Intro to Psychology Flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Meetings 1,2,3,4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Empiricism
This is the scientific method way of thinking about the world around us.
However, the limitations associated with this are….
The way that we observe physical things is not always how they work. For example it may appear that the sun revolves around us (the earth) but in truth we revolve around the sun.
Mental processes cannot be observed physically which is specific to psych.
Method
A set of rules and techniques for observations that allows the observer to avoid the illusions, mistakes and bad conclusions that observation can produce.
Three Specific Problems with Psychological Science
Complexity
Variability
Reactivity
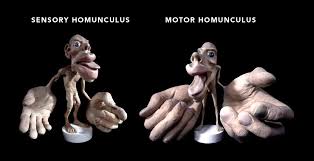
Sensory Motor Homunculus
Depicts how much of the somatosensory cortex is designated for sensory input.
How to make an experiment out of an abstract concept?
Have an abstract property such as sensitivity.
Have an operational definition which just means in what physical way can you measure your abstract property. For example, ticklishness.
Figure out a method to measure this operational definition. For example, laughs per minute.
Your operational definition that connects to your abstract property should be both…
Reliable
Valid
Construct Validity
The idea that there must be a clear and conceptual relationship between your abstract property and the operational definition in your experiment.
Also that all your observational definitions should generally give you similar results.
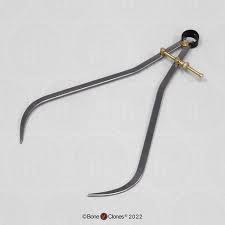
Calipers
A physical tool that can be used to measure threshold.
It can be applied to any body part in which to measure how sensitive a particular part of the body is.
Discriminant Validity
The tendency for a measure to produce different results when it is used to measure different things.
Theory
A hypothetical account of how and why a phenomenon occurs.
Hypothesis
A testable prediction made by a theory.
A measure should have…
Discriminant validity
Reliability
A observational defintion should have…
Convergent validity
Construct validity
Conclusions in psychology are based on…
Variability
The mean difference
In order to determine that they are statistically significant.
What would smaller variability hint?
That the variable you are analyzing is more statistically significant.
Bias
Any factor that distorts your measurement of a group of subjects.
Subject Bias
Humans are social creatures that may attempt to appease the observer by analyzing demand characteristics and try to figure out what the observer wants them to say.
How to combat subject bias?
Anonymity
Measure involuntary or not obvious behavior
Keep the subject blind to the hypothesis.
Observer Bias
Observers may try and skew their data to fit their idea of what is happening.
How to combat Observer Bias?
Double blind technique where the observers and the subject are both blind to the hypothesis so that the observer cannot skew the data to fit what they think it might mean.
Correlation
When the variation of two variables is synchronized. To analyze this you could use a scatter plot and correlation coefficient.
Correlation enable prediction not CAUSATION.
Correlation Coefficient and Meaning
Range between -1 and 1.
1 is a perfect positive relationship in which both variables increase as the other increases.
-1 means that there is a negative relationship in which one variable increases and the other sharply decreases.
0 means that there is no relationship.
Causation
Causation can be ruled out of your experiment and prove that the correlation you are seeing is not just coincidental. You do this by holding the third variable constant.
Experiment
A technique for establishing the causal relationship between variables.
Holding Constant
Ensuring that the groups that your are testing are treated identically except for your manipulation that you are testing.
Problem w/ Self Selection
This could immediately bias your results because people may self select based off of other variables that you either cannot control or don’t know about.
The solution to this is random assignment.
The tools for control are…
Holding constant
Random assignment.
Marrs’s Levels of Analysis
Computation
What is the problem the organism is trying to solve?
Survival and procreation
Algorithm
What is the procedure for solving the problem?
Implementation
How is this procedure physically implemented?
Darwinian Evolution
Individuals exhibit variation.
Individuals born with ore favorable characteristics are able to survive and reproduce at higher rates than those that don’t have those characteristics. They end up passing off their genes.
Natural Selection
In order for natural selection to work…
Variations must be heritable.
What effect does our environment have on evolution?
The enviornment detemines what is advantageous.
Evolution is slow and cannot keep up with the rapid chnage in enviornment.
Our bodies as well as our psychology are affected by the enviornemnt.
Naturalistic Fallacy
The idea that things are right betcause they evolved that way.
Deterministic Fallacy
Things are inevitable because they ate natural.
Natural Selection Pitfalls
Deterministic Fallacy
Naturalistic Fallacy