BACTE_FInals_Lec: Anaerobes (in progress)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

69 Terms
why anaerobes are sensistive to aerobic condirons
Oxygen becomes Superoxide anion, which reacts with hydrogen perooxide to generate hydroxyl radical (OH-)
enzyme that protects strict aerobes and facultative anaerobes from superoxide anions
exogenous
endogenous (microbiota of humans and animals)
Anaerobes
found in mucosal surfaces
linings of oral cavity
GI Tract
Genitourinary (GU) Tract
Anaerobes at specific anatomic sites
P. acnes
an opportunistic pathogen that casues acnes
B. fragilis group, such as B. vulgatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, and B. distasonis
Common anaerobes in GI Tract
Bacteroides fragilis
most common species of anaerobic bacteria isolated from soft tissue infections and bacteremia
True
T/F
anaerobic bacteria colonize the distal urethra - not considered to be a cause of uncomplicated urinary tract infections
anaerobic cocci, Fusobacterium, Prevotella, Bacteroides, and Lactobacillus
Colonizers of GU Tract

Conditions that exposes individuals to anaerobe-associated infections or diseases
Aspirates* and biopsy
best specimen collection for anaerobes
Anaerobic chamber
provides the anaerobic environment
palladium-coated alumina pellets
These are catalysts that removes residual oxygen in the anaero. chamber
silica gel or alternative: solid-state dehumidifier
5% H2, 5-10% CO2, 85-90& Nitrogen
Anaerobic gas composition in the chamber
Methylene Blue (colorless in anaerobic conditions)
resazurin (
digital oxygen indicators
note: chemicals do not react to small amounts of oxygen
Redox indicator in the chamber
GasPak jar
Used by small laboratories
Uses an envelope gas generator (waterless or requires water)
Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) - reducing reagents
NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate) - pH buffer
Palladium pellets - catalyst for H & O2 rxn to form H2O
Components of GasPak
prone to explosion when exposed to flammables due to accumulation of Hydrogen molecules in the GasPak
Disadvantage of GasPak
Anaerobic bags
• Ziplock bag
• Oxygen removal system (strips)
• Can be used in conjunction with jars
• Can be used for transport
Anaerobic blood agar (ex. CDC agar)
Preferred media for anaerobic culture
Bacteroides bile esculin agar
selective medium for Bacteroides fragilis
contains 20% bile which inhibits most anaerobes
contains gentamicin (inhibits aerobes)
Phenylethyl alcohol agar
Media:
this inhibits the swarming proteus spp.
inhibits the growth of fac. anaerobes
C. perfrigens
Clostridium sp.
has a double zone hemolysis (inner - beta, outer - alpha)
Clostridium
All spore-forming anaerobic bacilli are classified in the genus _____
C. perfringens
C. ramosum
C. innocuum
All Clostridium are motile except
C. perfringens
The only encapsulated Clostridium sp.
C. tetani
C. perfringens
C. botulinum
Exogenous Clostrium spp. (3)
C. tetani
This bacteria causes tetanus
C. perfringens
This bacteria causes gas gangrene (myonecrosis) food posioning
C. botulinum
This bacteria causes botulism
C. difficile
this bacteria causes antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis
Myonecrosis
aka gas gangrene
usually occurs when organisms contaminate wounds, through trauma or surgery
alpha-toxin (a-toxin)
found in C. perfringens that is a lecithinase (phospholipase C) produced by all strains of C. perfringens
C. septicum
Clostridium sp.
often a marker organism for a malignancy in the GI tract
Clostridium botulinum
aka Canned food bacillus
Foodborne botulism
result from ingestion of preformed botulinum toxin
types associated with Foodborne botulism
infant botulism
ingestion of C. botulinum spores
This type of botulism is associated with contaminated honey - food most commonly associated
Wound botulism
type of botulism:
contamination of wounds with spores of C. botulinum
prevents the release of acetycholine in the neurons which leads to paralysis and death
Why is C. botulinum lethal?
C. botulinum
causes Flappy Baby syndrome
B-hemolysis
hemolytic pattern of C. Botulinum
C. tetani
aka Tack head bacillus
tetanospasmin
neurotoxin produced by C. tetani which causes Tetanus
C. tetanus
This causes spastic type of paralysis, with continuous muscular spasm leading to trismus (lockjaw), risus sardonicus (distorted grin), and difficulty breathing
diptheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
vaccine for tetanus
Cycloserine Cefoxitin Fructose Agar (CCFA)
ideal plating medium for C. difficile
C. difficile
This bacteria:
BAP - “horse stable” odor; non-hemolytic
Actinomyces israelli
results to a lumpy jaw (maxillary region)
erupt to the surface and drain pus that may contain so-called sulfur granules
ID:
* White, opaque and resemble “molar tooth”
Gram positive, branching filamentous rods
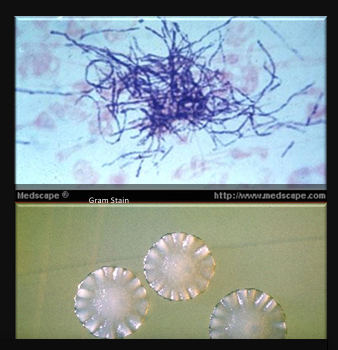
Propionibacterium acnes
Associated with inflammatory process in acne
also cause subacute endocardities
P. acnes
ID:
Gramstain: Gram positive pleomorphic diptheroid appearance
Colonial Appearance: Small and white to large yellowish tan
Bifidobacterium spp.
Colonial Appearance • convex, cream to white, smooth, glistening, and soft
In mixed infections of abdomen, pelvis and GUT
Bifidobacterium spp.
• variable in shape, ranging from coccobacilli to long branching rods • ends of the cells may be pointed, bent, club-shaped, spatulated, or bifurcated (forked)
True
T/F:
Anaerobic Gram- Negative Bacilli are endogenous, found in oral cavity and GI tract
Anaerobic Gram- Negative Bacilli
B. fragilis group
Porphyromonas,
Prevotella
Fusobacterium
Bacteroides fragilis
• Gray and non hemolytic in BAP
• Dark gray with dark gray zone (esculin hydrolysis) and precipitate (bile) in Bacteroides Bile esculin agar
Bacteroides fragilis
• Growth in 20% bile (resistantto bile)
• Saccharolytic
• Bile esculin hydrolysis positive
• Resistant to kanamycin, vancomycin and colistin
Prevotella spp.
• Non hemolytic and fluoresces brickred when viewed in 365 nm UVlight.
• Black pigment in Lakedkanamycin‐ vancomycin blood agar
Prevotella spp.
Some Prevotella spp: have protoprohyrin which is a brown to black pigment
Porphyromonas spp.
• Dark brown to black, more mucoid than Prevotella (BAP)
• Fluoresces brick red when viewed under 365 nm UVlight
• Black pigment in Laked kanamycin‐ vancomycin blood agar
Do not ferment carbohydrates (assaccharolytic)
• Inhibited by 20%bile
• susceptible toVancomycin and resistant to colistin
• Most __________ spp. are spot indole–positive
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Gram negative spindle‐shaped with pointed or tapered ends (fusiform)
Finegoldia magna
most pathogenic of the anaerobic cocci and the one most often isolated in pure culture.
Anaerobic Cocci | Gram stain |
Veillonella | (-) |
Peptostreptococcus | (+) |
Anaerobic Cocci
Anaerobic Cocci | Gram stain | |
Veillonella | ||
Peptostreptococcus |