IB Introduction to Economics
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes Chapter 1: What is Economics? & Chapter 2: How do economists approach the world?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Economics
the study of how resources are allocated to satisfy the unlimited needs and wants of individuals, governments, and firms in the economy.
Economic Agents
Economic decision makers that interact for the purpose of production and consumption. They are households, firms, and governments.
Microeconomics
the study of the actions of firms & households.
Deals with specific markets/segments in the economy
Welfare and profit maximization
assumes rationality of individuals
Macroeconomics
the study of the operations of the economy as a whole.
Deals with broad economic topics, based on decisions made by governments and countries.
maximization of economic goals
less consensus due to different schools of thought
more emphasis on statistics and empirical data
WISE ChoICES
key concepts of IB Economics. They are:
Well-being
Interdependence
Scarcity
Efficiency
Choice
Intervention
Change
Equity
The Basic Economic Problem
How to best allocate scarce resources to satisfy the unlimited wants and needs of individuals, firms, and governments
Factors of Production
are the four categories of resources that are required to produce any good or service, namely land, labor, capital and enterprise.
Land
natural capital
includes every natural resource
renewable and non-renewable resources
Labor
human capital
both physical and intellectual labor
Capital
physical capital
all-man made resources
Entrepreneurship
the ability to innovate, take business risks, and seek new opportunities for the opening and running of business.
the skills, creativity, and risk-taking ability that a business person requires to combine and manage the other factors of production
National Minimum Wage
price floor in the labor market. Employers are required to pay at least this amount to their employees
Profit
total revenue minus total cost.
Income
sum of collective rewards from all factors of production in the production process.
Scarcity
shortage of resources in the economy at any moment in time.
Needs
essential goods & services for human survival
Wants
goods & services that are human desires
Goods
tangible products that can be produced, bought, and sold.
Services
intangible products provided by firms & individuals and paid for by customers
Economic Goods
a.k.a products. goods & services that have utility.
Renewable Resources
Resources that can be used repeatedly and replenish naturally.
Opportunity Cost
the cost of an economic decision measured in terms of the best alternative choice forgone.
Free Goods
products with a natural abundance of supply; do not require any deliberate effort in acquisition. There is no opportunity cost attached to these goods.
Private Sector
The sector of the economy where private firms and individuals produce goods and services.
Public Sector
the sector of the economy where the government produces or supplies certain goods and services.
Economic System
describes the way in which an economy is organized and run, including alternate views on how resource should be allocated
Free Market Economy
Economic system that relies on the market forces of demand and supply to allocate scarce resources via the private sector of the economy
Planned Economy / Command Economy
Economic system where the government (or public sector) allocates scarce resources.
Mixed Economy
Economic system that with some resources being owned and controlled by private individuals and firms while others being owned and controlled by the government. Combination of free market + planned economies.
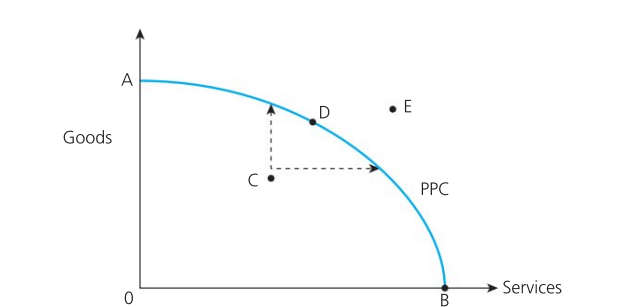
Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
Model of the maximum combination of two products that an economy can produce, when all its resources are used efficiently. It show the productive capacity of the economy at any moment of time
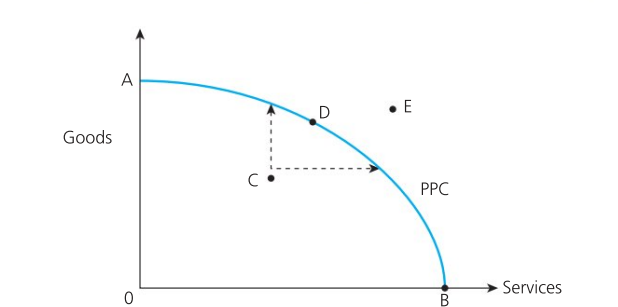
Marginal Rate of Transformation / Rate of Substitution
Gradient of the PPC; shows the opportunity cost of the two products.
Pareto Efficiency
Occurs when it is not possible to make one person better off without making someone else worse off.
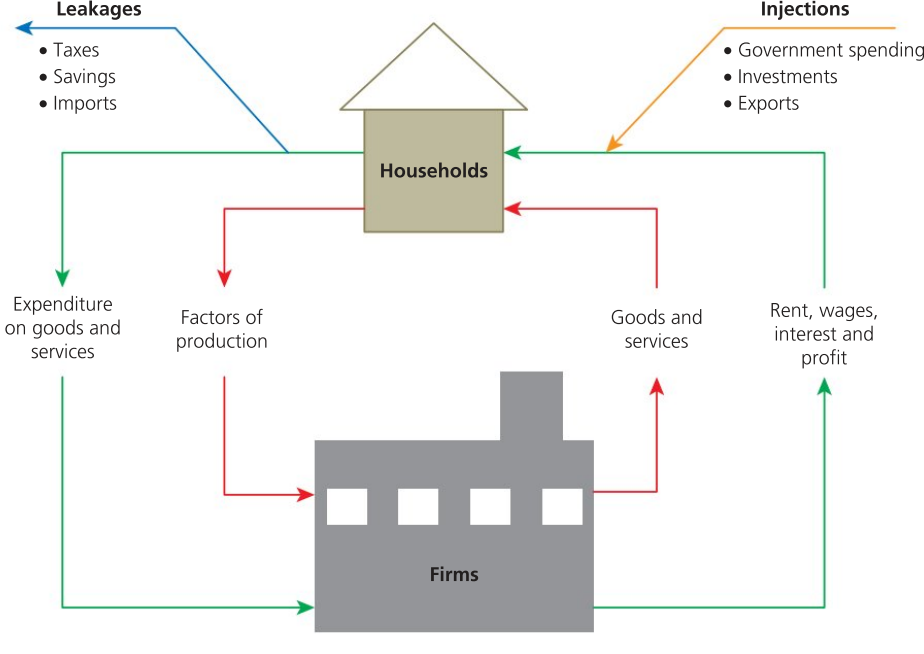
Circular Flow of Income
Model used to explain how economic activity and national income are determined based on the interactions of economic decision makers.
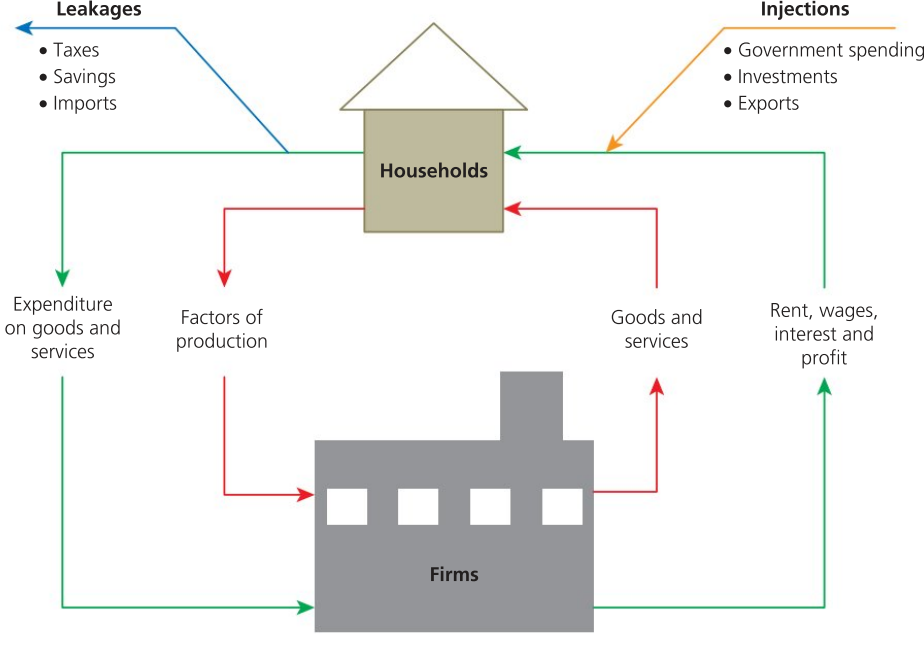
Closed Economy
Part of the circular flow of income. Includes households, firms, with the addition of government i.e. domestic economic decision makers.
Open Economy
art of the circular flow of income. Includes households, firms, with the addition of government and foreign sector (accounts for imports and exports)
Leakages / Withdrawals (W)
Take money out of the circular flow of the income. They are savings (S), taxation (T) and imports (M), that is, W = S + T + M.
Injections (J)
Put money into the circular flow of the income. They are government spending (G), export earnings (X) and investment expenditure (I), that is, J = G + I + X
Economic Methodology
Study of processes, practice, and principle in relation to economics as a social science. Includes the models, theories, and assumptions apart of the discipline.
Positive Economics
Study of what the economy actually is. Study of economics that is provable. based on logic, reasoning and empirical evidence
Logic
refers to rationality and reasoning in explanations of economic phenomena and policy.
Hypothesis
An assumption, notion or educated guess before conducting research
Model
A hypothesis that has been tested repeatedly, is proven or rejected, and can be used to explain the real world
Theory
A broad generalization used to explain situations supported by economic evidence or data from models
Ceteris Paribus
Latin phrase which means “all other factors remaining constant”. Allows economists to explain the cause and effect of specific economic variables.
Empirical Evidence
first-hand data and information collected through observation and experimentation.
Refutation
the act of a statement or theory being proved wrong or false by empirical evidence
Normative Economics
Study of what an economy should be and it’s supposed to work. It considers the opinions and beliefs of people. It is subjective.
Value judgements
the beliefs of individuals and societies about what is right and what is wrong
Equity
Concept in which there is economic fairness in the distribution of resources.
Equality
Concept in which all are equal and should have equal recognition. It is about collectivism and social fairness
Economic Thought
Refers to the historical account of different economic ideas, beliefs, and principles over time.
Laissez-faire
Approach to economics that allows transactions to take place without government interference.
Invisible Hand
metaphor used to describe how the behaviors and decision-making of individuals ends up benefitting society as a whole because they are incentivized to act in their own self-interest
Finite Resources
factors of production being limited in supply
Classical Economics
main economic school of thought during the 18th-19th centuries. focuses on self-regulation of market forces to allocate resources efficiently.
Utility
refers to the level of satisfaction derived from the consumption of a product
Marginal Utility
refers to the satisfaction gained from the consumption of additional units of a product
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
As individuals consume more of a product, the satisfaction gained from each additional unit of consumption (marginal utility) declines.
Say’s Law
The ability to purchase a product depends on the ability to produce or supply (which generates income). Supply creates it’s own demand
Marxism
approach to macroeconomic policy that focuses on meeting the needs and values of the masses, rather than for the privilege of a minority of capitalists.
Keynesian Economics
Interventionist approach to macroeconomic policy. The idea that increased government expenditure and lowering taxes will stimulate demand in the economy
Monetarists
economists that believe monetary policy is a more powerful and effective macroeconomic stabilization policy than fiscal policy
Monetarism
Macroeconomic school of thought that emphasizes monetary policy analysis and the role of money supply in the economy.
New Classical Counter Revolution (NCCR)
Economic school of thought that favored supply-side macroeconomic policies. Led to popularity in privatization of state-owned companies and the withdrawal of government regulation of markets.
Sustainability
The ability to conduct economics indefinitely, achieving economic goals that increase living standards without jeopardizing the needs and wants of future generations.
Circular Economy
an economic system in which raw materials, components and other resources are used sustainably to generate output.