MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATION OF THE CERVICAL SPINE (P1; anatomy and subjective)
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Heavily Magee Based,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
True or False:
The cervical spine sacrifices stability for mobility
TRUE
Two areas of the spine:
Upper cervical spine is called (C0-C2) : _________________
Lower cervical spine is called (C3-7): _________________
Two areas of the spine:
Upper cervical spine is called (C0-C2) : cervicoencephalic / cervicocranial
Lower cervical spine is called (C3-7): cervicobrachial
Injuries in this region have the potential of involving the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord, what cervical region am I talking about?
cervicoencephalic / cervicocranial
Sx include:
headache
fatigue
vertigo
poor concentration
hypertonia of the sympathetic nervous system
irritability
cognitive dysfunction
cranial nerve dysfunction
Uppermost joint of the cervical region
atlanto-occipital joints
ellipsoid jt. ; works in unison with the atlanto-axial joint ; most complex articulations of the axial skeleton.
ROM of flexion and extension for the atlanto-occipital joints
15° to 20°
ROM of side flexion for the atlanto-occipital joints
10°
ROM of rotation for the atlanto-occipital joints
Negligible
Ligament supporting the anterior atlanto-occipital membrane of the atlanto-occipital jt.
anterior longitudinal ligament
Ligament between the atlas and occiput; replaces the ligamentum flavum.
Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
A broad band covering the dens and its ligaments, is found within the vertebral canal.
Tectorial membrane
The tectorial membrane is a continuation of what ligament?
Posterior Longitudinal ligament
Two strong rounded cords found on each side of the upper dens passing upward and laterally to attach on the medial sides of the occipital condyles.
Alar ligaments
limit flexion and rotation and play a major role in stabilizing C1 and C2, especially in rotation
Joints that constitute the most mobile articulations of the spine
atlanto-axial joints
ROM of flexion and extension in atlanto-axial joints
10°
ROM of side flexion in atlanto-axial joints
5°
ROM of rotation in atlanto-axial joints
approx 50°
True or False:
With rotation, there is a decrease in height of the cervical spine at this level as the vertebrae approximate because of the shape of the facet joints
True
Middle Atlanto-Axial joint is a pivot (trochoidal) joint
Lateral Atlanto-Axial joints (facet joints) are plane joints.
Main supporting ligament of the atlanto-axial jt.
transverse ligament of the atlas
It is this ligament that weakens or ruptures in rheumatoid arthritis.
As the transverse ligament crosses the dens, there are two projections off the ligament, one going superiorly to the occiput and one inferiorly to the axis. The ligament and the projections form a cross, and the three parts, taken together are called the?
cruciform ligament of the atlas
The vertebral artery passes through the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae through the transverse foramen, starts at the level of ________ but can enter as high as the level of __________.
The vertebral artery passes through the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae through the transverse foramen, starts at the level of C6 but can enter as high as the level of C4.
Quick fax abt the vertebral artery:
supplies 20% of the blood supply to the brain (primarily the hindbrain)
lies close to the facet joints and vertebral body where it may be compressed by osteophyte formation or injury to the facet joint.
vascular risk factors (e.g., hypertension, high fat or cholesterol levels, diabetes, smoking) may contribute to altered blood flow in the arteries.
vertebral and internal carotid arteries are stressed primarily by what cervical motions?
rotation, extension, and traction
True or False:
Rotation and extension of as little as 10° have been shown to significantly decrease vertebral artery blood flow.
FALSE:
Rotation and extension of as little as 20° have been shown to significantly decrease vertebral artery blood flow.
The greatest stresses are placed on the vertebral arteries in four places:
where it enters the transverse process of C6
within the bony canals of the vertebral transverse processes
between C1 and C2 (greatest potential for problems)
between C1 and the entry of the arteries into the skull (greatest potential for problems)
True or False:
The most common mechanism for nonpenetrating injury to the vertebral artery is neck flexion, with or without side flexion or rotation.
FLASE:
most common mechanism for nonpenetrating injury to the vertebral artery is neck extension, with or without side flexion or rotation.
Given the type of VA injury possible, symptoms may be delayed.
Symptoms related to the vertebral artery include:
vertigo
balance deficits
arm paresthesia
nausea
tinnitus
“drop attacks” (i.e., falling without fainting)
visual disturbances
in rare cases, stroke or death.
Pain in this cervical area is commonly referred into the upper extremity, what is the cervical area called?
cervicobrachial area (C3-7)
True or False:
Pathology in this region leads to both neck and arm pain, but never neck pain alone or arm pain alone.
False:
Pathology in this region leads to neck pain alone, arm pain alone, or both neck and arm pain.
Symptoms of cervicobrachial injury (skim thru):
include neck and/or arm pain
headaches
restricted range of motion (ROM)
paresthesia
altered myotomes and dermatomes
radicular signs
Cognitive dysfunction (not common)
cranial nerve dysfunction (not common)
sympathetic dysfunction
Injury to both areas (cervicobrachial and cervicoencephalic), if severe enough, may result in psychosocial issues.
How many facet (apophyseal) joints in the cervical spine (C1 to C7)?
14
True or False:
The upper four facet joints in the two upper thoracic vertebrae (T1 to T2) are often included in the examination of the cervical spine.
True
True or False:
Cervical rotation cannot happen without some forward flexion and vice versa, this is called coupled movement.
False:
Cervical rotation cannot happen without some side/lateral flexion and vice versa, this is called coupled movement.
Between which vertebra in the cervical region do coupled movement occur in the opposite direction?
i.e left rotation occurs with right lateral flexion and vice versa
C0-C2 & C7-T1
Between which vertebra in the cervical region do coupled movement occur in the same direction?
i.e left rotation occurs with left lateral flexion and vice versa
C2-C7
The greatest flexion-extension of the facet joints occurs between which vertebrae?
C5 and C6
Common levels of degeneration due to excess movement:
C5 and C6
C4 to C5
C6 to C7
Cervical Spine
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Cervical Spine
Resting position: Midway between flexion and extension
Close packed position: Full extension
Capsular pattern: Side flexion and rotation equally limited extension
The intervertebral discs make up approximately how many percent of the height of the cervical spine?
25%
True or False:
No disc is found between the atlas and the occiput (C0–C1) or between the atlas and the axis (C1–C2).
True
True or False:
It is the vertebrae that give the cervical spine its lordotic shape
False:
It is the discs rather than the vertebrae that give the cervical spine its lordotic shape
Which part of the IV disc acts as a buffer to axial compression in distributing compressive forces?
Nucleus Pulposus
Which part of the IV disc acts to withstand tension?
Annulus Fibrosus
The intervertebral disc has some innervation on the periphery of the annulus fibrosus.
a generalized disease of aging initiated by intervertebral disc degeneration.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is often seen in what age?
25 y/o or older
Spondylosis is present in 60% of what age group?
Older than 45 years
Spondylosis is present in 85% of what age group?
Older than 65 years
Symptoms of osteoarthritis do not usually appear until a person is _____ years of age or older
60 years of age
Diff Dx for spondylosis:
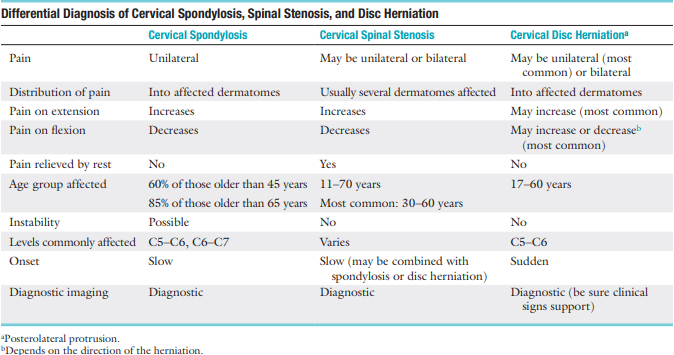
S/Sx of cervical symptom pathology
Location of the symptoms may help determine what level of the cervical spine is involved (e.g., tingling in the middle finger may indicate a problem at C6 to C7)

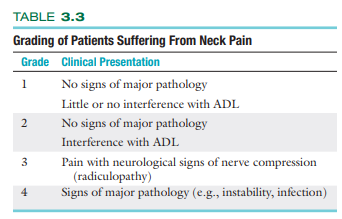
Grading of Patients Suffering From Neck Pain:
Watkins severity scale for neurological deficit (Severity Score)
mild episode =
moderate episode =
severe episode =
Watkins severity scale for neurological deficit (Severity Score)
mild episode = 4
moderate episode = 4 to 7
severe episode = 8 to 10
Watkins severity scale for neurological deficit (Return to activity Score)
minimum risk =
moderate risk =
severe risk =
Watkins severity scale for neurological deficit (Return to activity Score)
minimum risk = 6
moderate risk = 6 to 10
severe risk = 10 to 15
True or False:
Acute post-whiplash syndrome can lead to anxiety, pain catastrophizing (negative or heightened orientation toward pain), and other adverse psychosocial factors over time, and it can play a major role in the symptoms felt by the patient
FALSE
Chronic post-whiplash syndrome can lead to anxiety, pain catastrophizing (negative or heightened orientation toward pain), and other adverse psychosocial factors over time, and it can play a major role in the symptoms felt by the patient
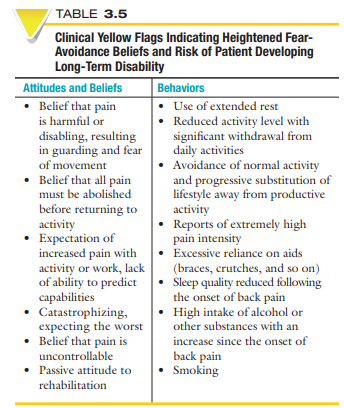
Yellow Flags
Red Flags
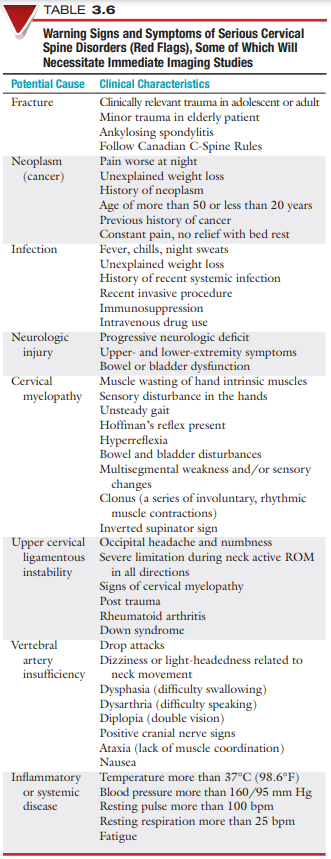
trauma may cause a whiplash-type (acceleration) injury or what type of disorder?
whiplash-associated disorder (WAD)
The Quebec Severity Classification of Whiplash-Associated Disorders:
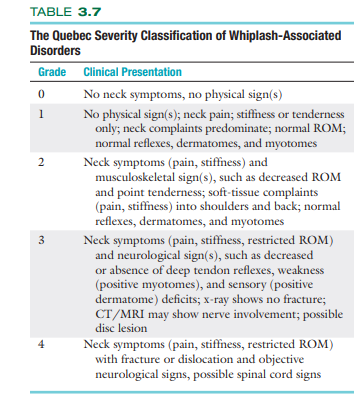
Trauma, compression, or stretch of the brachial plexus:
Burners or Stingers
typically occur from a blow to part of the brachial plexus or from stretching or compression of the brachial plexus
overuse or sustained postures may result in what type of symptoms?
Thoracic outlet symptoms
This type of palsy has symptoms, commonly bilateral, that are related to the brachial plexus (i.e., paresis, numbness, paresthesia, and painless motor weakness in the shoulder girdle and elbow flexor muscles).
Associated with carrying a heavy backpack
Backpack palsy (BPP)
In chronic cases of pain or headache, what can be useful to help determine pain patterns or factors that trigger the pain or headaches?
Pain Diary
Factors That Increase Chances of Recovery From an Episode of Neck Pain:
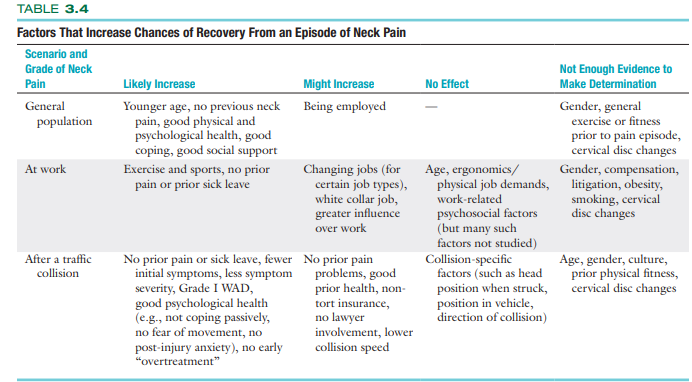
True or false:
Upper cervical symptoms may result from excessive nodding
True
True or False:
Cervicobrachial joint problems are often painful when activities that require push and-pull motion (such as lawn mowing, sawing, and cleaning windows) are performed.
FALSE
Cervicothoracic joint problems are often painful when activities that require pushand-pull motion (such as lawn mowing, sawing, and cleaning windows) are performed
True or false
Bone pain usually occurs immediately, but muscle or ligamentous pain only occurs several hours or days later
FALSE:
Bone pain usually occurs immediately, but muscle or ligamentous pain can either come on immediately (e.g., a tear) or occur several hours or days later
how many percent of whiplash patients reported immediate symptom occurrence?
70%
Myofascial pain syndromes demonstrate generalized _______ and at least ______ trigger points, which have lasted for at least ____ months with no history of trauma
Myofascial pain syndromes demonstrate generalized aching and at least three trigger points, which have lasted for at least 3 months with no history of trauma
True or False:
For a C4 nerve root injuries and above, symptoms do not go down the arm.
True
C2 and C3 nerve roots go to the lateral neck while C4 and C5 nerve roots go to the lateral neck and shoulders.
Injury to the nerve roots in the cervical spine
Cervical radiculopathy
True or False:
Cervical radiculopathy presents primarily with bilateral motor and sensory problems, myotome affectation and dermatome affectation and reflex hypoactivity
False:
Cervical radiculopathy presents primarily with unilateral motor and sensory problems, myotome affectation and dermatome affectation and reflex hypoactivity
Acute radioculopathies commonly associated with =
Chronic radiculopathies commonly associated with =
Disc Herniation
Spondylosis
True or false:
Disc herniations in the cervical spine increase in pain on coughing, sneezing, jarring or straining
TRUE
Disc injury in the cervical spine can refer pain to the thoracic spine:
Which disc refers pain to the cervicothoracic junction and ipsilateral upper trapezius?
Which disc refers pain to the superomedial border of the scapula?
Which disc refers pain to the midscapular area?
Which disc refers pain to the lower scapular area and along the medial scapular border?
C3-4
C4-5
C5-6
C6-7
An injury to the spinal cord itself:
Cervical Myelopathy
Sx of cervical myelopathy:
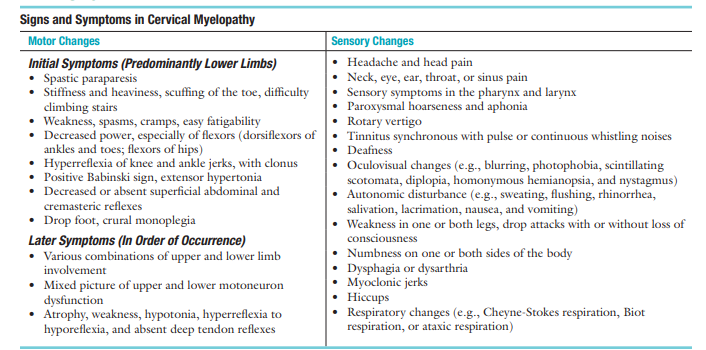
Hand symptoms found early in cervical myelopathy:
Myelopathic hand
weakness then loss of adduction and extension of the ulnar two or three fingers (Wartenberg sign)
inability to grip and release these fingers rapidly
grip and release test = grip and release for 10 seconds.
Normal range = 20+ reps
True or False:
when an athlete experiences a “burner,” the sensation is a lightning-like, boring pain into the shoulder and arm, followed by a period of heaviness or loss of function in the arm.
False:
when an athlete experiences a “burner,” the sensation is a lightning-like, burning pain into the shoulder and arm, followed by a period of heaviness or loss of function in the arm.
If the pain is affected by laughing, coughing, sneezing, or straining, an increase what type of pressure affects the condition?
Intrathoracic, Intraabdominal
These headaches occur as a symptom of musculoskeletal dysfunction in the cervical spine, especially C1, C2, and C3
Cervicogenic headaches
Clinical Criteria for the Diagnosis of Cervicogenic Headache:

Craniovertebral joint dysfunction commonly is accompanied by headaches:
headaches occur at the base and top of the head =
headaches are referred to the temporal area =
Craniovertebral joint dysfunction commonly is accompanied by headaches:
headaches occur at the base and top of the head = C1
headaches are referred to the temporal area = C2
Basically dermatome distribution (doesn’t count as a headache if the dermatome isn’t on the head)
True or False
Cervical arterial dissection, which is common, may result in neck pain and a migraine-like headache.
False
Cervical arterial dissection, although rare , may result in neck pain and a migraine-like headache.
If the headache is a major complaint especially following trauma, then the examiner should take a blood pressure measurement, assess the mental state of the patient as is done with a concussion, and assess the cranial nerves
Dissection of a cervical artery usually results in “unusual” acute moderate to severe neck pain that is different from anything previously experienced. This may be followed by what?
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke
Differentiation Between Features of Cervical Artery Dissection and Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency (important)
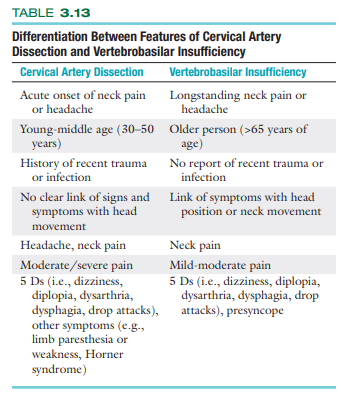
True or False
Many patients of cranial artery dissection have transient neurological signs and symptoms days or weeks prior to dissection.
True
Internal carotid artery dissection sx:
unilateral frontal pain
retro-orbital pain
constriction of the pupil
facial palsy
Sign when pain and referred symptoms are decreased or relieved by placing the hand or arm of the affected side on top of the head.
indicative of problems in the C4 or C5 area.
Bakody Sign
True or False:
Unilateral symptoms usually indicate either systemic disorders
False
Bilateral symptoms usually indicate either systemic disorders
You have a patient with a blood pressure of 130/90, is the patient susceptible to carotid and vertebral artery diseases?
Yes
hypertension can be a risk factor for carotid and vertebral artery disease
True or False:
Instability due to problems with the craniovertebral ligaments could compromise neurological and muscular tissues in the upper cervical spine.
False:
Instability due to problems with the craniovertebral ligaments could compromise neurological and vascular tissues in the upper cervical spine.
Risk factors related to vertebrobasilar insufficiency :
cardiovascular disease
TIA
blood clotting disorders
anticoagulant therapy
oral contraceptives, smoking
long-term use of steroids
and past history of trauma to the neck.
This finding may indicate a severe problem affecting the spinal cord in cervical conditions.
lower-limb symptoms (lahat basta lower limb myelopathy)
indicative of myelopathy
__________ canal problems or ___________ problems can lead to dizziness
Semicircular canal problems or vertebral artery problems can lead to dizziness
True or False:
Dizziness from a semicircular canal problem is commonly associated with other symptoms.
FALSE:
Dizziness from a vertebral artery problem is commonly associated with other symptoms.
Falling with no provocation while remaining conscious is sometimes called a _______________.
Drop Attack
S/Sx of VBI (skim)

5 D’s Of VBI
Dizziness
Diplopia (double vision)
Drop attack
Dysarthria (diff in speaking)
Dysphagia (diff in swallowing)
Sympathetic symptoms may be indicative of injuries to what structures / system?
Cranial Nerves / Sympathetic Nervous System
True or False:
Severe injuries (e.g., acceleration/whiplash type) can lead to hypotonia of the sympathetic nervous system.
False:
Severe injuries (e.g., acceleration/whiplash type) can lead to hypertonia of the sympathetic nervous system.