Microbiology-Cell Chemistry
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Importance of microbes
decaying process
DNA rep. and genetic engeneering
food production
Bio remediation
What are the three forms of carbs?
monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
what is the structure of a monosaccharide?
1-2-1, C6H12O6
what are the 5-carbon monosaccharides?
deoxyribose and ribose
what are the 6-carbon monosaccharides?
glucose, galactose, fructose, and mannose
what is the formula and the types of disaccharides?
C12H22O11-sucrose, maltose, and lactose
what is the formula and types of polysaccharides?
1-2-1, glycogen, starch, cellulose, and dextran
what are the functions of mono and disaccharides?
covert energy into ATP (energy source)
Make up DNA & RNA
what are the functions of a polysaccharide?
structural components
provide an energy source
what are the two types of lipids?
Simple and compound
what is a simple lipid?
made up of glycerol and fatty-acids
what is a compound lipid?
lipids bonded to other structures
what are the functions of lipids?
provide energy
store energy
provide structure to build hormones
What is the structure of a protein?
amino group, side chain (R chain), carboxyl group; folding; hydrophilic or hydrophobic
what does it mean for a protein to be hydrophilic?
water-soluble (outside of the cell)
what does it mean for a protein to be hydrophobic?
water resistant (inside the cell)
Primary structure of protein
amino acid sequence (bonds)- genes
secondary structure of proteins
double helix (folding)
what is the tertiary structure of protein
polypeptide chain (how bonds between R groups interact)
What are the functions of a protein?
structure of the cell
enzymes
movement, communication, etc.
aqueous (found in water)
what is a Nucleic Acid in DNA?
genetic code information is needed to build and maintain a cell and to be transcribed into RNA
what is a Nucleic Acid in RNA?
transcribed into a protein (the process of protein synthesis)
what is the structure of a nucleotide?
deoxyribose/ ribose
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
what are the bases of DNA?
adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine
what are the bases in RNA?
thymine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine
where does replication begin in Prokaryotes?
bacteria; binary fission in the beginning of the process
where does replication begin in Eukaryotes?
Plants and animals; mitosis in interphase
why is DNA replication important for humans?
growth, replacement, repair process
why is DNA replication important for bacteria?
replication of itself
semi-conservative
half of the original DNA is conserved in the 2 daughter cells, then a new half is manufactured during replication process, which is synthesized
DNA Polymerase functions
reads parental strand
matches nucleotides
proofreading
replaces RNA with DNA
3 types of RNA
messenger RNA; mRNA
transfer RNA; tRNA
ribosome RNA; rRNA
what is the process of gene expression?
DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into a protein
what percentage of DNA has to be replicated to form new daughter cells?
100%
Cells ____________ synthesize proteins
Constantly
`how many genes are transcribed at a time per protein?
ONLY 1
what carbon is a base attached to?
carbon-1
what carbon is the 2nd nucleotide bonded with?
carbon-3
what direction does DNA polymerase add to?
5 → 3
what is the function of the Helicase?
breaks through hydrogen bonds between bases on the parent strands, separating them
what is a phosphodiester bond?
dehydration synthesis; has nucleotides together
what does an anticodon sequence do?
determines the specific amino acid carried during protein synthesis
where does translation occur?
in the cytoplasm of the ribosome
what does tRNA do during protein synthesis?
takes the amino acid to the ribosome
what happens to the replication fork?
an enzyme breaks the bond between the hydrogen bond and the bases
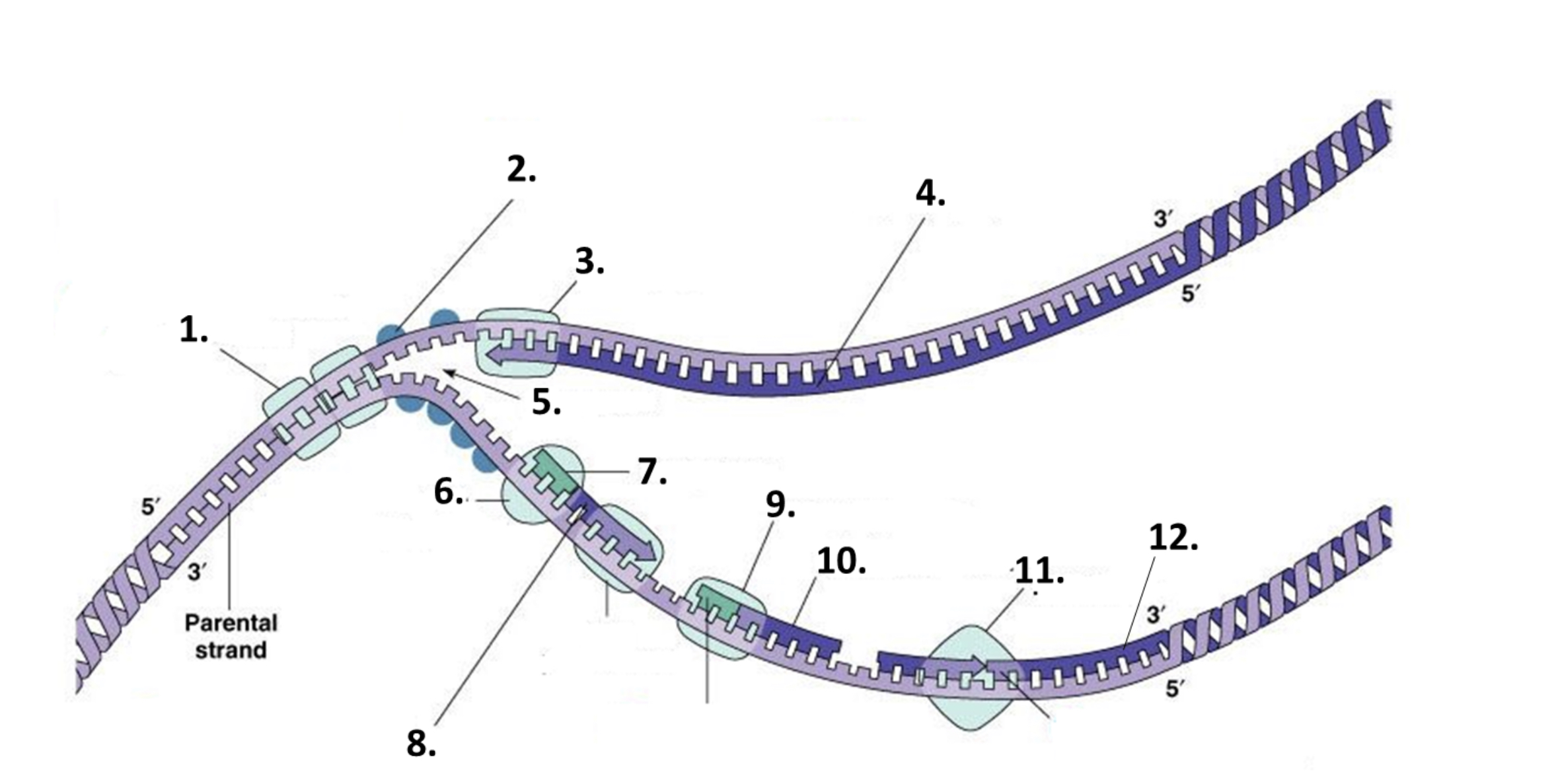
what is number 7 on the diagram?
RNA primer