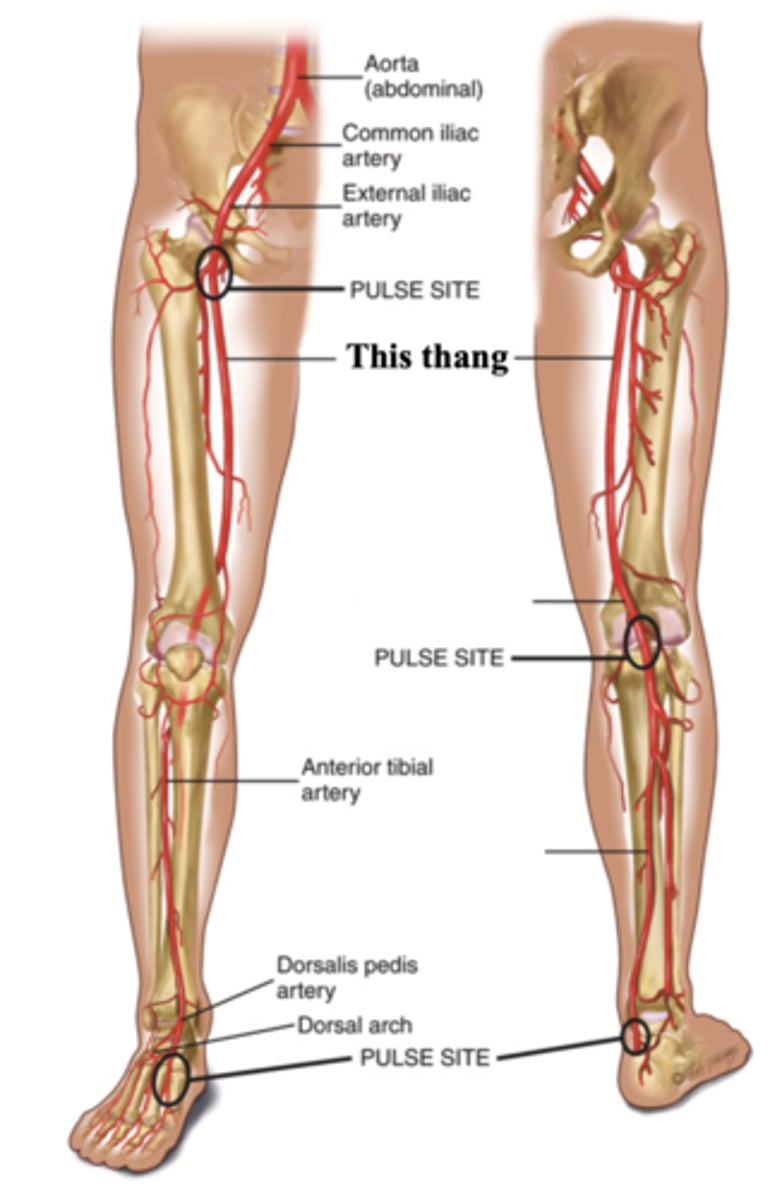
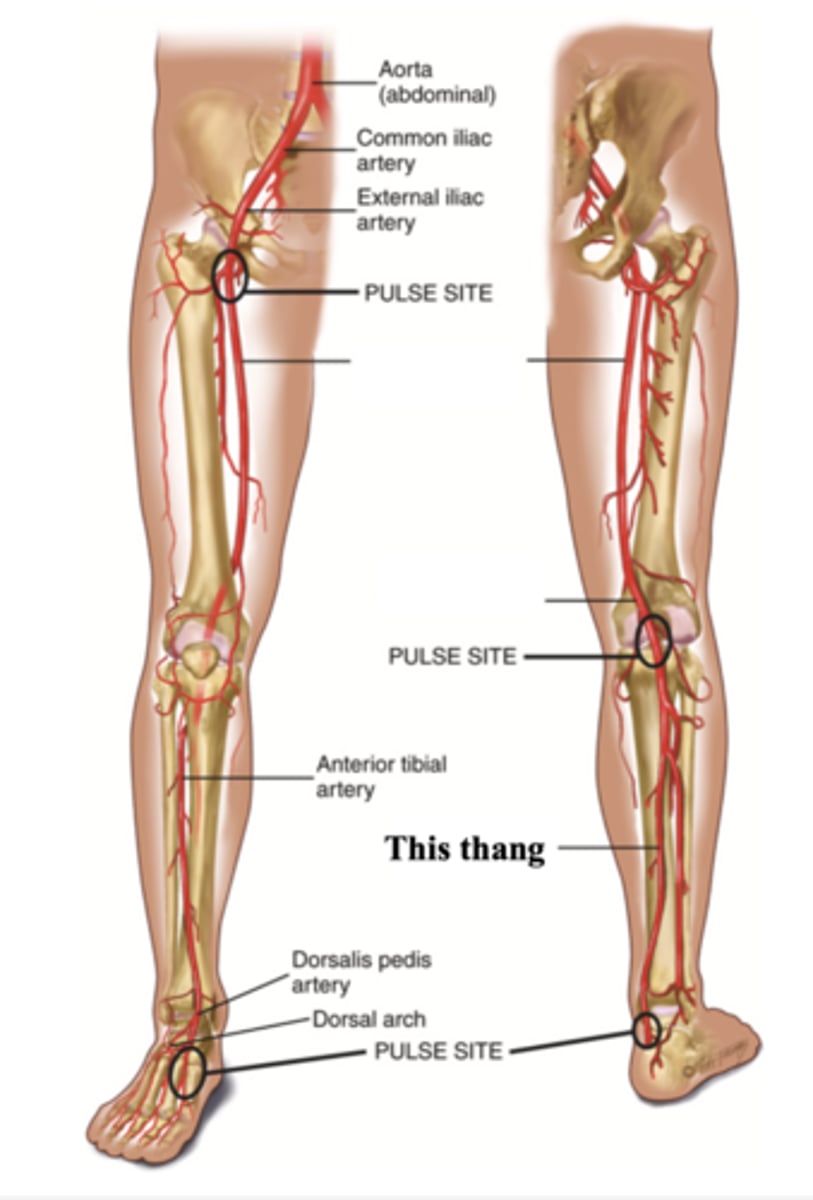
Popliteal Artery
The artery found behind the knee
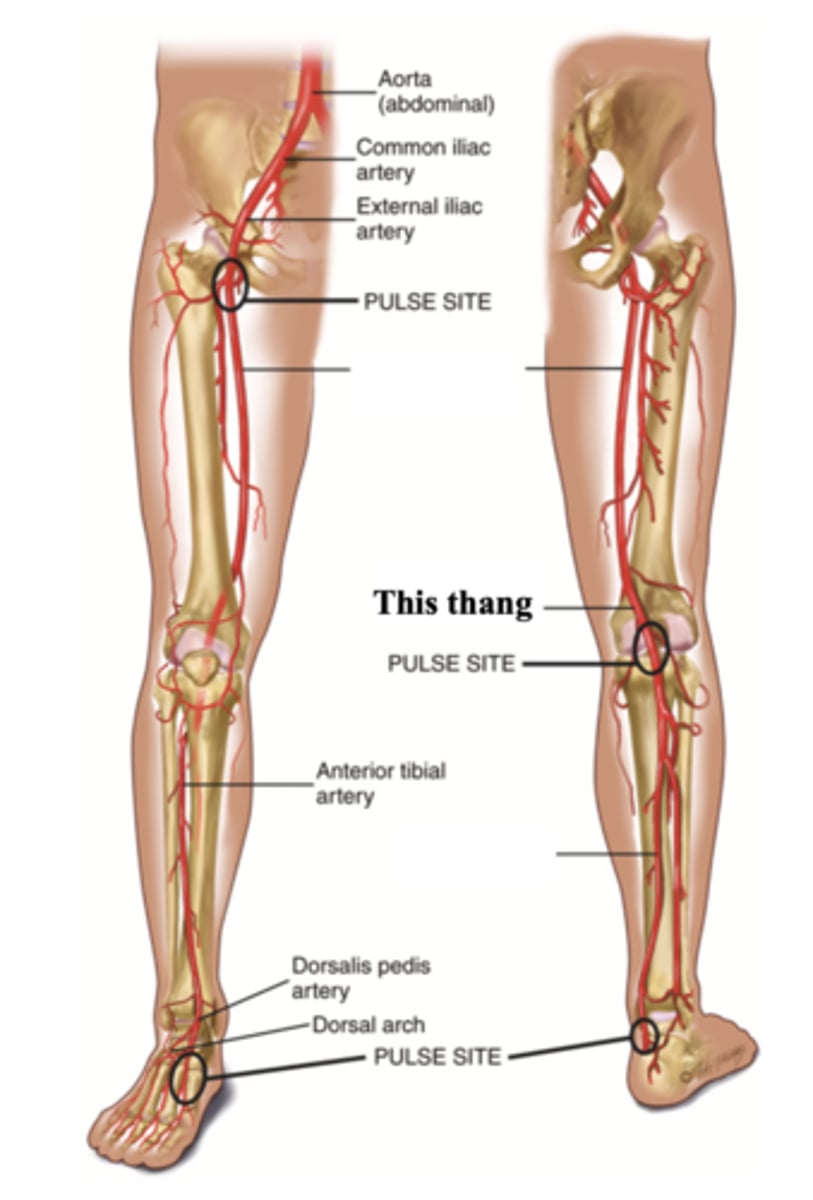
Dorsalis Pedis
The artery found at the top of the foot arch
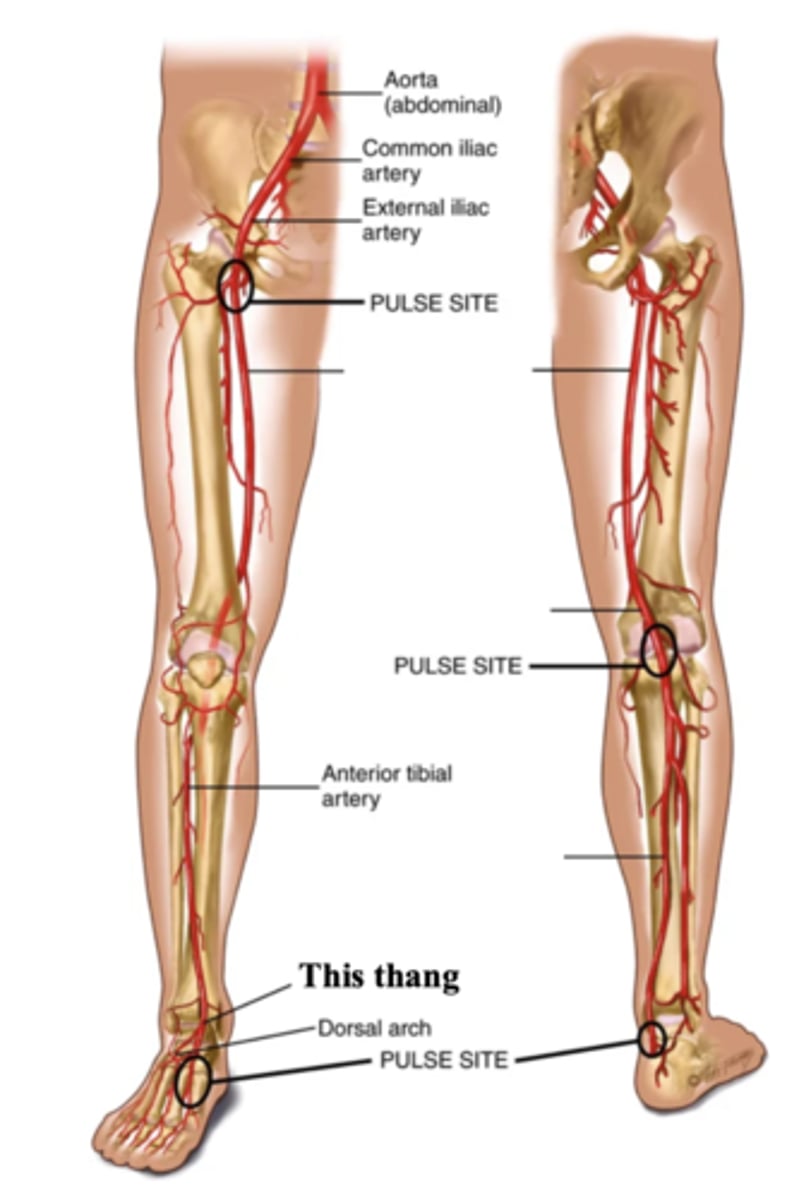
Posterior Tibeal Artery
The artery supplying the foot, found behind the medial ankle
Major Veins
- Jugular
- Veins in the arm
- Veins in the leg
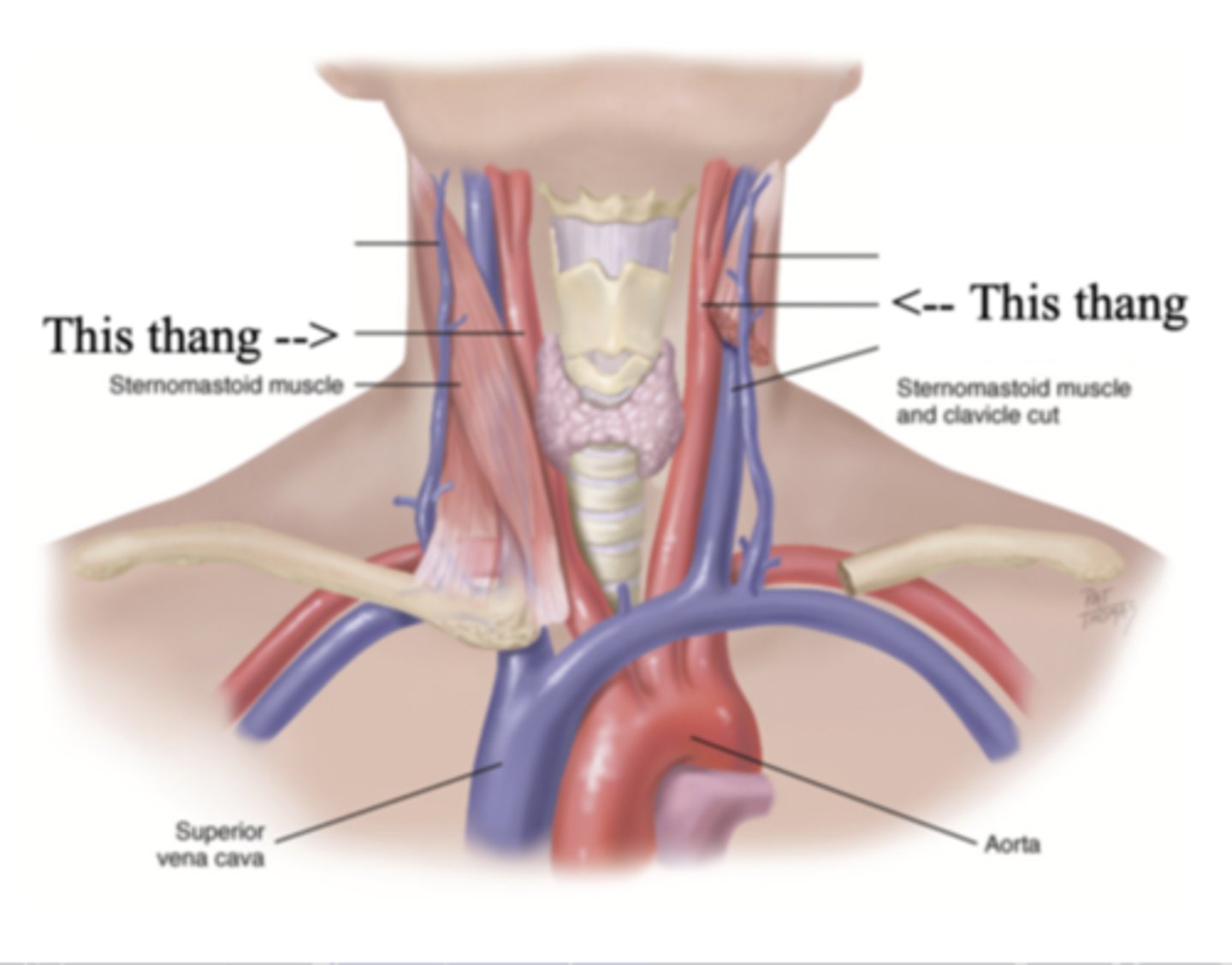
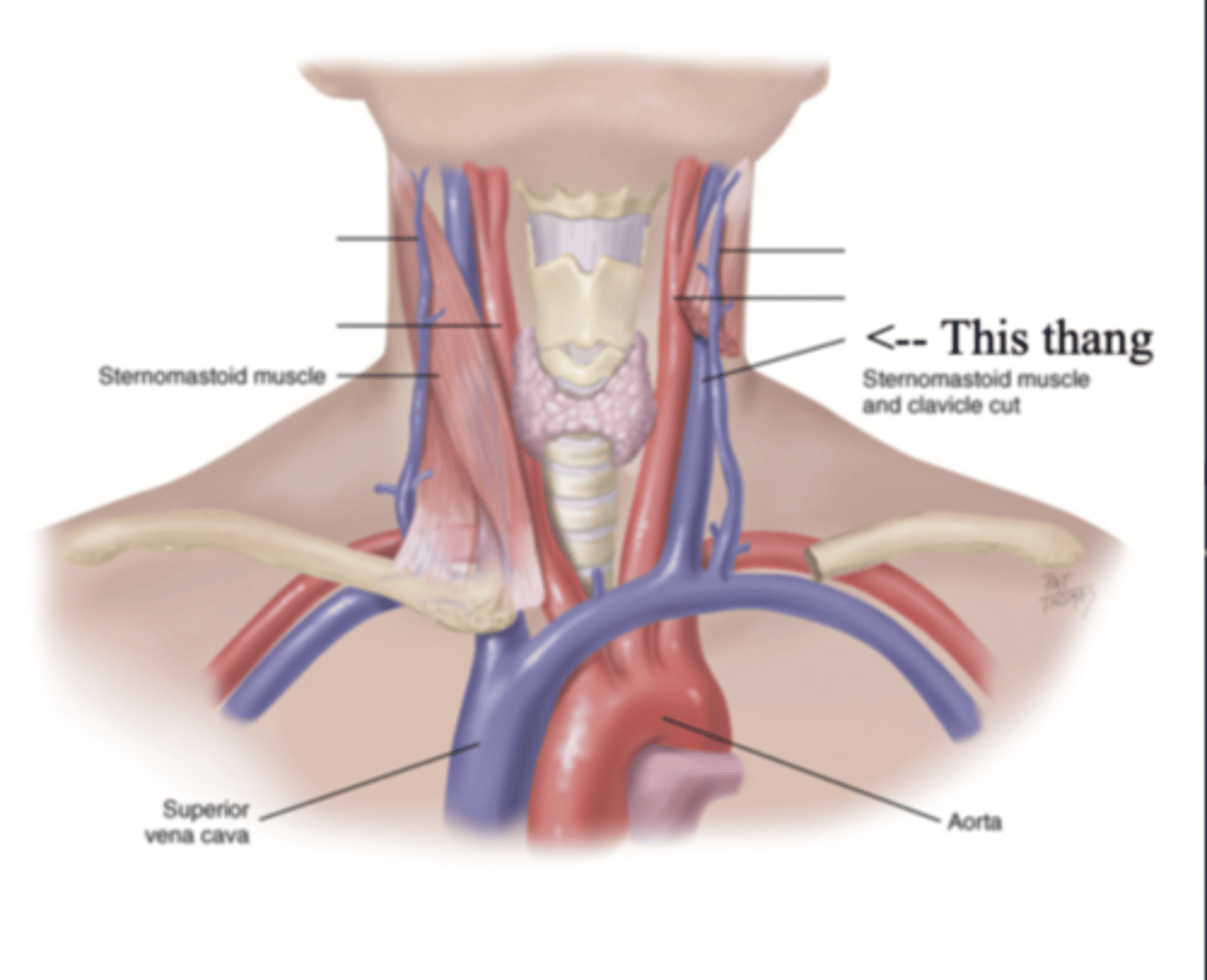
2 Parts of the Jugular Veins
- External
- Internal
External Jugular Veins
The more superficial jugular vein that lies lateral to the sternocleidomastoid and above the clavicle
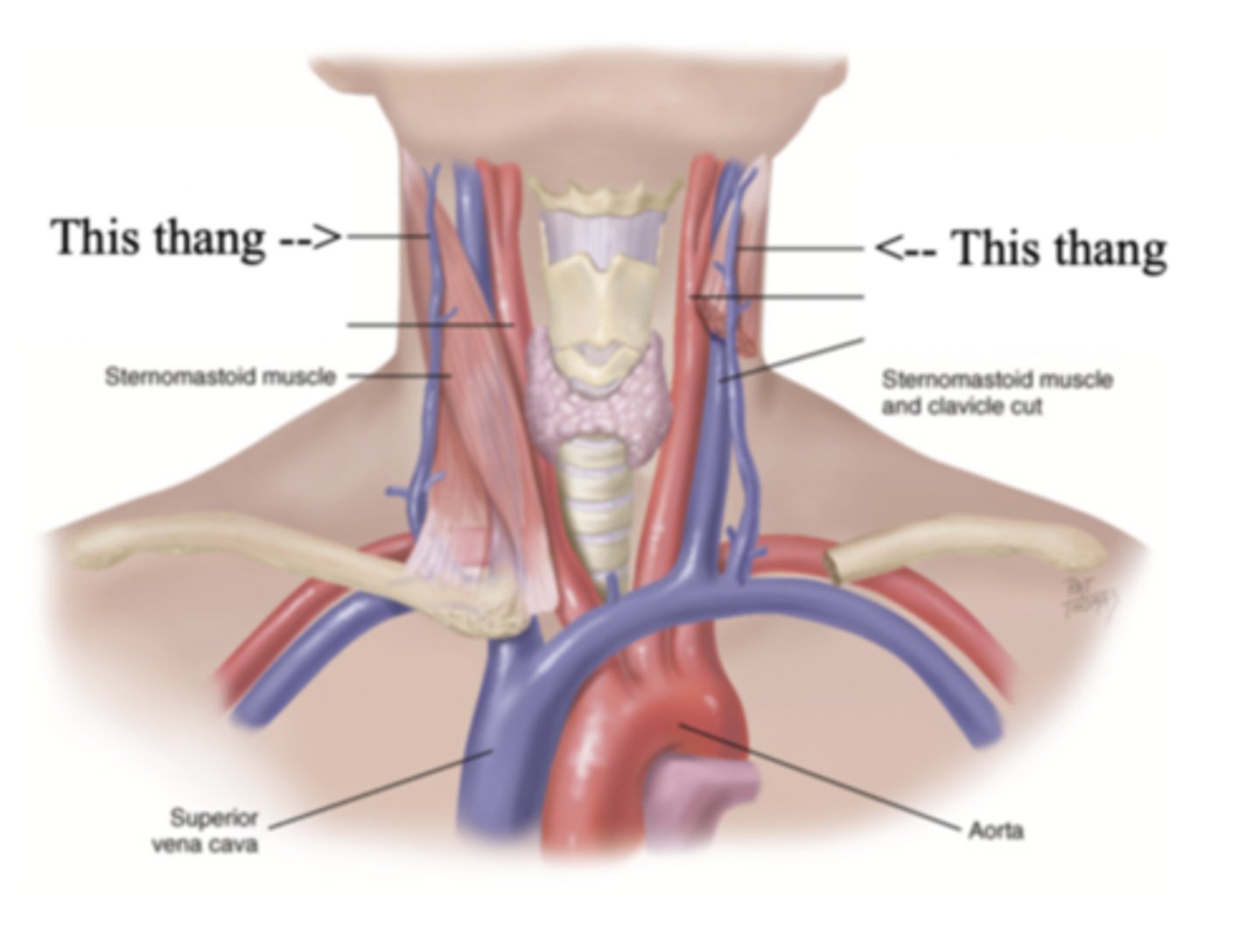
Internal Jugular Veins
The deeper jugular vein that lies medial to the sternocleidomastoid
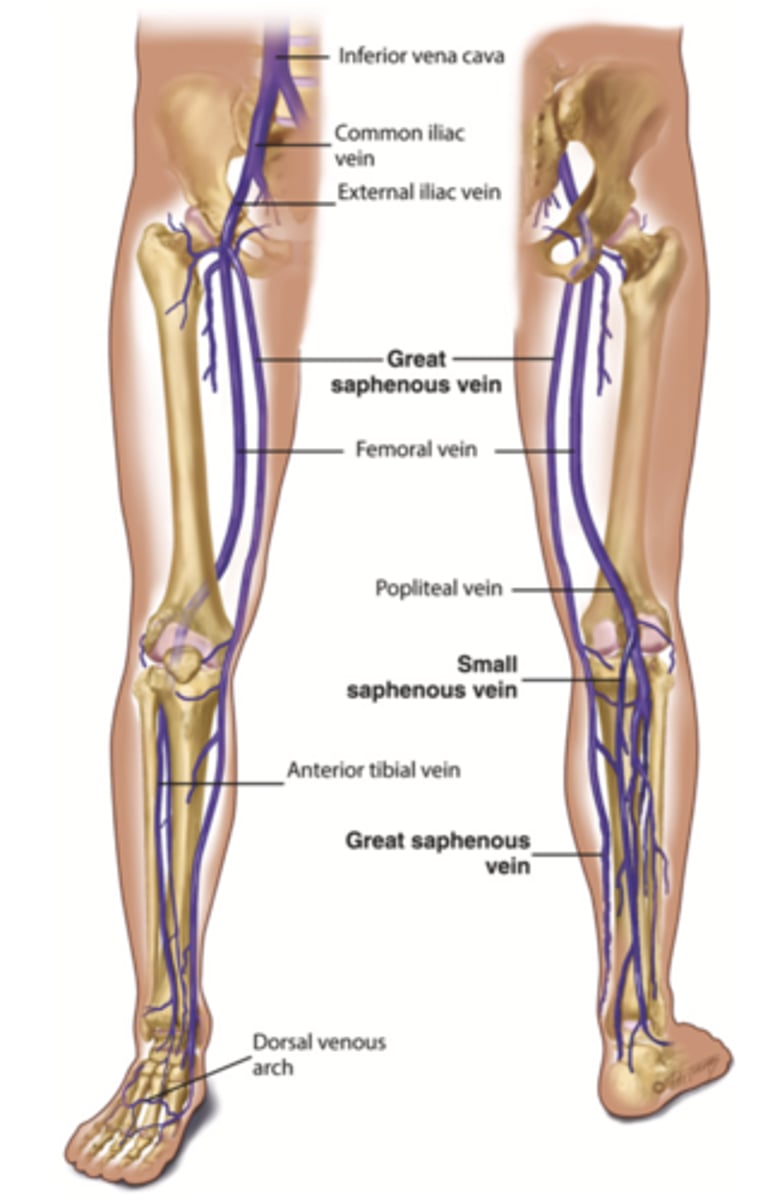
3 Types of Veins in the Leg
- Deep leg
- Superficial leg
- Perforators
The 2 Deep Leg Veins
- Femoral
- Popliteal
Femoral Vein
The deep vein found in the thigh
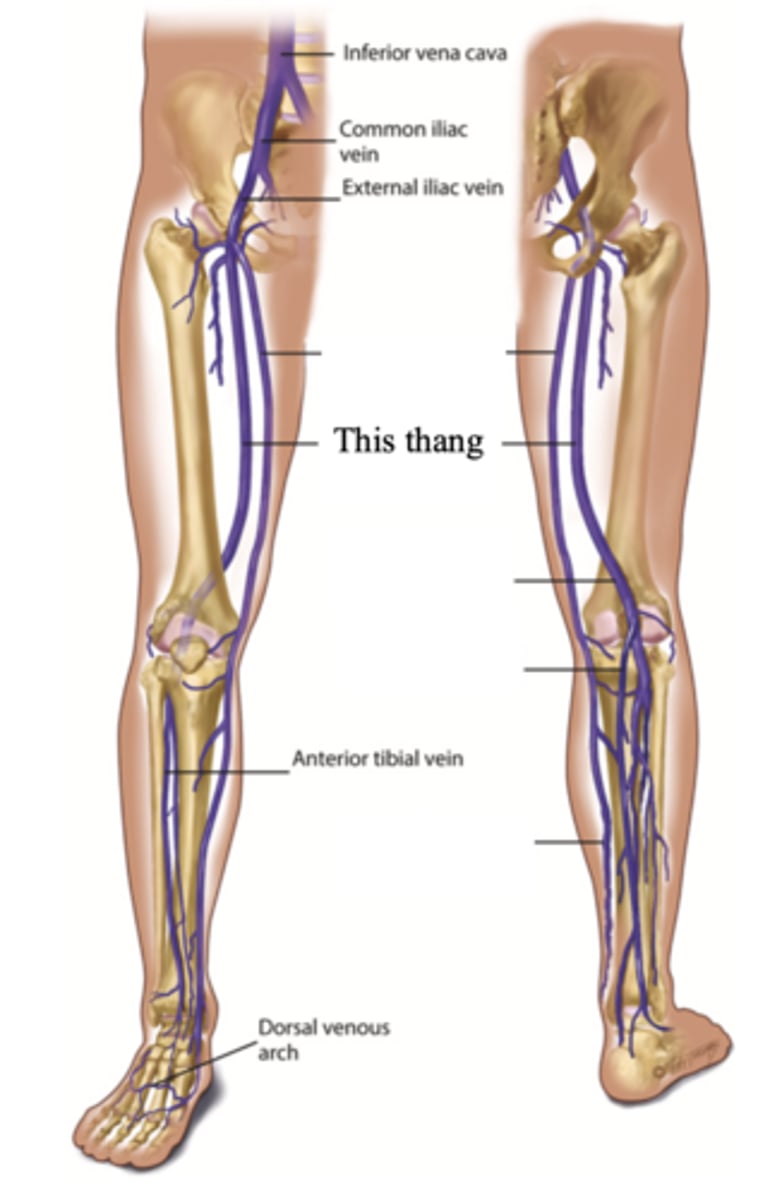
Popliteal Vein
The deep vein found behind the knee
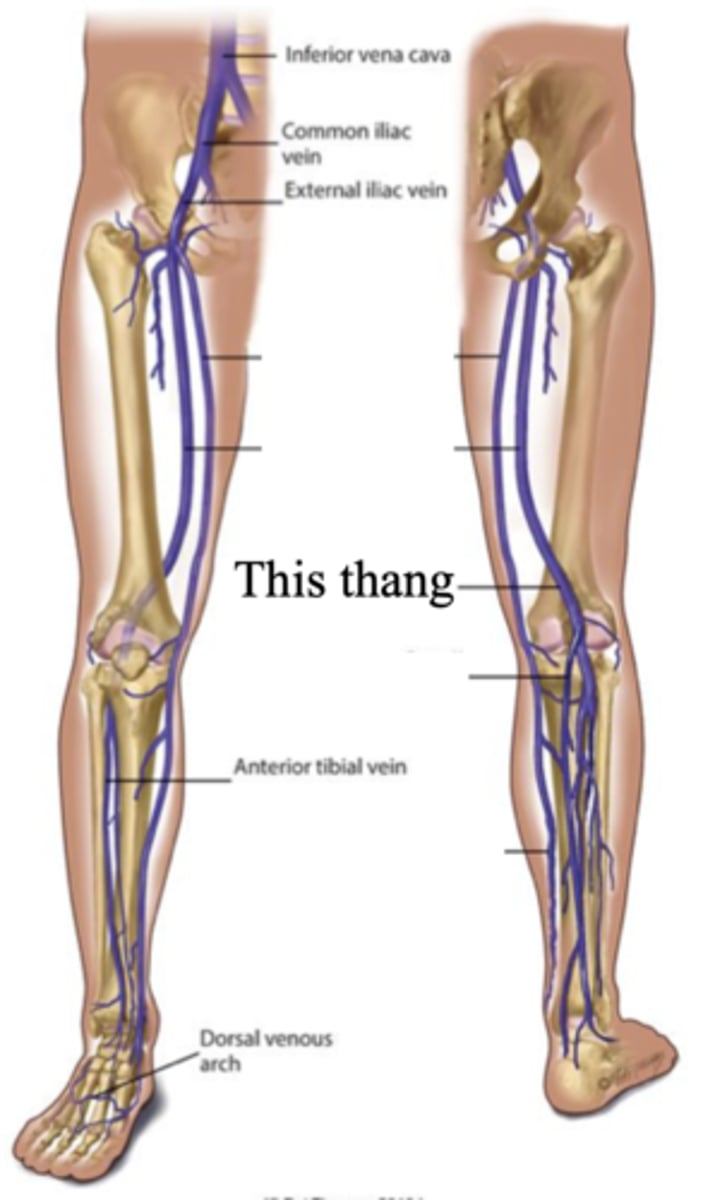
The 2 Superficial Leg Veins
- Great saphenous
- Small saphenous
Great Saphenous Vein
The superficial vein in the leg that starts at the medial side of the dorsum of the foot., then ascends in front of the medial malleolus. It crosses the tibia obliquely and ascends along the medial side of the thigh
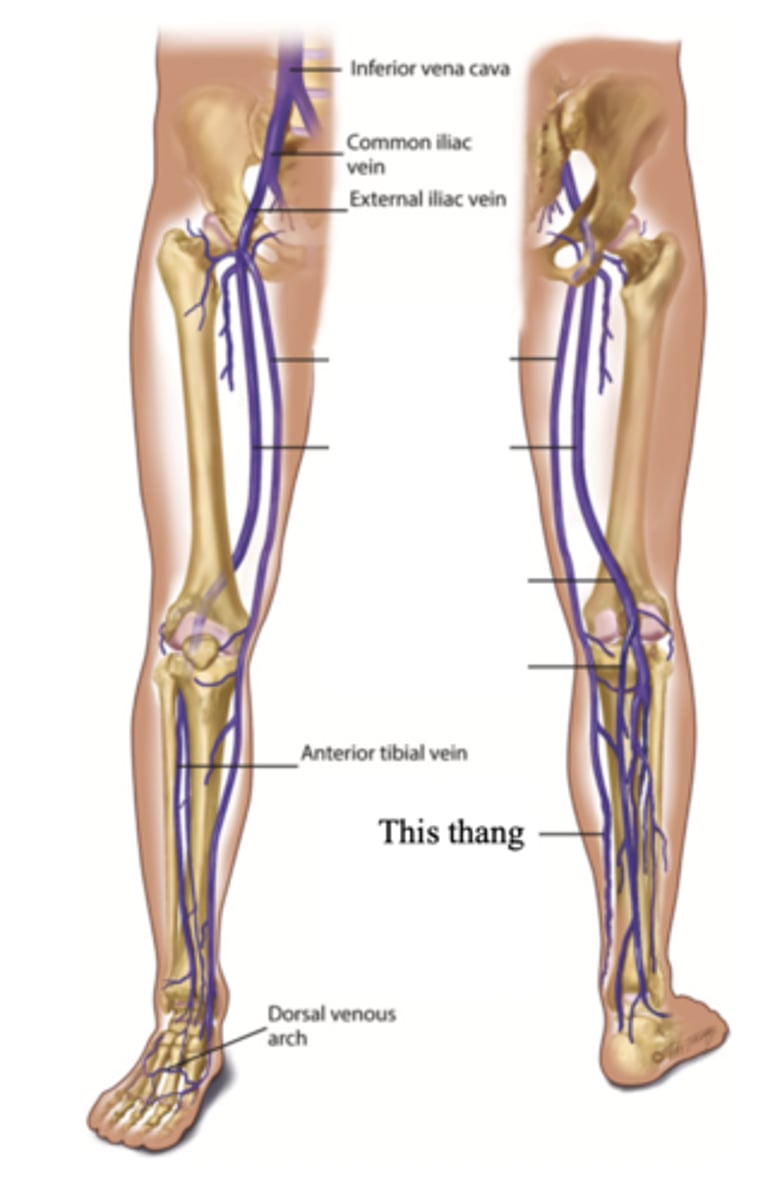
Small Saphenous Vein
The superficial vein in the leg that starts on the lateral side of the dorsum of the foot and ascends behind the lateral malleolus and up the back of the leg, where it joins the popliteal vein
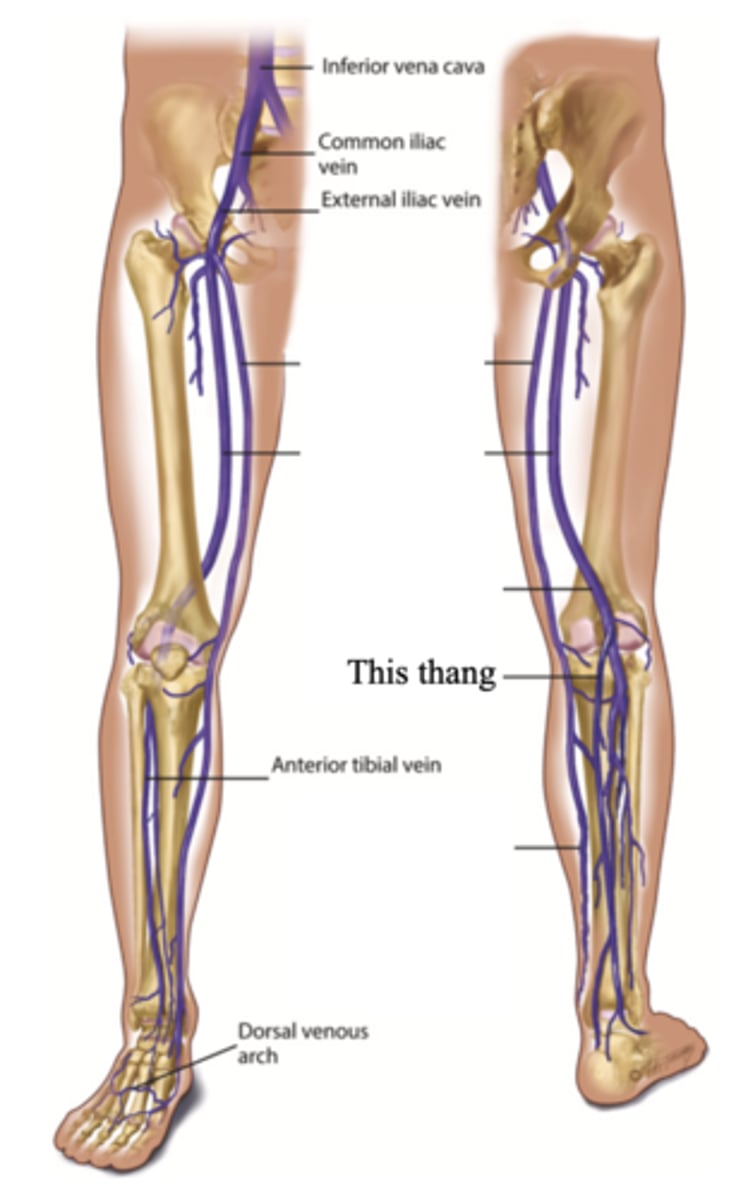
Perforators
Connecting veins that join two sets; connects the superficial veins to the deep veins in the legs
Arteries
- Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
- High-pressure system
Veins
- Blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart
- Low-pressure system
How Venous Blood Flow is Accomplished
1.) Contraction of the skeletal muscles
2.) Pressure gradient caused by breathing
3.) Intraluminal valves
4.) Calf pump
Inspiration decreases . . .
Thoracic pressure
3 multiple choice options
Inspiration increases . . .
Abdominal pressure
3 multiple choice options
Intraluminal Valves
Valves within the veins that opens toward the heart and closes to prevent back flow of blood
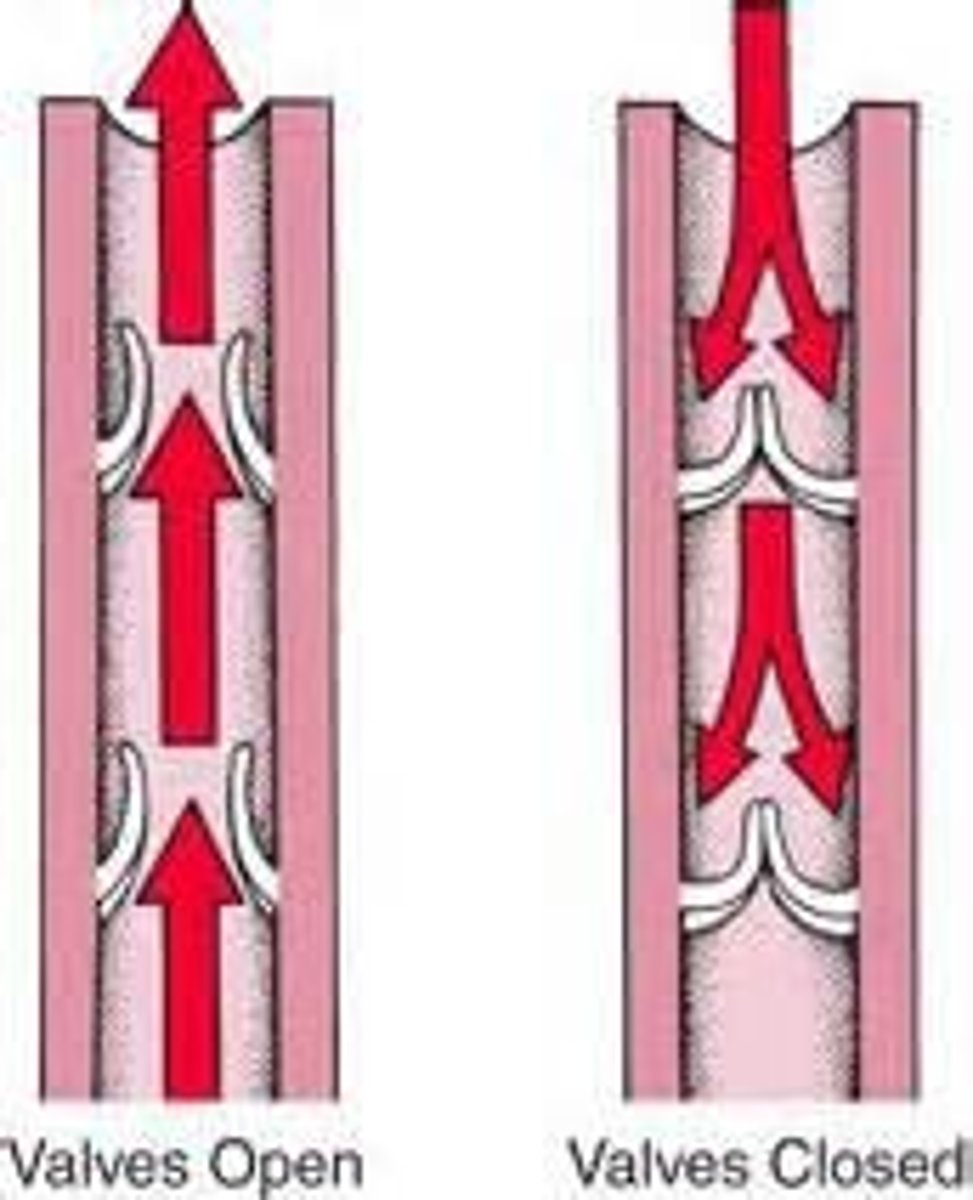
Calf Pump (Peripheral Heart)
The phenomenon that occurs when the calf muscles alternately contract and relax during systole and diastole respectively
The 2 Major Lympathic Vessels
- Right lymphatic duct
- Thoracic duct
Right Lymphatic Duct
The lymphatic vessel that drains the right side of the upper body and empties into the right subclavian vein
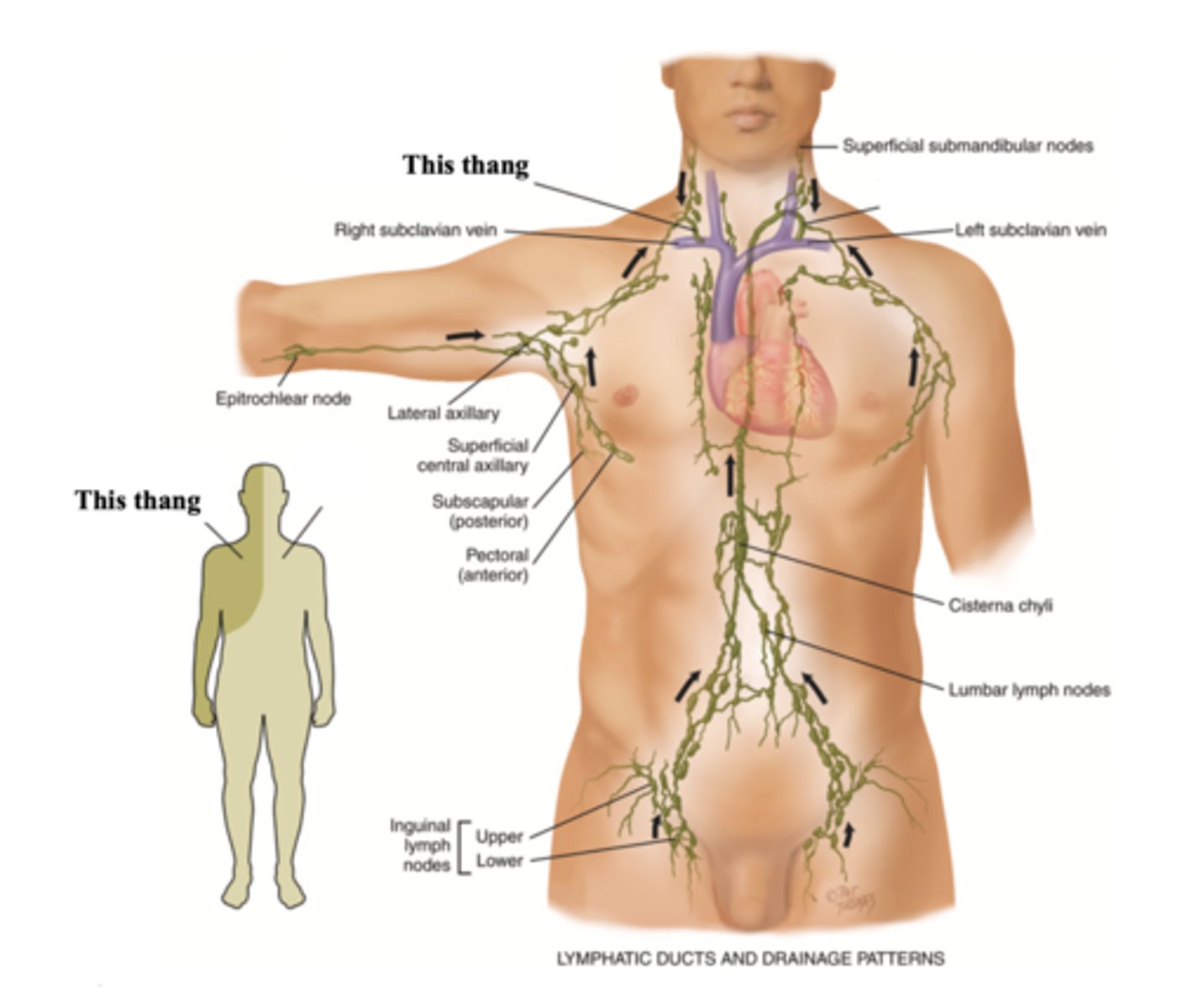
Thoracic Duct
The lymphatic vessel that drains the rest of the body and empties into the left subclavian vein
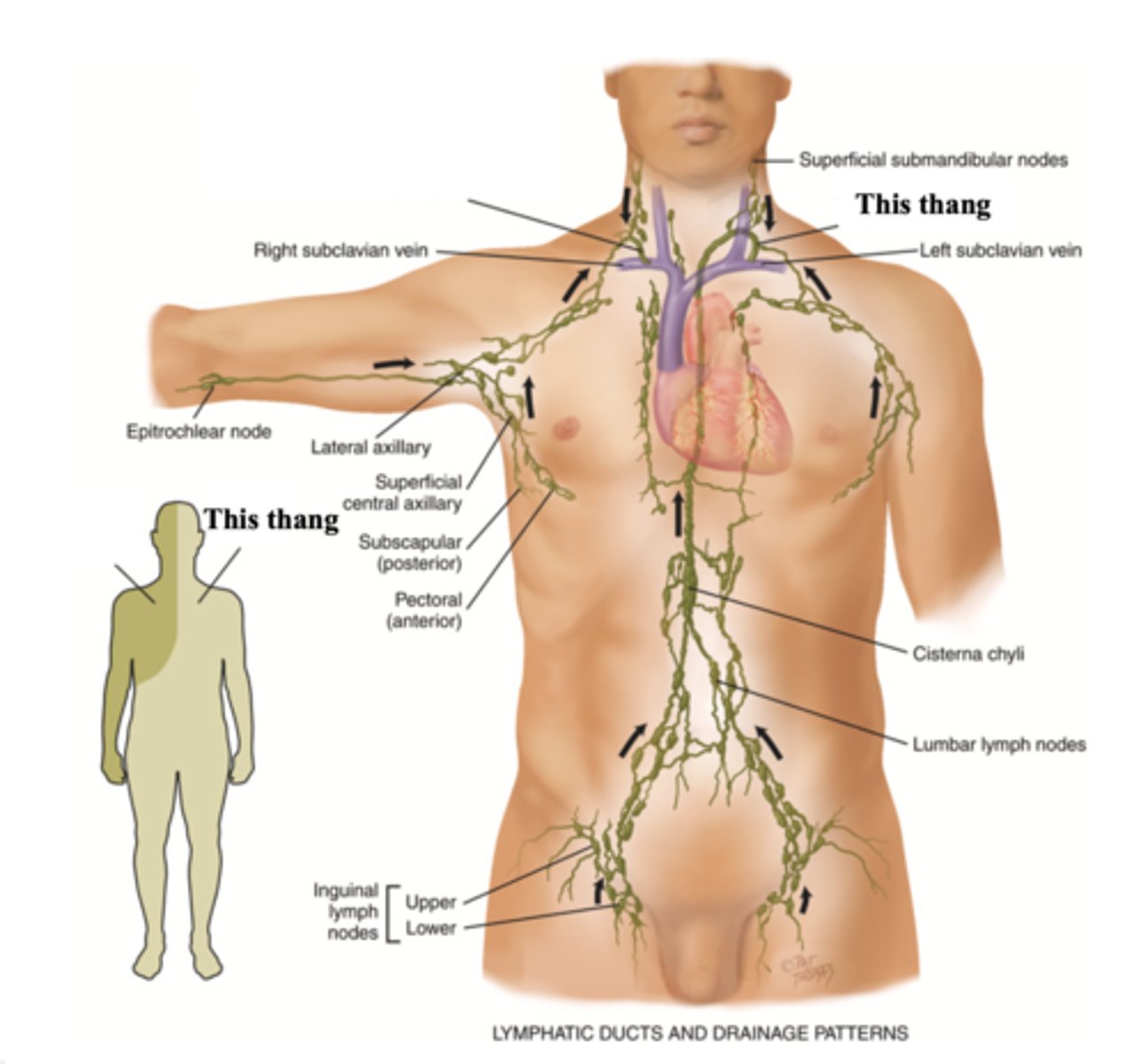
Functions of the Lymphatic System
- Conserve fluid and plasma proteins
- Form a major part of the immune system
- Absorb lipids from the intestinal tract
Major Lymph Nodes
- Cervical
- Axillary
- Epitrochlear
- Inguinal
- Cisterna chyli
Cervical Lymph Nodes (10)
- Preauricular
- Posterior auricular
- Occipital
- Submental
- Submandibular
- Jugulodigastric (tonsil)
- Superficial cervical
- Deep cervical chain
- Posterior cervical
- Supraclavicular
(Party People Often Sell Sardines Just So Dogs Pee Silver)
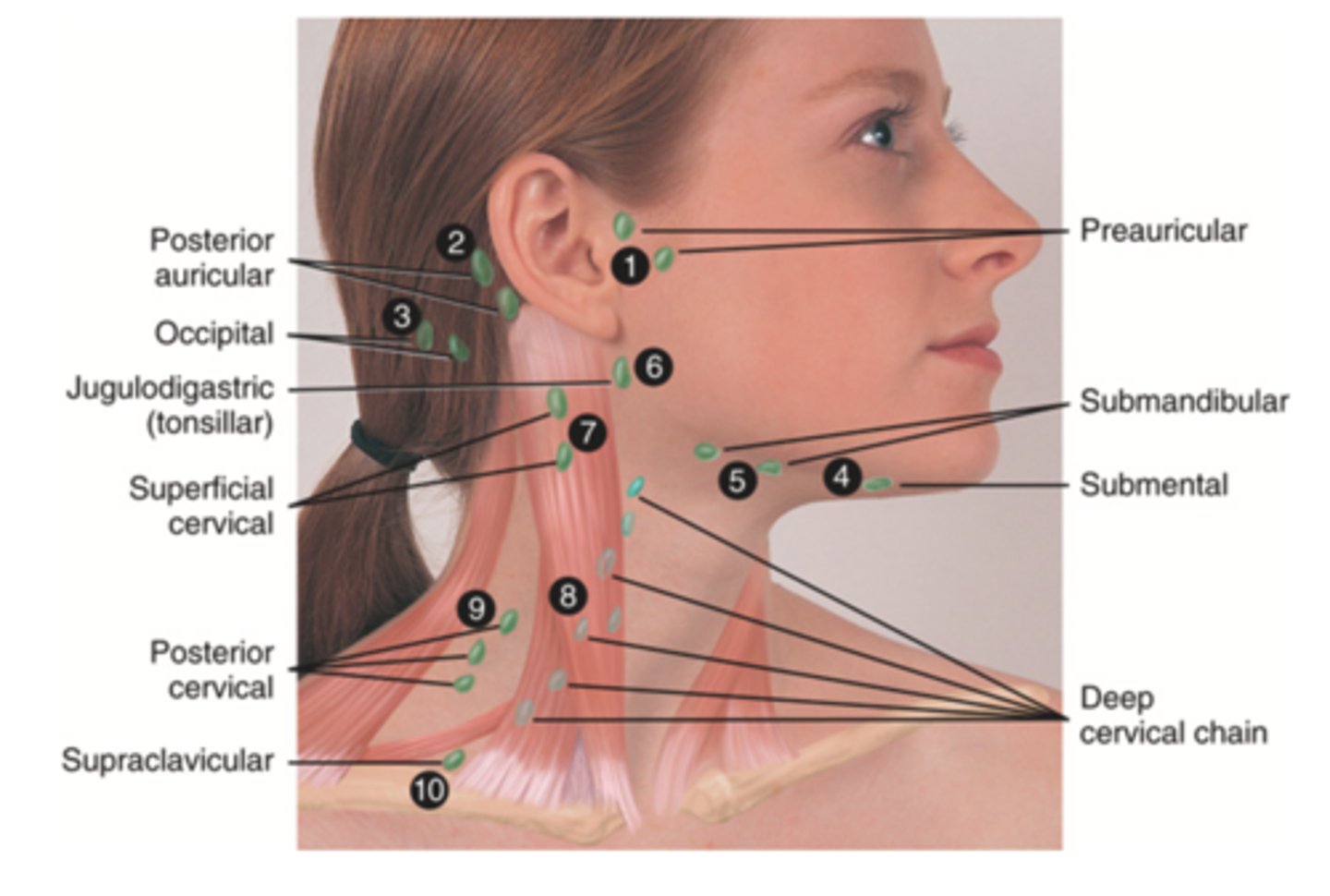
Preauricular Lymph Node
Lymph node in front of the ear (1)
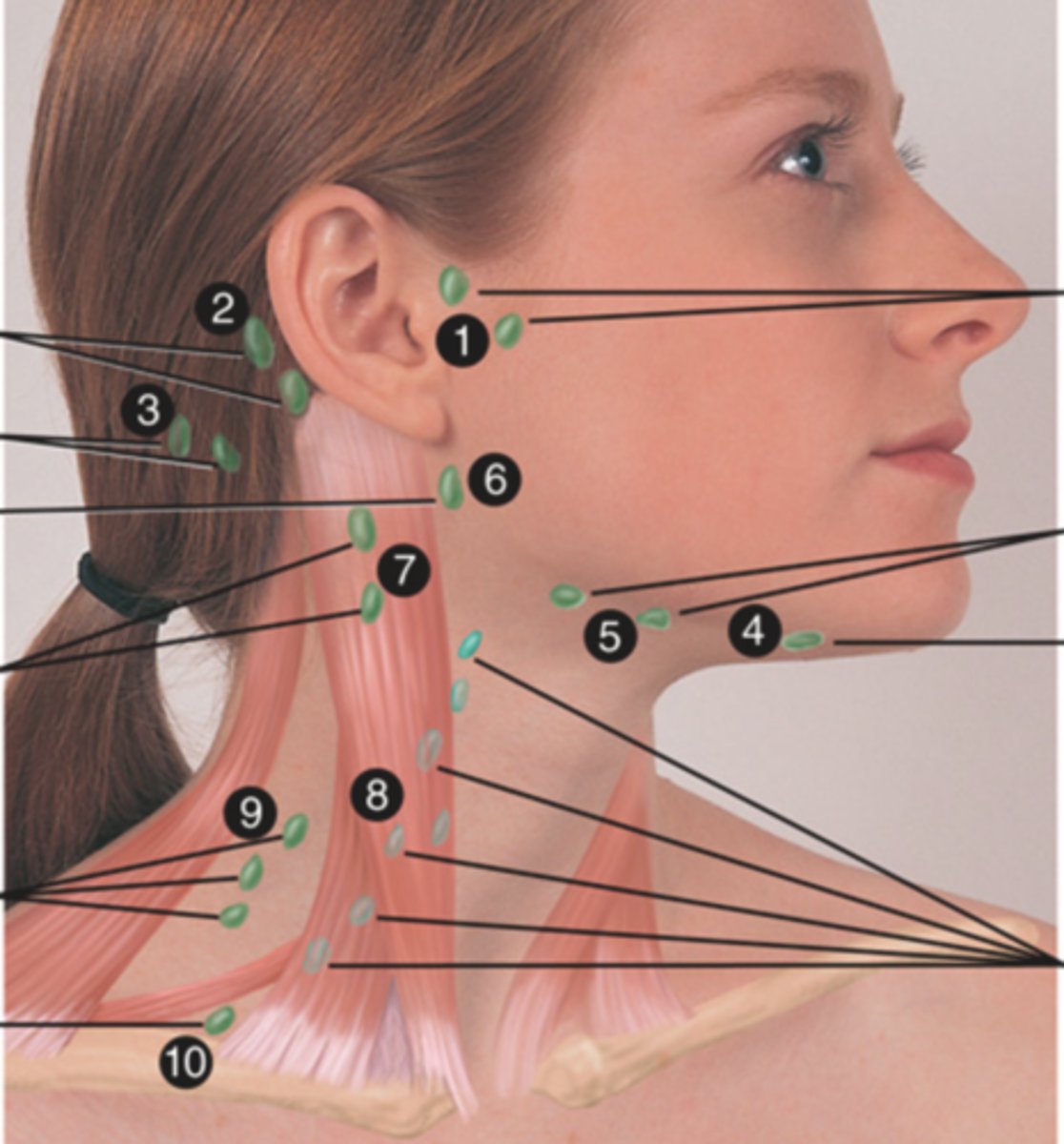
Posterior Auricular Lymph Node
Lymph node behind the ear (2)
Occipital Lymph Node
Lymph node at the base of skull (3)
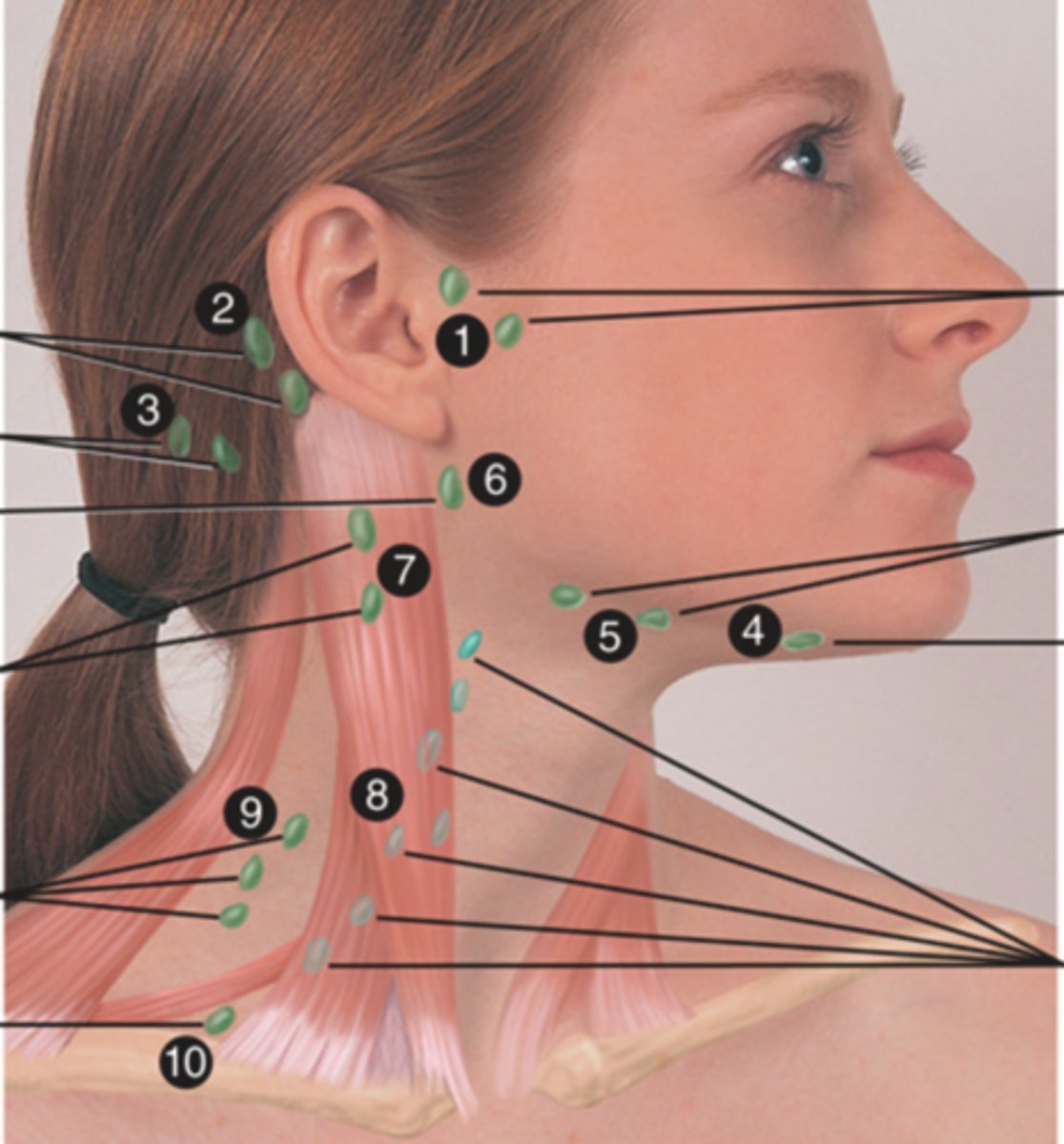
Submental Lymph Node
Lymph node under the chin (4)
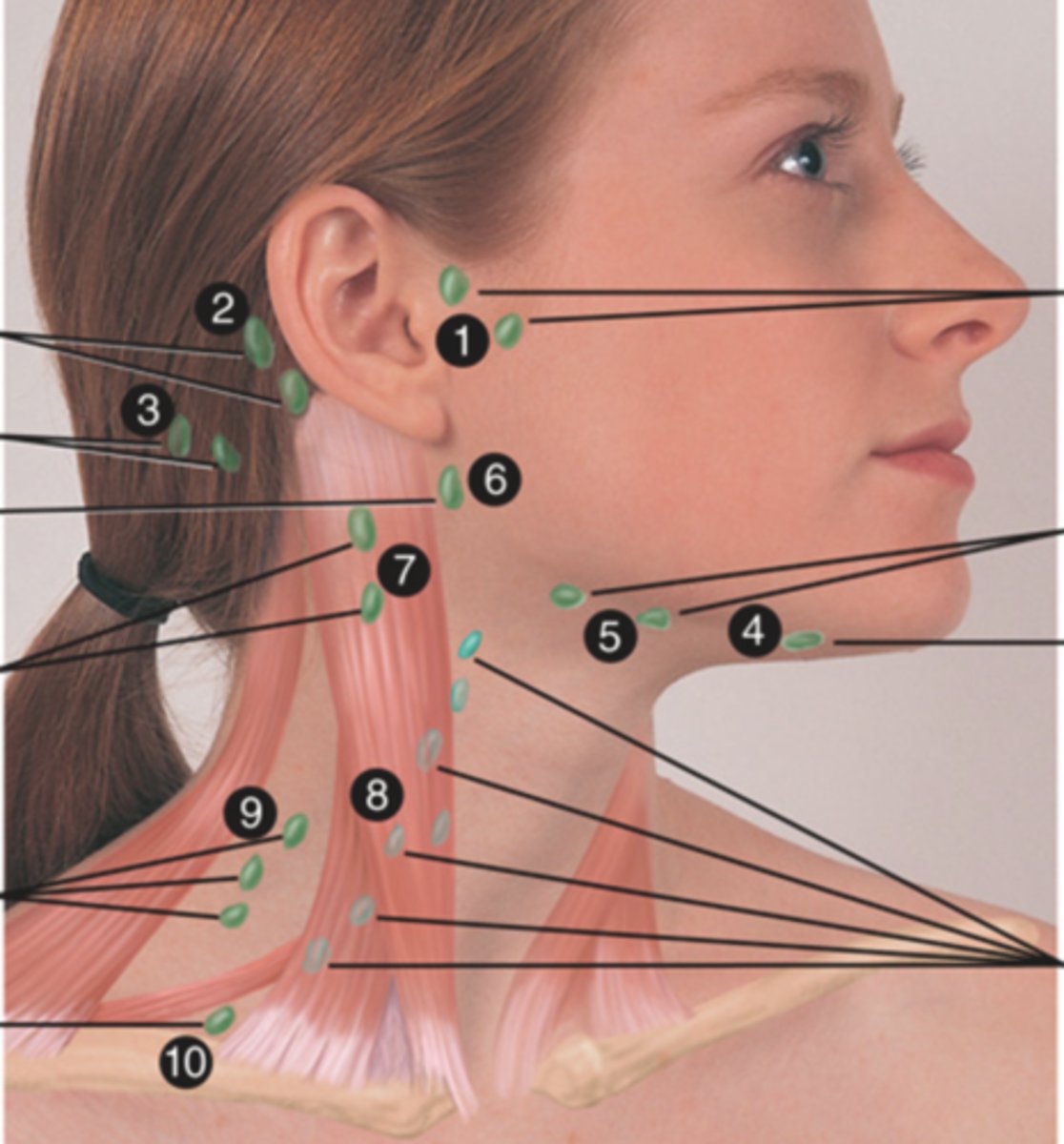
Submandibular Lymph Node
Lymph node along base of mandible (5)
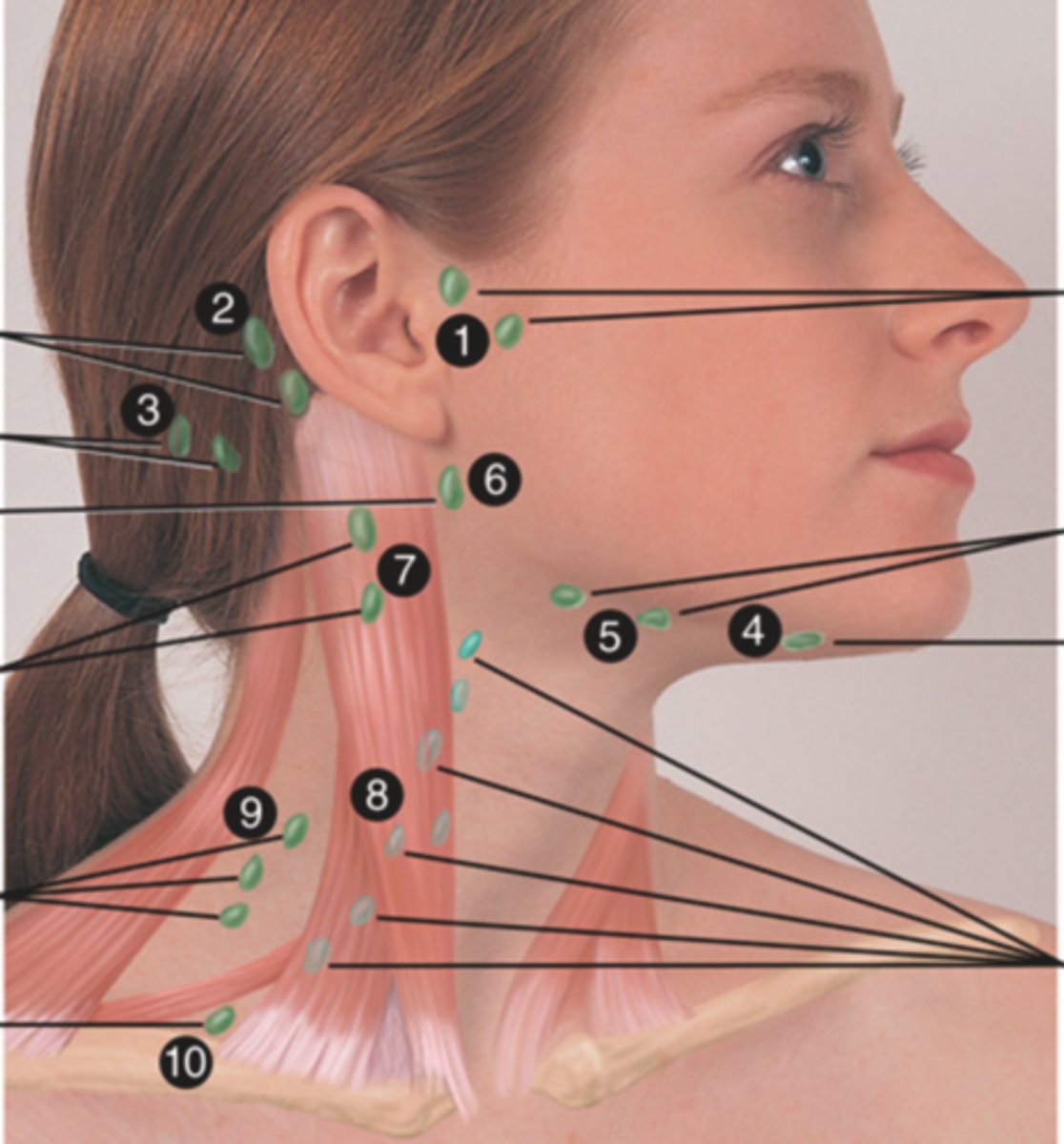
Jugolodigastric (Tonsillar) Lymph Node
Lymph node under the angle of the mandible (6)
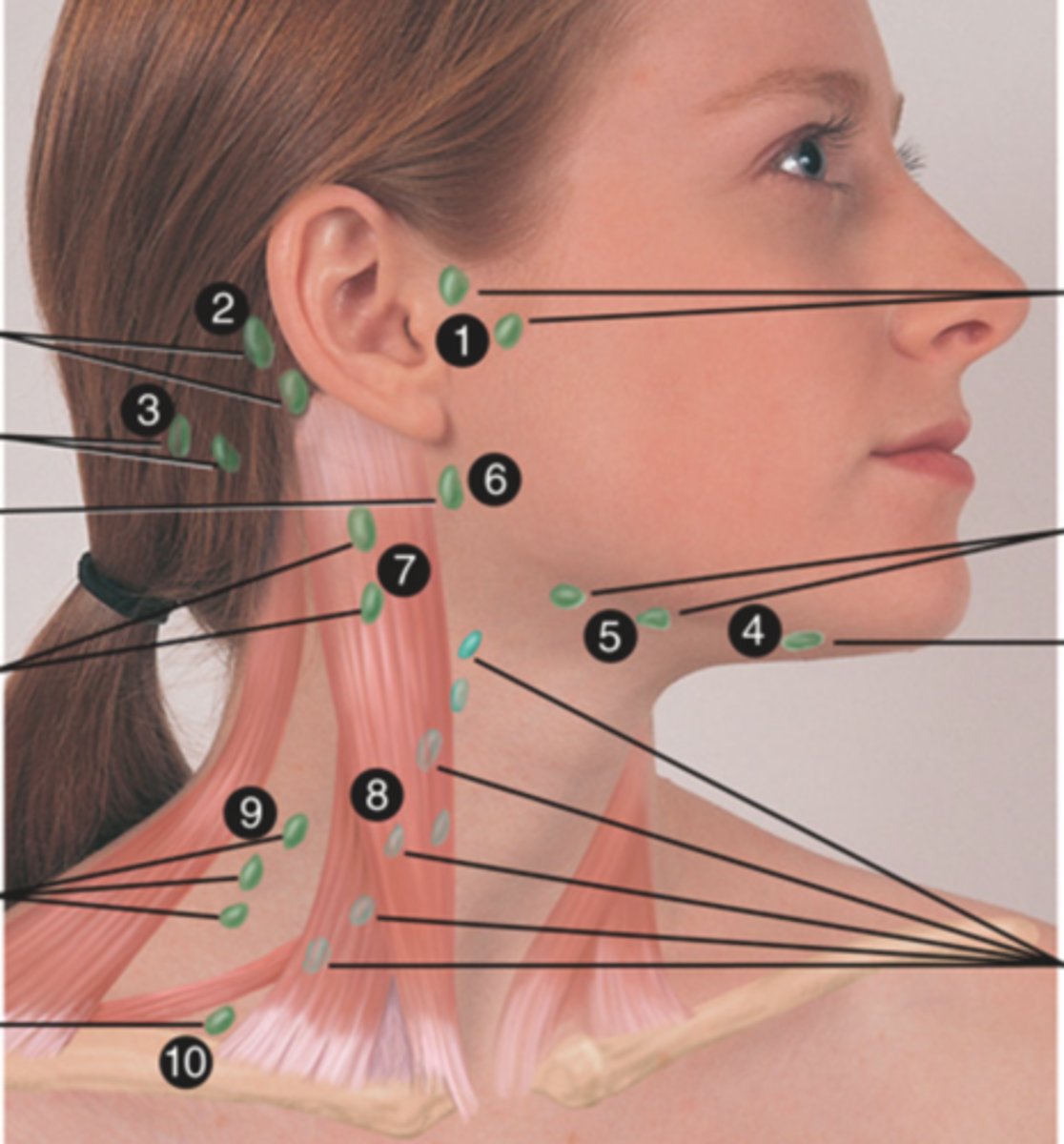
Superficial Cervical Lymph Node
Lymph node overlying the sternomastoid muscle (7); can feel enlarged even when there are no problems
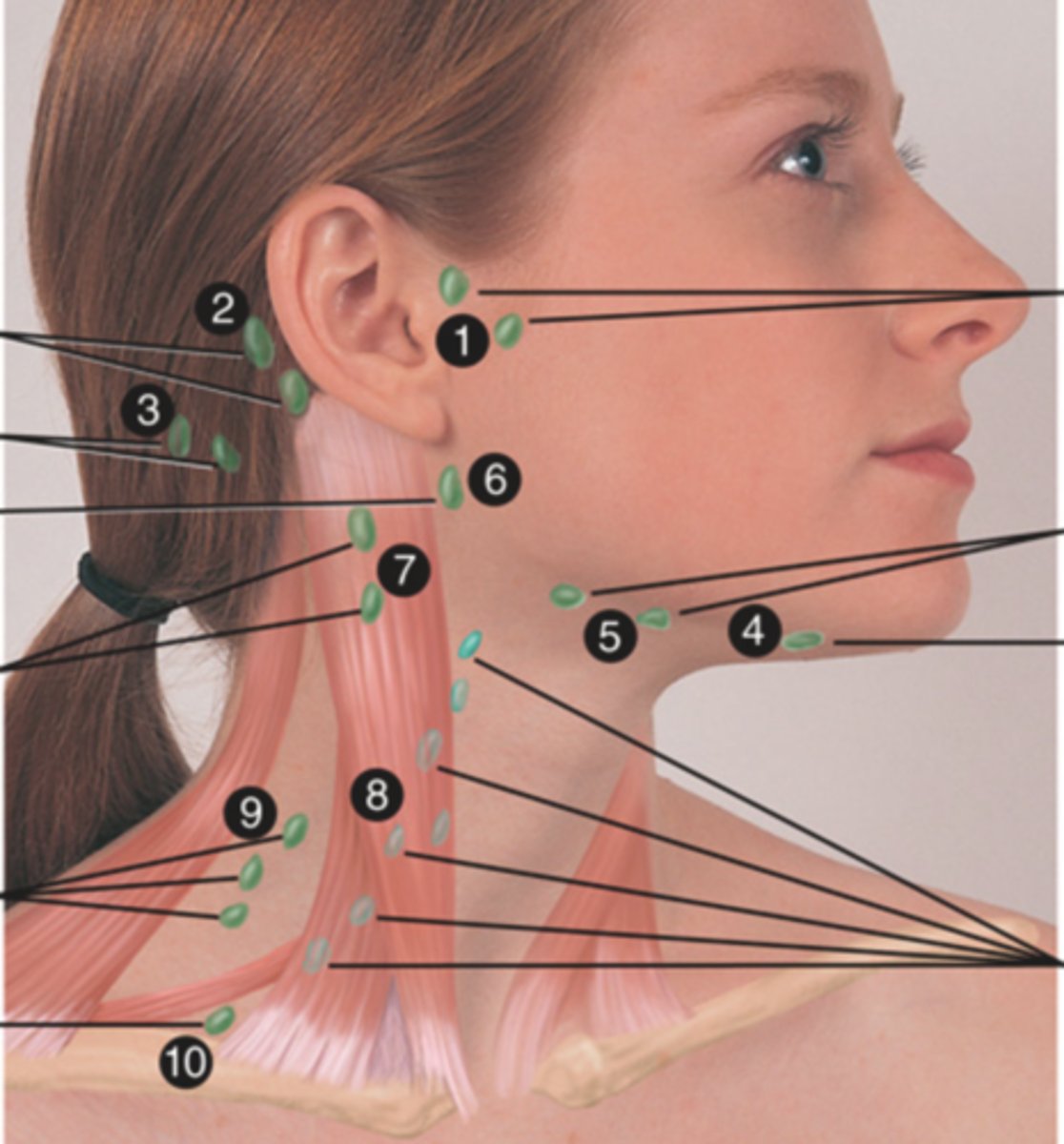
Deep Cervical Chain Lymph Node
Lymph node located on the posterior triangle of the neck (8)
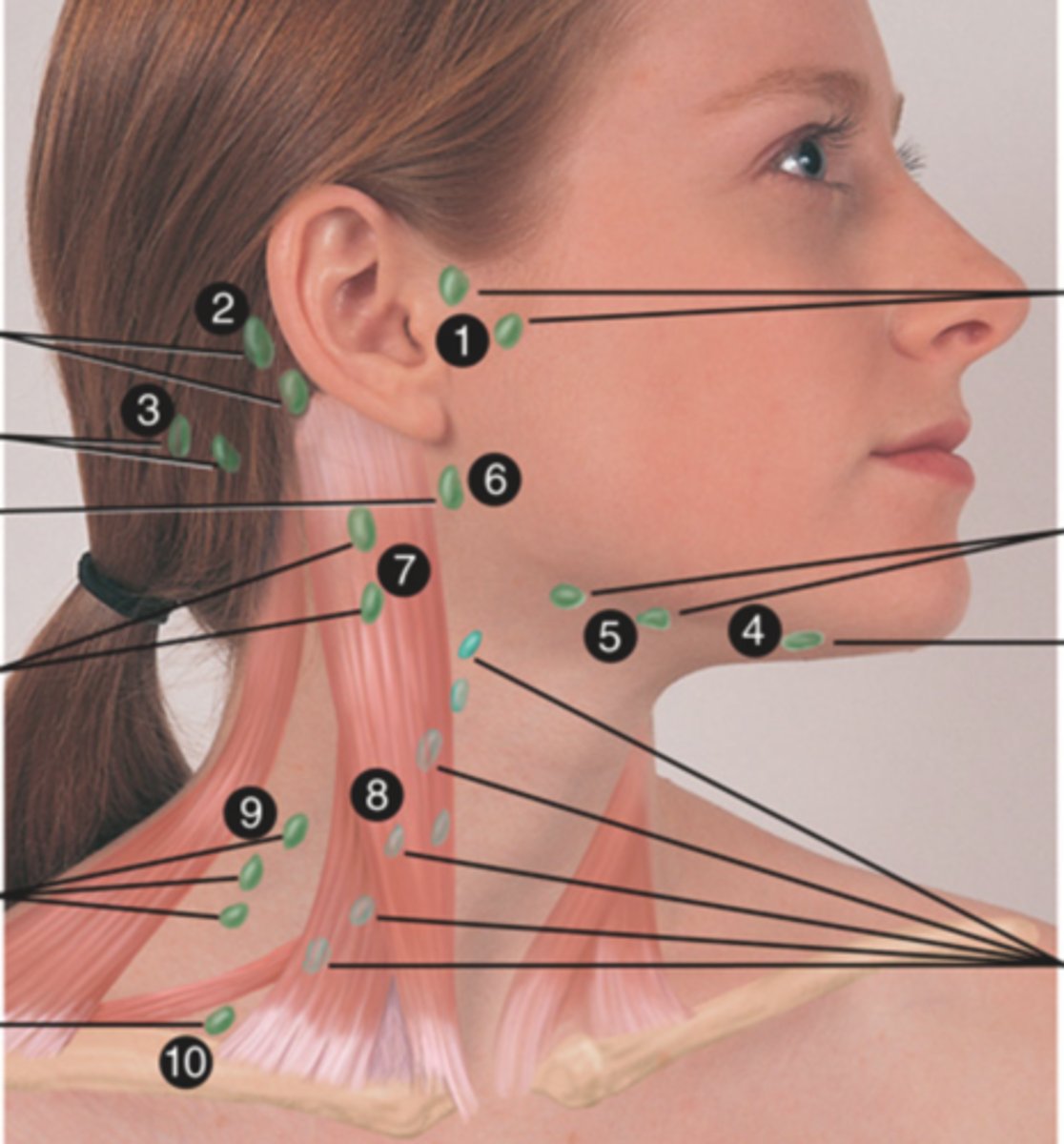
Posterior Cervical Chain Lymph Node
Lymph node in the posterior triangle along the edge of the trapezius muscle (9)
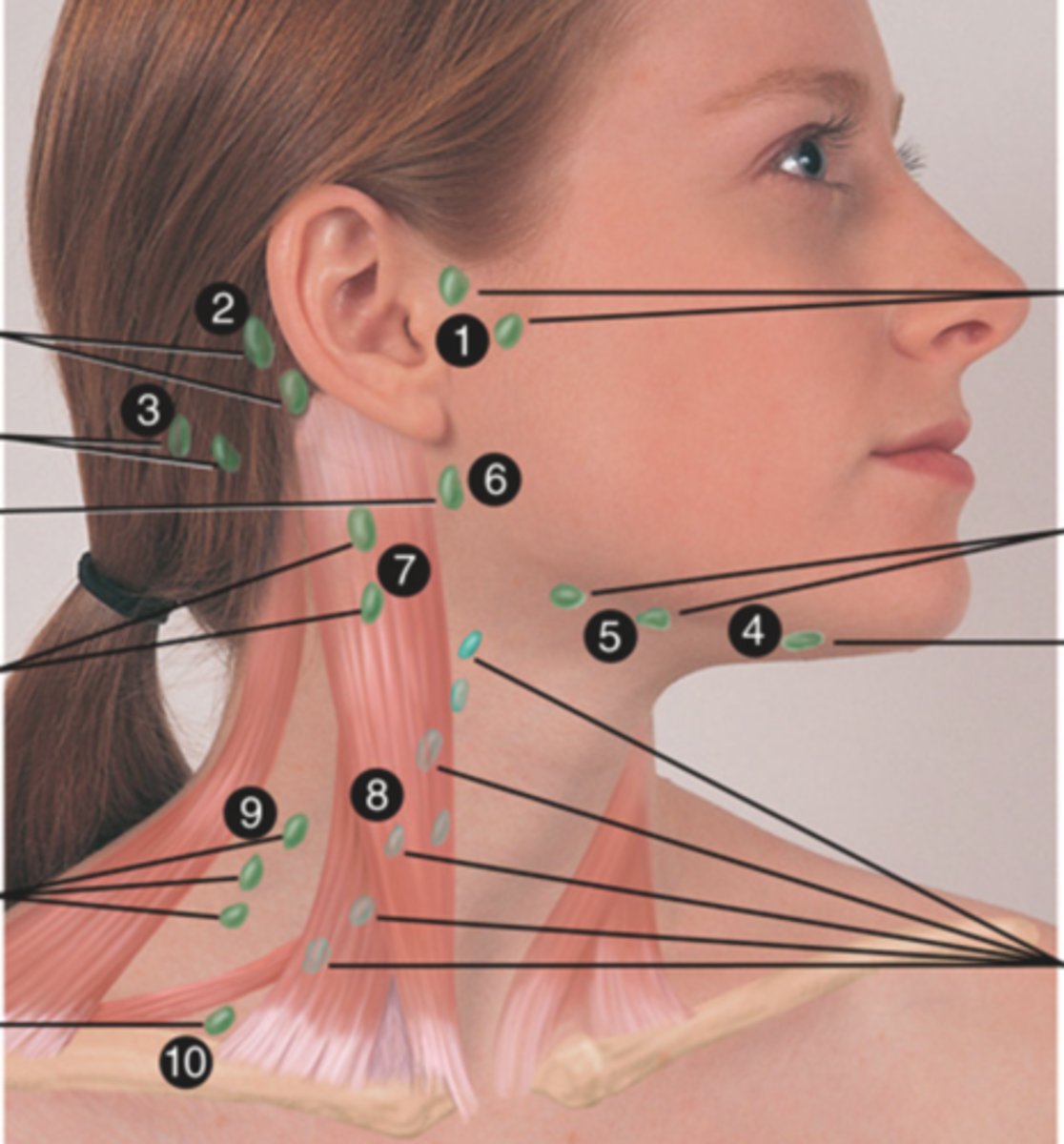
Supraclavicular Lymph Node
Lymph node just above and behind the clavicle, at the sternomastoid muscle (10)
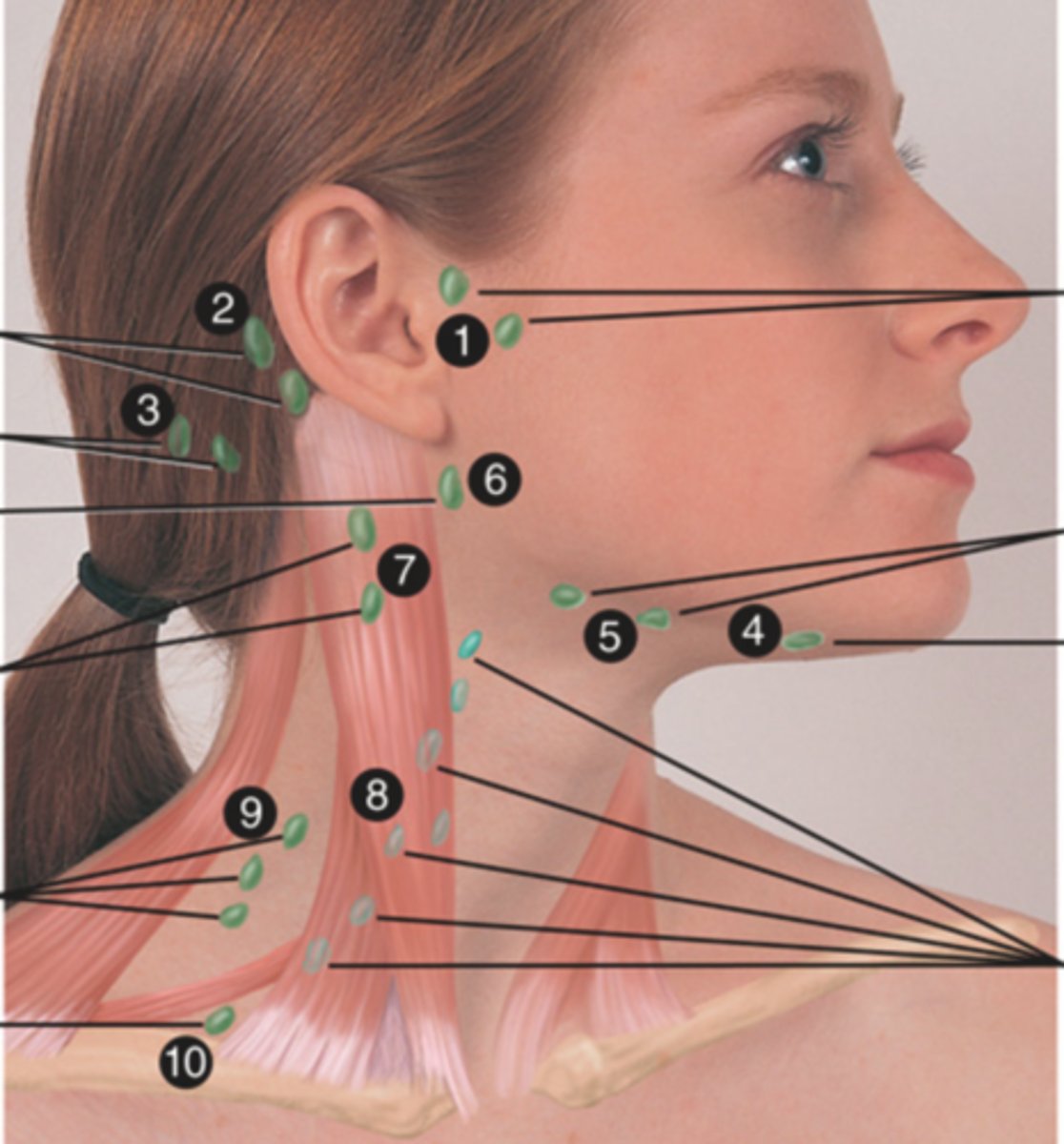
Axillary Lymph Node
The superficial lymph node in the armpit
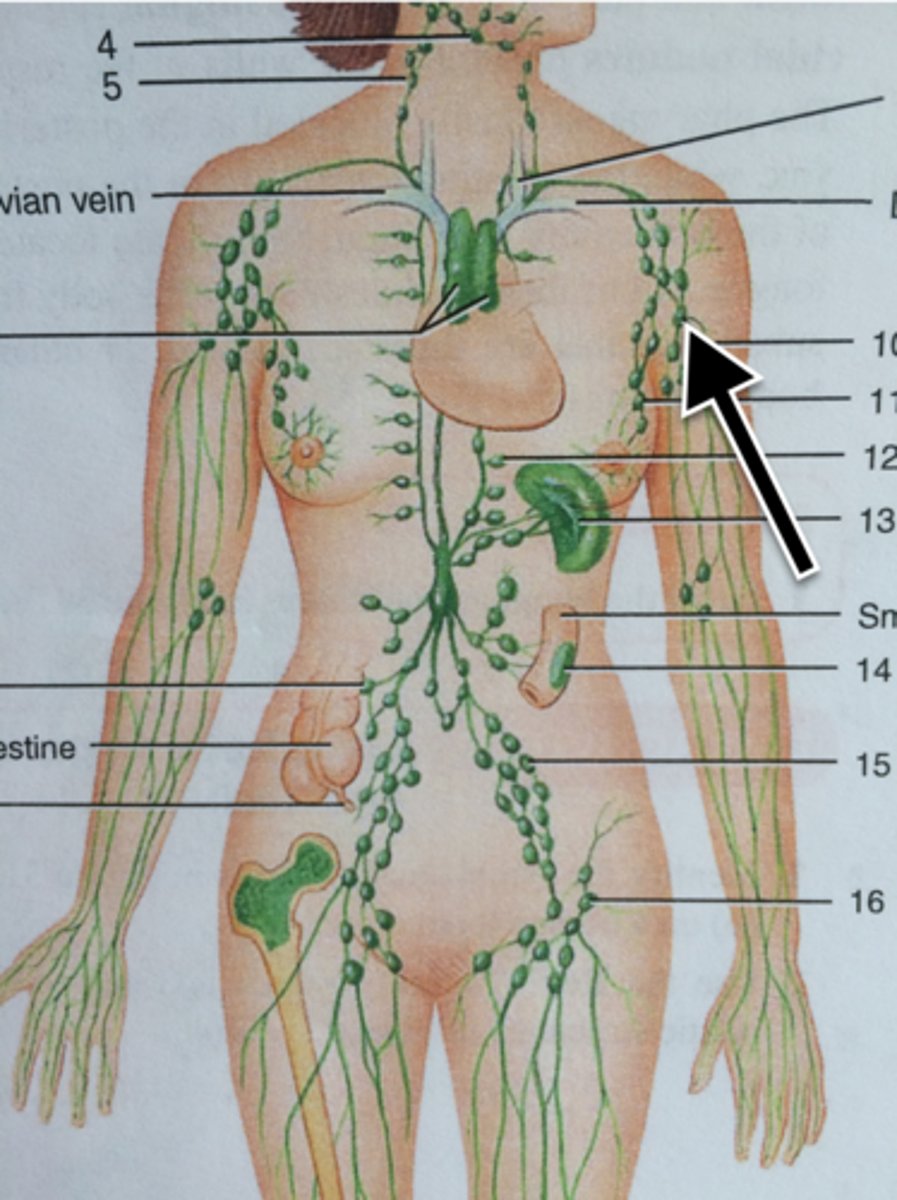
Epitrochlear Lymph Node
The lymph node in the depression above and behind the medial condyle of humerus; normally not palpable
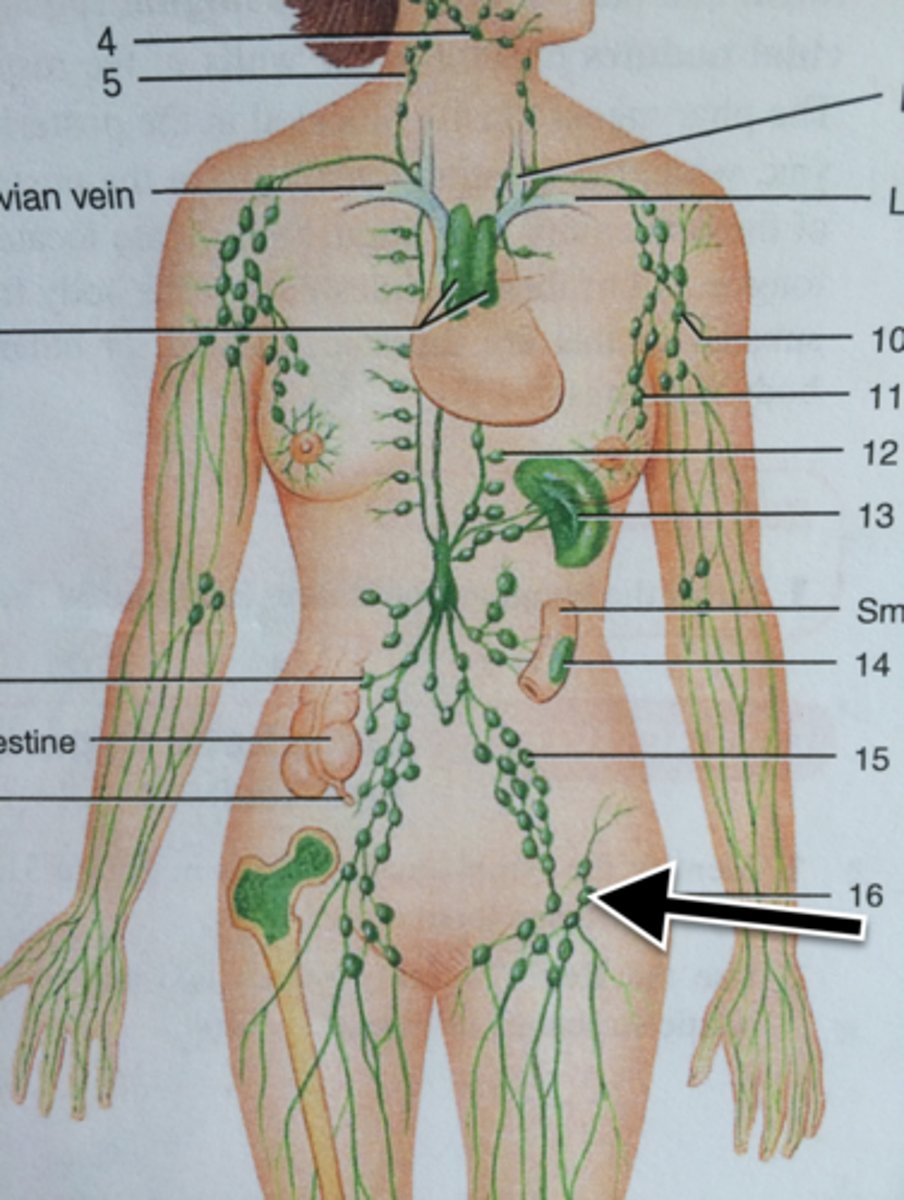
Inguinal Lymph Node
Superficial lymph node located on the upper inner thigh
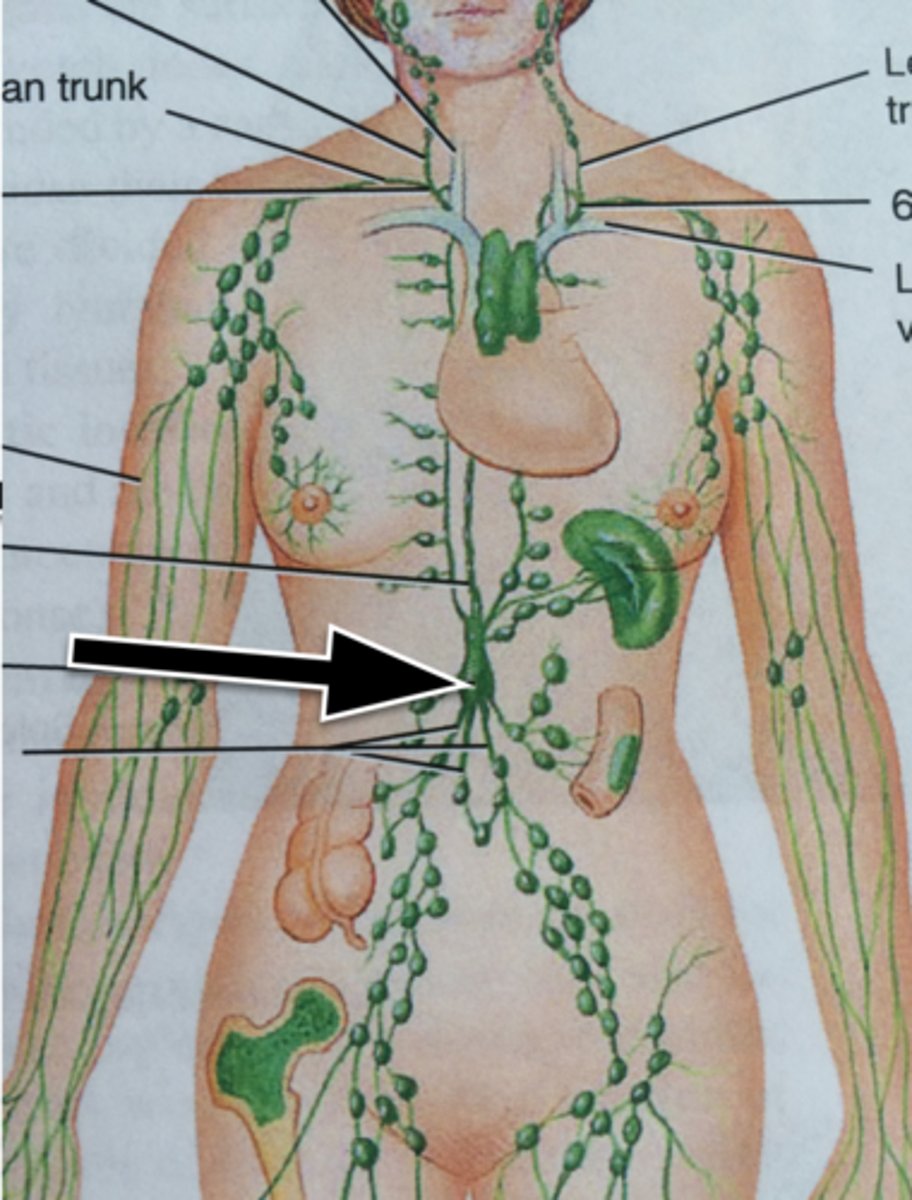
Cisterna Chyli
An enlarged pouch on the thoracic duct that serves as a storage area for lymph moving toward its point of entry into the venous system
4 Functions of the Spleen
- Destroy old RBC
- Produce antibodies
- Store RBCs
- Filter micro-organisms from blood
Tonsils
Masses of lymphatic tissue in the back of the oropharynx; reacts to local inflammation
The 3 Tonsils in the Mouth
- Palatine
- Adenoid
- Lingual
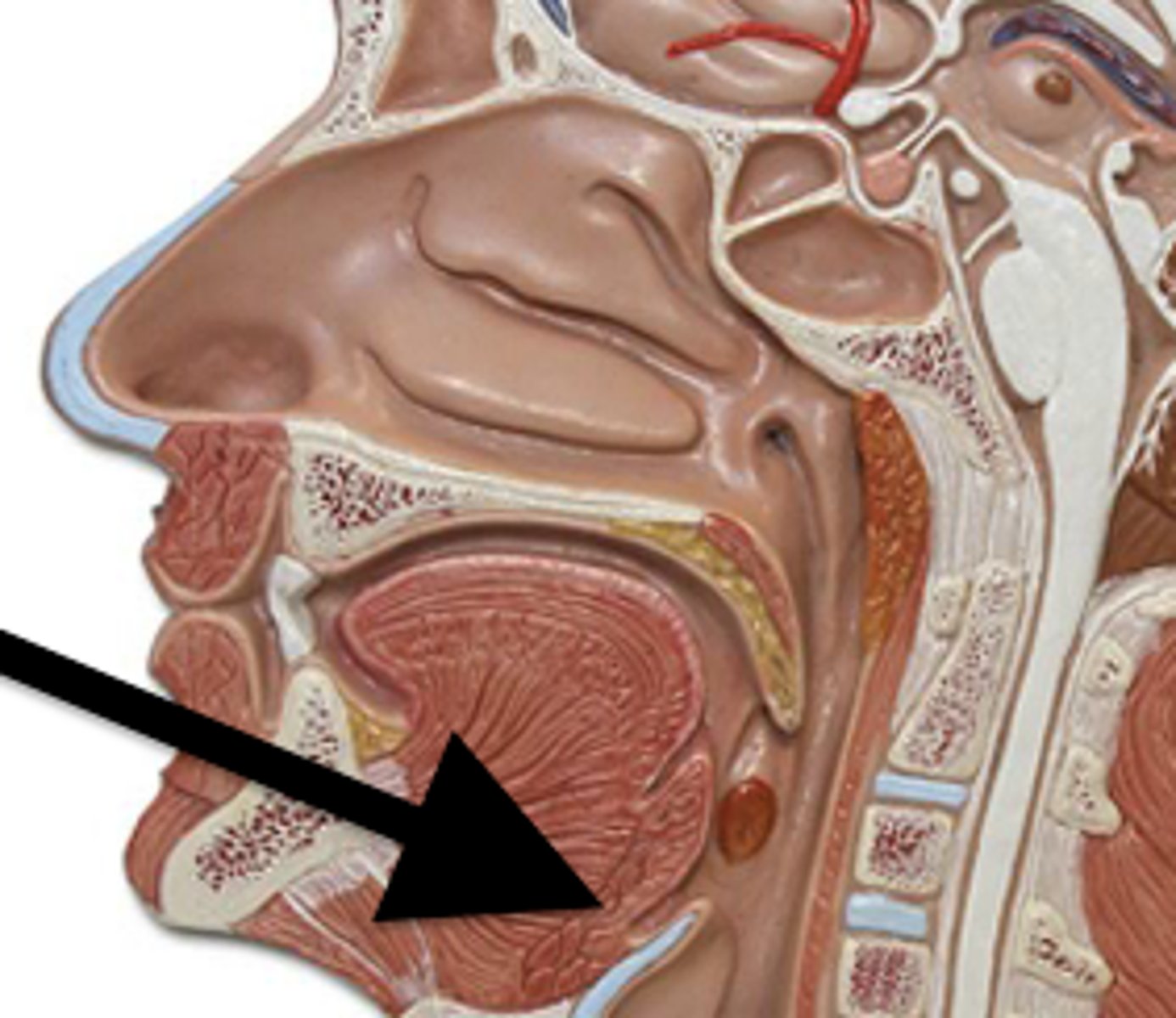
Palatine Tonsil
One of a pair of almond-shaped masses of lymphatic tissue in the oropharynx
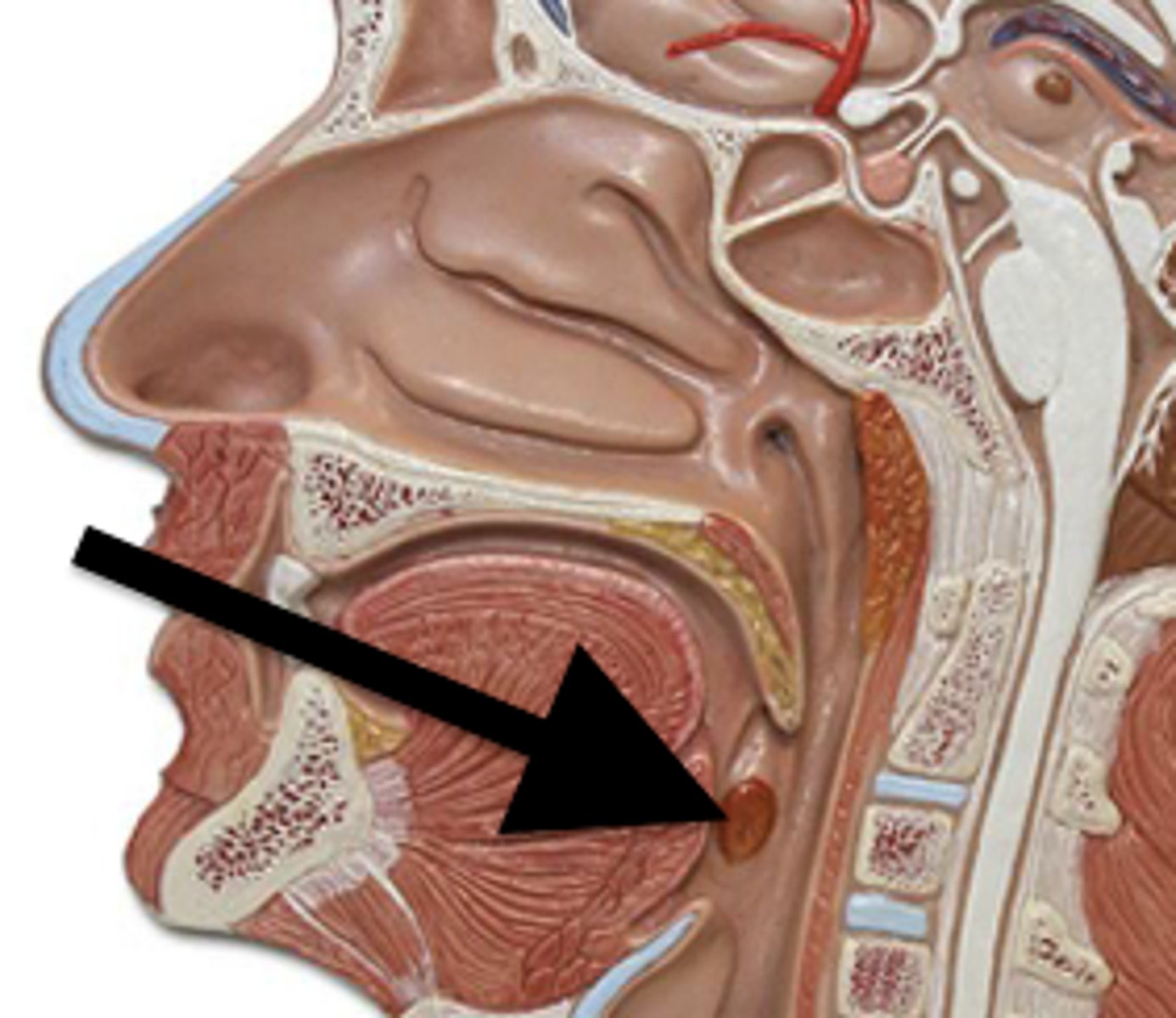
Adenoid Tonsil
Pharyngeal tonsil
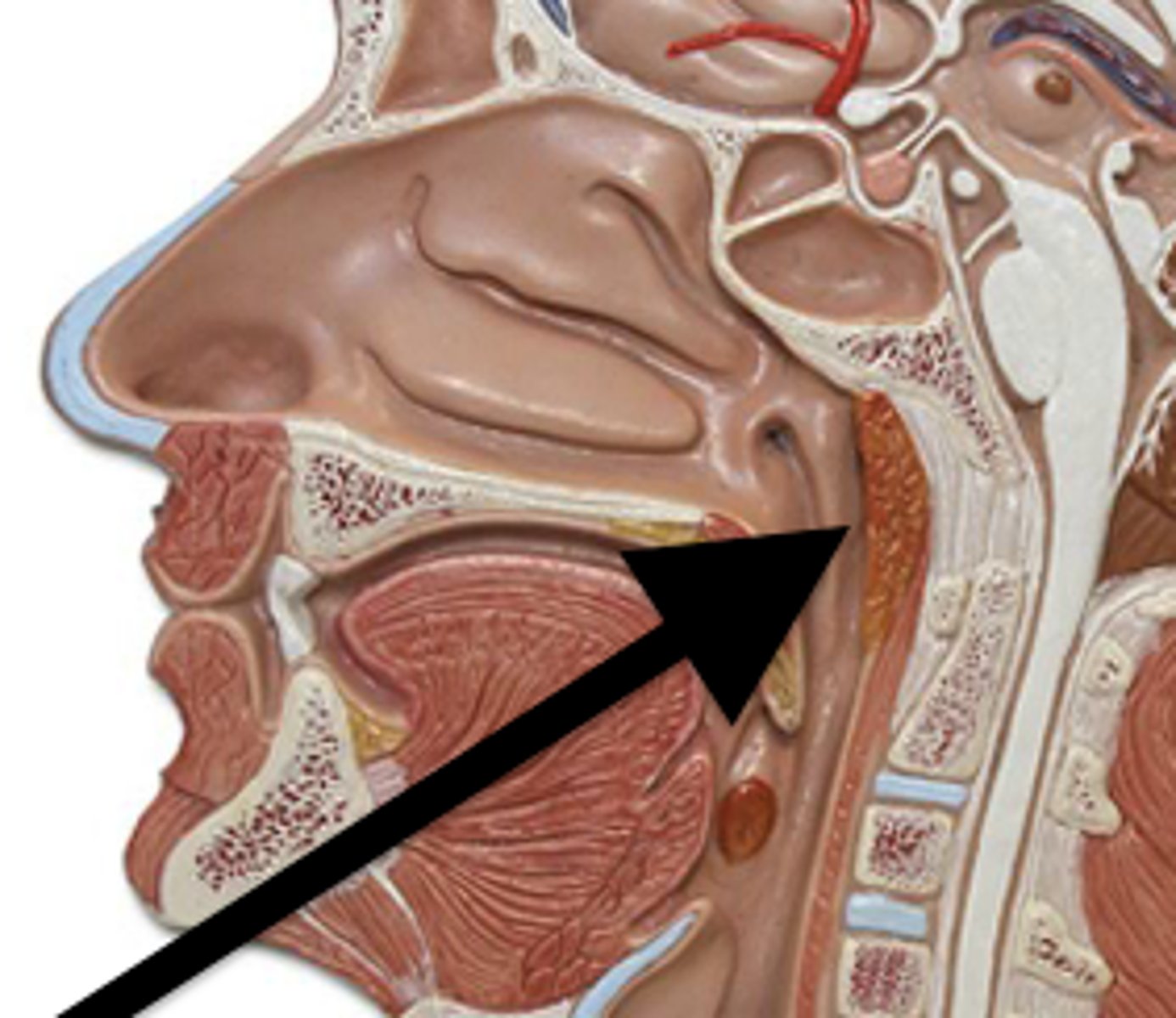
Lingual Tonsil
Tonsil located at the base of tongue
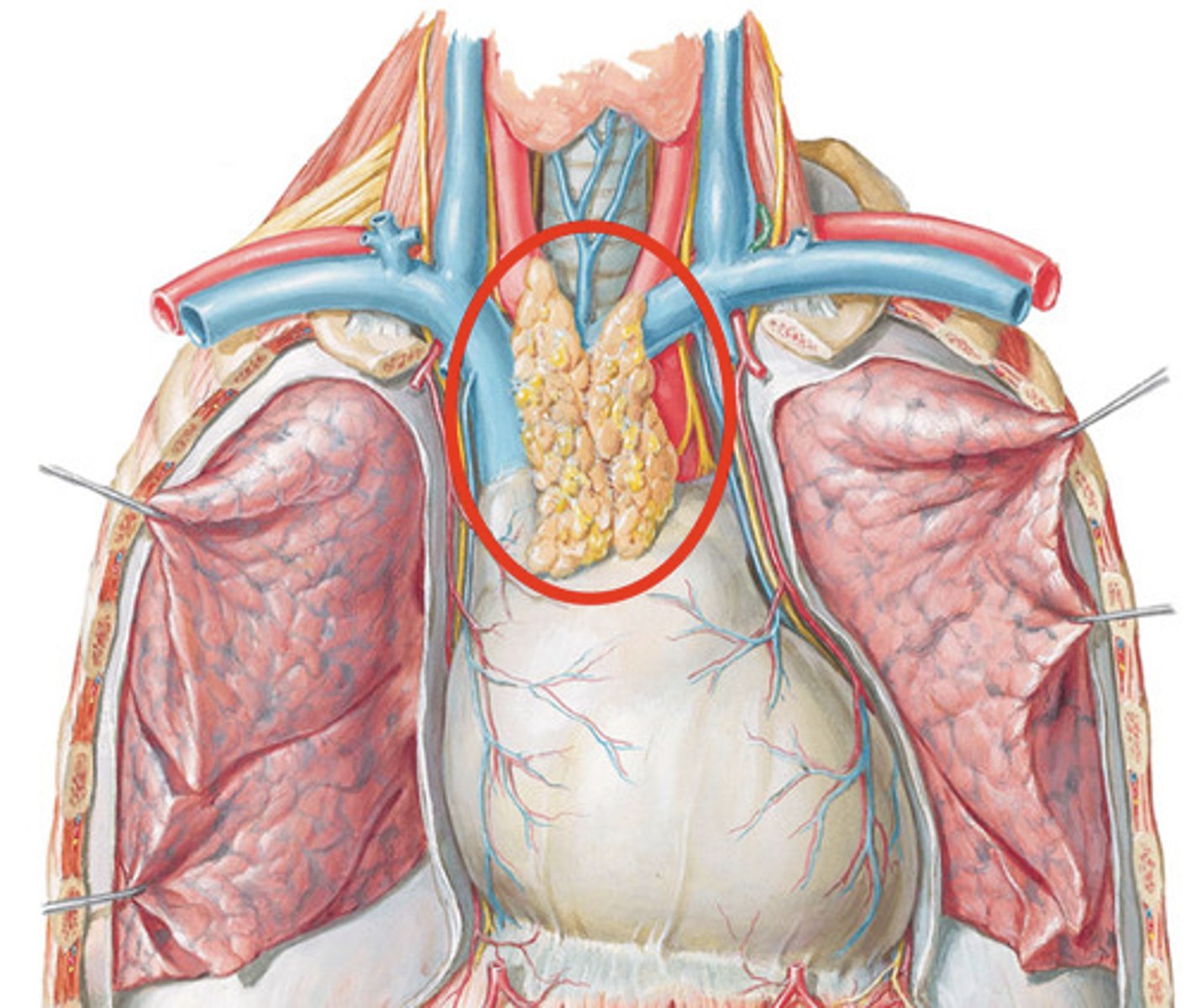
Thymus Gland
- A flat, pink-grey organ, located in the superior mediastinum behind the sternum and in front of the aorta
- Develops T lymphocytes in children, but is useless to adults
Developmental Considerations for Infants and Children Related to the Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System
- Lymph nodes are relatively large and palpable
- Respiratory infection and enlarged tonsils
- Transient acrocyanosis and skin mottling
Transient Acrocyanosis
Cyanosis of the hands, feet, or phase
Developmental Considerations for Pregnant Individuals Related to the Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System
- Growing uterus obstructs drainage of iliac vein and inferior vena cava
- Dependent edema and varicose veins
Dependent Edema
Swelling in the lower body caused by fluid pooling due to gravity
Pitting Edema
The indentation left after the examiner depresses the skin over swollen tissue
Varicose Veins
Dilated tortuous veins with incompetent valves
Developmental Considerations for Older Adults Related to the Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System
- Arteriosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis
- Increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses become more difficult to palpate
- Trophic changes associated with arterial insufficiency
Arteriosclerosis
Hardening of the arteries
Atherosclerosis
Condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries, which can cause an occlusion
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A blood clot in a deep vein, most often an extremity
Subjective Data to Assess for the Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System
- Leg pain/cramps
- Skin changes on arms/legs
- Swelling in arms/legs
- Lymph node enlargement
- Medication
Claudication Distance
Number of blocks walked or stairs climbed to produce pain
Modified Allen Test
An advanced practice that involves occluding both ulnar and radial arteries and asking the patient to open and close their hands. You then release the pressure on the ulnar artery and see if the colour of the skin returns within 2-5 seconds (if it doesn't, the circulation is not adequate)
Ankle-Brachial Index
Ankle pressure/brachial pressure (<0.9 suggests peripheral vascular disease)
3 multiple choice options
2 Types of Compression Stockings
- Anti-embolism
- Medical
Anti-Embolism Compression Stockings/Thrombo-Embolic-Deterrent (T.E.D.)
Type of compression stockings used to increase blood flow to prevent blood clots from forming in non-ambulatory patients
Medical Compression Stockings
Type of compression stockings designed for ambulatory patients
People who Should Wear Compression Stockings
- Family history of venous disorders
- Advanced age
- DVT risk
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Sedentary
- Hormonal changes
- Long-distance travelling
- Athletes
- Occupational risks (Ex. prolonged sitting/standing)
- Lymphedema or lipedema
4 Levels of Compression Stockings
- 15-20 mmHg
- 20-30 mmHg
- 30-40 mmHg
- 40 mmHg
Who Uses 15-20 mmHg Compression Stockings
People who have leg fatigue from prolonged sitting/standing or for the prevention of any complications
Who Uses 20-30 mmHg Compression Stockings
People who have heavily fatigued, aching legs and already have mild symptoms (Ex. edema and varicose veins)
Who Uses 30-40 mmHg Compression Stockings
People who already have moderate varicose and/or edema
Who Uses 40 mmHg Compression Stockings
People who have severe varicose veins and/or edema
CEAP Classification
- Clinical symptoms
- Etiology
- Anatomy
- Pathophysiology
Objective Data to Assess for the Arms
- Skin colour
- Edema/lesions
- Finger profile/capillary refill
- Temperature
- Texture
- Turgour
- Radial pulse
- Brachial pulse
- Epitrochlear node
Objective Data to Assess for the Legs
- Skin colour
- Size (symmetry)
- Hair distribution
- Venous pattern
- Lesions/ulcers
- Temperature
- Tenderness
- Inguinal lymph nodes
- Femoral artery
- Popliteal artery
- Posterior tibial artery
- Dorsalis pedalis artery
Raynaud's Disease
A peripheral vascular disease characterized by episodes of abrupt progressive tricolour change of the fingers in response to cold, vibration, or stress

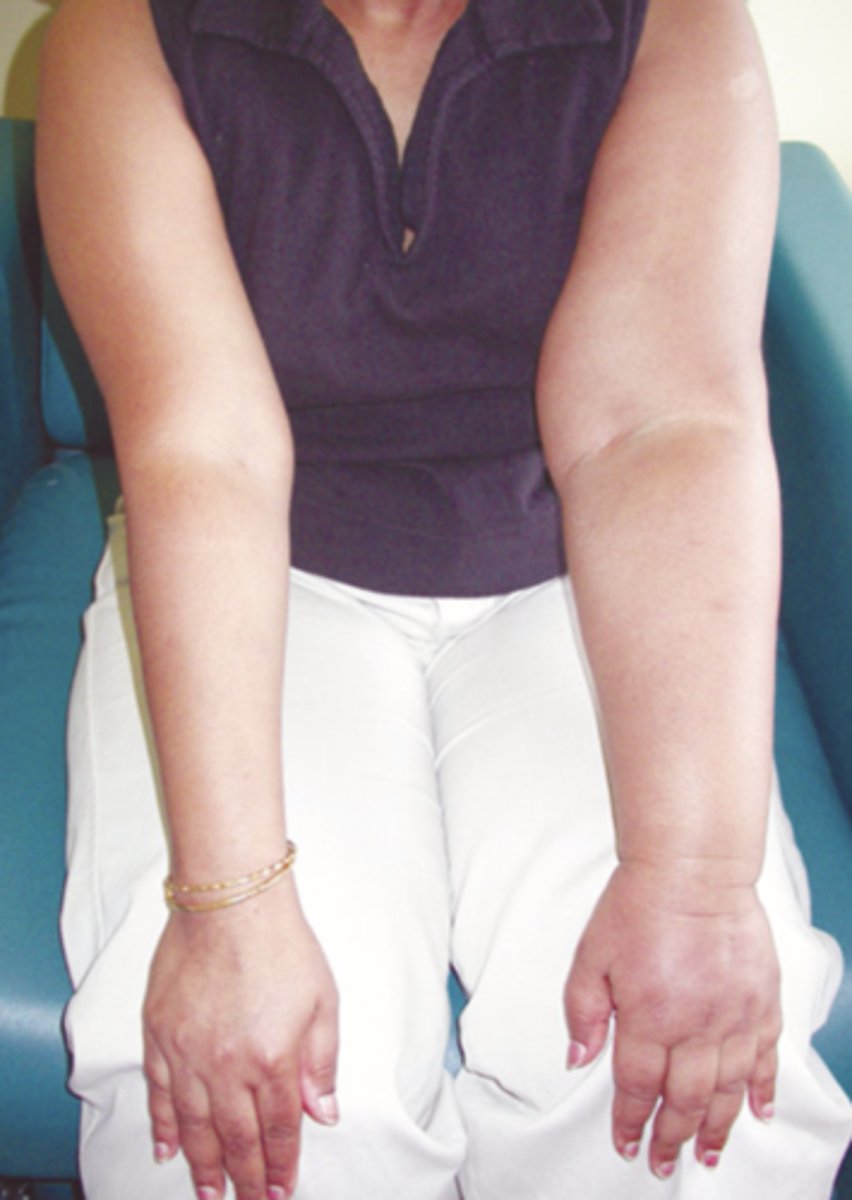
Lymphedema
A peripheral vascular disease characterized by swelling due to an abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid within the tissues; common after breast cancer treatment

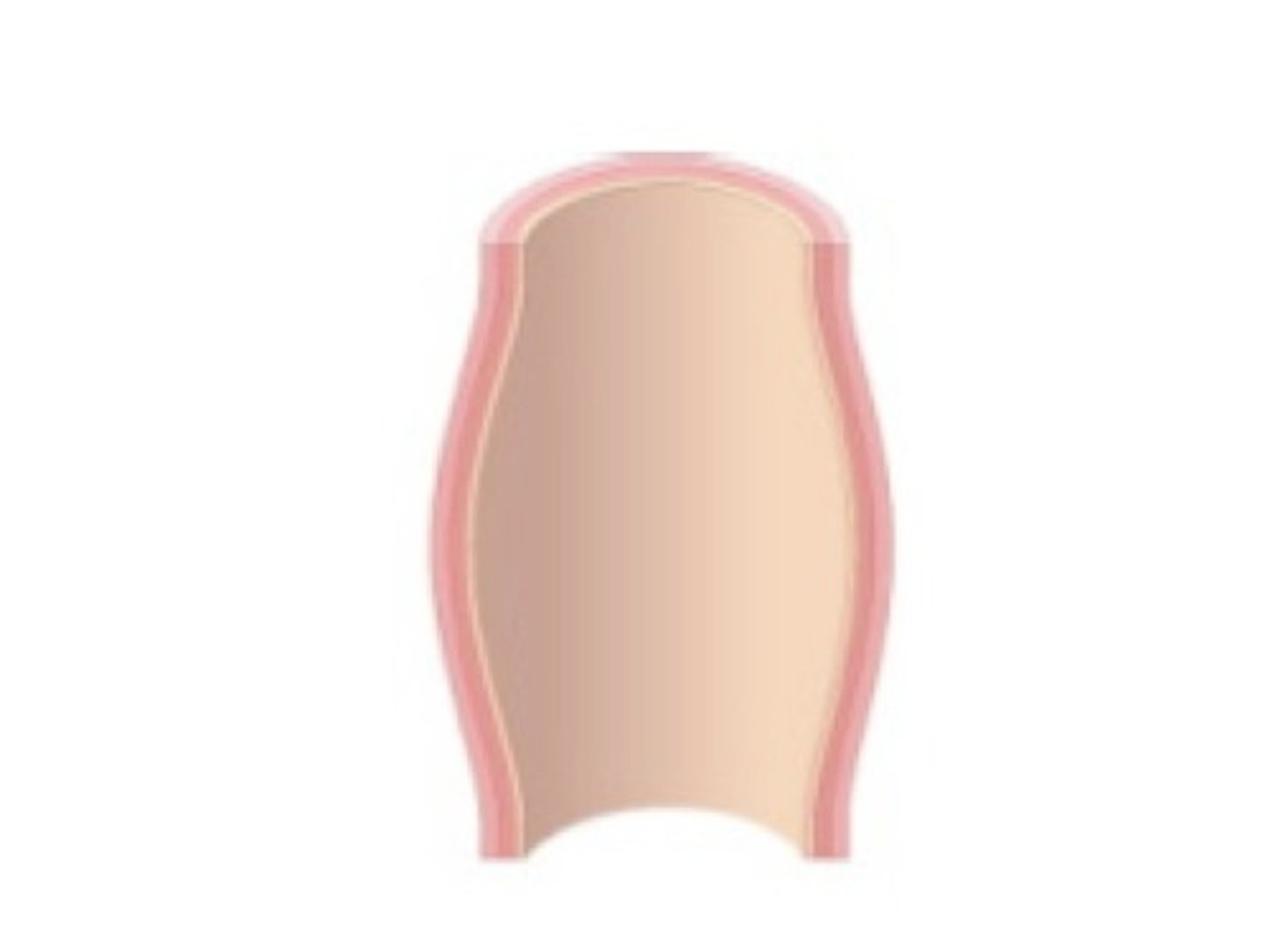
Aneurysm
A sac formed by dilation in the artery wall

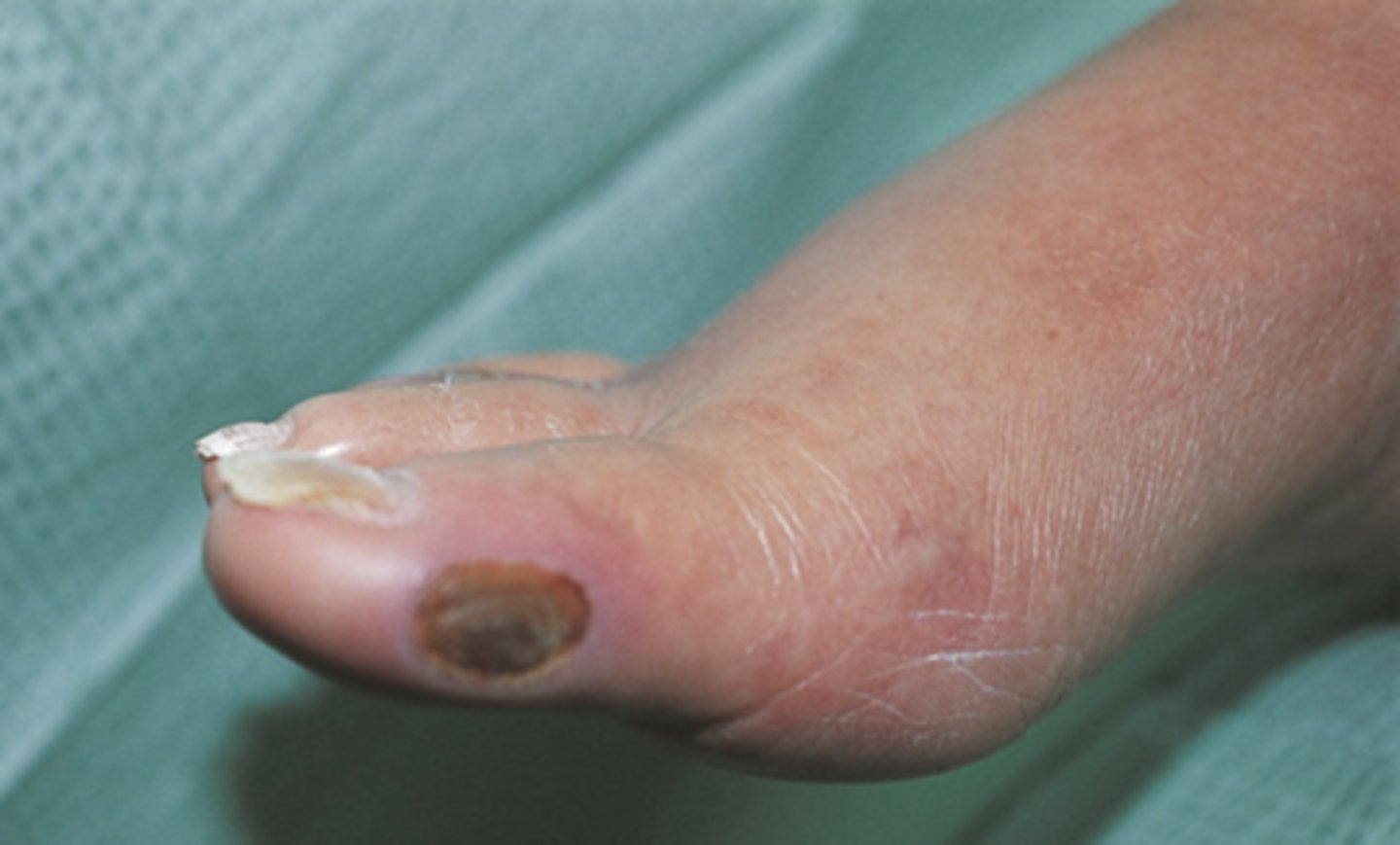
Arterial/Ischemic Ulceration
- Ulcerations that result from the buildup of fatty plaques on intima (atherosclerosis) plus hardening and calcification of the arterial wall (arteriosclerosis)
- Occur at toes, metatarsal heads, heels, and lateral ankle
- Characterized by well-defined edges and no bleeding
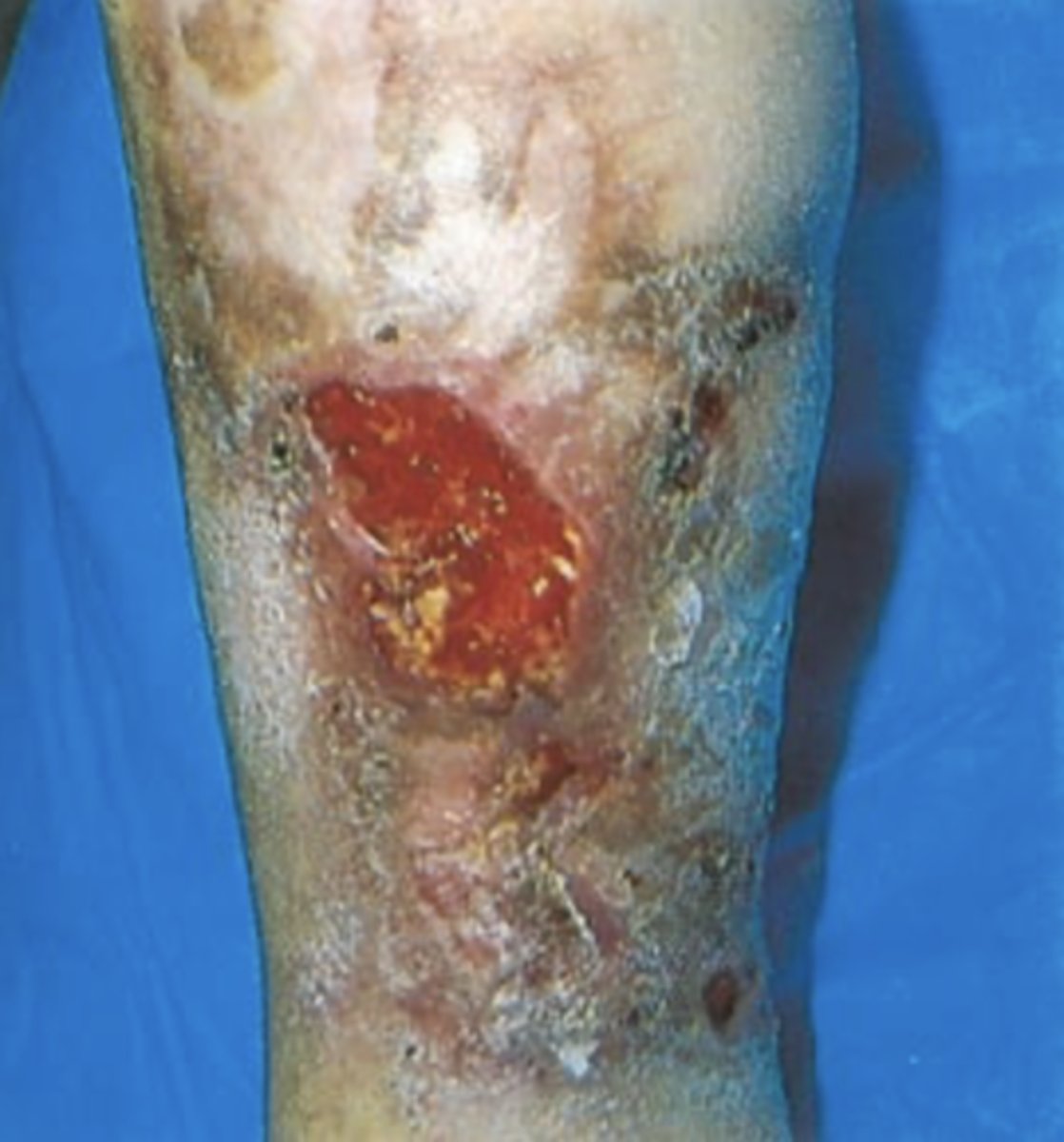
Venous/Stasis Ulceration
- Ulcerations that occur after acute DVT or with chronic incompetent valves in deep veins
- Occur at medial malleolus
- Characterized by bleeding and uneven edges
- Brown discolouration can occur if chronic
Virchow's Triad
- Stasis
- Hypercoagulability
- Endothelial dysfunction
Signs/Symptoms of DVT
- Redness
- Warmth
- Edema
- Pain
Risk Factors for a Pulmonary Embolism with DVT
- Sudden SOB
- Pain with breathing
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnea
- Hypoxia
Treatment for DVT
- Elevate limbs
- Avoid pressure
- Notify health care provider
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)
Disease of blood vessels away from central region of body, most typically in legs; symptoms include pain, numbness, and impaired circulation
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
- Disease affecting the arteries supplying the limbs
- Usually caused by atherosclerosis and less commonly by embolism, hypercoagulable states, or arterial dissection
Characteristics of PVD Chronic Arterial Symptoms
- Deep muscle pain, usually in calf, but may be in lower leg or dorsum of foot
- Intermittent claudication that feels like cramping, numbing, tingling, or cold
- Onset gradual after exertion
- Aggravated by activity and elevation
- Relieved by rest and dangling
- Associated with a cool, pale skin
Characteristics of PVD Acute Arterial Symptoms
- Varies, distal to occlusion, may involve entire leg
- Feels like throbbing
- Sudden onset
- Associated with the 6 Ps
Characteristics of PVD Chronic Venous Symptoms
- Calf, lower leg
- Characterized by aching, tiredness, and feeling of fullness
- Increases at the end of day
- Aggravated by prolonged standing/sitting
- Relieved by elevation, lying, and walking
- Associated with edema, varicosities, and weeping ulcers at the ankles
Characteristics of PVD Acute Venous Symptoms
- Intense, sharp; deep muscle tender to touch
- Sudden onset
- Pain can increase by sharp dorsiflexion of foot
- Associated with red, warm, swollen legs
Characteristics of Good Foot Care
- Check feet everyday
- Keep blood flowing to feet
- Wear comfortable-fitting shoes
- Fit shoes to larger foot
- Wear low-heeled shoes
- Keep skin soft and smooth