Physiology Exam 1 (Cell Physiology)
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Which two of the following are examples of mediated transport?
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport
Primary active transport
is the transport of molecules against a concentration gradient by the use of energy from ATP.
Secondary Active Transport
is another type of active transport that uses the electrochemical gradient in the transport of molecules against the concentration gradient.
Facilitated diffusion
is a passive transport mechanism that allows molecules to cross cell membranes with the help of specific transport proteins, moving down their concentration gradient without the use of energy.
Simple diffusion
passive diffusion from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
In each cycle of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump, Blank______ ions of sodium are transported and Blank______ ions of potassium are transported
3,2
Symport (cotransport)
Moves two different molecules together
Same direction (both into the cell or both out)
Antiport (countertransport)
Moves two different molecules in opposite directions
GLUT
They use a carrier protein
They move glucose down its concentration gradient
They do not require ATP
So they are mediated, but not active transporters.
Isotonic
water moves in and out at the same rate, cell keeps its normal shape
cell Hypotonic to its surroundings
water out → cell crenates
cell Hypertonic to its surroundings
water in → cell swells
Down‑regulation
decreasing the number of receptors
Up‑regulation
increasing the number of receptors
Protein receptors that bind intercellular chemical messengers can be found in what target cell locations
plasma membrane, cytosol, nucleus
A cell will only respond to those signals for which it has
receptor
signal transduction pathways initiated by water-soluble messengers.
Signaling via G‑protein‑coupled receptors, signaling via receptors that function as enzymes, Signaling via cytoplasmic Janus kinases, Signaling via ligand‑gated ion channels.
When a chemical messenger combines with its receptor and changes its conformation
receptor activation
second messengers
The molecules that diffuse throughout the cell to serve as chemical relays from the plasma membrane to the biochemical machinery inside the cell are collectively called
In a signal transduction cascade, extracellular chemical messengers that bind to their specific plasma membrane receptors are sometimes referred to as
first messengers
An enzyme that changes another protein’s three‑dimensional conformation to alter the protein’s activity by transferring a phosphate group to them from ATP is called a
Protein Kinase
Phopholipase C catalyzes the breakdown of
phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP₂)
Calcium ions frequently act as
second messengers
The entire nervous system is divided into two anatomical regions
Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord. It’s the main control center that processes information and coordinates responses.
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. It carries information to and from the CNS
axon
The long process that carries information away from a neuron's cell body
dendrites
Thin branching processes that extend from a neuronal cell body and receive information from other neurons
oligodendrocytes
Cells responsible for producing the myelin sheath that surrounds axons in the central nervous system
The nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the Blank______ of certain axons
mylein sheeth
dendrites
Highly branched cellular processes of a neuron that receive input from other neurons (in the CNS)
Speeding up conduction of the electrical signals along the axon and conservation of energy are the two main functions of the
myelin sheath
retrograde transport
The type of axonal transport where substances travel within neuronal axons from the axon terminals toward the cell body
axonal transport
The movement of materials between the cell body and distant parts of neurons along microtubule "rails"
In the PNS, myelin sheaths around peripheral axons are formed by
Schwann cells.
nodes of Ranvier
Unmyelinated regions of an axon in between regions covered by myelin
functions of astrocytes?
Absorption of K⁺ from the extracellular fluid
Stimulate the formation of tight junctions between the cells that constitute the blood‑brain barrier
Which is a function of the myelin sheath?
Increase the speed of action potential propagation
excitability
The ability of cells with voltage-gated ion channels to produce electrical signals
ionotropic receptors
Receptors found in postsynaptic densities of synapses that both bind to neurotransmitters and act as ion channels
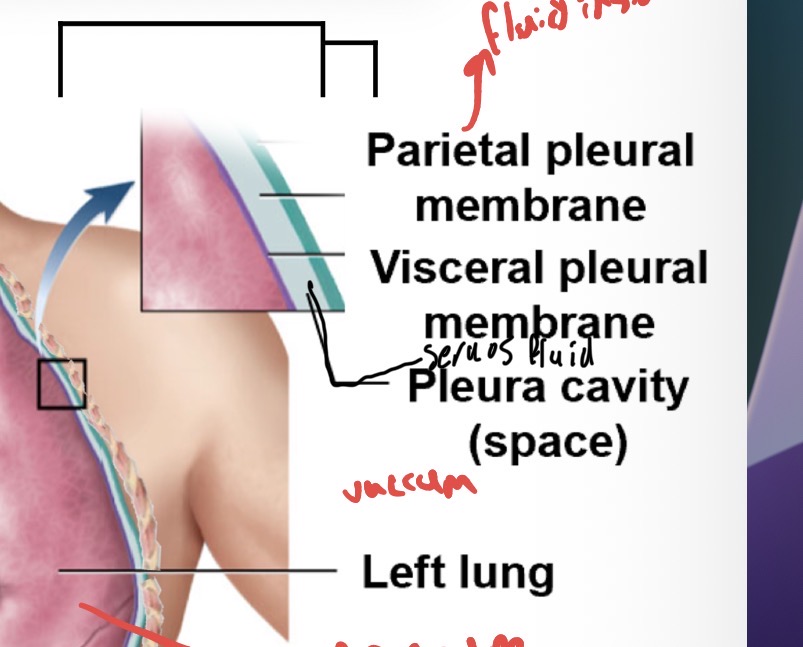
Lungs
Surrounded by the left and right pleural cavity In the thoracic cavity
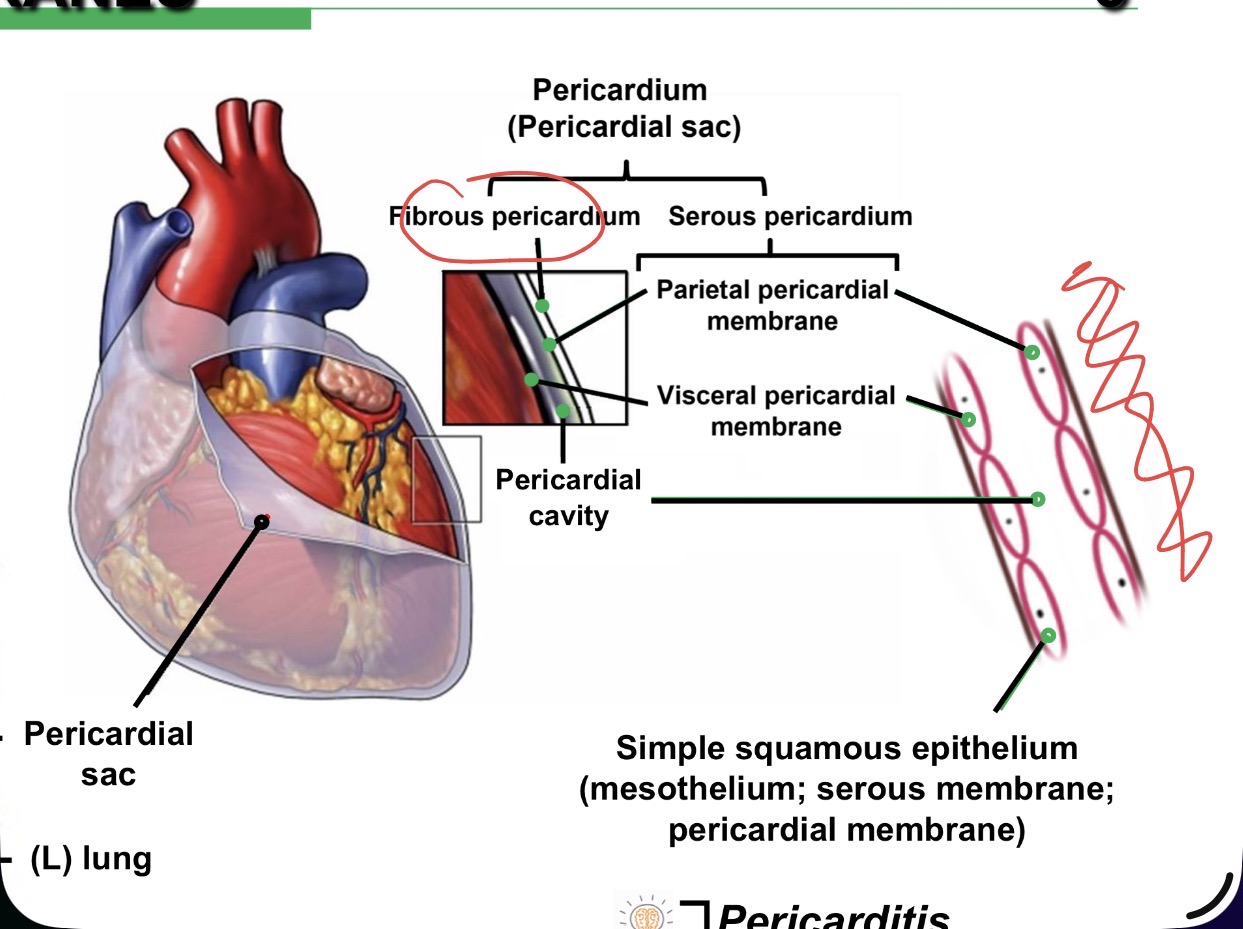
Heart
Surrounded by the Pericardial cavity —> thoracic cavity —> ventral body cavity.
Abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity: contains one subcavity (the peritoneal cavity) which surrounds the digestive organs.
Pelvic Cavity: contains the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems.
Dorsal cavity
Cranial cavity + spinal cavity
Heart membrane
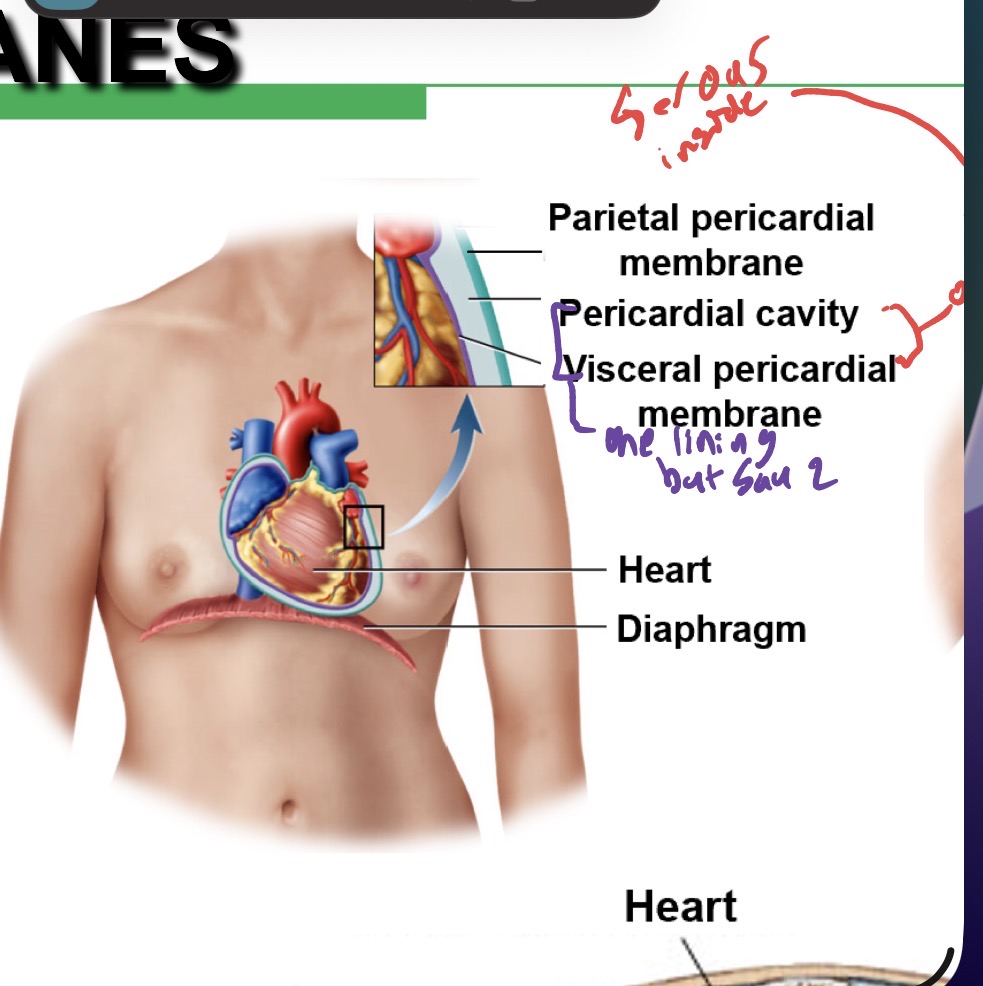
Lung membrane
Pericardium
Intracellular
Intra meaning inside. Inside the cell contains intracellular fluid (ICF) 67% of total body water. 28L in male and 20L in female
Intersititial fluid
Between cells any fluid outside the cell. 26% total body water. (ISF) 11L male 8L female
Intravasclar fluid (IVF)
Any fluid outside the cell plasma. 7% total body water. 3 L male and 2L female
Homeostasis
A state of dynamic equilibrium of an organism achieved by the ceaseless exchange between and organisms internal environment and the external environment, and the body system integration of the organism.
Negative feedback
a fundamental biological mechanism where a system responds to a change (stimulus) by initiating processes that counteract it, restoring internal conditions to a set point. EX regulating body temperature
Positive feedback
process where a system's output amplifies or reinforces the original input, creating a self-reinforcing loop that pushes the system further in the same direction, EX child birth. Works to enhance a deviation from a set point or normal range
Homeostatic control loop
Receptor EX: sensors in the skin —> (afferent signal) —> control center EX: hypothalamus —> (efferent signal) —> effectors EX: sweat glands (increase secretion) Blood vessels (vessels in skin dilate) —> back to set point.
Vasodilation
When hot causes vessels to open up —> more blood goes through —> blood evaporates —> body cools down.
Vasiconstriction
When cold —> causes vessels to shrink —> less blood goes through —> reduced heat radiation at the skin surface —> blood temp rises.
Normal blood glucose regulation
70-100
Fat Cell (adypoctye)
specialized mesenchymal-derived cells that primarily store energy as triglycerides (white adipocytes) or generate heat through thermogenesis (brown adipocytes). Lipogensis —> attaches 3 glucoses —> creates fat acids for storage.
Lipogensis
the metabolic process of synthesizing fatty acids and triglycerides from non-lipid precursors like excess carbohydrates
Liver cells (hepatocyte)
These specialized epithelial cells are responsible for protein synthesis, bile production, carbohydrate/lipid metabolism, and immune regulation. Gylcogensis —> links together glucose using covalent bonds —> creates glycogen. Glycogenolysis —> glycogen —> glucose. Gluconogensis —> lactate —> glucose.
Glycogensis
the metabolic process of synthesizing glycogen from glucose, occurring primarily in the liver and skeletal muscles to store excess carbohydrates.
Skeletal muscle cell myocyte
Glycogensis —> glucose —> glycogen. Glucose —> ATP
Glycogenolysis
The breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
Gluconeogensis
The production of glucose from scratch EX lactate —> glucose
Acute hypoglycemia
Acute hyperglycemia
Blood pH Range
7.35 - 7.45
Acidosis
condition where there's too much acid (or too little base) in the body fluids, lowering blood pH, typically from lung issues (respiratory) or kidney problems/acid production (metabolic).
Alkalosis
condition with an arterial blood pH >7.45, resulting from excess base or, more commonly, excessive loss of acid (hydrogen ions) or metabolic bicarbonate accumulation.
Bicarbonate Buffer System
CO2 + H2O←→ H2CO3 (acid)← → HCO3-(buffer) + H+
Regulates blood pH. Blood becomes more acidic when equation leans toward right and more basic when leaning toward the left.
Carbonic anhydrase
crucial, zinc-containing enzyme found throughout the body (erythrocytes, lungs, kidneys, stomach) that catalyzes the rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water into bicarbonate and protons (
CO2+H2O⇌HCO3− +H + CO2+H2O⇌HCO−3+H
acute hyperglycemia
high glucose pancreatic beta cell → plasma insulin increases → Fat Cell or Liver Cell or Skeletal Muscle Cell → low plasma glucose.
acute hypoglycemia
low glucose pancreatic beta cell → plasma glucagon increases → Liver Cell → high plasma glucose.
Feedforward
information sent forward in a pathway to prepare for physiological process yet to occur EX: seeing food → stomach growls or smell food → salivate
plasma membrane is made up of what
98% lipid and 2% protein
Membrane Lipids
75% are phospholipids - principle building blocks
20% is cholesterol - membrane integrity
5% are glycolipids - identity markers, protection.
Membrane Proteins
Leak channels, gated channel, carrier, receptor, enzyme
uniport
1 at a time one direction
passive transport
simple diffusion (across membrane, no protein) and facilitated diffusion (though a protein down concentration gradient)
Leak channels
non-gated ion channels that remain continuously open, allowing specific ions to passively flow across cell membranes, playing a crucial role in maintaining the resting membrane potential.
ligand gated channel
ligand binds to receptor channel opens and ions move down concentration gradient.
voltage gated channel
change in polarity of membrane near the channel cause it to open and ions move down concentration gradient until polarity goes back to normal.
mechanically gated channel
open in response to mechanical stimuli, playing crucial roles in sensory perception and cellular signaling.
osmotic potential
areas with low osmotic potential have high solute concentration, so water movies from areas with high osmotic to areas with low osmotic potential.
N+/K+ ATPase pump
moves 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell using ATP against the concentration gradient.
Ca2+ Pump
PMCA (Plasma Membrane Ca²⁺-ATPase):
Ca²⁺ → out of the cell
SERCA (Sarcoplasmic/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca²⁺-ATPase):
Ca²⁺ → into the SR/ER
all use ATP
ventral body cavity
Separated by the diaphragm into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
mesenteries
they help stabilize organs within the abdominal and thoracic cavities
Sodium-Glucose transporter (SGLT)
uses the sodium gradient as a power source to bring glucose into the cell by taking sodium out of the cell using Na+/K+ channel and bring it back to power glucose into the cell.
vesicular transport
endocytosis moves material into the cell
exocytosis moves material out of the cell.
endocytosis
The movement of material into the cell occurs in three forms: pinocytosis, receptor-mediated, and phagocytosis.
phagocytosis (endocytosis)
(“cell eating”)
What it is: Engulfing large particles, like bacteria, dead cells, or debris.
Mechanism: The plasma membrane wraps around the particle to form a phagosome.
Example: Macrophages engulfing bacteria.
pinocytosis (endocytosis)
(“cell drinking”)
What it is: Uptake of fluids and dissolved solutes.
Mechanism: The membrane folds inward to form small vesicles containing extracellular fluid.
Example: Absorption of nutrients in kidney tubules or intestinal cells.
receptor-mediated (endocytosis)
What it is: Highly specific uptake of molecules.
Mechanism: Molecules bind to specific receptors on the membrane → membrane invaginates → forms a clathrin-coated vesicle.
Example: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) uptake into liver cells.
Membrane Potential
The electrical voltage across a cell’s plasma membrane.
It happens because there’s a difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell.
Transmembrane Potential (TMP)
the voltage difference across a cell’s plasma membrane, i.e., inside of the cell relative to the outside.
It’s called “transmembrane” because it’s measured across the thickness of the membrane.
Resting membrane potential (RMP)
is the voltage across the plasma membrane when the cell is at rest (not sending signals).
It’s usually negative inside relative to outside.
Typical value: –70 mV in neurons.
depolarization
a decrease in RMP
Hyperpolarization
is an increase in RMP
Juxtracrine Signaling
cell-cell communication via direct physical attachment to one another. EX: white blood cells
Neurocrine Signaling
chemical signals (messengers) released by neurons to affect other cells.
These signals are produced by neurons and usually act on target cells nearby or at a distance. Very local
Neuroendocrine Signaling
neurons release chemical messengers into the blood which then act at distant target cells.
basically a bridge between the nervous system and the endocrine system.