Chemistry - 14 The Earth's Resources - 14.1 Finite and Renewable Resources & 14.2 Water Safe to Drink & 14.3 Treating Waste Water
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Renewable
resources that will not run out and reform as they are used
Finite
resources that will run out and cannot reform at the same rate as they are used
Natural resources [5]
- wood
- rubber
- fossil fuels
- metal
- water
Man-made resources [4]
- plastic
- glass
- paper
- alloys
Sustainable development
development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the needs of the future
Biofuels
fuel derived directly from living matter
Ore
rock that contains enough metal to make it economically worth extracting
Advantages of mining [2]
- creates employment opportunities
- brings money to local and country economy
Disadvantages of mining [4]
- metals are finite
- noise and dust pollution from machines
- greenhouse gases from machinery
- damages habitats and settlements
How can ethanol be made? [2]
- fermentation of glucose
- cracking of ethene
What features define a 'good' fuel? [4]
- strongly exothermic
- easy to make/extract
- non-toxic (including products)
- cheap
Advantages of fermentation to produce ethanol [3]
- sugar cane regrows (renewable)
- sugar cane absorbs carbon dioxide as it grows
- low energy process
Disadvantages of fermentation to produce ethanol [3]
- ethanol produced is impure
- large areas of land required
- slow process
Advantages of cracking ethene to produce ethanol [2]
- pure product
- faster process
Disadvantages of cracking ethene to produce ethanol [2]
- high energy process (requires high temperatures)
- uses finite resources
Potable
suitable and safe to drink
Groundwater
water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock
Surface water
water that collects on the surface of the ground, such as in rivers and lakes
Fresh water
water that contains insignificant amounts of salts, as in rivers and lakes, from rain
Sterilising agent
removes microorganisms from an object or substance
Sterilising agents used to treat drinking water [3]
- chlorine
- ozone
- UV light
Treating fresh water process [6]
- water travels through screens to filter out debris
- settlement tank allows sand and soil to settle out
- aluminium sulfate and lime are added to cause particulates to clump and sink
- passed through a filter made from fine sand and gravel
- sterilising agents are added to kill pathogens
- potable water is kept in a reservoir
Pure water
only contains H₂O molecules
Pure water is made by ...
distillation
Why is drinking water not distilled? [4]
- time-consuming
- high energy process
- expensive
- unnecessary
Why might desalination be needed? [2]
- surface water evaporates in hotter areas
- drier regions may not get enough rain for their population
How is an appropriate source for potable water found? [2]
- samples are evaporated and crystallised
- solids are weighed and compared to total mass
Desalination
removing salt from water
Methods for desalination [2]
- distillation
- reverse osmosis
Flash distillation
reducing pressure so that water's boiling point becomes lower, which saves on energy and money
Reverse osmosis
water is pressurised through a partially permeable membrane, removing 98% of salts
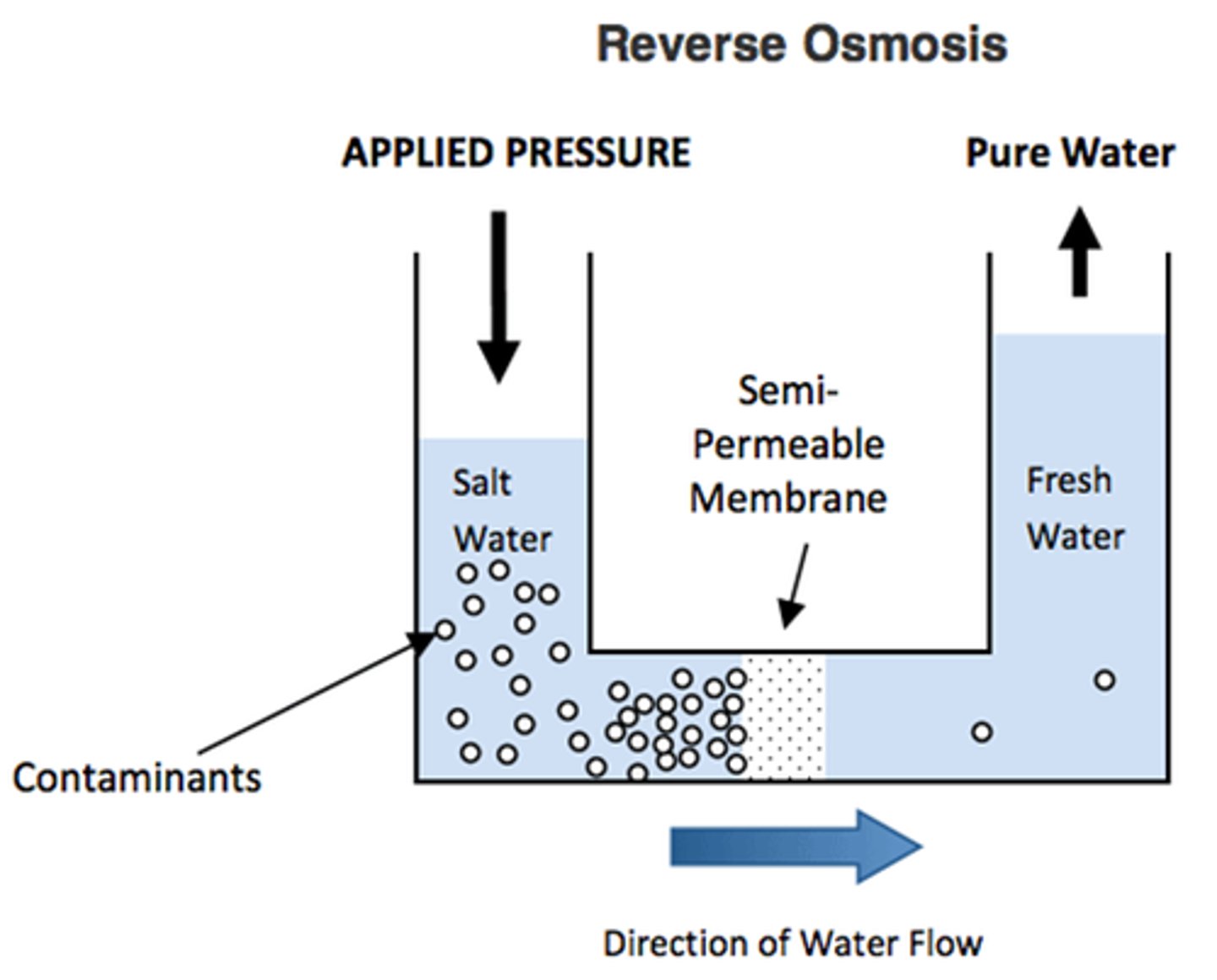
Problem with reverse osmosis
requires high energy and money
Sewage
solid and liquid waste from homes, businesses and agriculture that is carried away by sewers or drains
What must be removed from sewage? [3]
- organic matter
- harmful live microbes
- harmful chemicals
Treatment of sewage [4]
- screening
- primary treatment
- secondary treatment
- final treatment
Screening
passing sewage through mesh screens to remove solid debris
Primary treatment [2]
- sedimentation
- separation of sludge and effluent
Sedimentation
allowing solid substances to settle out of the sewage
Sludge
solids from sewage
Effluent
sewage without solid debris
Secondary treatment [1]
- aerobic digestion of effluent
What is the purpose of aerobically digesting effluent?
breaking down any remaining organic matter, including harmful microbes
Final treatment [3]
- secondary sedimentation
- (optional) filtering
- (optional) sterilisation
Secondary sedimentation
allows remaining organic matter, including both harmful and helpful microbes, to settle out
Sludge treatment [2]
- anaerobic digestion
- drying out
Anaerobic digestion of sludge [2]
- can take up to 30 days
- releases biogas which can be used as fuel
Drying sludge
can be dried into 'cakes' which can be burnt to generate electricity