4 - Dose-Response Curves
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
a. increases
When the dose-response curve shifts to the right, the dose
a. increases
b. decreases
b. Quantal dose response curve
All or non-dose response curve
a. Graded dose response-curve
b. Quantal dose response curve
a. Therapeutic index
The ratio of LD50 and ED50
a, Therapeutic index
b. Therapeutic window
c. DOA
d. Therapeutic classification
b. The dose of Drug B is greater than Drug A to provide similar effect
Drug A is more potent than drug B. This means
a. The dose of Drug A is greater than Drug B to provide similar effect
b. The dose of Drug B is greater than Drug A to provide similar effect
c.The dose of Drug B is similar is to the Drug A since they have the same efficacy
d. AOTA
b. Partial agonist becomes an antagonist
Full agonist + Partial agonist
a. Full agonist becomes an antagonist
b. Partial agonist becomes an antagonist
c. Partial agonist becomes a full agonist
d. Full agonist becomes an inverse agonist
a. the lower the potency
The higher the dose
a. the lower the potency
b. the lower the efficacy
c. The greather the safety
d. the higher the potency
Coma
ingestion of 10mg of Atropine can lead to
Graded Dose-Responsive Curve
Involves one patient only
Assesses safety
Relationship between dose & magnitude or intensity of effect
Continuous scale
Potency
Dose required to produce 50% effect
Right shift
↓ potency = ___ shift
Left shift
↑ potency = ___ shift
↑potency
↓ dose = ___ potency
Ceiling Dose
safety of the drug
minimal dose that produces maximal (100%) response
Ceiling effect
dose beyond which there is no additional effect
Full Agonist + Competitive Antagonist
“Parallel”
Potency: ↓ (right shift)
Efficacy: same
Full Agonist + Non-competitive Antagonist
“Anti-Parallel”
Potency: ↓ (right shift)
Efficacy: ↓ (down shift)
Full Agonist + Partial Agonist
Potency: ↓, ↑, same
Efficacy: ↓ (down shift)
Quantal Dose-Response Curve
Involves many patients
Relationship between DOSE & frequency of effect
Aka ALL or NONE
Therapeutic Index
Measure of drug’s relative safety
Therapeutic Window
Measure of drug’s clinical safety
Dosage range at which a drug is BOTH safe & effective
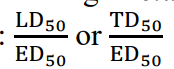
Formula for Therapeutic Index
Unsafe
narrow therapeutic index means what?
1000 → 50 → 10 → 0.1
Rank from the safest to unsafe therapeutic index
0.1, 10, 50, 1000
the higher the safety profiles
The higher the Therapeutic Index, the ___ safety profile
Safe and Effective
drugs should be both __ & __