AP Chemistry Unit 2 Review
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hopefully I won't bomb this next test like I did the first
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
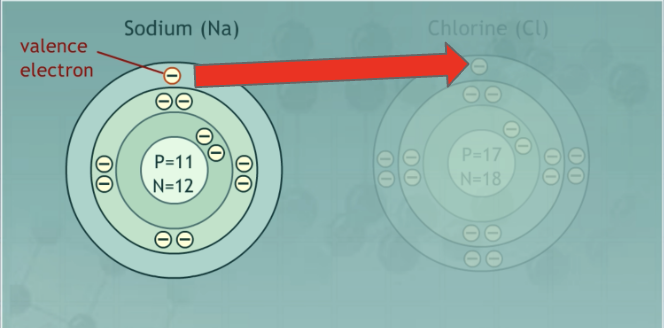
Ionic bond
A bond between a metal and nonmetal in which the metal loses an electron and the nonmetals gains one.
Avg. EN: Medium (one high, one low)
Difference in EN: Large
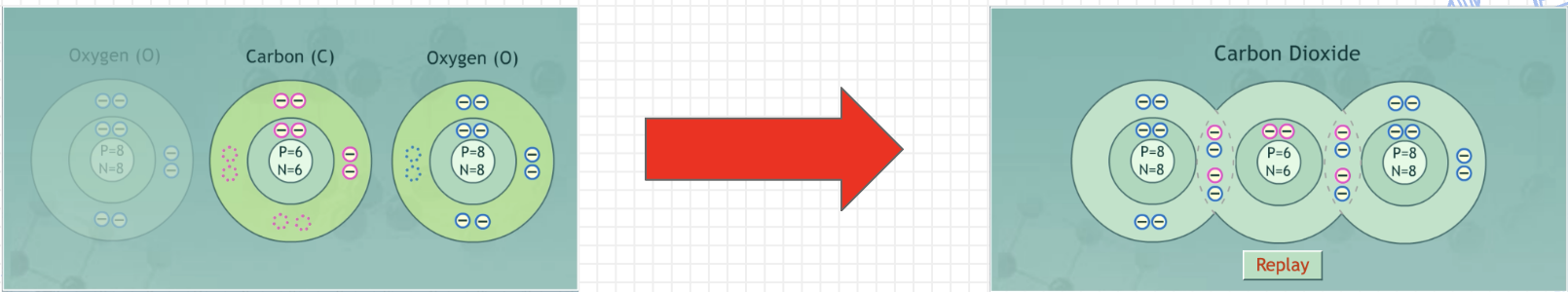
Covalent/Molecular Bond
A bond between nonmetals in which atoms share electrons to fill their valence shells; they all “grab” electrons
Avg. EN: High
Difference in EN: Small (lower if nonpolar, medium if polar)
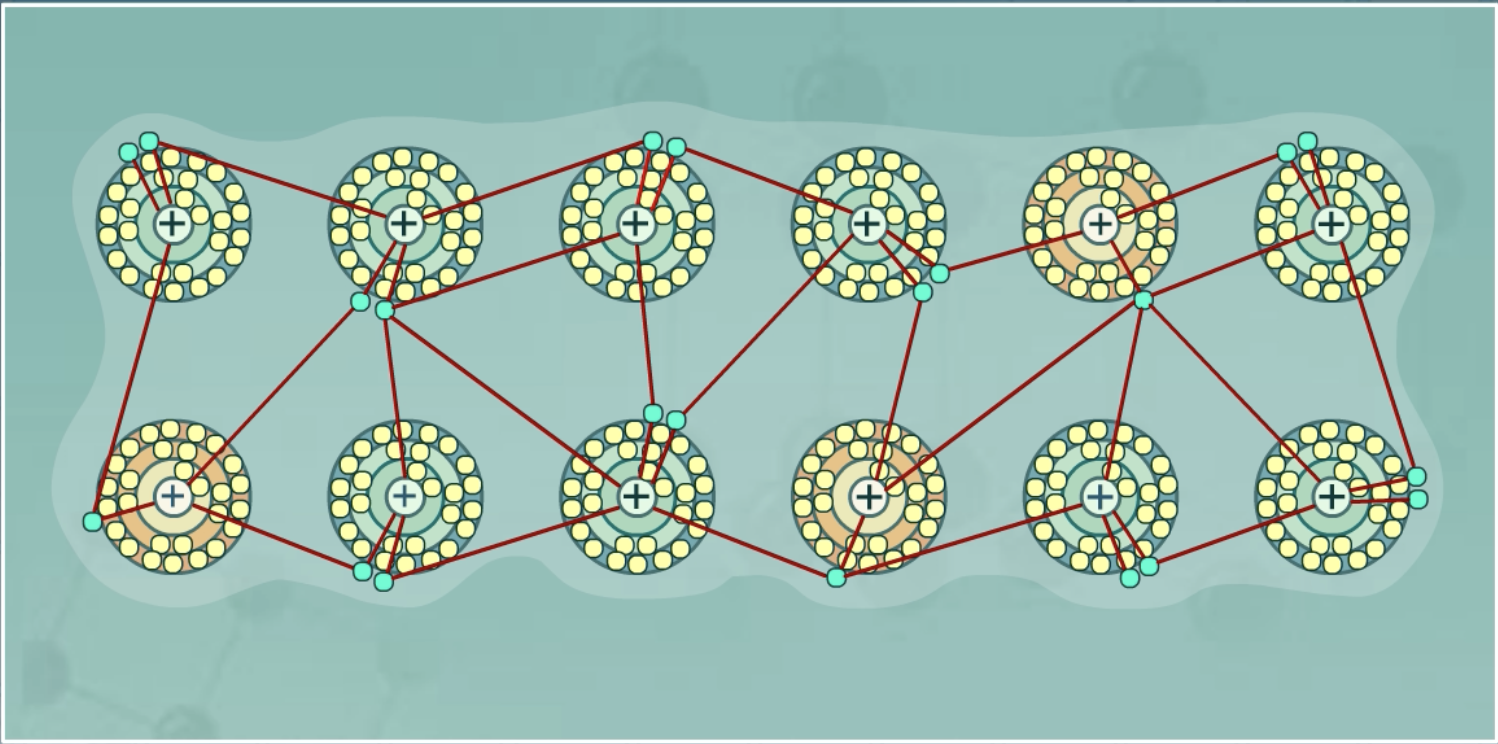
Metallic bonds
A bond between metals in which metallic cations (positive ions) are attracted to a sea of electrons
Avg. EN: Low (metals want to lose electrons)
Difference in EN: Small
Electronegativity
A quantitative value used to measure the ability/desire of an atom to attract electrons to itself
Bond Polarity
Polar = electrons are shared unequally.
The more unequal the EN, the more polar a bond is.
Dipole Moment
The bigger the dipole moment, the more polar a bond is.
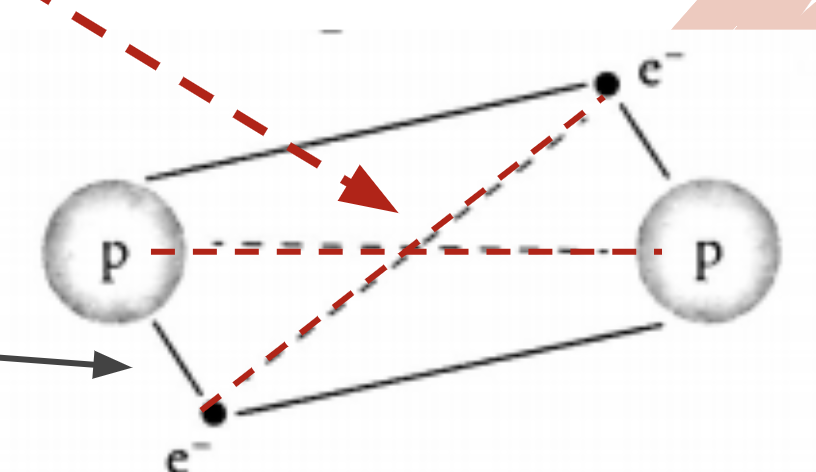
Intramolecular Forces
There are two main forces within a molecule:
2 nuclei repel each other, 2 electrons repel each other
Nuclei + electrons attract each other
Bond Types
Single: 1 pair (2 electrons)
Double: 2 pairs (4 electrons)
Triple: 3 pairs (6 electrons)
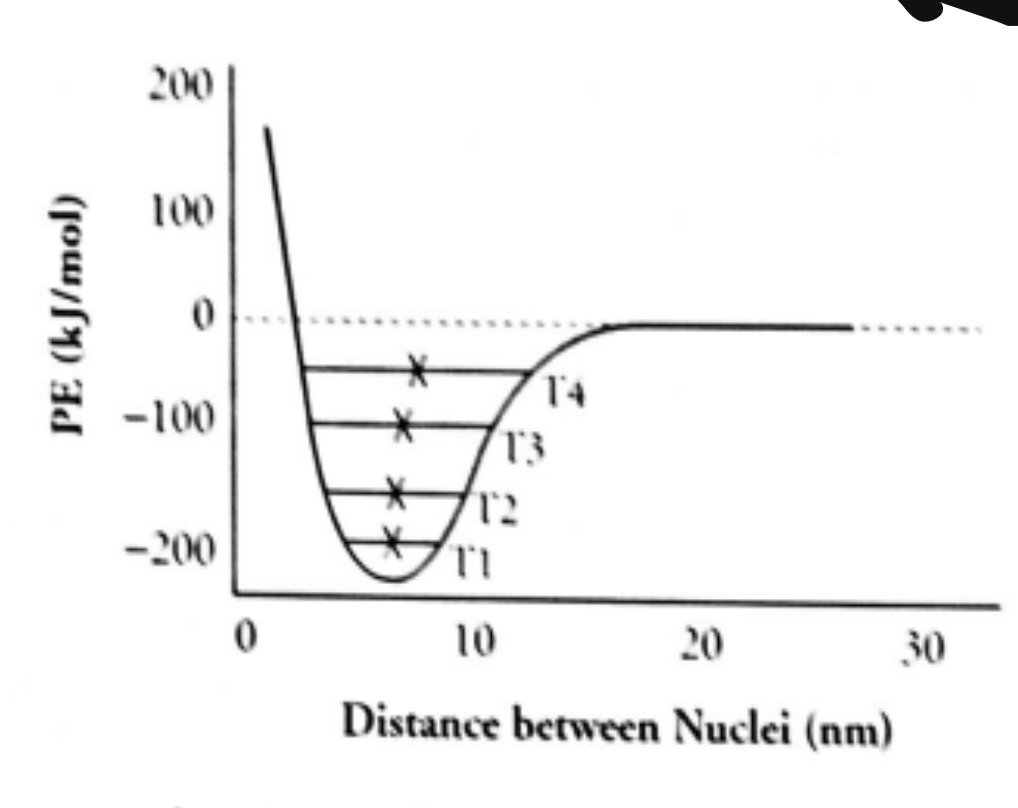
Potential Energy
When there is little distance between atoms, there is a strong force of repulsion between the two, pushing them apart. When they reach a certain distance, called a “goldilocks zone,” there is a perfect amount of attraction between them. If they go too far apart, however, there will be no more attraction or repulsion between them.
Enthalpy
The average change in energy when a bond is broken- calculated by subtracting the total bond energy of the resulting bond from the energy from the starting bonds.
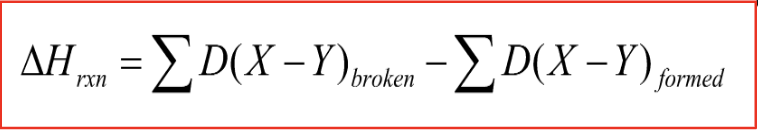
Lattice Energy
The energy required to separate 1 mol of solids into gaseous ions (similar to enthalpy, but for lattices)
Factors that determine Lattice Energy
(In order)
Ion Charge: More positive/negative = stronger attraction = more lattice energy
Ion Radius (size): Smaller = fewer energy levels = stronger Coulombic attraction = more lattice energy
Higher lattice energy means…
…harder, higher melting point, less soluble (prone to being dissolved) in water
Electron Removed From Metal
Ionization Energy
Electron Added to Nonmetal
Electron Affinity/Electronegativity
Ions Attract Each Other & Form Lattice
Opposite of lattice energy
Metal Characteristics
Easily molded, electrically conductive
Alloy
A material that contains multiple elements and has the characteristic properties of metals (examples: stainless steel, brass, etc.)
Substitution Alloy
The solute (what’s being dissolved) takes positions normally occupied by a solvent (what causes the dissolving)

Interstitial Alloy
Solute (what’s being dissolved) takes position in the holes between solvent (what causes the dissolving) atoms

Resonance
Structures with different electron arrangements
Isomers
Structures with different atom arrangements
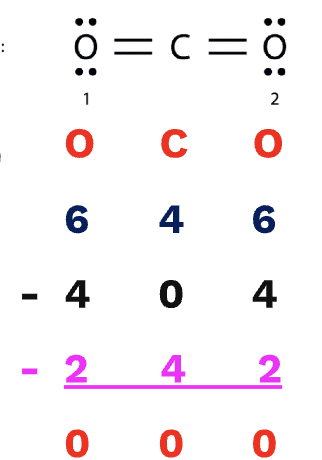
Formal Charge
The original number of valence electrons subtracted by the amount of unbonded electrons subtracted by half of the shared electrons
Dominant Structure
When formal charges are closest to zero OR when negative formal charge is on a more electronegative atom
Traits of Delocalized Double Bonds
Extra stability
Between single bond & double bond in terms of length and strength
The more places delocalized, the closer it is to a single bond
Electron Domain
A group of electrons doing one “thing-” bonding or a lone pair (on the central atom)
Electron Geometry
The 3D spatial arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom so that they are as far away from each other as possible.
Molecular Geometry
The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
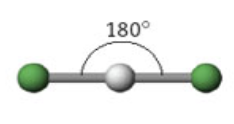
2 domains
Name: Linear
Angle measure: 180º
Hybridization: sp
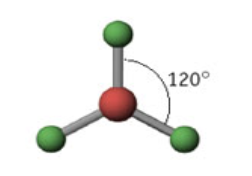
3 domains
Name: Trigonal Planar
Angle measure: 120º
Hybridization: sp2
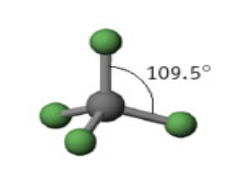
4 domains
Name: Tetrahedron
Angle measure: 109.5º
Hybridization: sp3
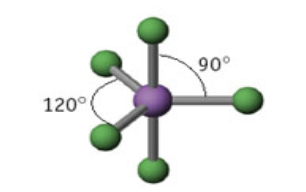
5 domains
Name: Trigonal Bipyramid
Angle measure: 90º AND 120º
Hybridization: sp3d
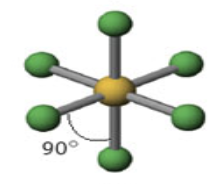
6 domains
Name: Octahedron
Angle measure: 90º
Hybridization: sp3d2
Traits of Polar Molecules
Some bonds must be polar
Its shape must be assymetrical
Sigma Bonds
Literally ANY bond. All bonds are sigma

Sigma Pi Bonds
Double Bonds
Sigma Pi Pi Bonds
Triple Bonds