Articulation and Phonology
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Definition of Articulation
speech production
Definition of allophones
variations in productions of phonemes, not changing the meaning of a word
Definition of Phonology
study of phonemes, how they are organized to create meaning - linguistic
What is an articulation disorder?
difficulty with motor planning for production of speech sounds
what is a phonological disorder?
difficulty with use of sound system and rules of combining phonemes
TRUE or FALSE: a combination of articulation and phonological errors can be made in both disorders
TRUE
what is a speech sound disorder?
Impairment to the systems of articulation and/or phonology
What are consonants made up of?
sonorant
obstruents
how are vowels classified?
tense/lax
lip configuration (round or unrounded)
tongue position (hi/low and front/back)
Definition of Place:
A. How the sounds are made by air flow/constriction
B. Presence or absence of vocal fold vibration
C. Location along the vocal tract where sound is made
C. Location along the vocal tract where sound is made
Definition of Manner:
A. How the sounds are made by air flow/constriction
B. Presence or absence of vocal fold vibration
C. Location along the vocal tract where sound is made
A. How the sounds are made by air flow/constriction
Definition of Voicing:
A. How the sounds are made by air flow/constriction
B. Presence or absence of vocal fold vibration
C. Location along the vocal tract where sound is made
B. Presence or absence of vocal fold vibration
fill in the blank: Consonants can have a acoustic or _________ characteristic used to describe a phoneme
articulatory
Who developed the binary system for consonants?
Chomsky and Halle (1968)
Define consonant
presence or absence of a feature to define a phoneme
who developed the 5 features of consonants?
jackobson and halle (1956)
what are the 5 features of consonants?
major class
cavity
manner of production features
source features
prosodic features
Fill in blank: vowels are produced with a relatively _____ vocal tract
open
definition of open sounds
limited constriction with airflow from vocal folds through oral cavity
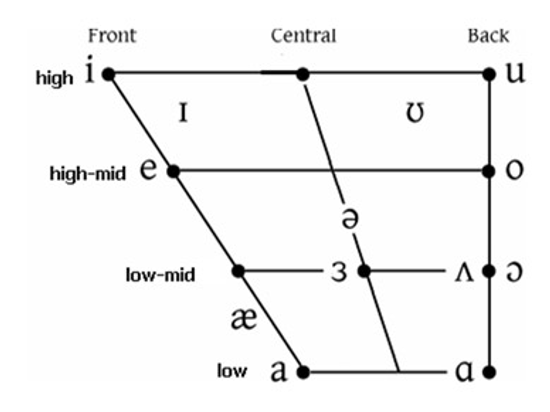
What is the purpose of the vowel quadrilateral?
schematic to illustrate position of tongue
purpose of phonetic transcription
provide accurate consistent means of recording and describing speech sound production
What are the 5 components of language?
phonology
morphology
syntax
semantics
pragmatics
definition of phonology
how sounds can be sequenced and how sounds are used to create meaning
definition of morphology
study of the structure of words and rules for combining word parts
definition of semantics
meaning of words and utterances
definition of acoustic phonetics?
study of the relationship between articulation and acoustic signal of speech
how articulation matches that sound wave
definition of speech perception
study of how phonetic decisions are made based on the signal
definition of articulatory phonetics
how the articulators make individual sounds
Which one is NOT a component of syntax?
A. Form of language
B. study how language is used
C. How words are sequenced to convey intended meaning
D. Word order changes meaning
E. Transformational
B. study how language is used
Definition of pragmatics
study of how language is used in communicative and social contexts
Fill in blank: Brain at birth is ___% of adult weight and grows to ____80% during the first few years of life
A. 30% & 80%
B. 20% & 90%
C. 25% & 80%
D. 80% & 25%
C. 25% & 80%
Dispel a common belief about speech sound disorders
do not usually result from problems in the mouth
therapy should not largely involve positioning of person’s articulators to make sounds
should nto be surprising children experience speech difficulties
Name at least 2 general principles regarding speech sound disorders
a person whose speech differs from his or her community’s may be identified with a speech disorder
speech disorders should be considered within social context of client
may impact other language domains
may have language basis, basis in production and perception, or combination
more than a problem pronouncing letters/sounds
In stage 1: birth to 12 months, what does speech look/sound like?
“laying foundations”
perception - universal abilities become restricted to their native language
production - limited sounds in vowels, consonants, and supersegmentals
perception-production link
communication - turn taking, but limited understanding of semantics
In stage 2: 12-24 months, what does speech look/sound like?
“becoming a word user”
perception - good, they can understand but often struggle in abnormal environments
production - babbling to start speech sounds
perception-production link - known for mismatch of higher level perception skills but limited production skills
communication - using words to express thoughts, feelings, and needs
In stage 3: 2-5 years, what does speech look/sound like?
“mastering basic speech elements”
perception - advanced abilities
production - huge explosion of mastery of basic sounds of speech
perception-production link - may be slight mismatch
communication - interacting more with unfamiliar people in unfamiliar places with more advanced syntax and morphology
In stage 4: 5 years - adolescence what does speech look/sound like?
“foundation for literacy”
perception - adult-like
production - might still see difficulties with individual consonants or consonant clusters
perception-production - continues to decrease
communication - using speech increasingly across various settings
what is the key player in articulation?
the tongue
What are the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
super longitudinals
inferior longitudinals
transverse
vertical
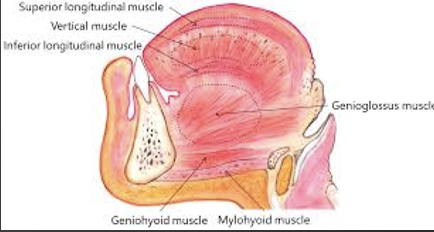
what is the role of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
change the shape
what are the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
genioglosus
hyoglossus
palatoglossus
styloglossus
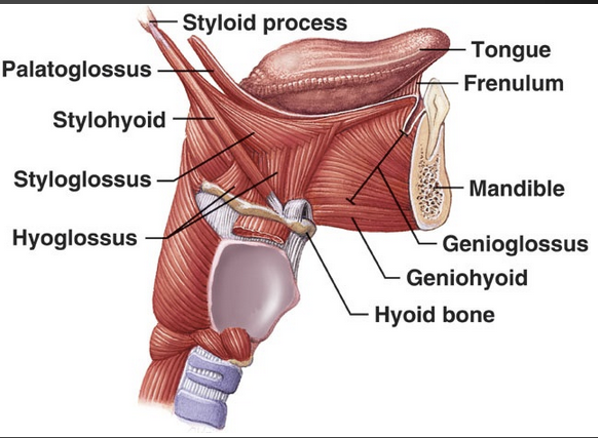
how does the mandible impact sound production?
increase or decrease size of oral cavity - impact airflow
supports tongue
responsible for changes in resonance
name the muscles of the soft palate (velum) that coordinate movement
levator veli palatini
tensor veli palatini
palatopharyngeus
palatoglossus
uvula
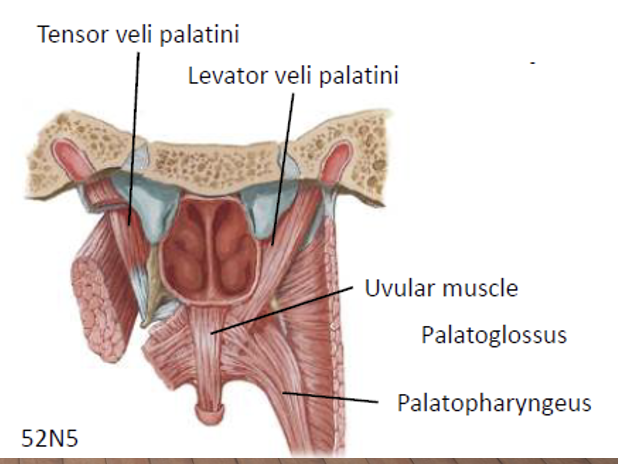
name the immovable/passive articulators
teeth
alveolar ridge
hard palate
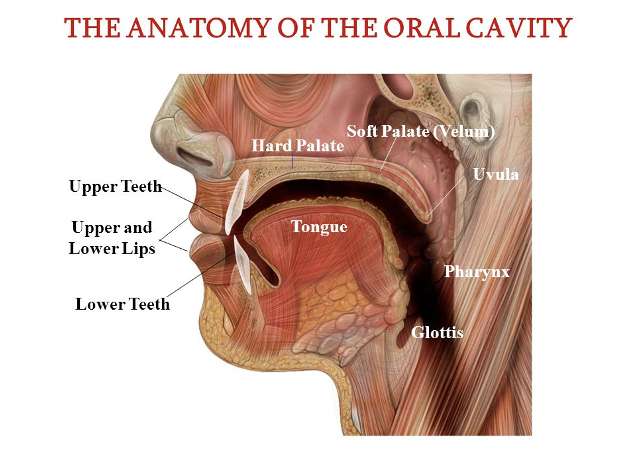
What are some of the differences we might see with an infant vocal tract vs adult?
shorter vocal tract
shorter pharyngeal cavity
tongue mass placed relatively forward in oral cavity
gradual angle in oropharyngeal channel
high larynx
close approximation or velopharyngeal and epiglottis
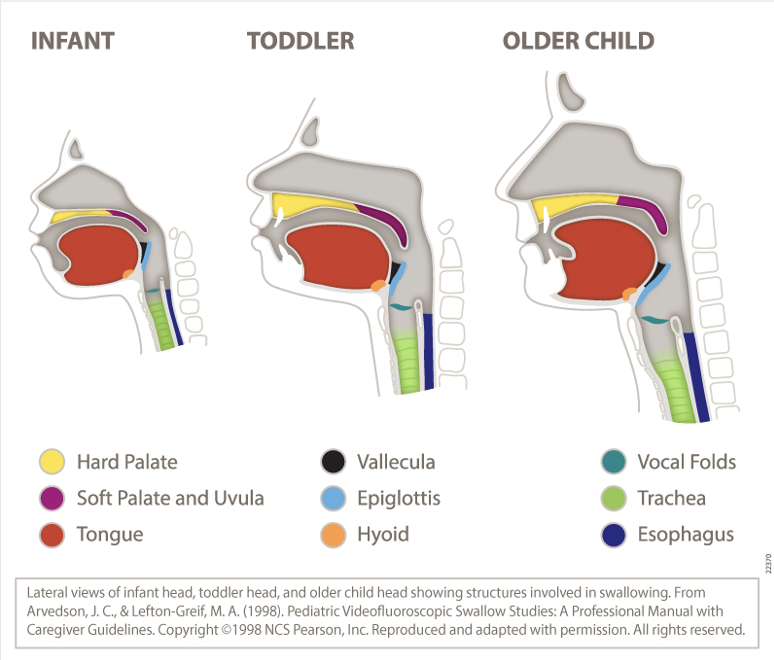
what are the five processes of speech?
cerebration
respiration
phonation
resonance
articulation
What is cerebration?
ability of brain to organize information
what parts of our body do we use for respiration?
lungs
rib cage
abdominal muscles
diaphragm
how does phonation work?
larynx sits on top of trachea
vocal folds vibrate the air
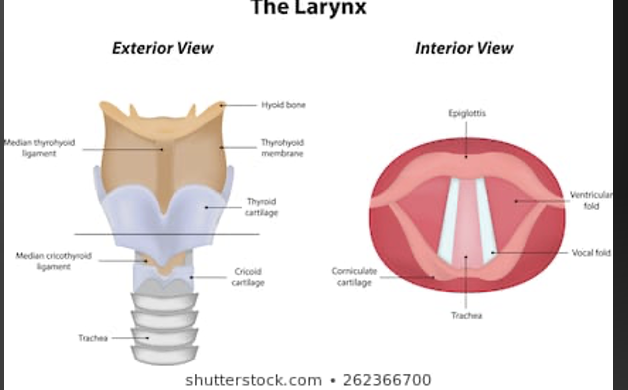
what is resonance?
modification. of sound energy as it passes through the oral and nasal cavities
relies on function of velopharyngeal port
what are sonorants?
littel constriction (nasals, liquids, glides)
what are obstruents?
lot of constriction (stops, fricatives, affricates)
what is a cognate pair?
place and manner are the same but voicing is different
what is a continuant?
manner of production in which the airstream continues to moves through the oral cavity (glides, liquids, fricatives)
TRUE or FALSE: all liquids, affricates, and glides are voiced
FALSE; all NASALS, LIQUIDS, GLIDES are voiced
What are nasal sounds?
airstream directed through the nasal cavity
open velopharyngeal port
/m/, /n/, /ng/
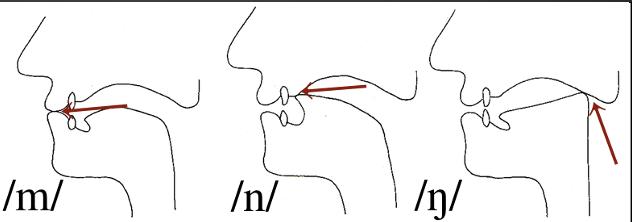
what are strident sounds?
noisy sounds
fricatives and affricates
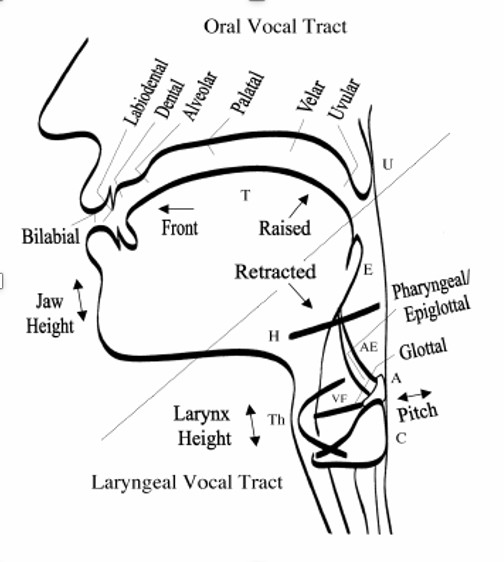
what are labial sounds?
a place of production
made with one or both lips
what are coronal sounds?
tongue blade raised above neutral state
sounds made with tongue blade or tip
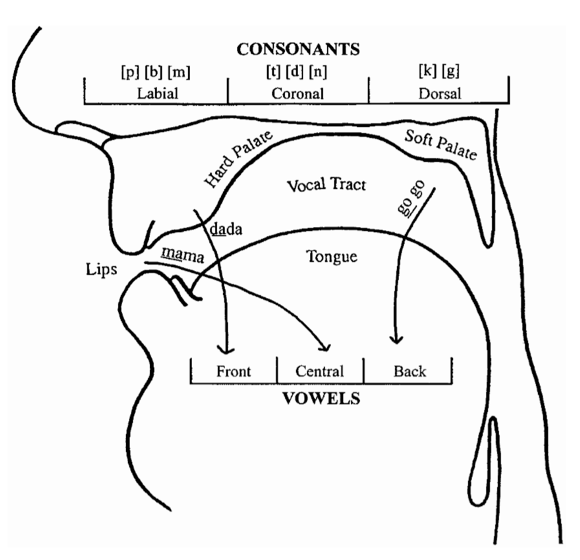
What are back sounds?
place of production
made in velar area with tongue body retracted
What is the name of the national system that represents productions of GAE?
IPA- International Phonetic Alphabet
Name a few diacritic markers used to indicate production features or quality changes
dentalization
lateralization
palatalization
voicing errors
nasality
unreleased stop-plosive
rounding
What are suprasegmentals?
characteristics of speech that involve larger units including syllables, words, phrases or sentences
what are characteristics of suprasegmentals?
stress
intonation
loudness
pitch level
juncture
speaking rate
clear vs. conversational speech
vowel reduction
new vs. given information
What is coarticulation?
influence that sounds exert on one another
name the 3 acoustic considerations
frequency - rate of vibration of a sound
amplitude - strength/magnitude of vibration of a sound
duration - total time over which a vibration occurs
What are the levels of linguistic complexity?
isolated sound
syllable
word
phrase
sentence
conversation
TRUE or FALSE: every syllable has a vowel
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: can add consonants on either end of a vowel but if a vowel is added, then it becomes another syllable because vowels are nuclei of a syllable
TRUE
What are the earliest developing phonemes (birth -3 years)?
p, b, m, h, n, w
What are the preschool developing phonemes (3-5years)?
t, d, k, g, f, ng, y, l, s, z, v
What are the later developing phonemes (5-7 years)?
sh, ch, j, r, th
Fill in blank: articulation is difficulty with _____ _______ __________ - motor planning and execution
speech sound
TRUE or FALSE: articulation does affect areas of language learning and development
FALSE: articulation DOES NOT affect…
Articulation is what type of errors?
Phonetic - usually one or two isolated phonemes
Phonology is what type of errors?
phonemic - usually classes of sounds
Fill in blank: phonology is difficulty with ___________ specific function of phonemes
Language
What is a phonological disorder?
disturbances in phonological organization of language system
TRUE or FALSE: phonological disorders may impact other domains of verbal and written language
TRUE
What are the two main categories in phonological development?
behavioral models
linguistic models
Theories rely on what 4 fundamental principles?
segments - on different levels are related systematically on phonological rules
features - each phonological segment is composed of some type of features
levels of representation - underlying and surface level
rules - generalization of phonological processes that apply to a given language
What is the phonemic theory?
recognition that speech sounds in a particular language can be grouped into classes
What are autosegmentals?
segments of speech that can be filtered out of the linear arrangement of speech
What is metrical phonology?
infinite number of stress values that you can put on a phrase
TRUE or FALSE: speech and language are learned behaviors
TRUE
Who introduced the behavioral model?
goldstein 2003
what is the structuralist model?
Hypothesizes discontinuity between babbling and onset of speech production
phonological development follows a universal and innate order of acquisition
what is the generative phonology model?
child comes innately equipped with universal set of phonological process that occur in his/her native language
What is the cognitive model?
word, rather than segment that serves as basic unit
uses individual strategies and external factors (individuality of early phonological development)
What is the biological model?
innate perceptual biases and dispositions to certain motor actions are at root of phonological acquisition
what is the linguistic model?
emphasize function of sounds and sound patterns and patterns of sound changes in a language
two groups: linear & non-linear
what is the linear linguistic model?
emphasizes that segmental properties/feature of phonemes are independent of each other and may be combined with other segments
what is the distinctive feature theory?
identifies specific acoustic or production features of sounds that serve function of differentiating meaning among words
What is generative phonology?
describes how deep form is transformed by modifications in phonetic form to equal surface representation through a set of rules and constraints.
definition of naturalness
simplicity of production + relative frequency of occurence in the language
definition of markedness
sounds are more difficult to produce and occur less frequently
Who developed “natural phonology”?
donegan and stampe 1979
what is natural phonology?
Natural phonology is a theory that proposes that phonological processes are innate and reflect natural tendencies in speech production, allowing for simplification of complex sounds.
What are factors of non-linear linguistic models?
focuses of the hierarchical nature of phonological segments or units
encompasses autosegmental, metrical, feature, optimality and sonority
emphasize the role of a set of more complex linguistic dimensions on development
what are the two tiers in phonology?
prosodic
segmental