Motor Development ◡̈
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
In a normal loading response, ____________ on the weighted side and ___________ on the unweighted side
Elongation; shortening
Random- Spontaneous Non-Purposeful Movements
Newborn can lift head momentarily and turn it to the other side
Random kicking and UE movements in supine and prone
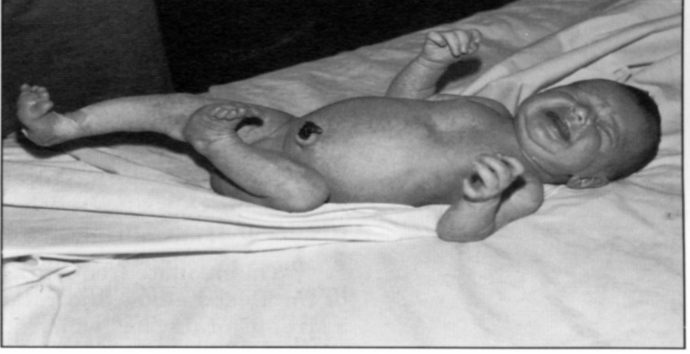
Bilateral Symmetry
Infant can lift head in prone and orient the head. The face is vertical and mouth is horizontal.
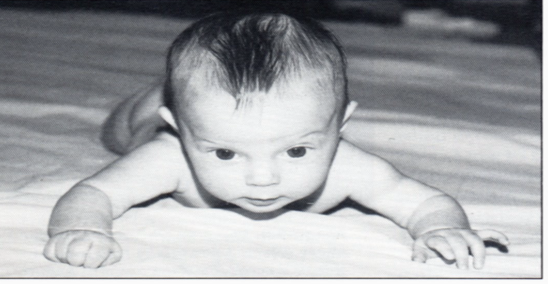
Why doesn’t a child have control over midline orientation of head at 3 months old in supine?
Antigravity flexor control is underdeveloped
Alternate Reciprocal Movements
At 3.5 months, baby lifts head in a bilateral symmetrical patterns and turns it to one side or other with purpose and control
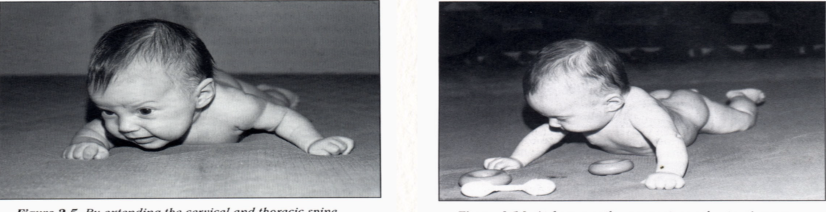
Unilateral Symmetrical
Flexor and extensor muscles on the same side work together and are balanced to produce lateral movement of the head and/or trunk
Unilateral Symmetrical movements are first seen during as…
Lateral tilting of the head @ 4 months
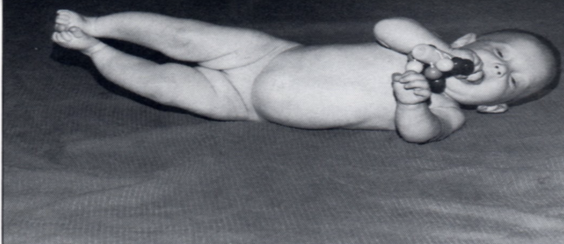
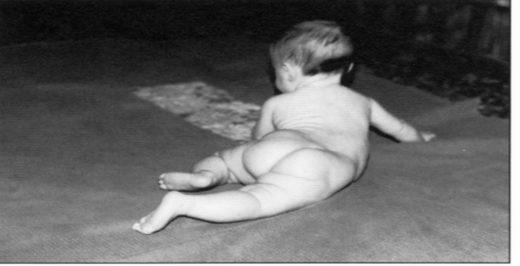
Diagonal Reciprocal
Most advanced, require the ability of the first four movements
Involves activity of the contralateral upper and lower extremities working across the trunk
There is a weight shift. Trunk will elongate (weighted) and shorten (unweighted)

Structural Stability
Soft tissue tightness due to in utero positioning, occurs when newborn is placed in prone
Baby can maintain a flexed position because of tightness of the flexor muscles
Positional Stability
Infants begin to move into antigravity posture
Achieved by using the body/body parts to create a large based of support (standing/sitting with legs widely abducted, support on arms)
Internal Stability
Develops righting reactions, protective extension, and equilibrium reactions
Has internal control mechanism that allows baby to maintain position or posture without the need for position control
As ___________ ____________ develops, the size of the base of support will ___________
Internal stability; decrease
Pull to Sit maneuver
In supine, grasp infant’s hands and pull towards you.
Head lag due to lack of antigravity flexor control until 3-4 months
Palmar Grasp

Radial Palmar Grasp
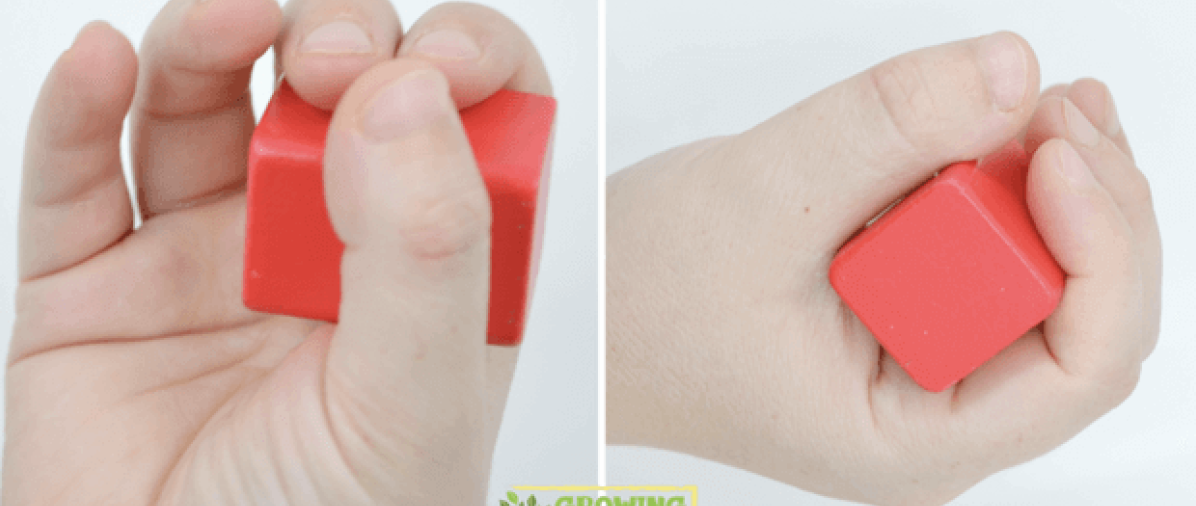

Lateral Pinch/Scissor Grasp

3 Jaw Chuck
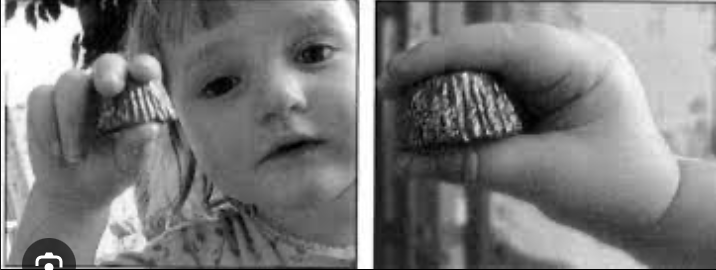
Superior Pincer Grasp

Inferior Pincer Grasp

Ring Sitting
Most stable position, used when engaged in fine motor skills

Long Sitting
Progresses from abduction and semi-extension of knees
Requires elongation of hamstrings
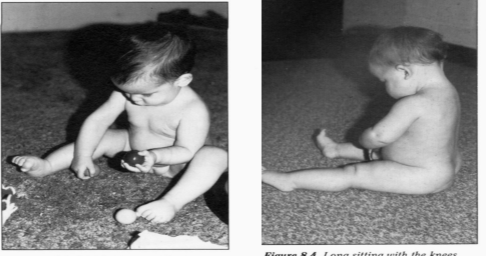
Side Sitting
Wide BOS with combination of internal and external rotation

W Sitting
Promotes muscle imbalances, hypotonia, inhibits transitions to other sitting positions, and inability to actively engage in play due to restricted ROM
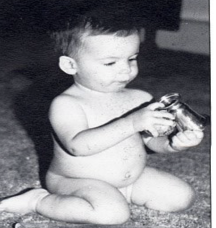
Physiological Flexion
Position of newborn in utero that elongates the extensor muscles, making these muscles powerful against gravity
When do the flexor muscles become stronger?
When the newborn begins to lift their head in prone. By 4 months, we see indications
Antigravity _________ control precedes antigravity _________ control
Extensor; flexor
What are the development and musculoskeletal benefits of side lying?
Provides new sensory experiences, stimulates lateral head righting and helps to shape the rib cage and chest.
Promotes gross motor development as the precursor to rolling over
Which reflex is only present in preterm and sometimes full term infants?
The Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex
What happens if the Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex doesn’t integrate?
Child is unable to achieve supine flexion or prone extension
Child is unable to lift head to clearly airway in prone
Child is unable to bring hands to mouth in supine
Moto development is delayed
Which reflex emerges at 1-2 months (strongest at 2 months) and should be integrated by 5-6 months?
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex
What happens if the ATNR persists?
CNS dysfunction
Inability to engage hands in midline
Scoliosis
Subluxation/dislocation of hip on skull side
Inability to grasp and regard an object at the same time
Inability to separate movements of the head from movements of the arms and trunk
Which reflex emerges at 5-6 months and integrates by 9-11 months?
Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex
What happens if the STNR persists (doesn’t integrate)?
Prevents child from moving trunk and extremities in rotational patterns when the head is in a sagittal plane
Inability to crawl
Tracking for the neonate is easiest when…
Objects are moving laterally and vertically
At what age can the infant only track objects from side to midline?
1 month old
For a 2 month old, what does tracking look like?
Tracks 180 degs horizontally
Can track past midline with concurrent eye and head movement
How does a 3 month old track?
Best when head is slightly extended
Downward tracking is poorly developed
Neonate’s Monocular Vision
Eyes function independently
May not coordinate movements of both eyes resulting in occasional eye wantder
Monocular Vision for the 1 month old
Better control of their eye muscles
Begin coordinating their eyes more effectively
At what age does binocular vision start?
2 months
Binocular Vision for 3 month old
Both eyes are working together to create a single unified image
This is critical for depth perception and accurately perceiving the three-dimensional world
The neonate’s acuity is best when
Object is 8-12 inches away
When is lateral vision better than midline vision
At 1 month old
At 2 months, infant is better as focusing on objects/faces within _____ __________
Arm’s reach
When does the infant begin to show interest in objects/patterns with high contrast (black or white)?
As a neonate
For a 3 month old, acuity looks like?
Can focus on objects at a moderate distance
Better at tracking and recognizing faces from a short distance
When does convergence begin?
At 3 months
Convergence increases
Midlines regard ability
At 4 months, how is reaching accomplished?
Active shoulder adduction with flexion and internal rotation, forearm pronation, and wrist/finger extension
Uses bilateral reaching patterns but one arm reaches the object first
Can’t actively control supination, manipulate or release the toy
In what way can you improve reaching in a 4 month old?
By applying pressure to abdomen
At what age is reaching for toys more successful near the chest but reaching into space is difficult?
4 months
At 5 months, what does reaching look like?
More refined and guided by vision, using a bilateral symmetrical approach
Can now reach to knees, lower legs, and feet due to improved control of shoulder flexion and adduction
In sitting, can reach out for toys when supported and bring to mouth
Manipulation begins
What grasp does a 5 month begin to use
Palmar grasp
At 6 months, what does reaching look like?
More directed/precise.
Can reach with one hand or both
Wrists are extended and can preshape hand when reaching with for a familiar object
Reaches with pronation and wrist/finger extension but uses wrist flexion depending on position or toy.
What grasps are used at 6 months?
Palmar or radial palmar grasps
Rocking forward and backward in quadruped helps with which arches
Longitudinal
Rocking laterally and diagonally in quadruped helps with which arches?
Transverse and oblique arches
The longitudinal arch runs from _____ to _________
Wrist; fingers
The transverse arch is the
Concavity of the wrist
The oblique arch is formed by
The thumb opposing the fingers
How does crawling help with the development of the arches of the hand
The repetitive movement and weight-bearing on hands helps to develop and strengthen arches
What motor skills are involved climbing?
Upper extremity and pelvic weight shifts, elongation of the weight bearing side, lateral righting of the trunk and pelvis, flexion, abduction, and external rotation of the unweighted leg.
What problem-solving abilities does climbing develop?
Managing the body on unfamiliar, uneven, and unsteady surfaces.
What gross motor skills are present/emerging in a typically developing 12-month old?
Sitting
Creeping
Climbing
Kneeling / Half-Kneel
Rise to Stand
Standing
Walking Unsupported
When does creeping integrate?
At 12 months, as unsupported walking starts