Halogenoalkanes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is a nucleophile?
A chemical which always has a lone pair of electrons that it donates to an electron deficient atom
How do nucleophiles react with haloalkanes?
Nucleophile attacks the positive carbon atom. The carbon has a small positive charge because of the electronegativity difference between the carbon and the halogen
What effects the rate of the substitution reactions?
Depends on the strength of the carbon and halogen bond. The weaker the bond the easier it is to break so the reaction is faster
High bond strength seen in c-f (fluoroalkane) makes it difficult to break. Reducing its reactivity.
Conditions for nucleophilic substitution with hydroxide ions.(OH-)
Use an aqueous solution of hydroxide ions. But haloalkanes are insoluble in water so ethanol is added. Ethanol solubilises the haloalkane so it can react with aqueous hydroxide ions.(Nucleophile and haloalkane mix properly). Then heated
Conditions for nucleophilic substitution with cyanide ions (CN-)
Haloalkane is mixed with ethanol and an aqueous solution of potassium cyanide. Then heated
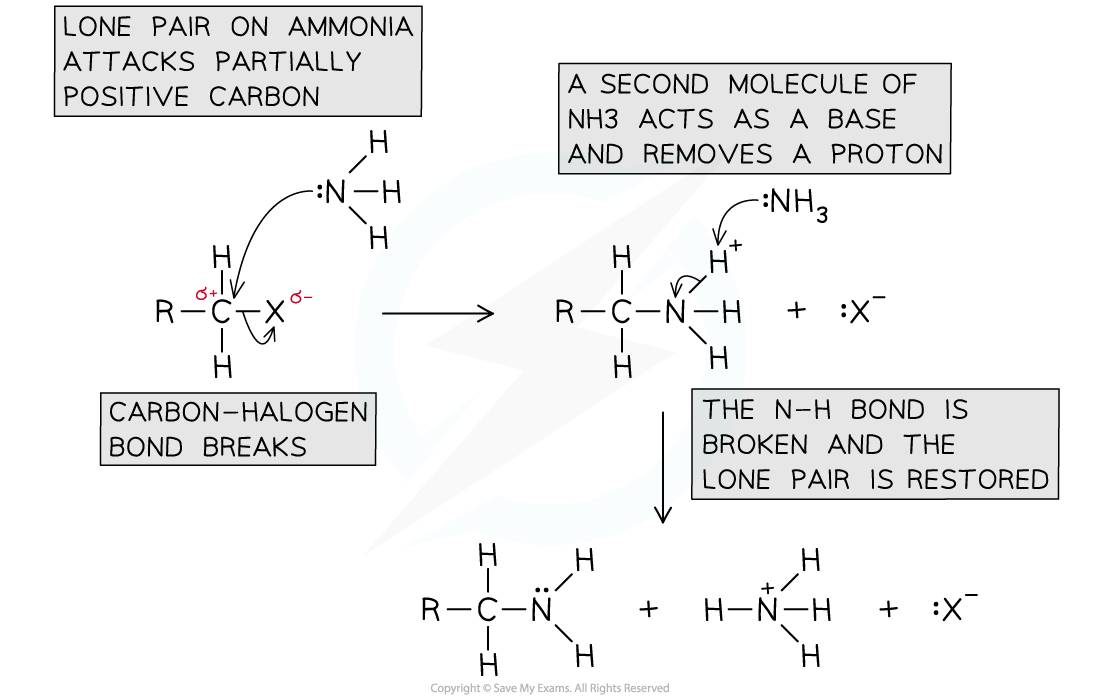
Conditions for nucleophilic substitution with ammonia (NH3)
Haloalkane is heated with a concentrated solution of ammonia in ethanol. Carried out in a sealed tube to prevent ammonia escaping as a gas
Why should excess ammonia be used?
Because in the first stage, the product amine still has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. This can act as a nucleophile which will keep reacting with any unreacted haloalkane.
Excess ammonia makes it more likely that the haloalkane will react with ammonia rather than the product amine.
What does the halogenoalkane become in elimination
Alkene
What reagents are used in elimination?
Sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide
Conditions for elimination
Haloalkane is dissolved in ethanol (alcohol)only and is heated
What is happening in an elimination reaction?
A hydrogen atom and halogen atom is being removed.
Mechanism for elimination
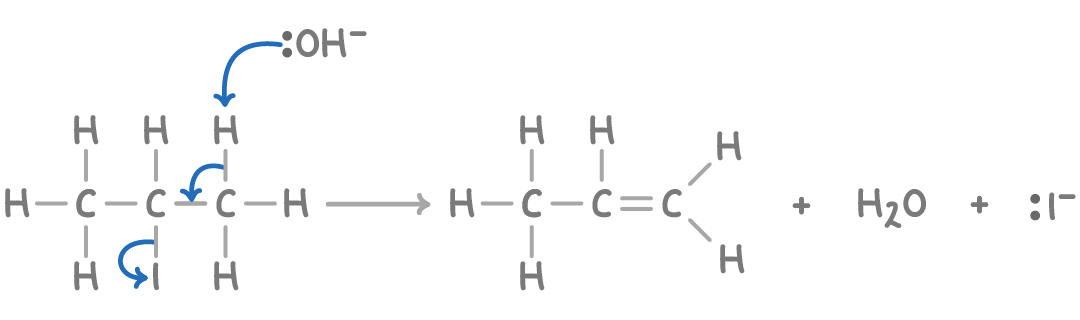
what effects the alkene formed in elimination
elimination can happen starting from any hydrogen atom as long as it is not connected to the same carbon atom the halogen is attached to. So position of double bond can change
mechanism for substitution with ammonia