THERMODYNAMICS HAVENT FINISHED
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the definition of the enthalpy change of formation of a compound?
the energy transferred when 1 mole of the compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions where all the reactants and products are in their standard states
What is the definition of the enthalpy of atomisation?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms is formed from the element in its standard states
What is the definition of the enthalpy of sublimation?
the enthalpy change of a solid metal turning to gaseous atoms and will numerically be the same as the enthalpy of atomisation
What is the definition of the bond dissociation enthalpy?
the standard molar enthalpy change when 1 mole of a covalent bond is broken into 2 gaseous atoms
\\what is the bond enthalpy of dissociation for diatomic molecules?
2x the atomisation energy of the element
What is the definition for the first ionisation energy?
the enthalpy change required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous ions with a +1 charge
What is the definition of the second ionisation energy?
the enthalpy change to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions to produce 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions
What is the definition of the first electron affinity?
enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of gaseous atoms gain 1 mole of electrons to form 1 mole of gaseous ions with a -1 charge
exothermic for atoms that normally form negative ions
What is the definition for the second electron affinity?
enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous 1- ions gains 1 electron per ion to produce gaseous 2- ions
endothermic as it takes energy to overcome the repulsive force between the negative ion and the electron
What is the definition of the enthalpy of lattice formation?
the standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic crystal lattice is formed from its constituent ions in gaseous form
What is the definition of the enthalpy of lattice dissociation?
standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic crystal lattice form is separated into its constituent ions in gaseous form
What is the definition of the enthalpy of hydration?
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions becomes aqueous ions
exothermic as bonds are made between the ions and water molecules
What is the definition of the enthalpy of solution?
standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic solid dissolves in a large enough amount of water to ensure that the dissolved ions are well separated and do not interact with onne another
What is the born-haber cycle of sodium chloride?
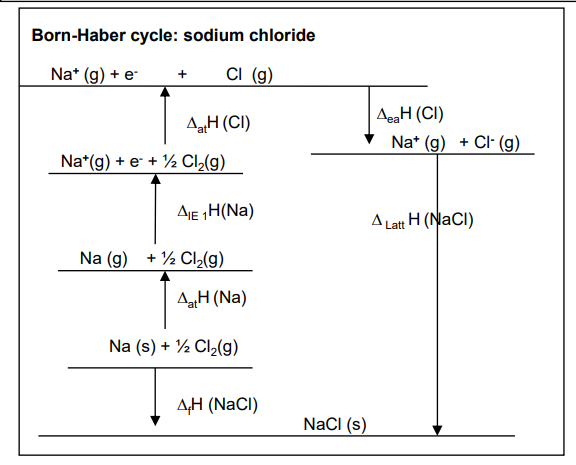
What does the strength of the enthalpy of lattice formation depend upon?
the sizes of the ions (larger ions means that they’re less negative)
charges on the ion (bigger the charge, the greater the attraction between ions)
What is the perfect ionic model?
ions are 100% ionic and spherical and attractions are purely electrostatic
When is there usually a tendency towards covalent character in ionic substances?
positive ion is small
positive ion has multiple charge
negative ion is large
negative ion has multiple negative charges
Why is there usually differences between theoretical and born haber lattice enthalpies?
the compound may show covalent character meaning the theoretical and born haber lattice enthalpies differ
the more covalent character the bigger the difference between the values
What happens to the theoretical value compared to the Born-haber value if a compound has covalent character?
tends towards giant covalent
lattice is stronger
charge cloud is distorted
born-haber would be larger than theoretical value
What happens when the negative ion becomes more covalent?
becomes distorted and polarised
metal cation is polarising the negative ion
What is a spontaneous process?
proceeds on its own without any external influence
What is the problem with an exothermic reaction?
produces products that are more thermodynamically stable
causes them to be spontaneous
What is entropy?
a description of the number of ways atoms can share quanta of energy
the higher the entropy the more ways the substances have to arrange their atoms and the more disordered energy there is
What do elements, simpler compounds and purer substances tend to have lower entropies than?
compounds, complex compounds and mixtures