physics midterm 2023
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/79
Last updated 1:59 AM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
Nuclear energy
Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
2
New cards
Chemical energy
A form of potential energy that is stored in chemical bonds between atoms (ex: battery, food)
3
New cards
Thermal energy
The TOTAL energy of motion in the particles of a substance
4
New cards
Radiant energy
Energy carried by light
5
New cards
Kinetic energy
The energy an object has due to its motion
6
New cards
Law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only altered from one form to another
7
New cards
Gravitational potential energy
Potential energy that depends on the height of an object
8
New cards
Electrical energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons
9
New cards
Elastic energy
The potential energy of an object that is stretched or compressed
10
New cards
Phase energy
The energy stored in the system due to the arrangement of particles that exert attractions on one another, increases when matter changes state of matter
11
New cards
Efficiency
The percentage of the input work that is converted to output work
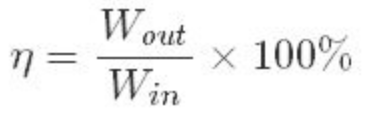
12
New cards
Fahrenheit
A temperature scale with the freezing point of water 32 degrees and the boiling point of 212 degrees
13
New cards
Freezing point
The temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid, equal to melting point
14
New cards
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid, equal to freezing point
15
New cards
Boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
16
New cards
Condensing
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
17
New cards
Evaporation
When some (not all) particles get enough energy to break free, liquid to gas
18
New cards
Specific heat capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1ºC
19
New cards
Absolute zero
The coldest temperature, 0 Kelvin, that can be reached. It is the hypothetical temperature at which all molecular motion stops.
20
New cards
Joule (J)
unit of energy, always capitalized
21
New cards
Frequency (f)
The rate of vibrations of a wave, measured in Hertz (Hz)
22
New cards
Period (T)
Amount of time for one cycle to be completed
23
New cards
Wavelength (λ)
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
24
New cards
Oscillation
Act of back and forth motion, cycle/vibration
25
New cards
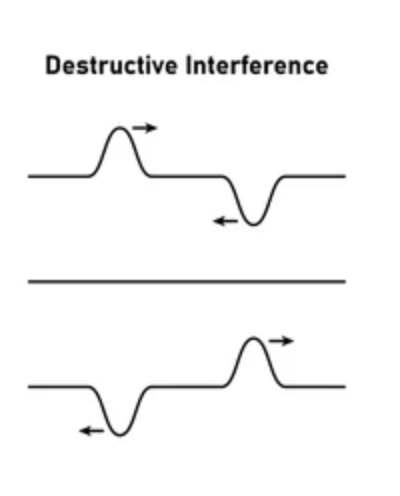
Destructive interference
The interference that occurs when 2 waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude, occurs when waves are out of phase
26
New cards
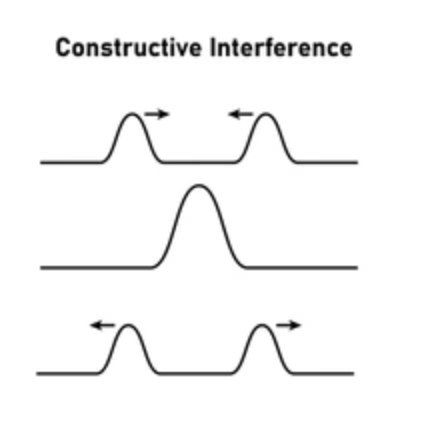
Constructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a larger amplitude, occurs when waves are in phase
27
New cards
Crest
The highest point of a transverse wave
28
New cards
Trough
tThe lowest point of a transverse wave
29
New cards
Wave
A repeating disturbance that transfers energy from place to place without transferring the medium
30
New cards
Rarefaction
The part in a longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart
31
New cards
Compression
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together
32
New cards
Pitch
a tone's experienced highness or lowness, depends on frequency
33
New cards
Amplitude
The maximum displacement on either side of the equilibrium position
34
New cards
Absorption
The wave is absorbed and disappears
35
New cards
Transmission/Propagation
Waves pass through a given medium
36
New cards
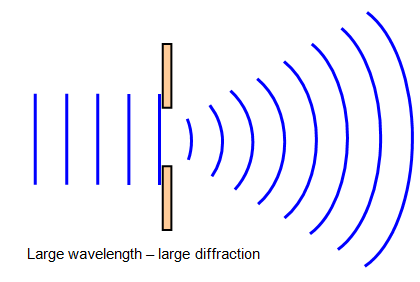
Diffraction
Occurs when an object causes a wave to change direction and bend around it
37
New cards
Reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a surface through which it cannot pass.
38
New cards
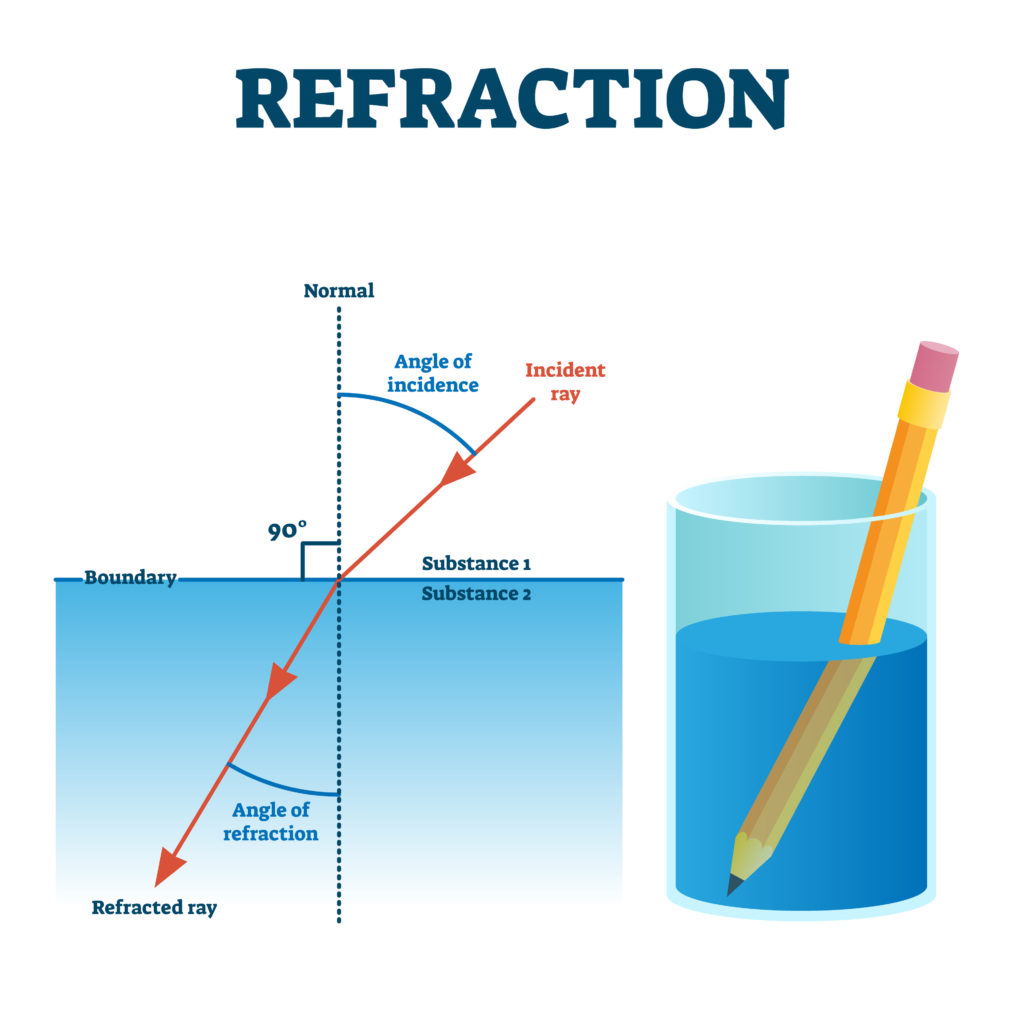
Refraction
The bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another
39
New cards
Resonant frequency
Frequency at which a standing wave occurs, natural/unforced resonance
40
New cards
Ultrasound
Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz
41
New cards
Interference
The combination of two+ waves that results in a single wave for a period of time
42
New cards
Electromagnetic (EM) waves
A type of wave that does not require a medium to propagate
43
New cards
Mechanical wave
A wave that requires a medium to propagate
44
New cards
Radio waves
EM waves with the longest wavelengths, lowest frequencies, and lowest energy
45
New cards
X-Ray Waves
Similar in size to an atom, used in telescopes and can be stopped by lead
46
New cards
Gamma rays
Electromagnetic waves with the shortest wavelengths (0.01 nm)and highest frequencies
47
New cards
Ultra-violet (UV) waves
longer than X-Rays but shorter than visible light waves, can cause cancer (100-400 nm)
48
New cards
Microwaves
very short electromagnetic wave, .1 cm to 30 cm
49
New cards
Visible light
Electromagnetic radiation that can be seen with the unaided eye, 740 to 435 nanometers.
50
New cards
Infrared waves
second on the electromagnetic spectrum going from lowest to highest frequency. can be felt as heat, 780nm - 1mm
51
New cards
Order of EM waves (longest to shortest)
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible, UV, x-ray, gamma
52
New cards
Latent heat of vaporization
The amount of energy required to change a unit mass of a substance from liquid to gas, Q = mL
53
New cards
Latent heat of fusion
The amount of energy required to change a unit mass of a substance from solid to liquid, Q = mL
54
New cards
Fission
The splitting of an atomic nucleus to release energy
55
New cards
Fusion
The process or result of joining two or more things together to form a single entity.
56
New cards
C
Specific heat capacity (J/kgºC)
57
New cards
d
Distance (m)
58
New cards
E
Energy (J)
59
New cards
Eff
Efficiency (%)
60
New cards
f
Frequency (Hz)
61
New cards
g
Gravitational acceleration (m/s)
62
New cards
Δh
Change in height (m)
63
New cards
KE
Kinetic energy (J)
64
New cards
λ
Wavelength (m)
65
New cards
m
Mass (kg)
66
New cards
Q
Heat added or removed (J)
67
New cards
v
Velocity
68
New cards
ΔT
Change in temp
69
New cards
T
Period (s)
70
New cards
ΔT
change in temperature
71
New cards
Celcius
Metric temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees
72
New cards
Elastic energy
The potential energy of an object that is stretched or compressed
73
New cards
Gravitational potential energy
Potential energy that depends on the height of an object
74
New cards
System
A group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements or parts that function together as a whole to accomplish a goal
75
New cards
Temperature
A measure of how hot (or cold) something is; specifically, a measure of the AVERAGE kinetic energy of the particles in an object
76
New cards
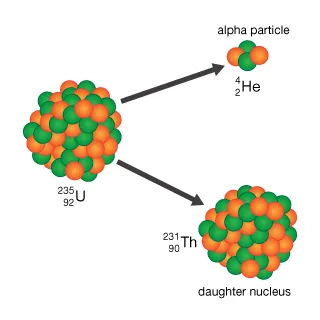
Alpha decay
A nuclear reaction in which an atom emits an alpha particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. This increases the atomic number by 2 and the mass number by 4.
77
New cards
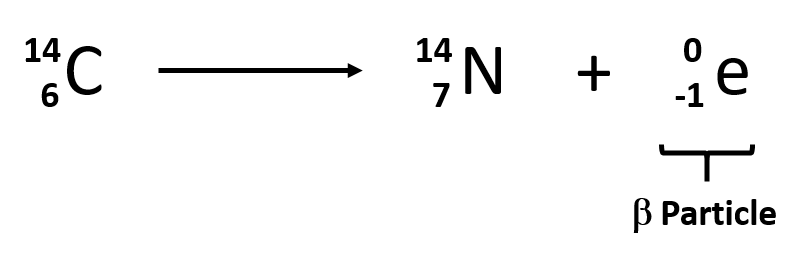
Beta decay
Radioactive decay which occurs when a nucleus with too many protons or too many neutrons emits an electron in order to transform one of the protons or neutrons into each other
78
New cards
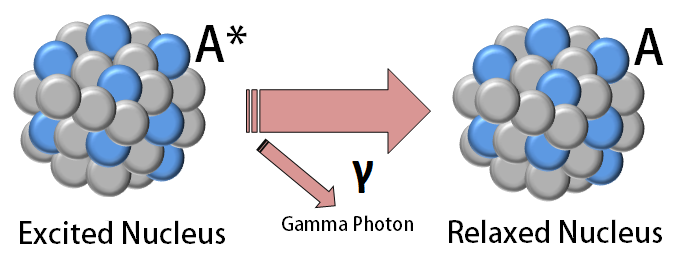
Gamma decay
Radioactive decay in which an unstable nucleus emits a gamma photon in order to dissipate excess energy and stabilize the nucleus
79
New cards
Neutron decay
One neutron is emitted from the nucleus
80
New cards
Pressure energy
Pressure in gases or liquids has the potential to move objects due to the force it can exert