Recombinant DNA Techniques: Southern, Northern Blot, SNPs, RFLP, STRs, VNTRs
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the purpose of a Southern blot?
To determine the copy number of a gene in a genome, compare homologous genes in different species, and screen for disease genes associated with restriction enzyme cutting patterns.
What type of RNA is used in Northern blot analysis?
Uncut mRNA
What does Northern blot analysis determine?
The size(s) of mRNA encoded by a gene and gene activity, including whether a specific mRNA is transcribed in a cell type.
What are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)?
Single base-pair differences between individuals that can lead to genetic disorders.
How can PCR be used to detect SNPs affecting restriction sites?
By designing primers to amplify a region containing the mutation, digesting the amplified fragment with a restriction enzyme, and analyzing the digestion pattern on a gel.
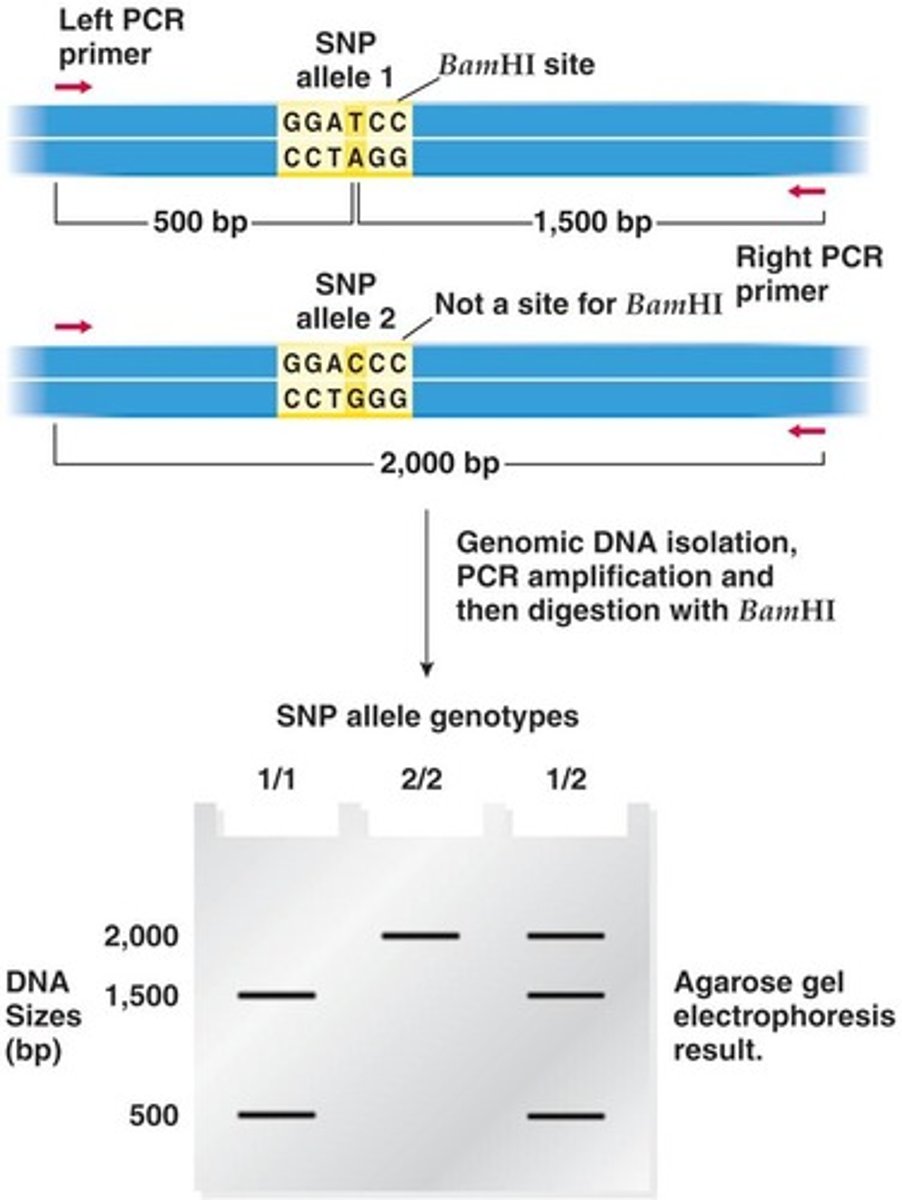
What does RFLP stand for and what does it represent?
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism, which arises from different restriction patterns due to mutations.
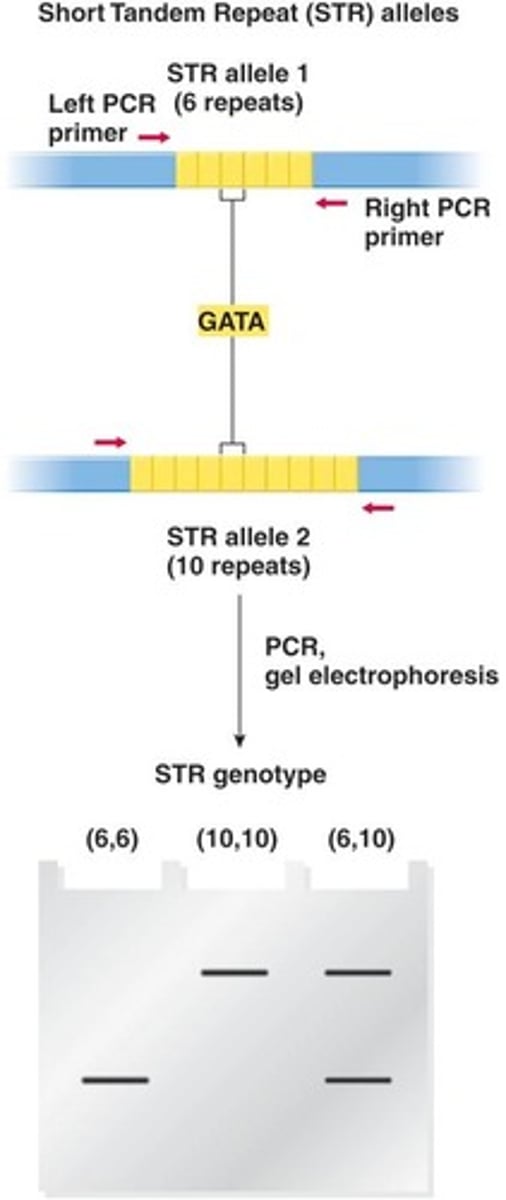
What are Short Tandem Repeats (STRs)?
Regions in the genome containing very short (2-6 bp) tandem repeats used for forensic analysis and paternity testing.
How are STRs typically typed?
By PCR with primers flanking the repeat sequence.
What are Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs)?
Longer repeat sequences (7-100 bp) in the genome, fewer in number than STRs, and typically analyzed using restriction enzyme digestion and Southern blotting.
How can VNTRs be used in paternity testing?
By comparing alleles inherited from parents; a baby inherits one allele from each parent, and matching alleles can indicate paternity.
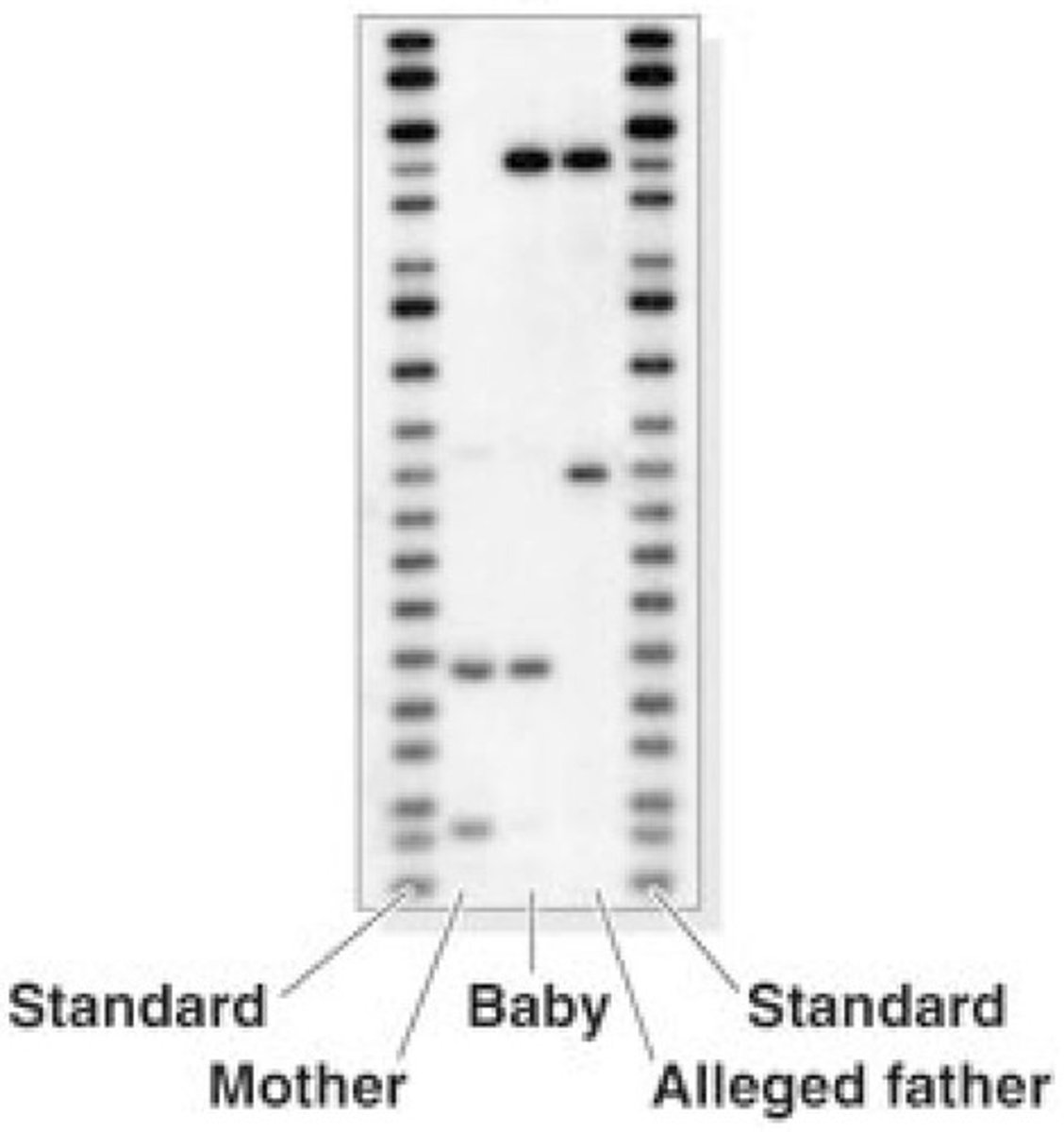
What is the significance of using multiple VNTR loci in paternity testing?
Examining multiple loci can statistically discriminate individuals, providing a high degree of certainty in establishing paternity.
What are the two types of VNTRs?
Unique VNTRs, which have only one copy in the genome, and multicopy VNTRs, which have many copies scattered throughout the genome.
What is the role of a labeled probe in Southern blotting?
To hybridize with complementary DNA fragments on the filter, allowing for visualization of specific DNA sequences.
What does the autoradiogram in Southern blotting represent?
The pattern of hybridized DNA fragments that indicates the presence and size of specific DNA sequences.
What is the first step in the PCR method to detect SNPs?
Design primers to PCR-amplify a region containing the point mutation.
What does a darker/thicker band in a Northern blot indicate?
Higher levels of mRNA transcription in that cell type.
What is the main application of DNA fingerprinting?
To determine the identity of an individual for forensic and paternity testing.
What is the relationship between mRNA species and gene expression?
Different mRNA species can arise from the same gene due to alternative splicing or differential use of promoters and terminators.
What is the significance of analyzing the digestion pattern in PCR-RFLP?
It allows for the identification of mutations based on the resulting fragment sizes after restriction enzyme digestion.