Types of Communication
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nurse's touch: Professional Communication -> Types of Communication
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Types of Communication
verbal
need validation of received message
nonverbal
dress
posture
facial expression
eye movement
vocal tone
written
demands clear, timely, & accurate info
more permanent
legal document of care
computer-mediated
EX: Electronic Health Records (EHRs) & emails
Communication modes
raised voice
gentle smile
abrupt email
Verbal Communication
Verbal
vaules
perceptions
culture
age
education
socioeconomic
Word choice and word meaning
make sure to be clear when speaking to a client - EX: supper to them may mean a mid day meal but to you it may mean an evening meal
Pace
slow = soothing
shifts = avoidance
Intonation - (EX: sarcasm)
Clarity - say exactly what you mean and using examples to improve clarity
Brevity - using the fewest words necessary
Timing - if inappropriate, impedes communication
Relevance - we should be addressing the client’s immediate concerns
Adaptability - align message with nonverbal cues / ability to remain focused on the conversation and respond appropriately. EX: seeing someone cry and adapt your verbal ques to it and ask them whats wrong
Credibility - convey confidence and provide accurate info
Humor - can relieve tension but be sure to use caution
Nonverbal Communication
may not match (EX: asking a patient what are their concerns but you turn your back to them)
majority of a message’s meaning
Physical cues can support or conflict with verbal message
EX: a patient is grimace but says she is fine. This gives a conflicting report
Cultural differences impact communication
EX: in some cultures, a smile mask anger or fear
Written Communication
usually takes the form of a nursing record
info must be timely and accurate
timely - include the date and time (in military time)
accurate - factual objective. No opinions. Use direct quotes from the client. Any changes in client status warrant documentation.
documents findings, supports actions
be sure it is clear and free of any spelling errors
clear - easy to read, legible. follows agency guidelines. signature and title
correct spelling - errors can lead to mistakes. avoid writing the word “error”, draw a line through it and place initials above the mistake
Computer-Mediated Communication
Electronic health records
integrate client visits
capture data
assimilate data easily for clinical trials and research purposes
email & text
most common
HIPAA requires safeguards
avoid email when client needs urgent information
avoid email, text with confidential information or abnormal results
instant messaging
social media
we must sort through information to provide valid data
avoid blurring personal & professional boundaries
Web conferencing
share information simultaneously
communicate long distance
EX: a patient with a mental health disorder can web conference with is therapist
Protect your computer passwords, log off from the computer, keep client information secure
Components of Communication
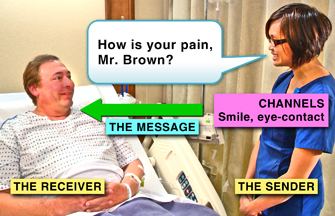
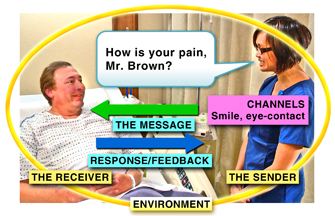
sender - transmits a message

message - what is said and the body language that accompanies the words

channels - means of sending and receiving various messages (visually, auditorily, or tactilely)
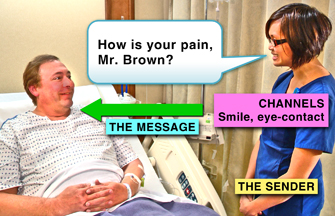
receiver - translates and responds to a message
response/feedback - the message that a receiver returns and the send assesses feedback and offers clarification (EX: “okay, I understand.”)

Environment - such as noise, room temp. etc may affect the ability to communicate effectively.
here we should identify and control concerns
Vocal inflection
EX: of nonverbal communication cues that include vocal inflection:
Volume
whisper indicates a need for secrecy & privacy
low volume - soothing, avoids disruption
shouting - frustration, anger
maintain normal volume, rate, tone with clients who have hearing loss
Posture & gait (walking)
good posture and brisk walking exude a sense of well-being and confidence
poor posture, shuffling gives off depression, fatigue, & discomfort
tense posture, rapid walking give off anxiety and anger
Eye contact
sign of respect, willingness to listen
get on client’s level
know that some cultures interpret eye contact differently
Personal expression
facial expressions - avoid shock, disgust facial expressions
Gestures
EX: holding your nose when something smells bad / this can create uncertainty in your patient and fear in some cases
Personal appearance - effect first impressions and perceptions
Personal space - provide you and your client a sense of identify, control, and security
varies by person, culture, relationship, situation
personal space is about an arms length between you and the client
ease the patient’s anxiety by building trust, displaying confidence, and the patient’s need for privacy
personal space provides you are you client a sense of control
personal space varies based on cultural needs
Vocal inflection occurs when there are pitch changes in your voice
doubt
suspense
confusion
inquiry
Telephone communication
Record date, time
Name of the Person reporting
Information you receive
Repeat information for accurately
Case Study Q1:

The nursing staff continues to communicate about the correct policy for e-mailing and text messaging. Which of the following should the nurse consider as a barrier to communication?
Changing the subject of conversation
Changing the subject projects a lack of empathy and gives the sender the feeling that her issue is unimportant. This is a barrier to communication. When the sender and receiver are facing each other, communication is enhanced. Intermittent eye contact is appropriate and conveys willingness to listen. Avoiding eye contact sends a message of disinterest.
Case Study Q2:

When Chandra warns Helen about her use of personal e-mail at work, she realizes nonverbal communication will affect how her message is received. Which of the following uses of personal space zones will strengthen Chandra’s communication?
Position self within arm’s distance
Placing self within arm’s distance is considered personal distance and will allow Chandra’s message to be received in a constructive manner. Standing or sitting behind a counter is considered social distance and is perceived as a more formal, remote style of communication typically used for general interaction. Distancing oneself with minimal eye contact is considered public distance and would detract from the message Chandra is trying to convey.
Case Study Q3:

Helen discusses with Allison the advantages and risks of electronic communication sent to the client per
the institution’s policy. Which of the following types of information should the nurse avoid sending to the
client?
Confidential information
The nurse should avoid sending confidential information that may jeopardize the client’s right to privacy. The nurse may send normal lab information to a client, but the nurse should avoid sending abnormal lab information due to questions the client may have for the provider. The nurse may send nonurgent information.
Case Study Q4:

Allison and Helen discuss the situation of a coworker who was fired for sending client information in an
e-mail. Which of the following methods of communication would be appropriate when sharing client
information with another nurse?
Locate the nurse manager and ask to speak to her in private.
The nurse manager and the nurse should arrange for a private place to share client information to maintain privacy and confidentiality. Calling the nurse at the nursing desk to discuss the client and sending e-mail to another nurse concerning a client are not appropriate methods of communication and may breach confidentiality.
Case Study Q5:

Helen is checking e-mail on her phone when Chandra approaches her. Which of the following is the
most appropriate statement from Chandra?
“Please follow the computer use policy of the hospital.”
"Please follow the computer use policy of the hospital" assertively conveys a congruent and straightforward message, which is that staff must follow hospital policy when using electronic messaging. “You know you shouldn’t be doing that” sends a passive mixed message with no concrete direction, and it avoids conflict. “Please complete your work assignment” sends a confusing message that may contradict the nonverbal message to avoid conflict.
Which of the following should not be included when discussing modes of computer-mediated communication?
Voice mail
Voice mail is not a mode of computer-mediated communication and should not be included in the discussion.
A nurse is planning to document a conversation with a client who is preparing for a surgical procedure. Which of the following client information is an accurate and factual form of written communication? (Select all that apply.)
"Client states, 'I have a throbbing pain on my left foot'" is correct. It is accurate and factual information about what the client said.
"Client states, 'I feel nervous about having my foot removed'" is correct. It is accurate and factual information about what the client said.
Which of the following should not be included when discussing components of the communication process?
Tone of voice
Tone of voice is not a component of the communication process.
A nurse manager is discussing the topic of personal space as it relates to nonverbal behavior with a staff nurse. Which of the following statements by the staff nurse indicates a need for further teaching?
"Use of personal space will increase the client's self-esteem."
Personal space does not increase the client’s self-esteem.
Electronic health records capture data for which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
Continuous quality improvement is correct. Electronic health records capture data for continuous quality improvement.
Utilization review is correct. Electronic health records capture data for utilization review.
Resource planning is correct. Electronic health records capture data for resource planning.
Risk management is correct. Electronic health records capture data for risk management.
A charge nurse is discussing with a staff nurse the establishment of credibility when providing nursing care. Which of the following statements made by the staff nurse indicates a need for further teaching?
"Using sympathy will help to build credibility."
Showing sympathy involves displaying personal emotions and does not improve the trusting relationship with the client, and it does not build the nurse’s credibility.
A nurse engages in verbal communication with a client. Which of the following is reflective of the nurse's word selection?
Personal values
Personal values, perceptions, culture, age, education, and socioeconomic background are reflective of word selection while engaging in verbal communication.
A nurse is counseling a client who recently received a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following is a component of nonverbal communication the nurse may display? (Select all that apply.)
Vocal inflection is correct. Vocal inflection is a component of nonverbal communication.
Volume is correct. Volume is a component of nonverbal communication.
Posture is correct. Posture is a component of nonverbal communication.
Gestures are correct. Gestures are a component of nonverbal communication.
A nurse is using a health-related Internet blog. Which of the following is an acceptable use of this form of communication?
Access information
A nurse should use blogs to access information and discover the most up-to-date evidence-based practice information available to health professionals.
Which of the following are characteristics of effective written communication? (Select all that apply.)
Factual is correct. Effective written communication is factual.
Objective is correct. Effective written communication is objective.
Accurate is correct. Effective written communication is accurate.
Concise is correct. Effective written communication is concise.