Inflammation and Wound Healing
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from the inflammation and wound healing lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
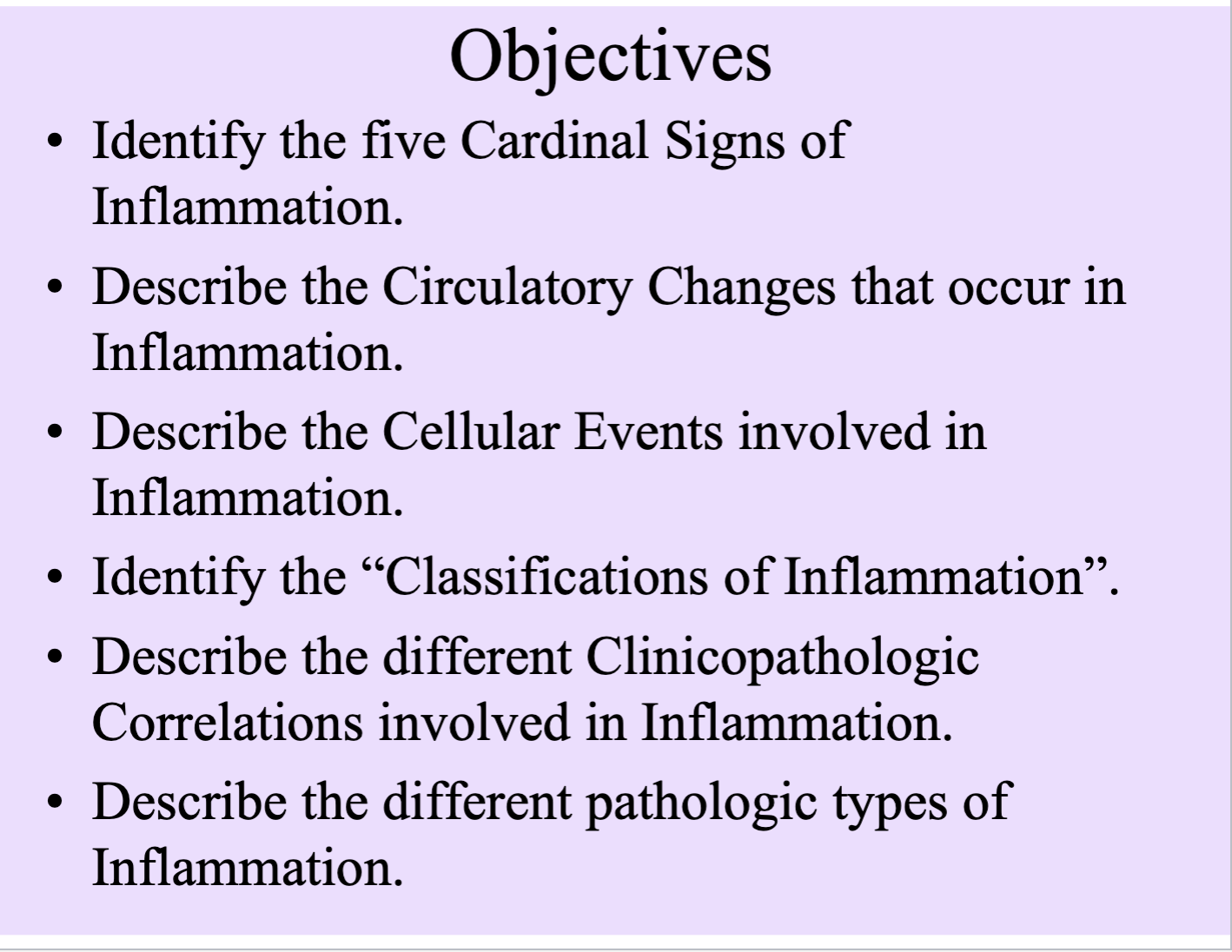
Objectives
.

Inflammation
Nonspecific, predictable tissue response to injury with vascular and cellular changes; dynamic process.
caused by many things
has several phases
protective role - uncontrollable = harmful (ie Pulmonary TB eroding pulmonary vessels)
Calor (Heat)
Inflammation cardinal sign; increased tissue temperature due to hyperemia.
Rubor (Redness)
Inflammation cardinal sign; redness from increased blood flow.
Tumor (Swelling)
Cardinal sign; edema from plasma leakage and capillary dilation.
Dolor (Pain)
Cardinal sign; pain from mediators irritating nerves during inflammation.
Functio laesa
Cardinal sign; loss of function of the inflamed tissue.
Acute inflammation
Sudden onset, short duration; protective but can have harmful effects like fever.
Chronic inflammation
Long-standing inflammation often with macrophages, lymphocytes and tissue destruction.
Signs of Inflammation
By Celsius
Calor, Rubor, Tumor, Dolor, Functio laesa
Circulatory Changes of Inflammation
Change in blood flow
Mech. stimulus stimulates the nerves to signal smooth muscle cells of pre-capillary arterioles = regulate inflow of blood into capillaries
Relaxation of smooth muscles = blood in capillaries → redness, swelling, warmth
First response of arterioles to injury = vasoconstriction (seconds) then vasodilation and relaxation
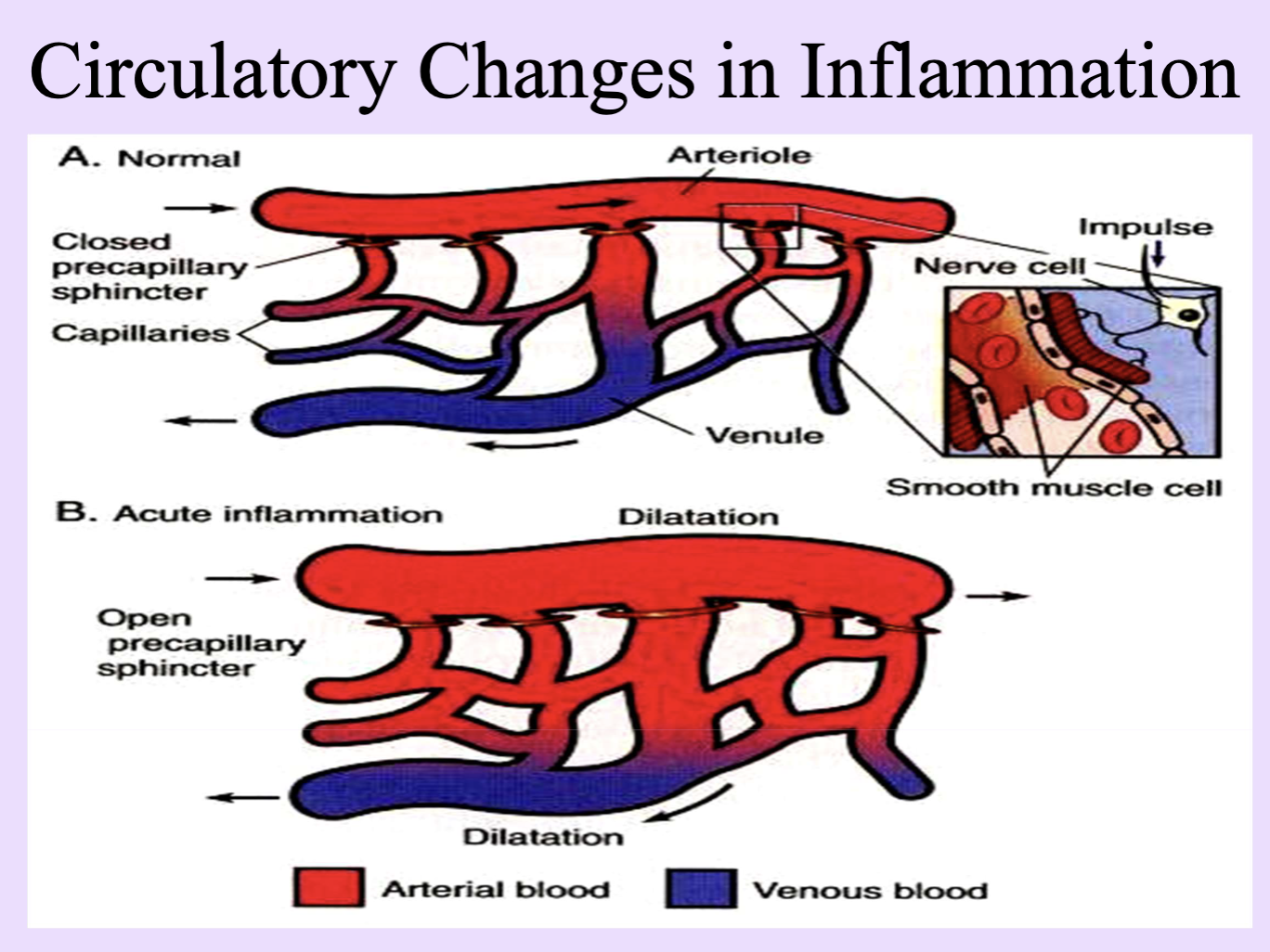
Hyperemia
Increased blood flow to inflamed tissue causing warmth and redness.
Vasodilatation
Relaxation of arteriolar smooth muscle; increased inflow of blood.
Precapillary sphincter
Sphincter regulating blood entrance to capillaries; its dilation promotes hyperemia.
Edema
Extravascular accumulation of fluid due to increased capillary permeability and filtration.
Rouleaux
Stacks of erythrocytes that slow capillary flow during inflammation.
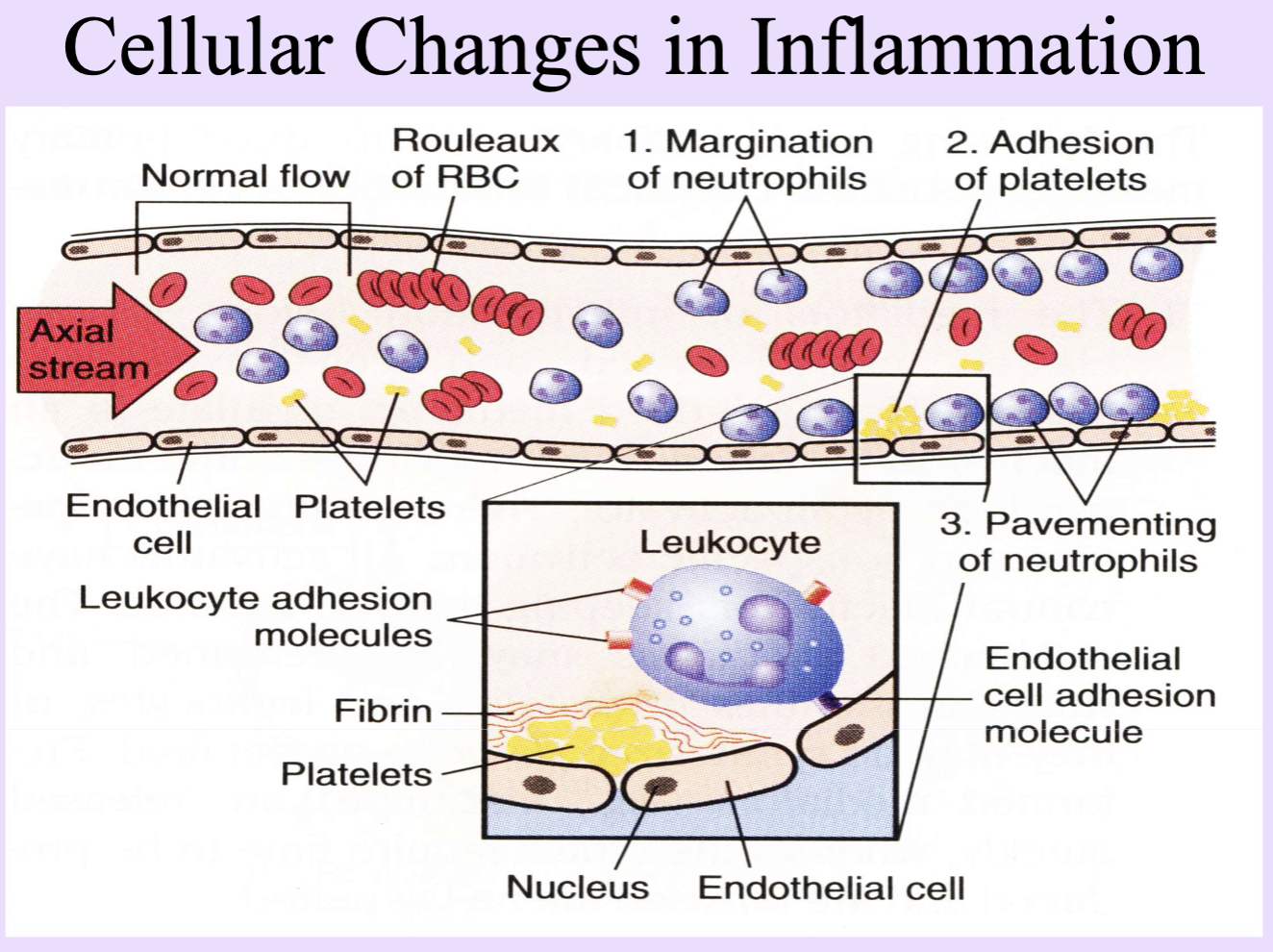
Margination and Pavementing
Margination and adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium at sites of injury. WBC
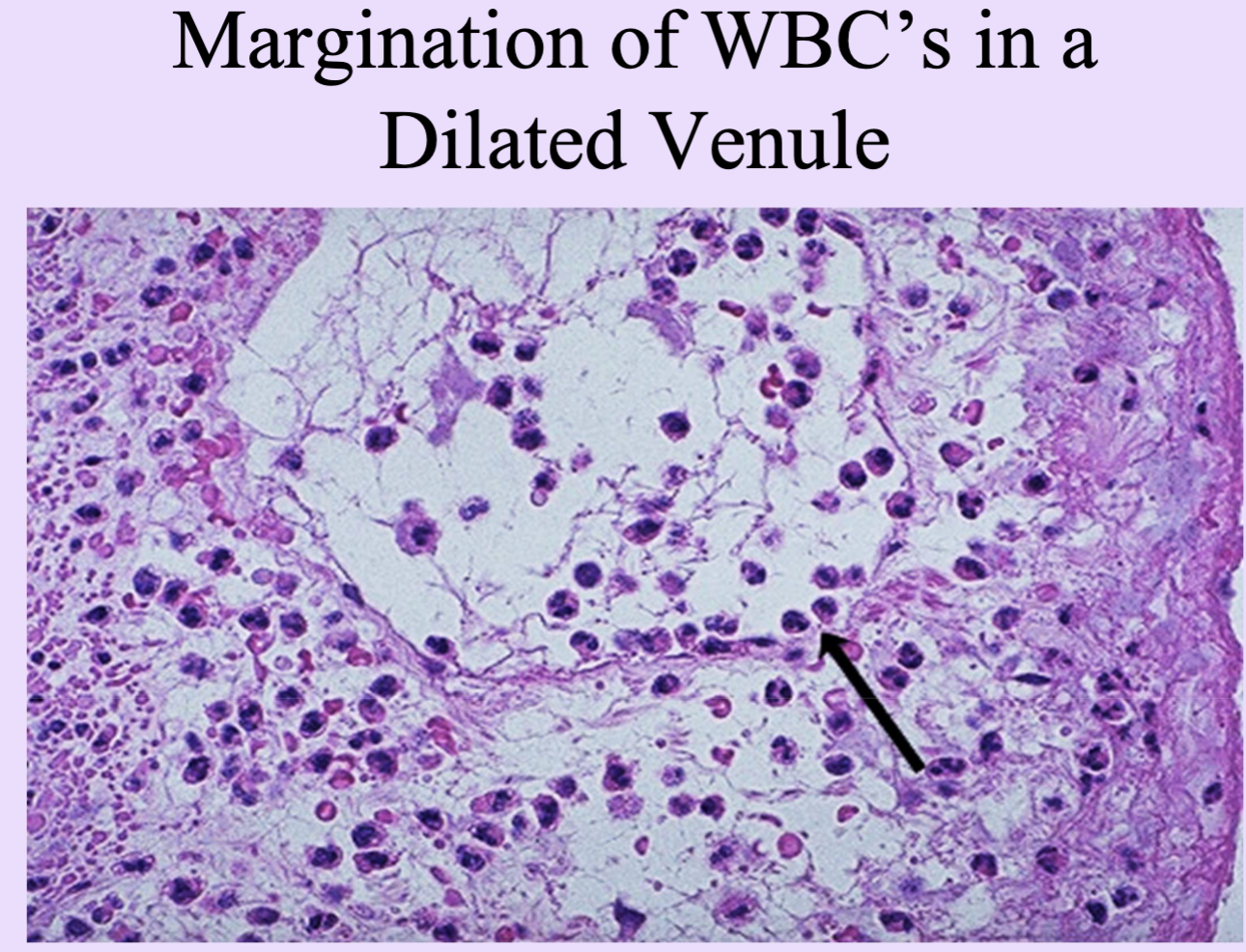
Margination and Pavementing
Leukocytes develop sticky protrusions on their cytoplasm and adhere to endothelial cells lining the capillaries
Diapedesis / Emigration
Leukocytes crossing the endothelium to reach tissue.
Leukocyte Adhesion Molecules
In leukocytes and endothelial cells
Interleukins
Cytokines driving inflammation; highest concentration at the site of injury.
Mediators of inflammation
Greatest concentration at site of inflammation
Emigration of Leukocytes
Adhesion of PMNs to endothelium
Insertion of cytoplasmic pseudopods btw junctions of endothelial cells
Passage through basement membrane
Ameboid movement away from vessel toward cause of inflammation
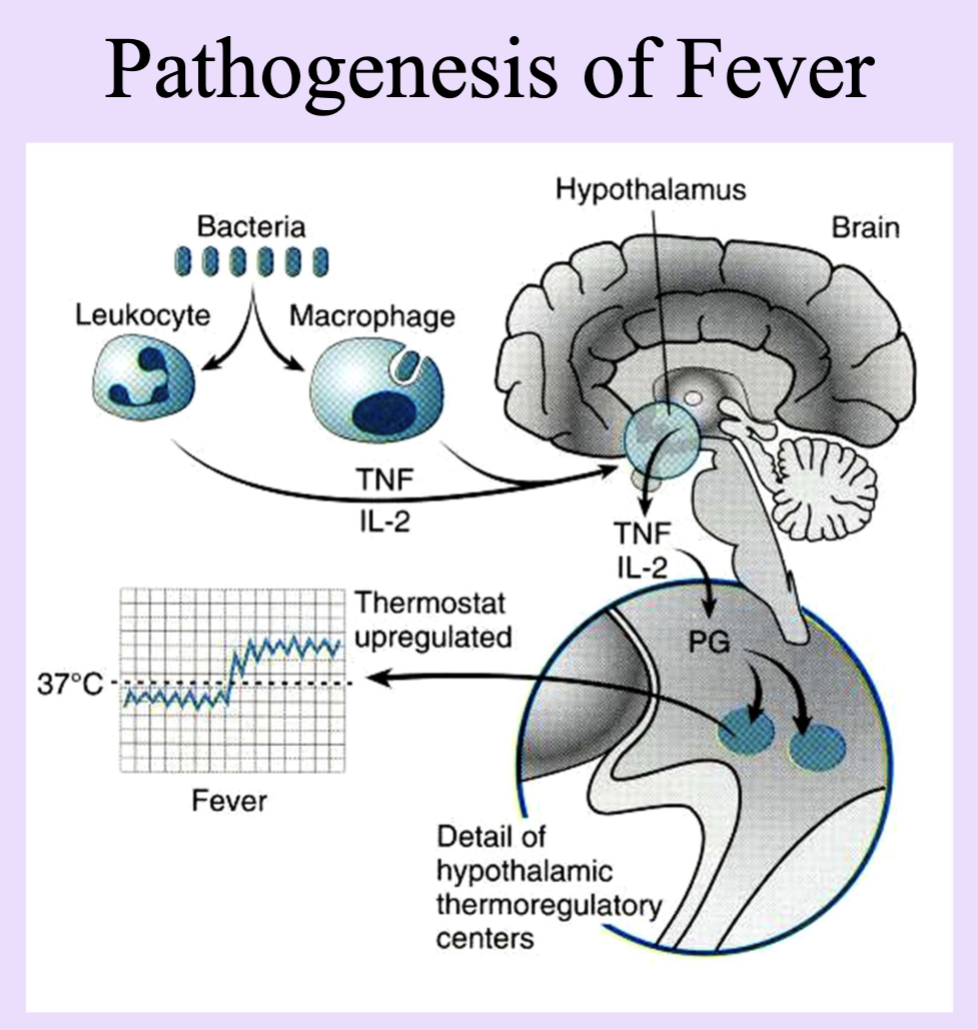
TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor)
Pro-inflammatory cytokine; mediates fever and inflammatory responses.
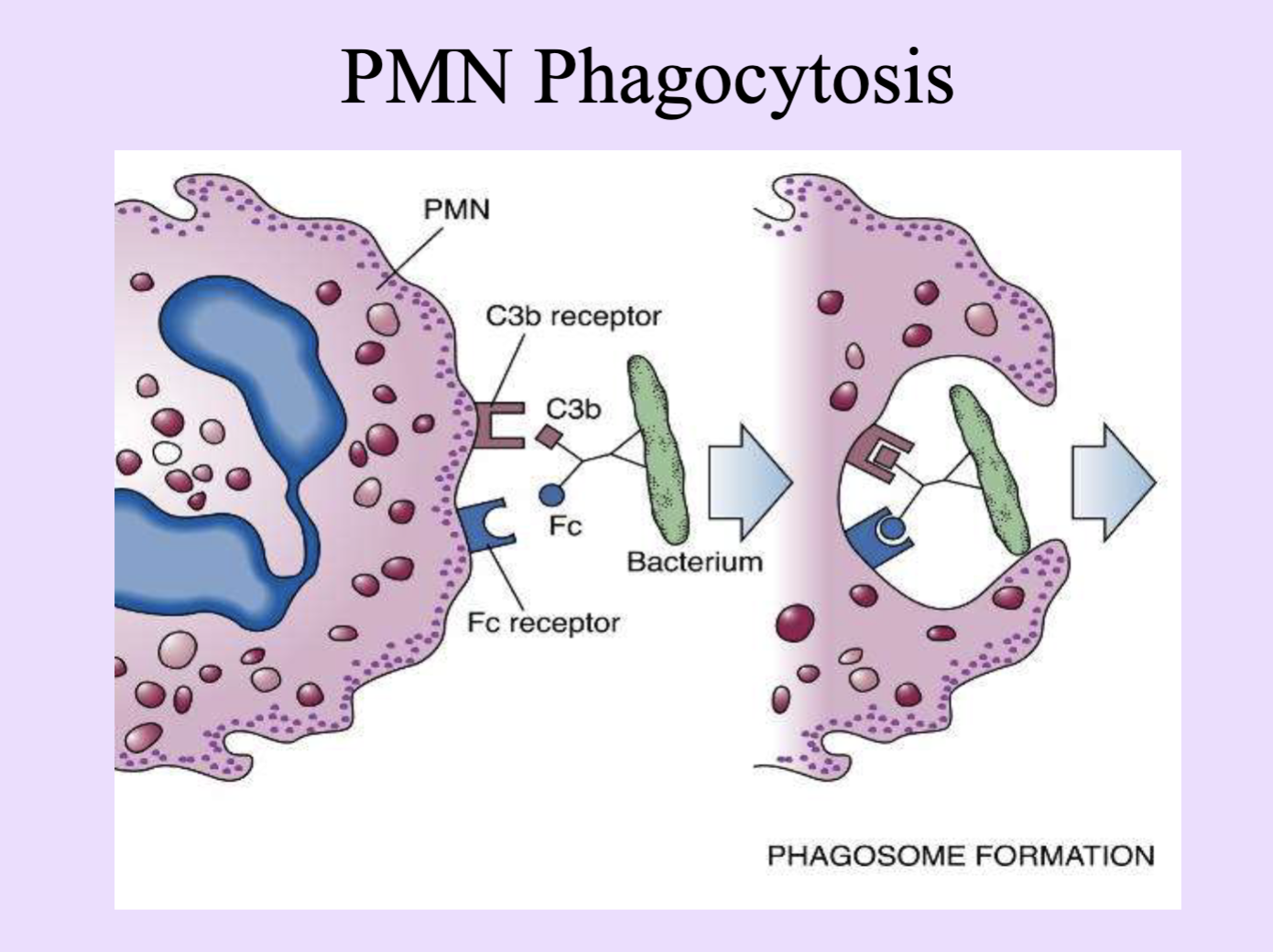
Opsonins
Molecules (e.g., Ig, C3b) that tag pathogens to enhance phagocytosis.
C3b (Complement)
Complement component; acts as an opsonin to enhance phagocytosis.
Phagocytosis
Engulfment and destruction of microbes by phagocytes.
Pus
Viscous yellow fluid of dead/dying PMNs and debris.
Inflammation Clinicopathologic Correlation
Usually produce fever or Leukocytosis
fever caused by acute inflammation from endogenous pyrogen
leukocytosis = number exceed 12-15,000 (normal is less than 10k) nonspecific symptoms
Serous inflammation
Mild exudate consisting of clear, watery fluid.
typical of viral infections and automimmune disorders like SLE
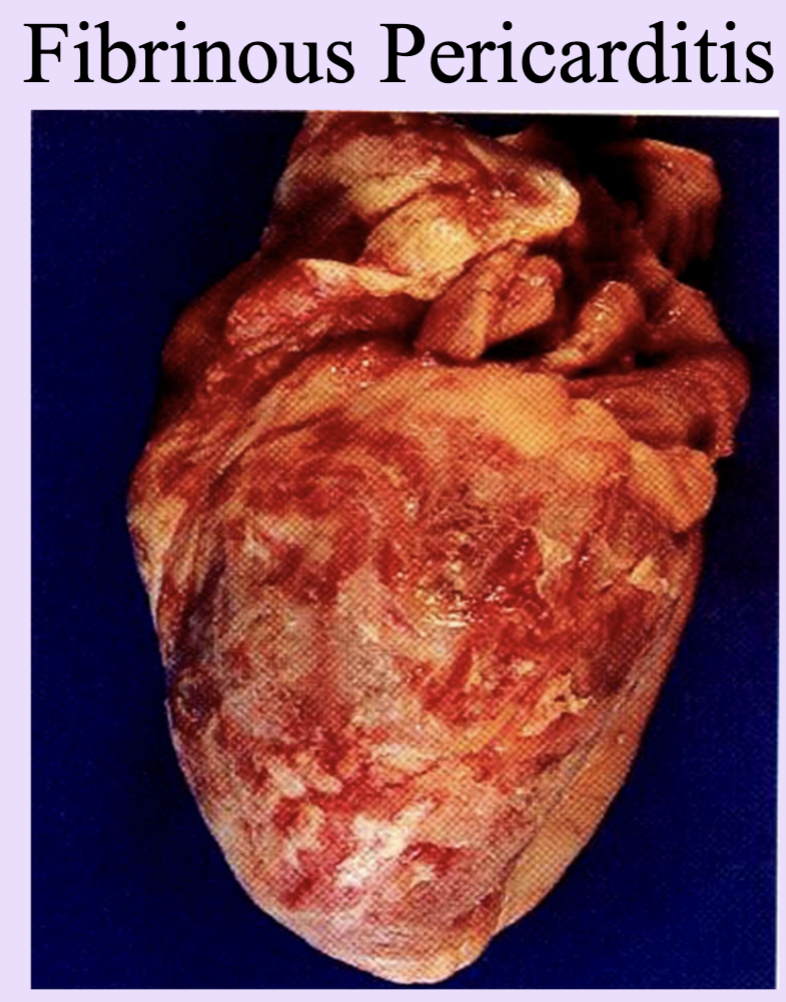
Fibrinous inflammation
Exudate rich in fibrin; can form shaggy layers on surfaces.
seen in many bacterial infections (Strept throat)
Also in Fibrinis pericarditis
Purulent Inflammation
Typically caused by pus forming bactera ie Strep and Staph
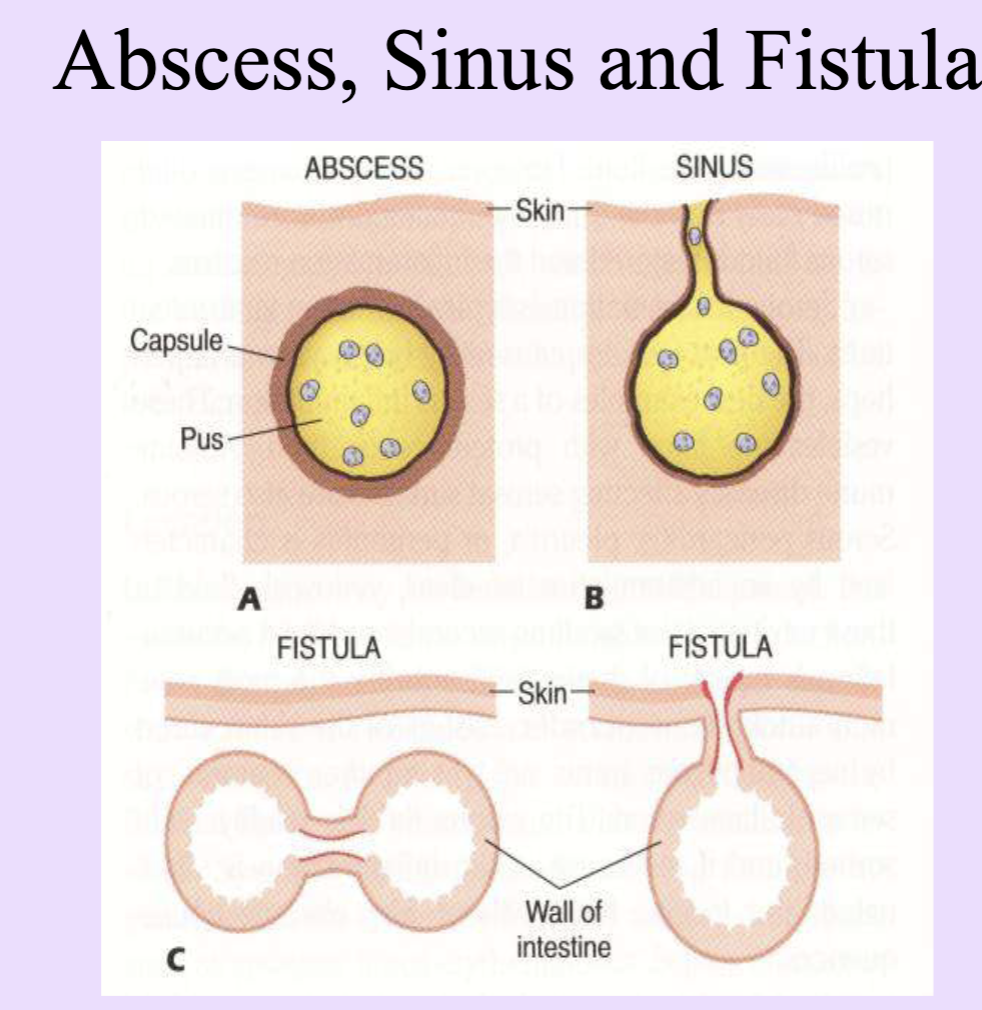
Localized collection of pus with an organ or tissue = abscess
An abscess has a central portion of purulent material surrounded by a wall capsule of fibrotic tissue
Ruptures abscess = sinus cavity or can form fistula (channels btw 2 preexisting cavities or organs and the surface of the body)
Pseudomembranous inflammation
Form of ulcerative inflammation
Inflammation with pseudomembrane formed by fibrinopurulent exudate (e.g., C. difficile colitis).
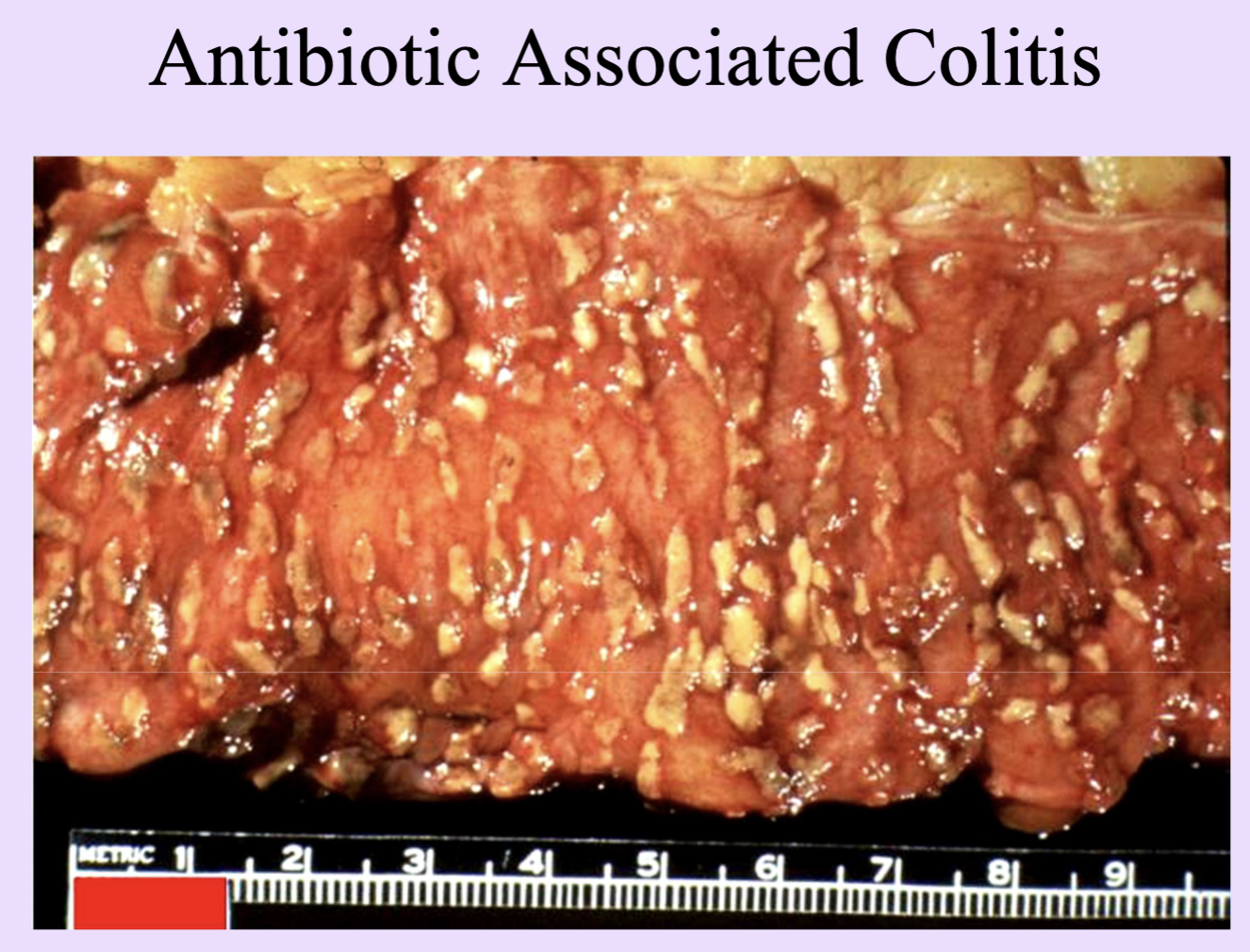
Ulcerative inflammation
Ulcer formation: defect of epithelium with possible deeper involvement.
Granulomatous inflammation
Special form of chronic inflammation with granuloma formation; TB is a prototype.
not preceded by an acute, PMN mediated inflammation
may be caused by antigens that evoke a cell mediated hypersensitivity rxn
TB is the prototype granulomatous disease
Caseating granuloma
Granuloma with central caseous necrosis seen in TB.
Wound healing
Repair of tissue after injury; can be by primary or secondary intention.
Classified into 3 groups based on capacity to proliferate
Most important cells are leukocytes, macrophages, connective tissue cells, epithelial cells
Labile cells
Continuously dividing cells (stem cell–like); e.g., intestinal crypt cells.
Stable (quiescent) cells
Do not divide regularly, but can
Injury-responsive cells that divide infrequently but can re-enter the cell cycle (e.g., hepatocytes).
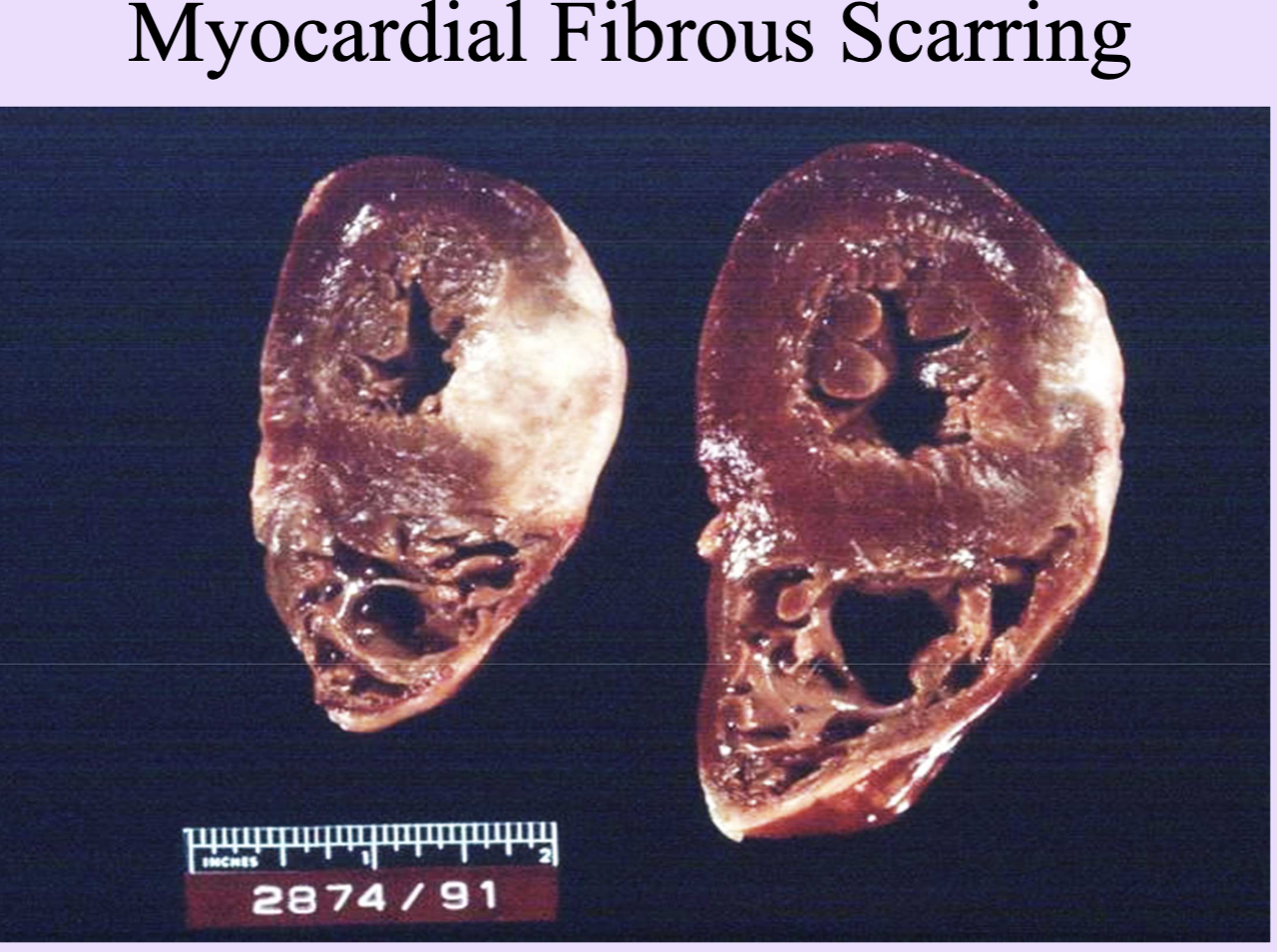
Permanent cells
Nondividing cells (neurons, myocardium) that repair by scarring.
heart repair = fibrous scarring
Brain repair by Gliosis
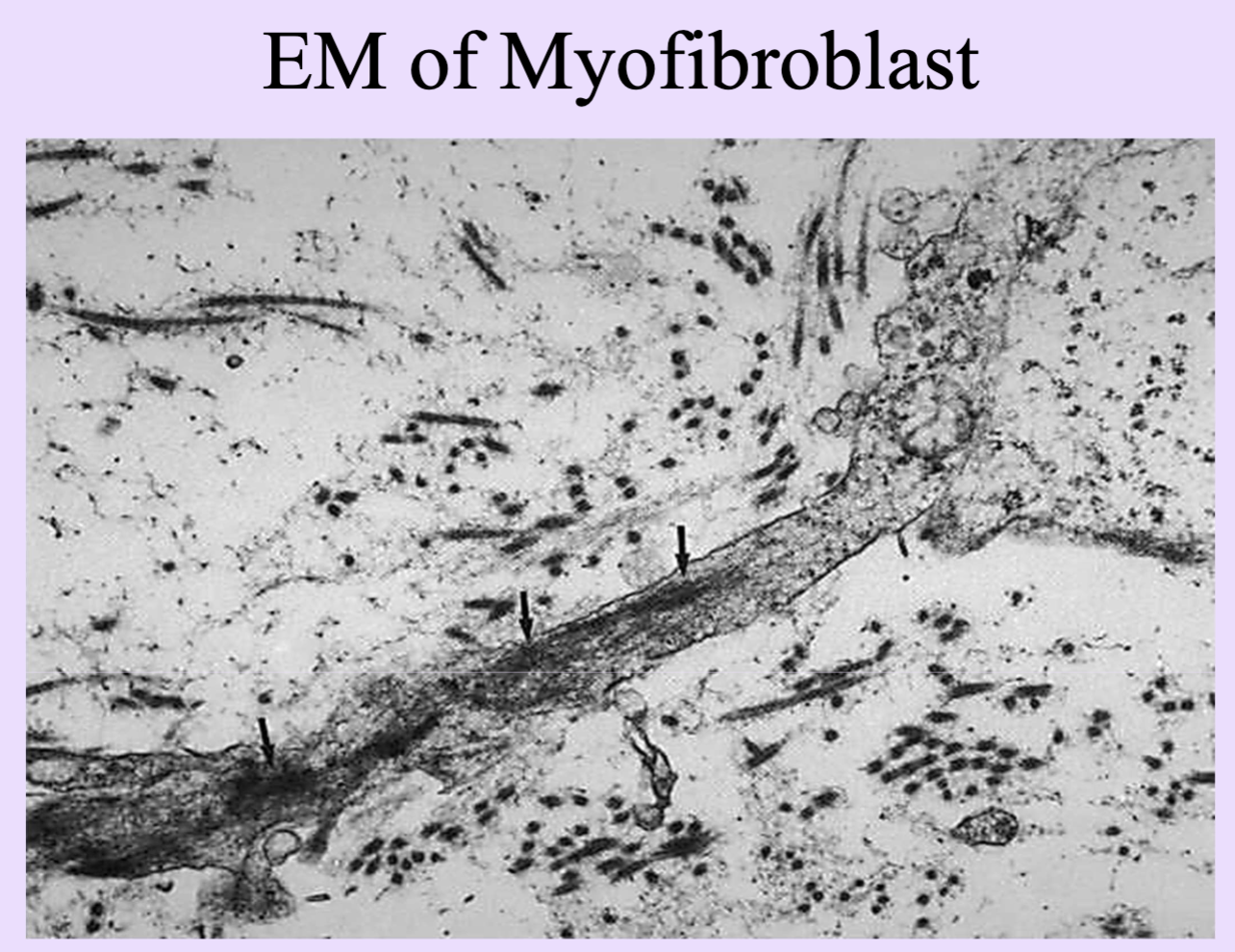
Myofibroblasts
Contractile fibroblasts that pull wound margins together during healing.
Enables proliferating epithelial cells to cover surface defect
First few days, properties of smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts
Angioblasts
Precursors of blood vessels
Vascular progenitor cells that form new blood vessels in healing tissue.
2-3 days after incision
Fibroblasts
Cells that produce MOST extracellular matrix; synthesize collagen and fibronectin.
Fibronectin - provides tensile strength and glues other substances and cells together
Collagen - first has immature type III collagen laid down by fibroblasts
Type I collagen
Mature, strongest collagen type; predominates in healed tissue.
Granulation tissue
Vascularized connective tissue with macrophages, myofibroblasts, angioblasts; temporary matrix.
Re-epithelialization
Epithelial cells proliferate and cover the wound surface from margins.
First intention (primary union)
Healing with apposed wound edges; scab formation and organized repair.
healing of sterile wounds
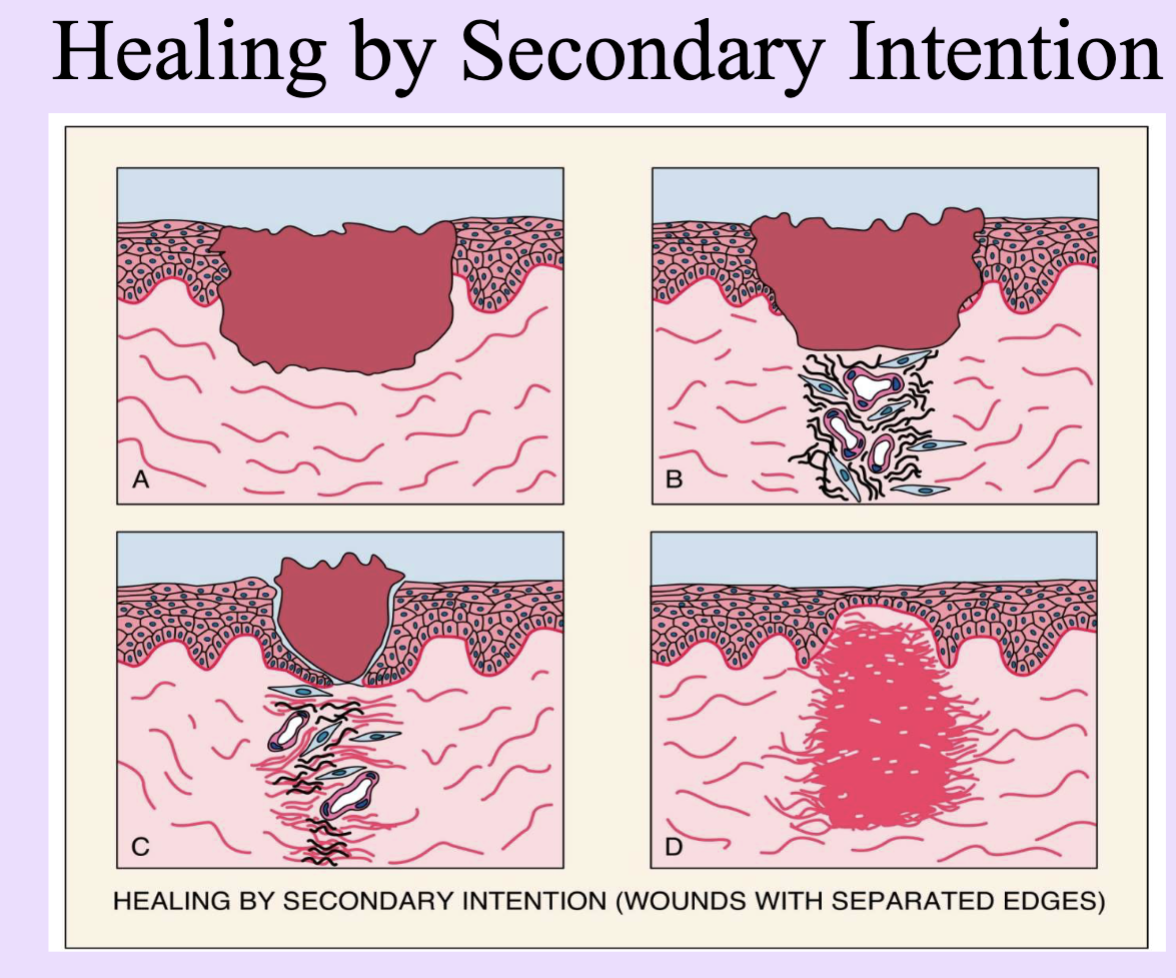
Secondary intention
Healing of large defects with separated edges; slower, more scar formation.
nonsterile, infected wounds
Delayed wound healing
Healing delayed by site, infection, mechanical factors, age, circulatory status, nutrition.
most important determinants of healing are; site, and infection
Mech. factors - minimal movement, juxtaposed edges, age, circulatory status (ie diabetes), nutritional and metabolic factors
Wound dehiscence
Separation of wound margins due to impaired healing or weakness.
Keloids
Hypertrophic scars with excessive Type III collagen; defective remodeling.
Scar
Final remodeled connective tissue with collagen, restoring strength.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
Nutritional factor essential for collagen synthesis and wound healing.
Complications of Wound Healing
Deficient Scar Formation - sluggish formation of granulation tissue in diabetic PTs due to ischemia and metabolic disturbances
inadequate collagen production in PTs with corticosteroid