Intro to Cellular Respiration / Aerobic Respiration
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
storage
Glucose is good for ?, not as fuel → we use ATP instead for fuel
Fermentation
one way to convert glucose to ATP
anaerobic
makes 2 ATP
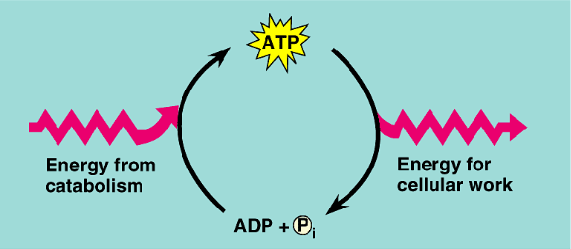
Aerobic Respiration
one way to convert glucose to ATP
aerobic
makes 36 ATP
NAD+ / NADH, FADH / FADH2
Electron carriers in Cellular Respiration
OUT
In the ETC of Cellular Respiration, NADH / FADH2 move high energy electrons to the ETC
as electrons move down the ETC, H+ ions are pumped ? of the matrix to the inner membrane space
H+ diffuses back the opposite way through ATP Synthase making ATP
This is the opposite of the Light Reactions
Cristae
The electron transport chain in Cellular Respiration takes place in the ?
Glycolysis
1st step of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Splitting glucose into 2 (3-Carbon) pyruvate
Takes place in cytosol
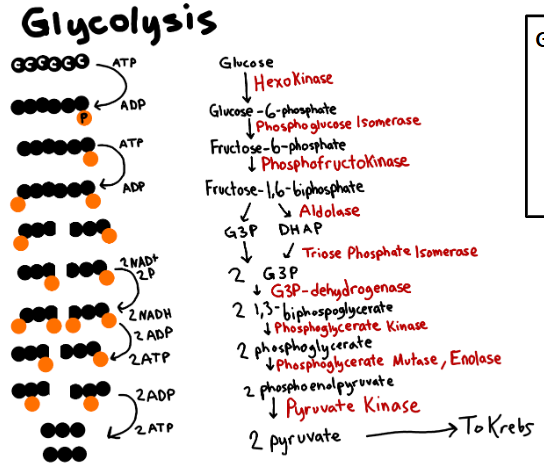
2 pyruvate
Glycolysis’s products
2, 4
Glycolysis uses ? ATP and produced ? ATP
only small organisms can live off of this
O2
What happens to pyruvate depends on the presence of ?
common ancestor
All living organisms utilize glycolysis, which is major evidence for a ?
Prep (Linking) Step
2nd step of aerobic respiration
Moves reaction into the mitochondria
Takes place in the matrix
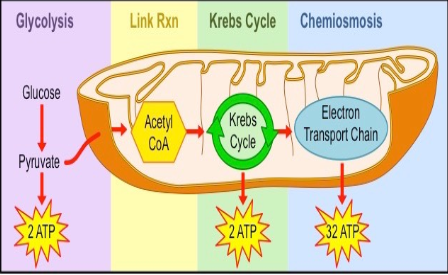
Acetyl-CoA
In the Prep (Linking) Step Pyruvate is converted into ?
Krebs Cycle
3rd Step of Aerobic Cellular Respiration (aka Citric Acid Cycle)
the point is to reduce the electron transporters (NAD+ / FADH) → a little ATP is made in the process (2)
takes place in the matrix
3, 1
One cycle of the Krebs Cycle makes ? NADH and ? FADH2
more electron carriers → more electrons in ETC → more ATP produced