Important Terms
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Money
any asset that people are generally willing to accept in exchange for goods and services or for payment of debts.
Asset
Anything of value owned by a person or a firm
Bartering
trading goods and services directly for other goods and services that requires a double coincidence of wants
Commodity money
goods used as money that also have value independent of their use as money—like animal skins or precious metals.
4 primary functions of money
Medium of exchange
Unit of account
Store of Value
Standard of deferred payment
Liquid
easily exchanged for goods
Characteristics of Money
Acceptable to most people
Standardized quality
Durable
Valuable relative to its weight
Divisible enough for low and high priced goods
Federal Reserve
the central bank of the United States
Fiat Money
any money, such as paper currency, that is authorized by a central bank or governmental body and does not have to be exchanged by the central bank for gold or some other commodity money
M1
narrow definition of the money supply, the sum of currency in circulation and checking account deposits in banks.
M2
broader definition of the money supply that includes M1, plus small-denomination time deposits, savings account deposits (including balances in money market deposit accounts in banks), and noninstitutional money market fund shares.
Reserves
deposits that a bank keeps as cash in its vault or on deposit with the Federal Reserve.
Required Reserve Ratio (RR)
the minimum fraction of deposits banks are required by law to keep as reserves; 10%
Excess Reserves
reserves that banks hold over the legal requirement.
Simple Deposit Multiplier
the ratio of the amount of deposits created by banks to the amount of new reserves
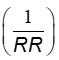
Fractional Reserve Banking System
banks keep less than 100% of deposits as reserves
Bank Run
many depositors simultaneously lose confidence in a bank and try to withdraw their money
Bank Panic
many banks experience bank runs at the same time
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
responsible for open market operations and managing the money supply in the United States.
4 Monetary Policy Tools
Open market operations
Discount policy
Reserve requirements
Interest on reserves
Open Market Operations
the buying and selling of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve in order to control the money supply.
Commercial banks
primary role is to accept funds from depositors and make loans to borrowers
Security
financial asset—such as a stock or a bond—that can be bought and sold in a financial market
Securitization
The process of transforming loans or other financial assets into securities.
Investment Banks
banks that do not typically accept deposits from or make loans to households; they provide investment advice and also engage in creating and trading securities such as mortgage-backed securities.
Money market Mutual Funds
funds that sell shares to investors and use the money to buy short-term Treasury bills and commercial paper (loans to corporations).
Hedge Funds
funds that raise money from wealthy investors, and make “sophisticated” (often non-standard, high-risk) investments
Quantity Equation
M: Money supply
V: Velocity of money: the average number of times each dollar in the money supply is used to purchase goods and services included in G D P.
P: Price level
Y: Real output
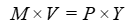
Quantity Theory of Money
A theory about the connection between money and prices that assumes that the velocity of money is constant