1 - Complex reconstructions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
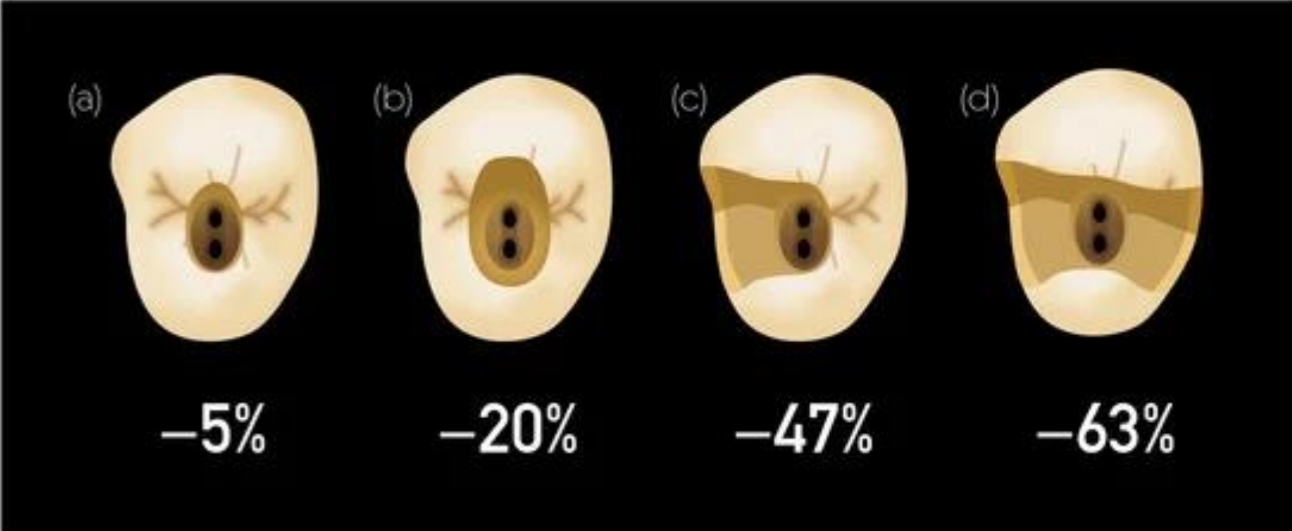
% Reduction in tooth stiffness from Endo/restoration
What are 6 factors that influence (And indicate) a direct restoration?
Retention and resistance
Cavity extension
Occlusion
Cusp restoration (active/inactive)
Root canal treated teeth
Socio-economic factors
(and other factors)
How can a root canal affect a tooth’s strength?
Loss of humidity and elasticity → Less resistance and more fractures. Fragility from structural loss makes the tooth harder to restore.
(Due to degradation of collagen fibres)
What strength of occlusal forces will cause tooth fracture?
More than 58 N/cm²
What can inadequate restorations of active cusps cause?
Fractures from occlusion
How do we restore active cusps if more than one cusp is affected?
Inlay or onlay
Do masticatory factors directly influence inactive cusps?
No
% Causes of failures of endodontically treated teeth?

What 3 things must restorations balance?
Function, Aesthetics, Longevity
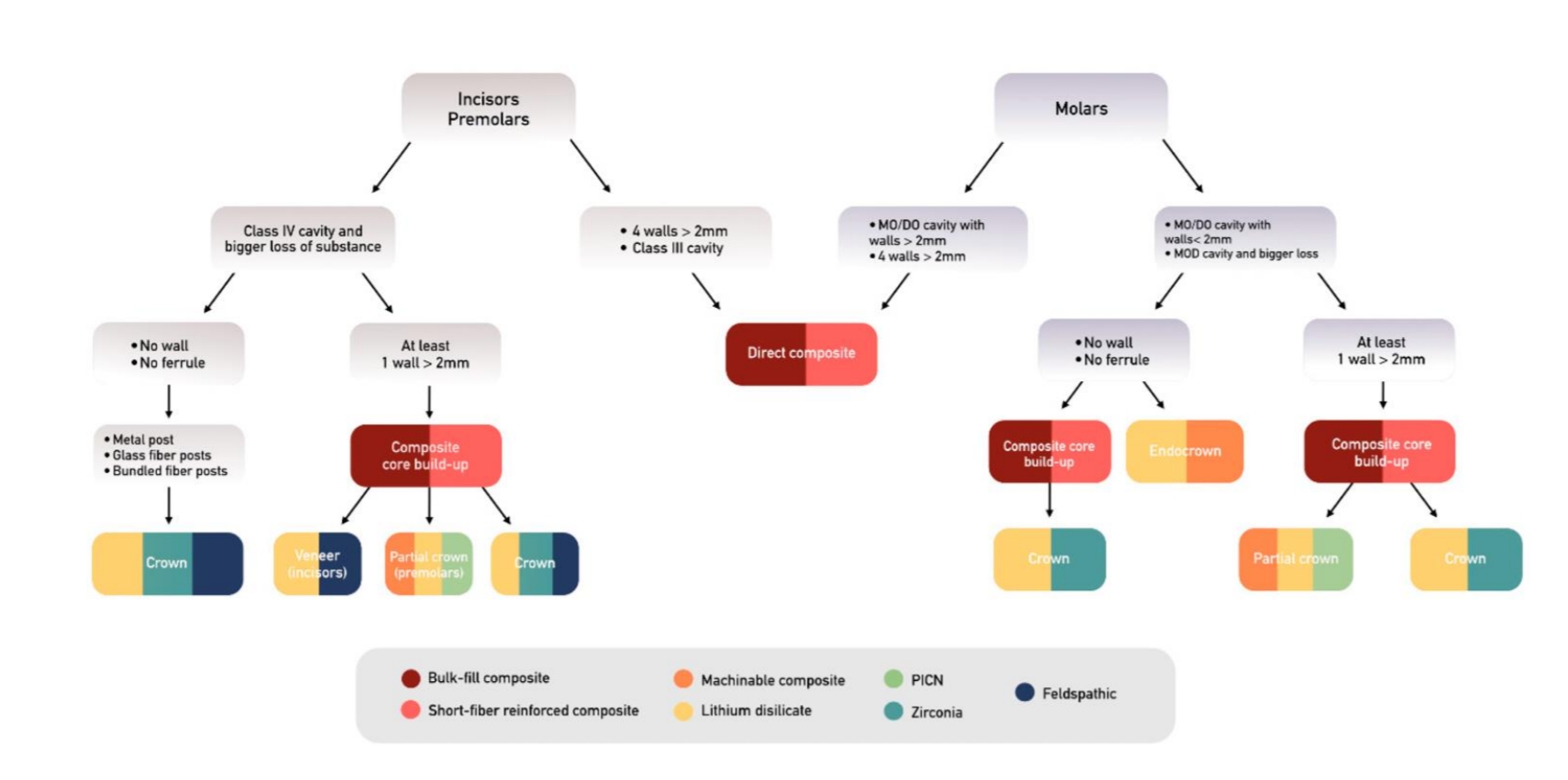
What are 3 restorative options for endodontic teeth?
Partial crowns & veneers - (when sufficient tooth structure remains)
Full crowns - (widely used)
Endocrowns - (suitable for molars)
What is a ferrule?
When we have at least 2mm of tooth structure above the bone.
In restorations of endo teeth, when is a post not preffered?
When a ferrule is present
What posts are favoured in endo teeth restorations?
Glass fibre posts better than metal (better stress distribution)
Bundled fibre posts are a promising innovation
What composites are reccomended for core build up when not using posts in endodontic tooth restorations?
High-filled bulk fill
Short-fiber-reinforced composites
What other factors influence a direct restoration?
Complete isolation
Inclined planes
Fragile cusps and marginal crests (eliminate them)
Cavitary base
Contact points
Matrix
What results from the absence of inclined planes?
Forces perpendicular to the main axis of the tooth that are harmful to the periodontum. Can also lead to break of cusp or dentinal wall.
What is septum syndrome?
Food impactation and gum inflammation from poor contact points
What is the purpose of a cavitary base?
Regularise surfaces, correct inclined planes without removing healthy dental tissue and isolate the pulp. (GIC better than compomer but both good)
Which materials release fluoride?
GIC
Compomer
(Ideal for use in children, and pit and fissure caries)
What are 5 desirable properties for a core material?
Compressive strength
Flexural strength
Biocompatibility
Easy to manipulate
Ability to bont to tooth, pins and posts
What are the key characteristics of amalgam?
High compressive strength and rigidity.
Not adhesive - needs mechanical retention (specific preparation)
What are 6 key aspects to consider before composite restoration of maxillary anterior teeth affected by wear?
Pattern of tooth surface loss
Interocclusal space availability
Space requirements for proposed dental restorations
Quantity and quality of dental hard tissue
Patients aesthetic demands
Speech
What are 5 important features when restoring maxillary incisors?
Height to width ratio for maxillary central incisor - 1.2:1
Incisal edge to lip line relationship and naso-labial angle
Morphology in frontal and lateral planes
Midline symmetry
Tooth shape respective to patient
What colour composite should you use to restore incisal edges?
Translucent
If the entire palatal surface of a tooth is eroded, what type of composite do we use?
First layers with dentin composite (dentin is exposed) and last layer with enamel composite (doesnt adhere to dentin)
Are glass ionomers, resin-reinforced glass ionomers, and most compomers weaker or stronger than tooth structure?
Significantly weaker - should be limited to use only where minimal tooth structure is missing and increased tooth strength and abutment retention aren’t required.
They have low flexural strength and fracture toughness
What are the materials of choice for high caries risk patients?
Fluoride releasing materials
GIC and RMGIC
What are the advantages of GIC?
Ion exchange adhesion
Continuing fluid reservoir
Acceptable aesthetics
Good wear factor on maturity
Low solubility on maturity
What are disadvantages of GIC?
Low fracture resistance
Can dehydrate in absence of saliva
What are the advantages of composite resins?
Excellent aesthetics
Excellent adhesion to enamel
Possible dentine adhesion
Polishable
Variety available for different uses
Chemical or light activation
Wear factor acceptable
Relatively inexpensive
What are the disadvantages of composite resins?
High risk of microleakage (compensatee with GIC base)
Difficult to restore coronal anatomy in extensive lesions
Longevity in large restorations may be relatively short
What are advantages of amalgam?
Relatively easy to handle
Relatively tolerant of poor placement techniques
Excellent longevity in medium to extensive-sized lesions
Relatively inexpensive
What are the disadvantages of amalgam?
Very poor aesthetics
Requires undue sacrifice of sound tooth structure
Difficult to restore full anatomical form
Wear factor too great for extensive restorations
Contains mercury
Decision tree for endodontically treated teeth (learn well)