Chemistry Final
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
VSEPR
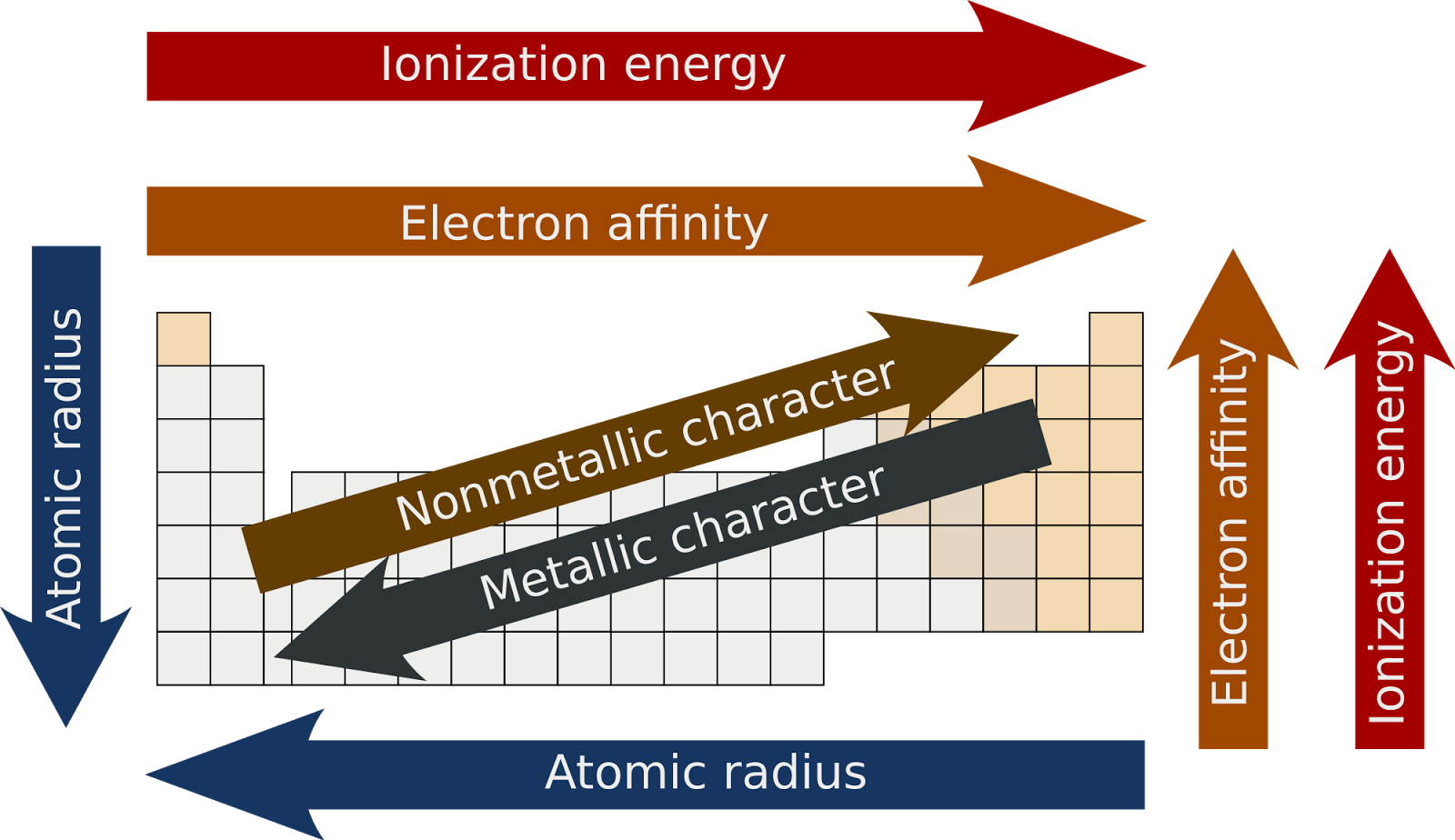
Periodic Trends
Periodic Trends
Ionic compounds
Higher melting point
Law of conservation of mass
Chemical equations mass cannot be created or destroyed
Physical change
A change in state of matter (Water to ice)
Chemical change
A substance is changed into a new one
The temperature changes
a gas is produced
a precipitate forms
the color changes
How to know if a chemical reaction has taken place
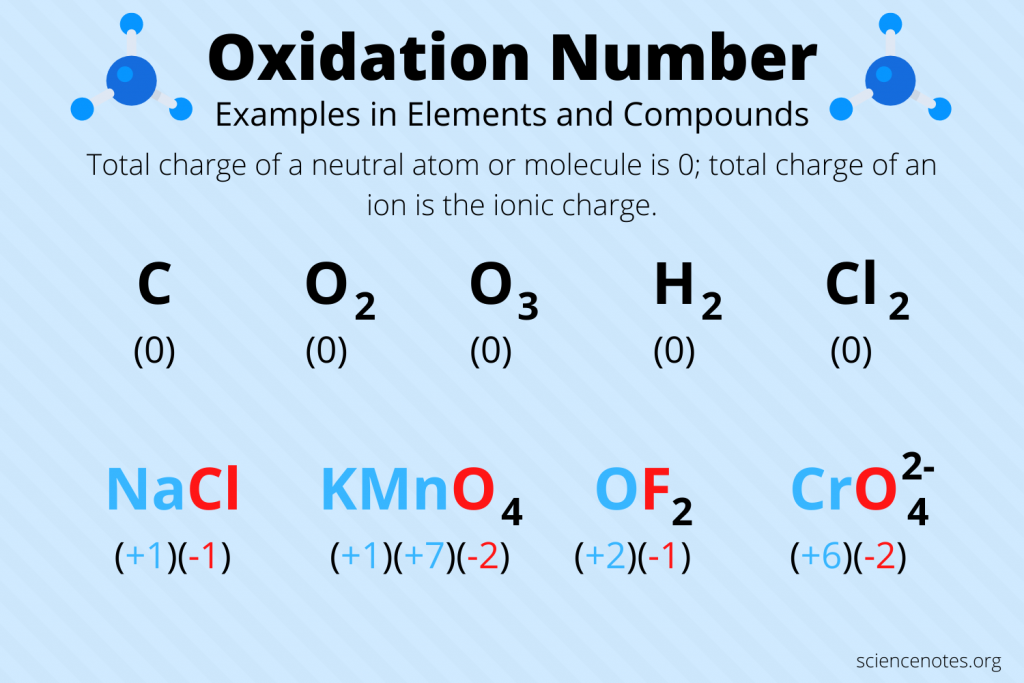
Oxidation numbers
Oxidation numbers
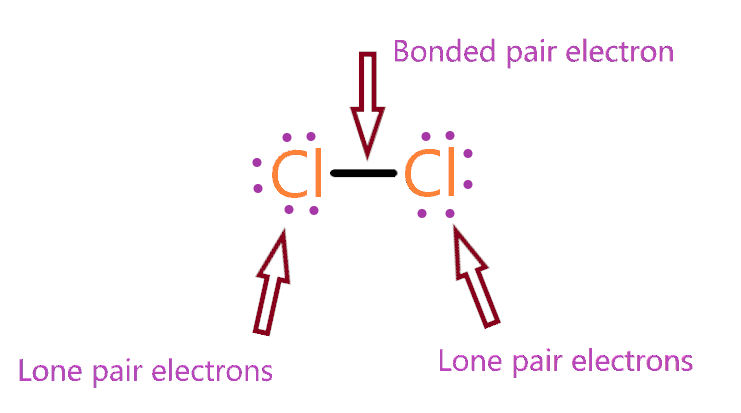
Lone and bond pairs
Lone and bond pairs
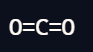
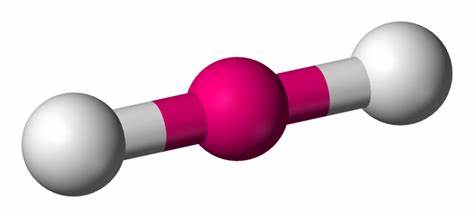
Linear
2 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
180 degrees

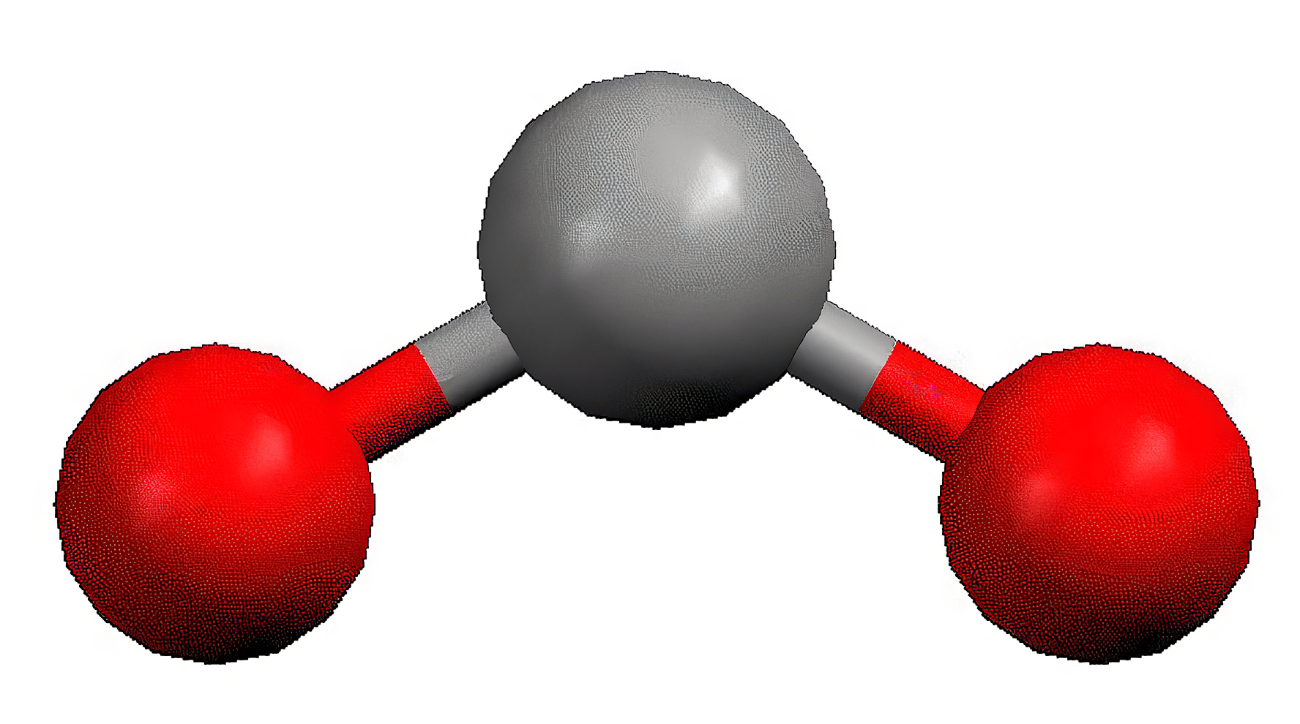
Bent
2 bond pairs
1 or 2 lone pairs
120 degrees
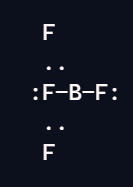
Trigonal Planar
3 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
120 degrees
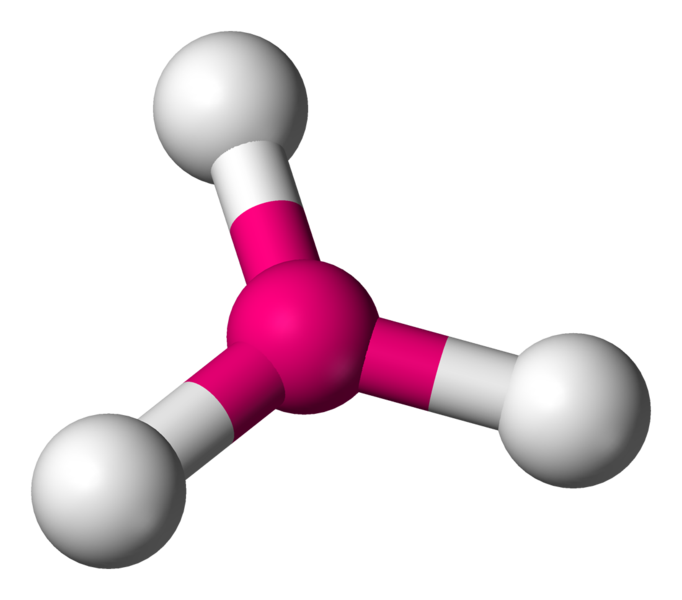
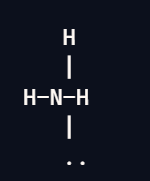
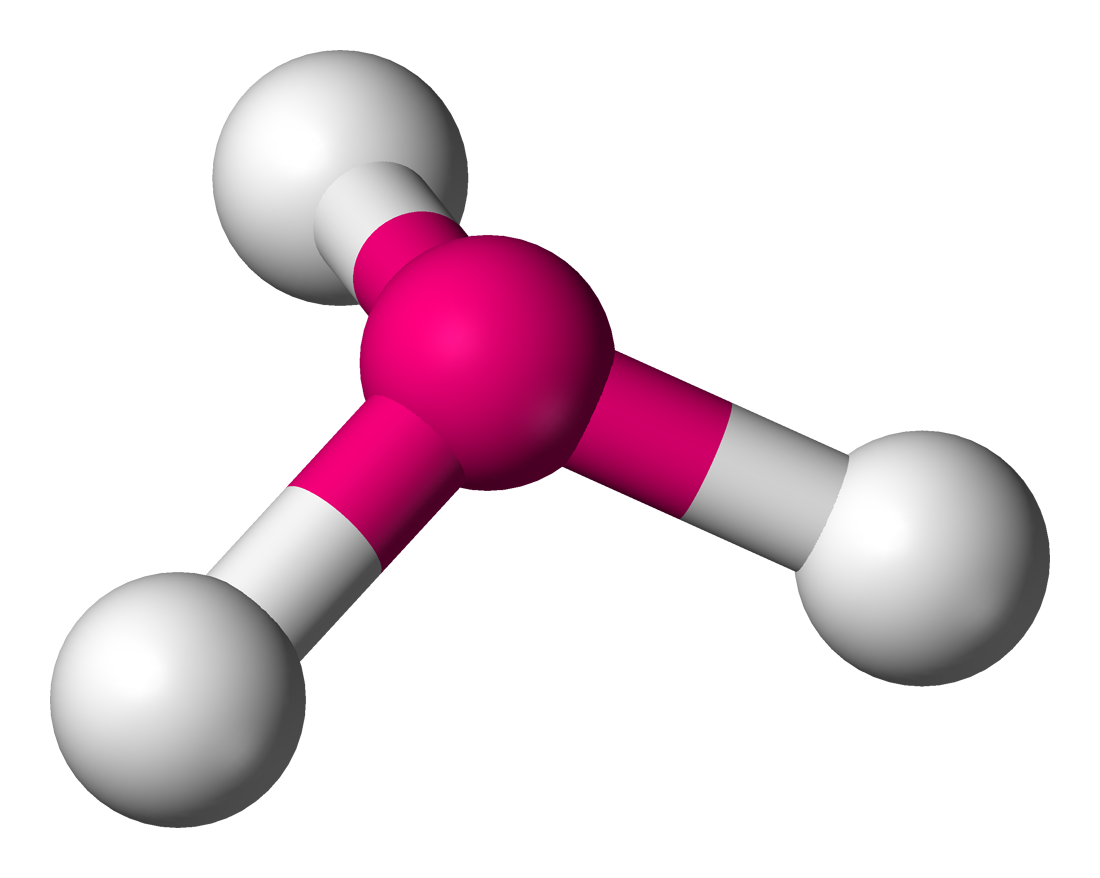
Trigonal Pyramidal
3 bond pairs
1 lone pair
109.5 degrees
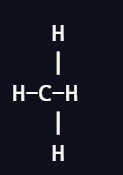
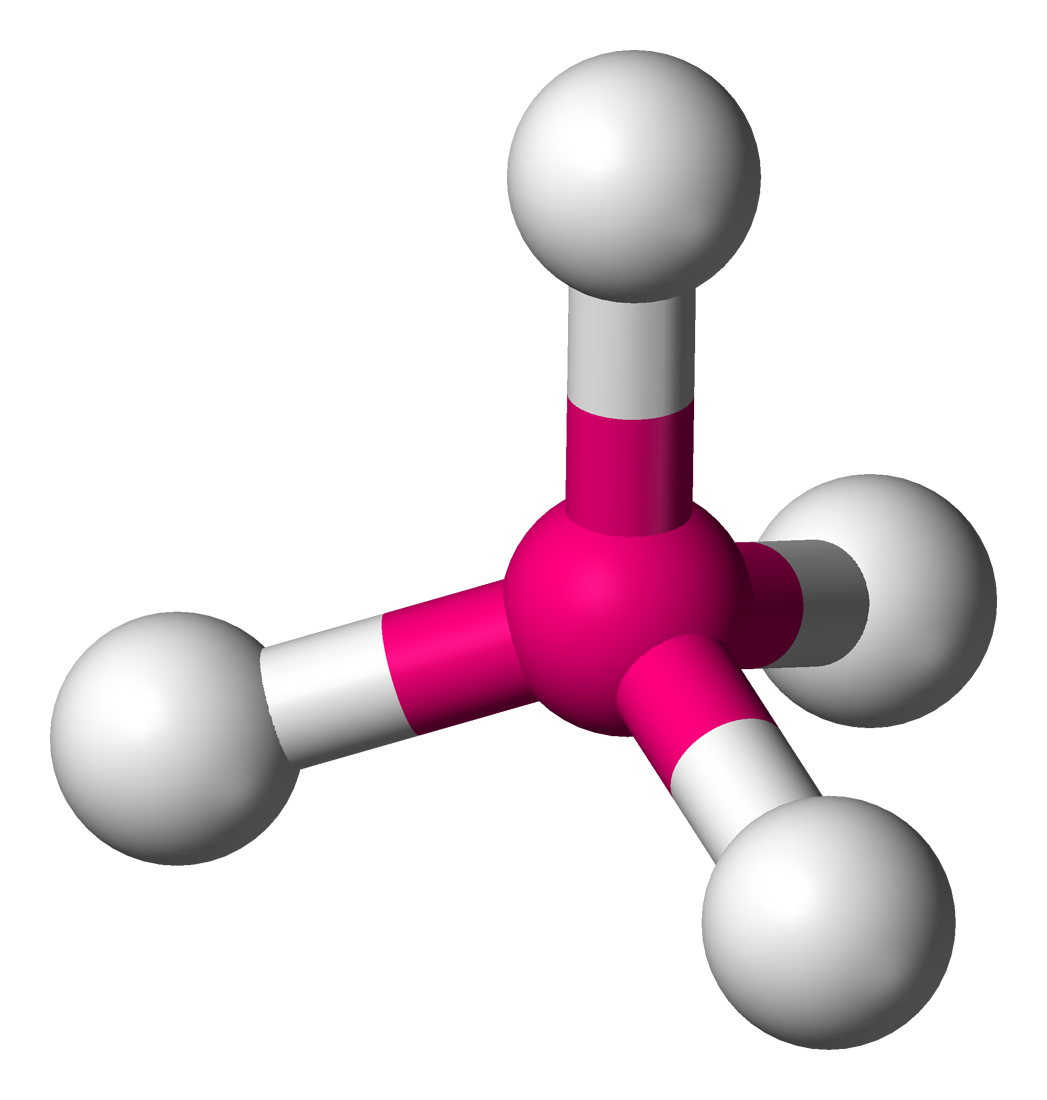
Tetrahedral
4 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
109.5 degrees
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
3 main types of chemical bonds
chemical reaction
a process where one or more elements or compounds are changed into different substances
product
the new substances
on the right side of a chemical reaction
reactant
the original substances
on the left side of a chemical reaction
chemical equation
what happens in a chemical reaction
counting moles and atoms
counting moles and atoms
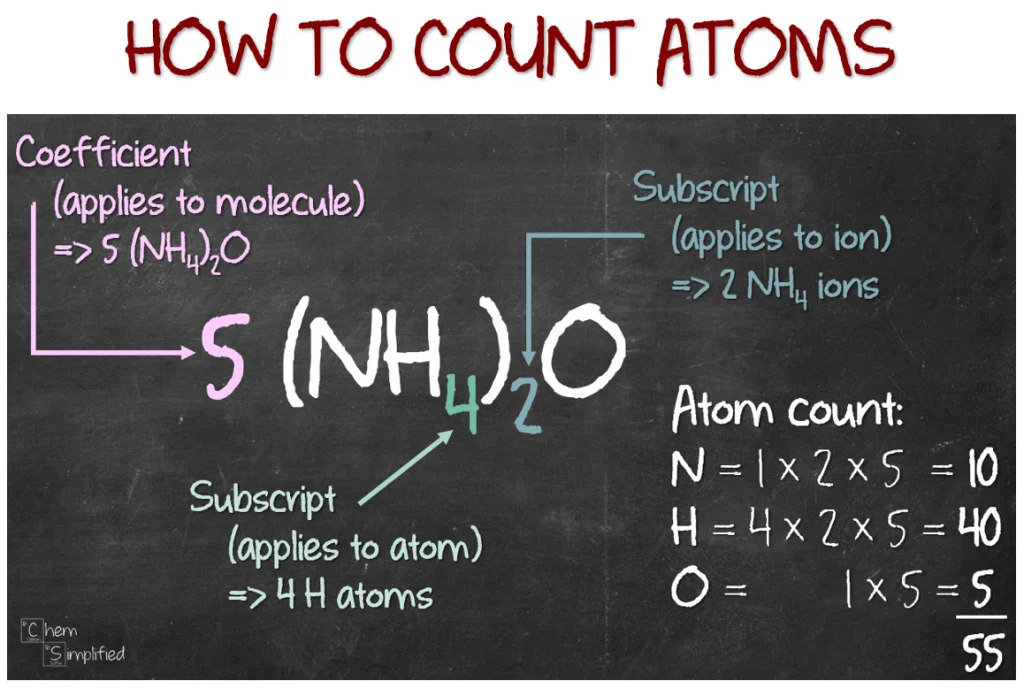
3
number of moles in 3CH4
15
number of atoms in 3CH4
synthesis
two or more substances combine to form a new compound
decomposition
a compound decomposes into two or more simpler substances
combustion
a substance will combine with oxygen, and in the process give off energy in the form of light and heat
single replacement
one element replaces another element in a compound
double replacement
two ionic compounds exchange ions in solution to form two new compounds