Bacterial Genomes and DNA Replication
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is a genome?
The entire compliment of of an organism’s genes - looks at genetic potential, organism relationships, virulence factors, and anti-microbial targets
The limitation of genomes?
It won’t tell us what genes are expressed at a given time
What can genome sequencing tell us?
It outlines the genetic potential of organisms; functions are assigned to genes (38.1% of e.coli genes have unknown functions)
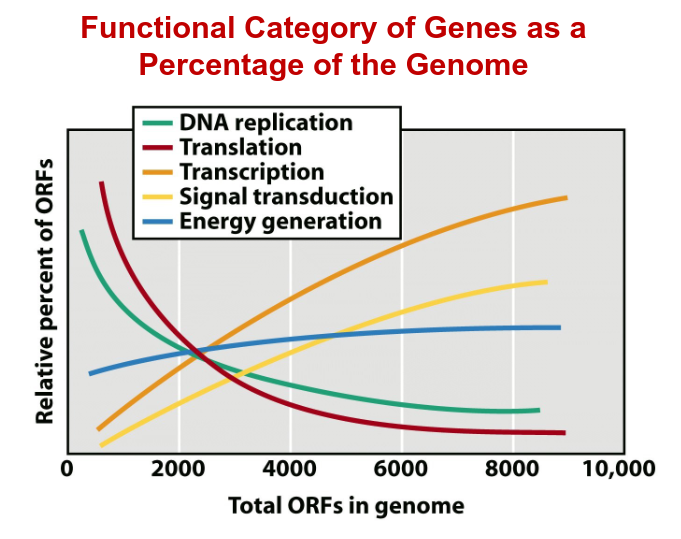
ORFs
“open reading force” - gene sequence predicted to code for a protein (note the positive/negative correlations in the diagram)
Characteristics of bacterial chromosomes
Most are circular, covalent closed
cells are haploid
DNA is condensed in nucleoid
One origin of replication
Most DNA sequence codes for proteins: “compact” genome (ex. intrams)
Central Dogma/Gene expression
DNA → mRNA → Protein
DNA packaging and condensation process?
Topoisomerases - cause the process; there is a nick in a single strand, supercoiling
Goals for replicating the chromosome
Generate 2 identical copies of genetic information; partition in the chromosome so that each daughter cell recieves one