Biology 🧪 🔬🧬🧫
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:47 PM on 1/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
How does water enter the cell membrane?
* Some water molecules don’t need proteins to enter the cell but they may need help due to the huge amount of water trying to enter the cells
* The water gets this help due to a specific type of transport protein known as aquaporin
* The water gets this help due to a specific type of transport protein known as aquaporin
2
New cards
What is the fluid mosaic model?
model used to describe a membrane’s structure(diverse protein molecules suspended in fluid phospholipid bilayer)
* in other words it describes the fluidity of the cel membrane
* in other words it describes the fluidity of the cel membrane
3
New cards
What does the plasma membrane allow?
selective permeability(lets certain things in and out of the cell)
4
New cards
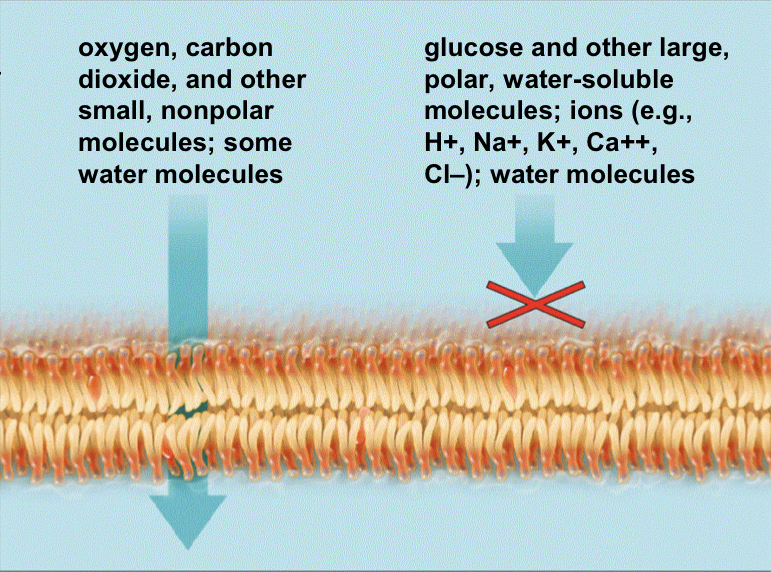
What molecules have an easier time going through the cell membrane?
* Smaller not charged molecules easily travel through the membrane
* Meanwhile, bigger,charged molecules have a hard time to pass through membrane and need special protein to pass through
* Meanwhile, bigger,charged molecules have a hard time to pass through membrane and need special protein to pass through
5
New cards
What do transport molecules do?
allow specific ions/molecules to enter or exit the cell
6
New cards
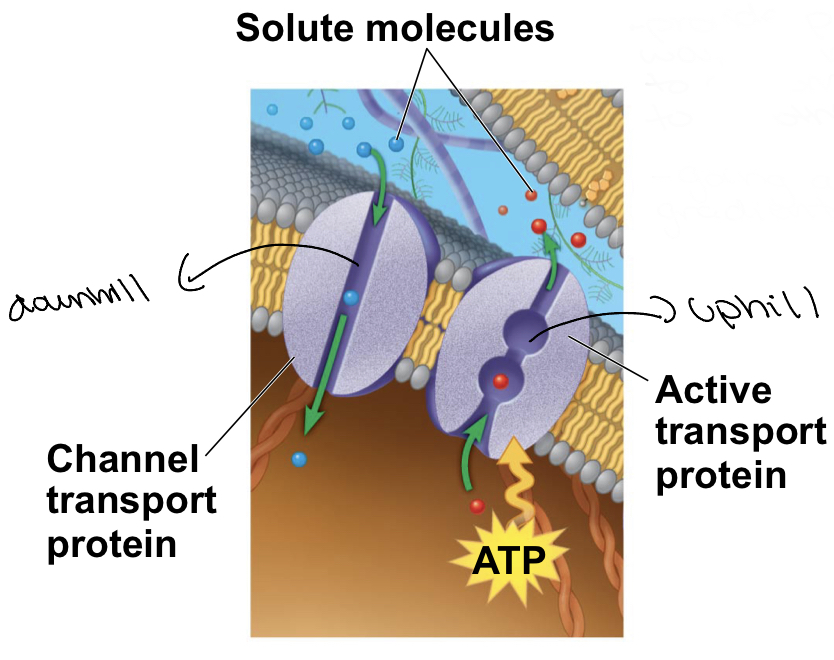
What is a channel transport protein?
This protein is one that allows the solute molecule into the cell and requires no energy to do so as it is “down hill/going with the gradient”
7
New cards
What is an active transport protein?
This protein is one that allows solute molecules to enter the cell by going “uphill/against the gradient” by requiring energy (ATP)
8
New cards
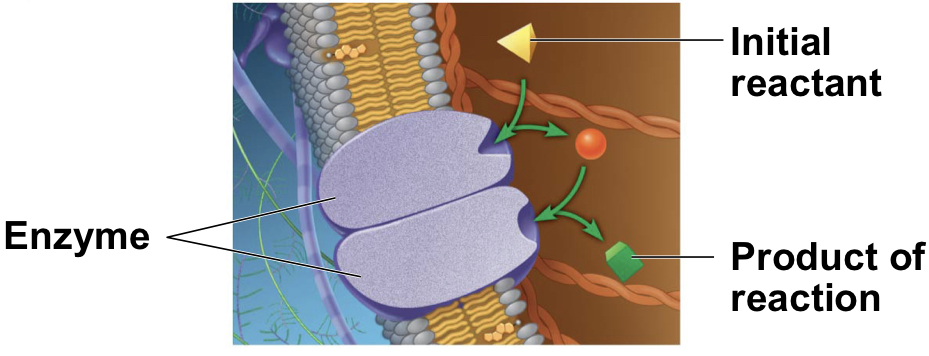
What is an enzyme?
* certain membrane proteins that carry out sequential reactions as well as modify one molecule through an interaction and create a new product
9
New cards
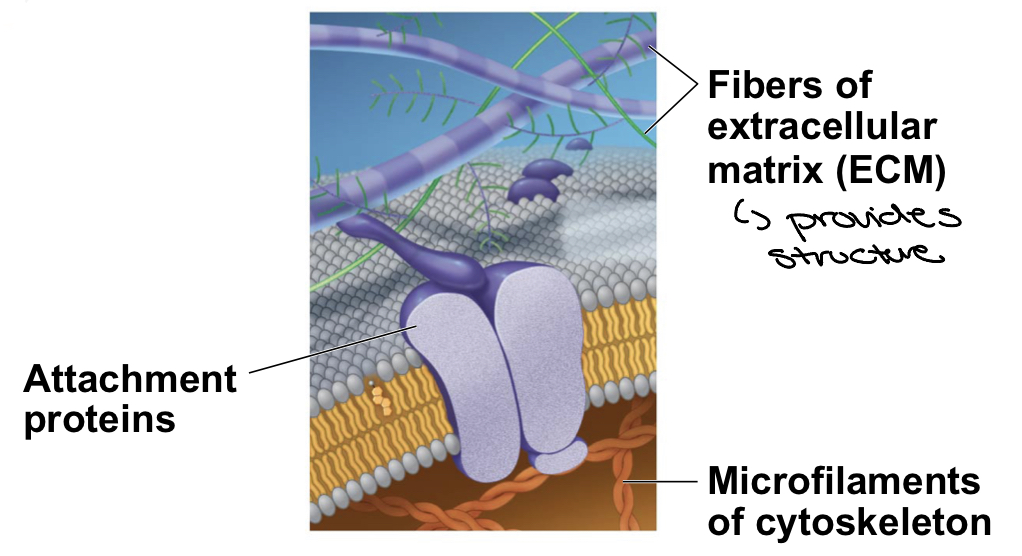
What are attachment proteins?
* attach to the extracellular matrix and cytoskeleton
* help support the membrane(attach from outer side of the membrane with the ECM to the inner side of the membrane with the cytoskeleton)
* can coordinate external and internal changes
* help support the membrane(attach from outer side of the membrane with the ECM to the inner side of the membrane with the cytoskeleton)
* can coordinate external and internal changes
10
New cards
Receptor Proteins
* signaling molecules bind to receptor proteins
* these receptor proteins then relay the message by activating other molecules inside the cell
* these receptor proteins then relay the message by activating other molecules inside the cell
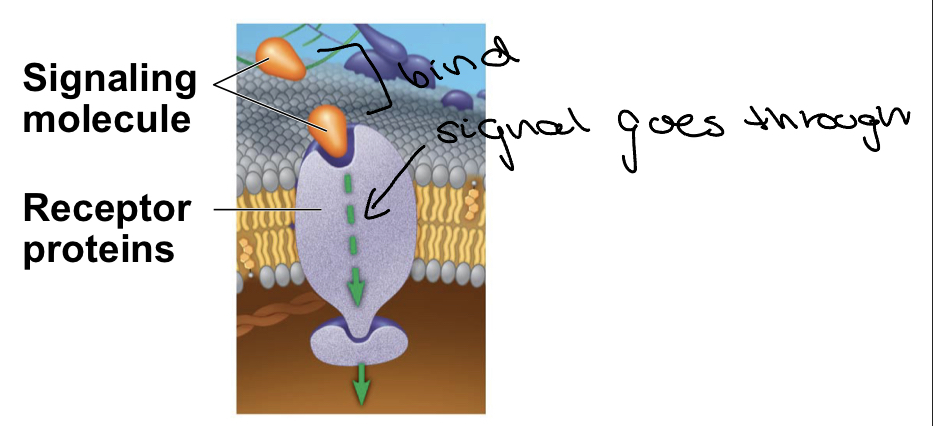
11
New cards
Junction Proteins
* form intercellular junctions that attach adjacent cells
* in other words they attach together to form tissue
* in other words they attach together to form tissue
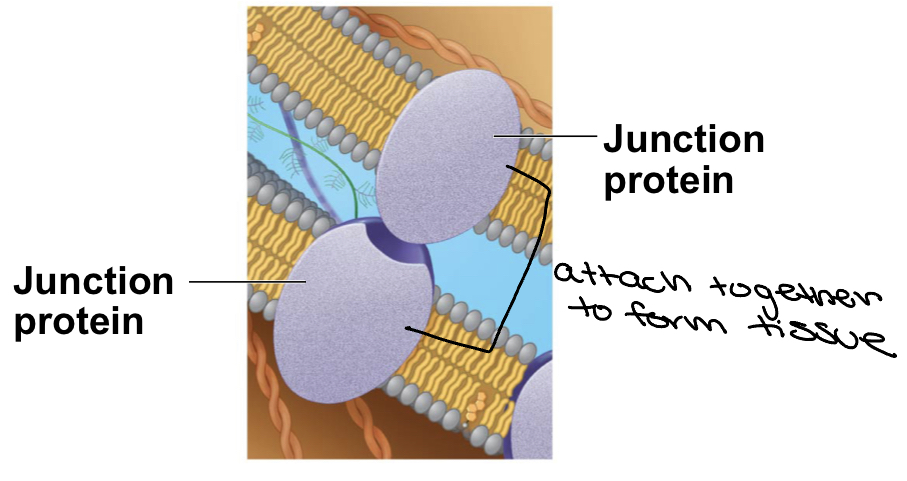
12
New cards
Glycoprotein
* serve as ID tags (recognize self from non-self)
* may be recognize by membrane proteins of other cells
* may be recognize by membrane proteins of other cells
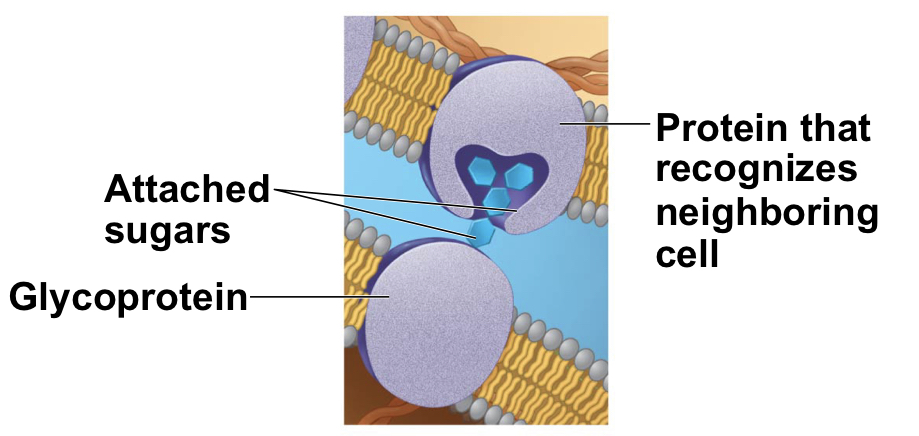
13
New cards
What is the overview of cell signaling?
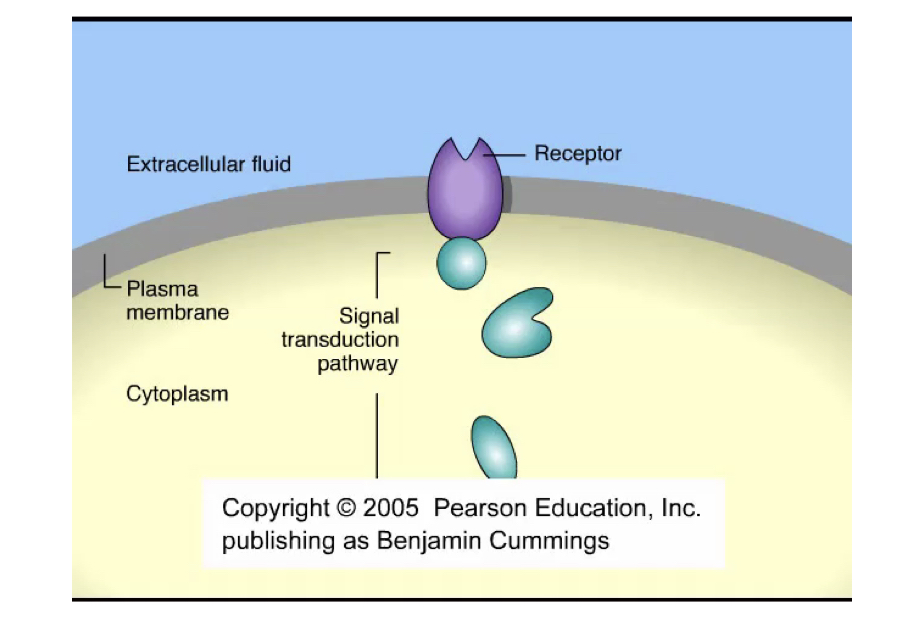
14
New cards
Give an overview for signal transduction pathways.
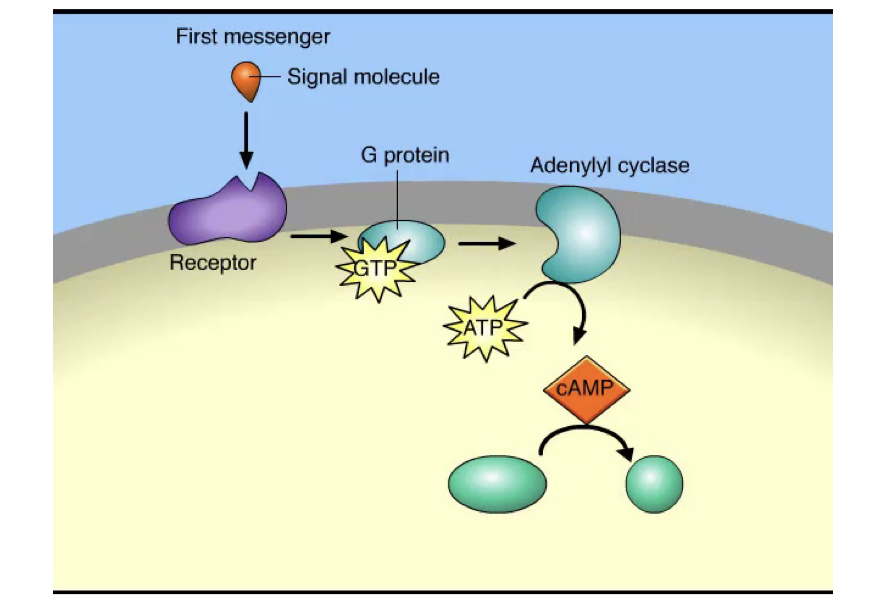
15
New cards
What does the cell membrane of cells look like and what are the different parts that compose them?
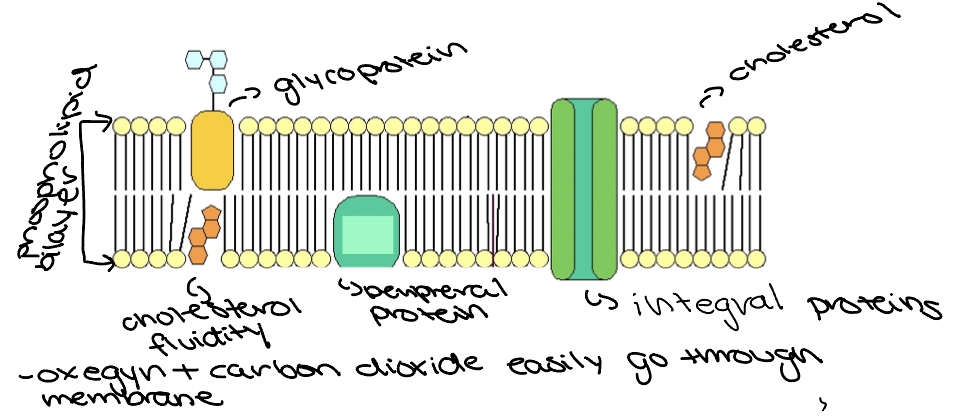
16
New cards
What is the general term “transport” in cells mean?
allows passage of substances across cell membranes
17
New cards
What does passive transport generally mean?
Transporting molecules into the cell by going “with the gradient” and not using energy
18
New cards
What does active transport generally mean?
the use of transporting molecules out of the cell by going against the gradient and using energy
19
New cards
What are the gradients movement ways for active and passive transport?
Active: Low to High
Passive: High to Low
Passive: High to Low
20
New cards
What are the different types of passive transport
1) Diffusion: molecules go from high to low concentration
2) Facilitated Diffusion: molecules go from high to low concentration with the help of certain proteins
3) Osmosis: diffusion of water from higher to lower concentrations across a selectively permeable membrane
2) Facilitated Diffusion: molecules go from high to low concentration with the help of certain proteins
3) Osmosis: diffusion of water from higher to lower concentrations across a selectively permeable membrane
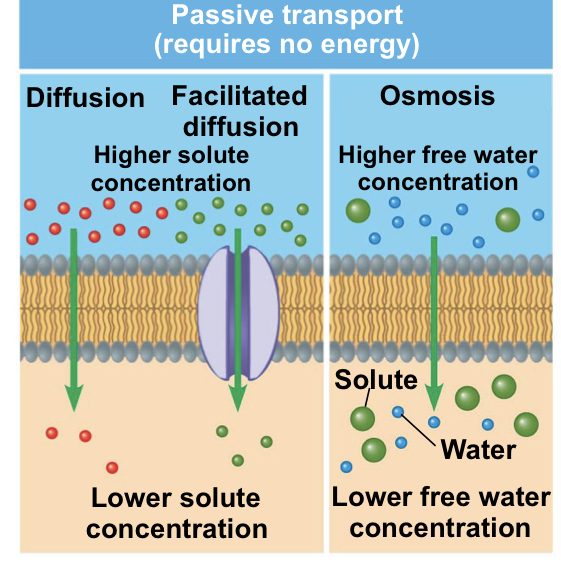
21
New cards
What is diffusion and its goal?
* tendency of particles to spread out evenly in an available space
* its goal is to find equilibrium among the same type of molecules
* its goal is to find equilibrium among the same type of molecules
22
New cards
Describe the U-tube experiment and what is signifies.
* In this experiment the amount of solute is uneven on both sides of the tube as a membrane is permeable to water but not the solute
* Due to this the water will cross the membrane and move down its own concentration gradient until the solute concentration on both sides is equal
* Due to this the water will cross the membrane and move down its own concentration gradient until the solute concentration on both sides is equal
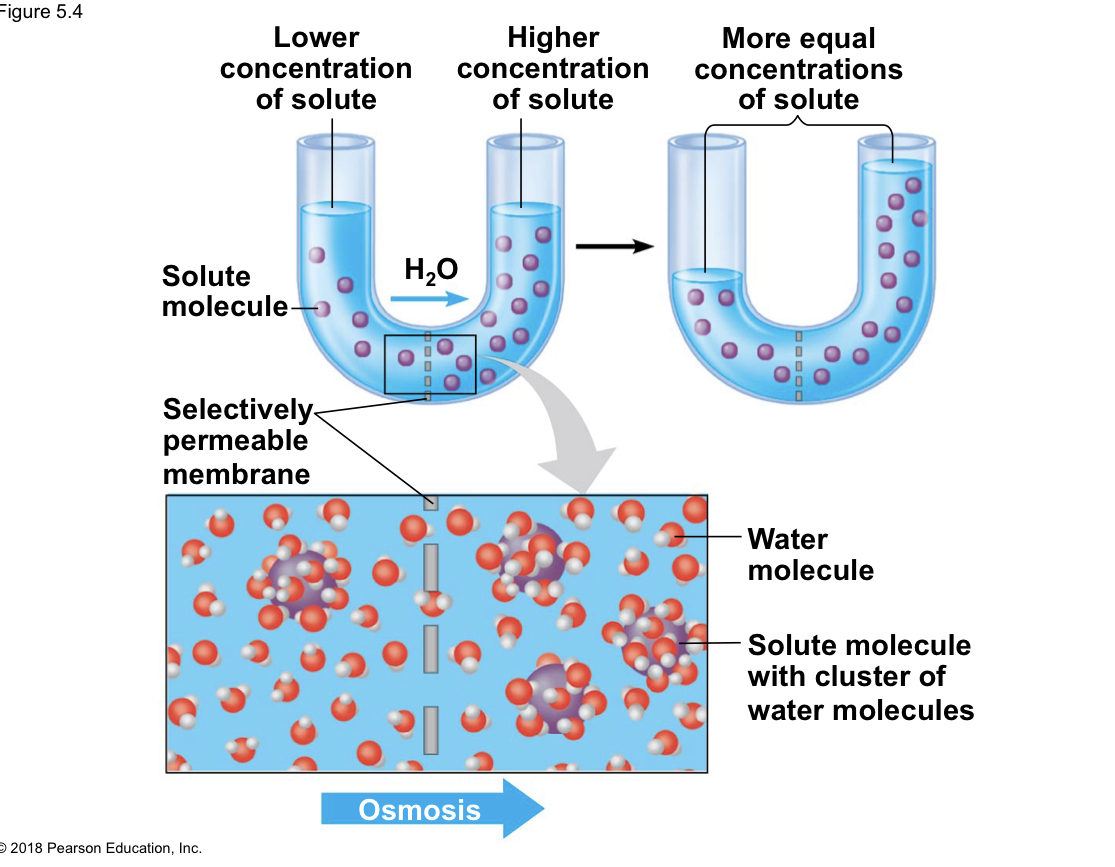
23
New cards
What is tonicity?
term that describes the agility of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water in order to reach equilibrium
24
New cards
What is a hypertonic solution and what is its effect on cells?
* causes cells to shrink and is a solution with high solute levels
25
New cards
What is a hypotonic solution and what is its effect on cells?
* Plant cells= Turgid(normal)
* Animal Cells=swelling till burst
* Solution with low solute levels
* Animal Cells=swelling till burst
* Solution with low solute levels
26
New cards
What is an isotonic solution and what is its effect on cells?
* animal cells=normal
* plant cells=flaccid
* solution with equal solute levels
* plant cells=flaccid
* solution with equal solute levels
27
New cards
What types of substances early diffuse across a cell membrane?
hydrophobic/nonpolar
28
New cards
What types of substances need help moving across membranes?
* hydrophillic/polar substances need help moving across the membrane with specific transport proteins
* this is known as **facilitated diffusion**
* this is known as **facilitated diffusion**
29
New cards
What is the general rule of thumb for transport proteins?
greater the number of transport proteins for a particular solute in a membrane, the faster the solute’s rate of diffusion
30
New cards
What is the importance of aquaporin?
* allows for the rapid diffusion of water into and out of certain cells as it is a channel protein
31
New cards
What happens in active transport?
a cell must expend ATP energy to move solutes against concentration gradient
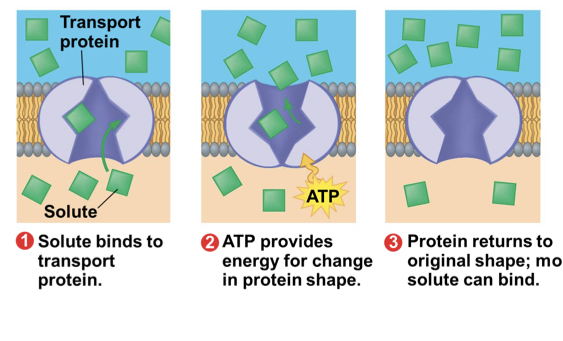
32
New cards
What are the two mechanisms to move large molecules across membranes?
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
Endocytosis
33
New cards
What is exocytosis?
used to export bulky molecules such as proteins or polysaccharides
34
New cards
What is endocytosis?
used to take in large molecules
35
New cards
What happens in both endocytosis and exocytosis?
material is transported after it is packaged within a vesicle that fuses with the membrane
36
New cards
What are the three kinds of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Pinocytosis
37
New cards
Phagocytosis
engulfment of a food practice by the cell wrapping cell membrane around it and forming a vacuole
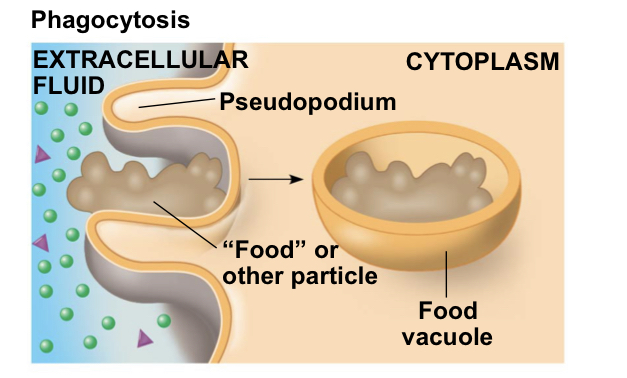
38
New cards
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
uses membrane receptors for specific solutes
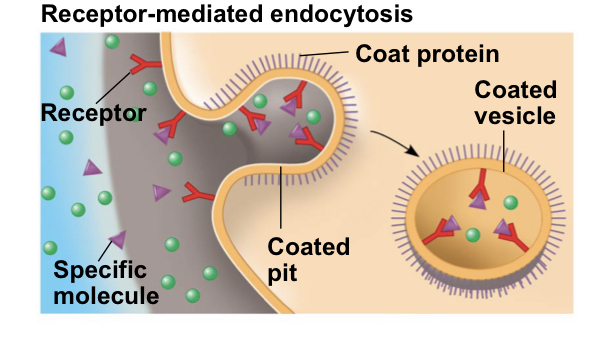
39
New cards
Pinocytosis
engulfment of small particles suspended in extracellular fluid
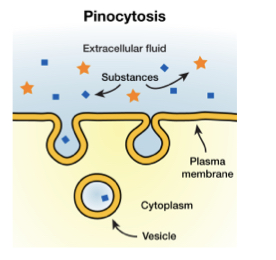
40
New cards
\
Energy
Energy
Ability to do work
41
New cards
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion
42
New cards
What does kinetic energy require?
Requires ATP via cellular respiration made via mitochondria
43
New cards
What are the two forms of kinetic energy?
thermal(heat) energy and light energy
44
New cards
What is potential energy?
Energy stored in the location or structure of matter
45
New cards
Chemical Energy
Type of potential energy that is available for release in a chemical reaction
46
New cards
What is an example of chemical energy?
The process of breaking down glucose to make ATP via cellular respiration
47
New cards
What can light be used to do?
Harness the power of photosynthesis
48
New cards
What is thermodynamics?
Study of energy transformations
49
New cards
What is system in terms of thermodynamics?
Matter under study
50
New cards
What is surroundings in terms of thermodynamics?
Everything outside of the study
51
New cards
What is a closed system?
Isolated from its surroundings like a liquid in a thermos
52
New cards
What is an open system?
Energy and matter can be transferred between system and surroundings
53
New cards
What type of system are organisms?
Open systems since they absorb light in organic molecules and release heat and metabolic waste
54
New cards
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
states that energy can be transferred and transformed, in other words “Energy is neither created nor destroyed”
55
New cards
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
states that every energy transformation must make the universe more disordered or entropy (quantity used as a measure of disorder, or randomness)
56
New cards
What is an exergonic reaction?
Releases energy
57
New cards
Exergonic Reactions
Huge amount of reactions into small amount of products with a side product of ATP
58
New cards
What are examples of exergonic reactions?
Hydrolysis(breaks down polymers to monomers and release energy) and Cellular Respiration
59
New cards
What are endergonic reactions ?
require energy and yield products rich in potential energy
60
New cards
What is an example of an endergonic reaction?
Photosynthesis
61
New cards
What does motabolism do?
encompasses all of a cell’s chemical reactions- a mix of both exergonic and endergonic.
62
New cards
How does ATP power cellular work?
transfer of a phosphate group from ATP forming ADP and P is involved in chemical, transport, and mechanical work
63
New cards
How exactly does the hydrolysis process work?
The process breaks down the bond between the second and third phosphates and releases energy therefore it is exergonic/ endergonic
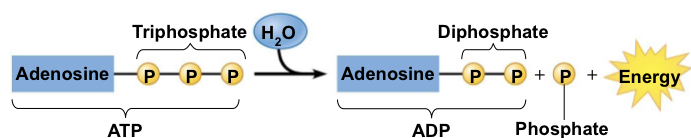
64
New cards
What are the three kinds of work does a cell do?
1)Chemical: driving endergonic reactions such as the synthesis of polymers from monomers.
2) Transport: pumping substances across membranes against the direction of spontaneous movement
3) Mechanical: beating of cilia, contraction of muscle cells, and movement of chromosomes
2) Transport: pumping substances across membranes against the direction of spontaneous movement
3) Mechanical: beating of cilia, contraction of muscle cells, and movement of chromosomes
65
New cards
What is dephosphorelation and phosphorylation?
Removing phosphate and adding phosphate
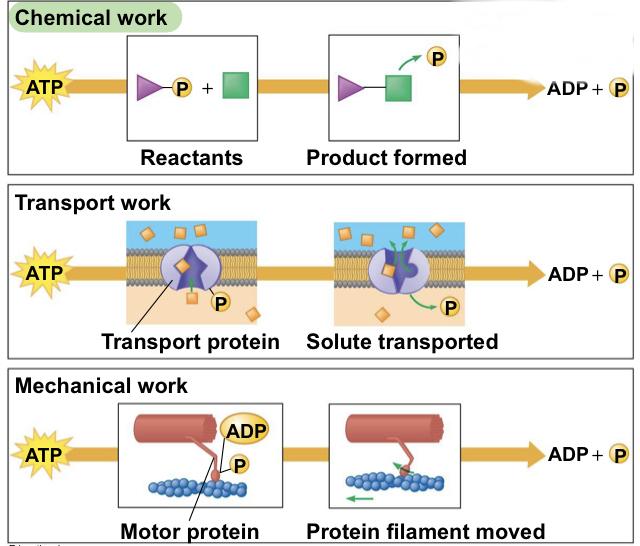
66
New cards
Describe the ATP to ADP+P cycle
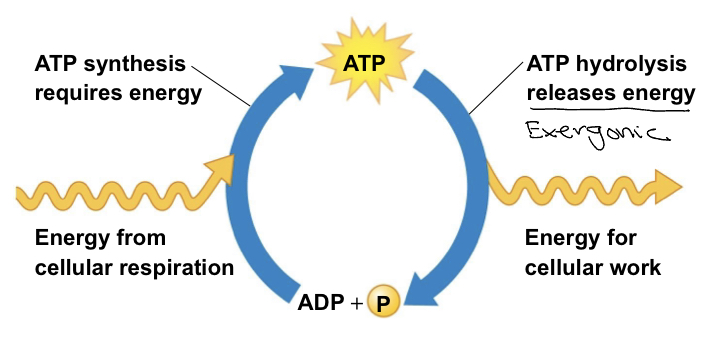
67
New cards
What are enzymes?
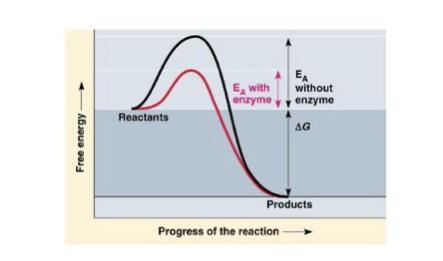
protein catalysts that decrease the activation energy needed to begin a reaction
68
New cards
What must a substrate do?
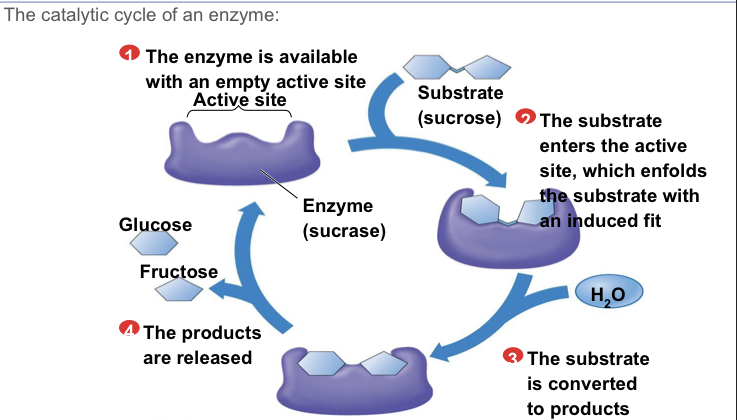
Fit specifically into an enzyme’s active site
69
New cards
What is activation energy?
amount of energy necessary to push the reactants over an energy barrier
70
New cards
What is the transition state
summit the molecules are at an unstable point
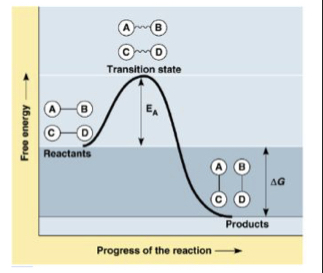
71
New cards
What is delta G?
The difference between free energy of the products and the free energy of the reactants
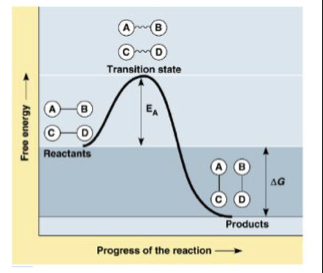
72
New cards
How do enzymes work?
Speed reactions by lowering activation energy and can be reached even at moderate temperatures
73
New cards
Describe the catalactic cycle of an enzyme
74
New cards
What is a competitive inhibitor?
competes with the substrate for the active site.
75
New cards
What is a non competitive inhibitor?
alters an enzyme’s function by changing its shape
76
New cards
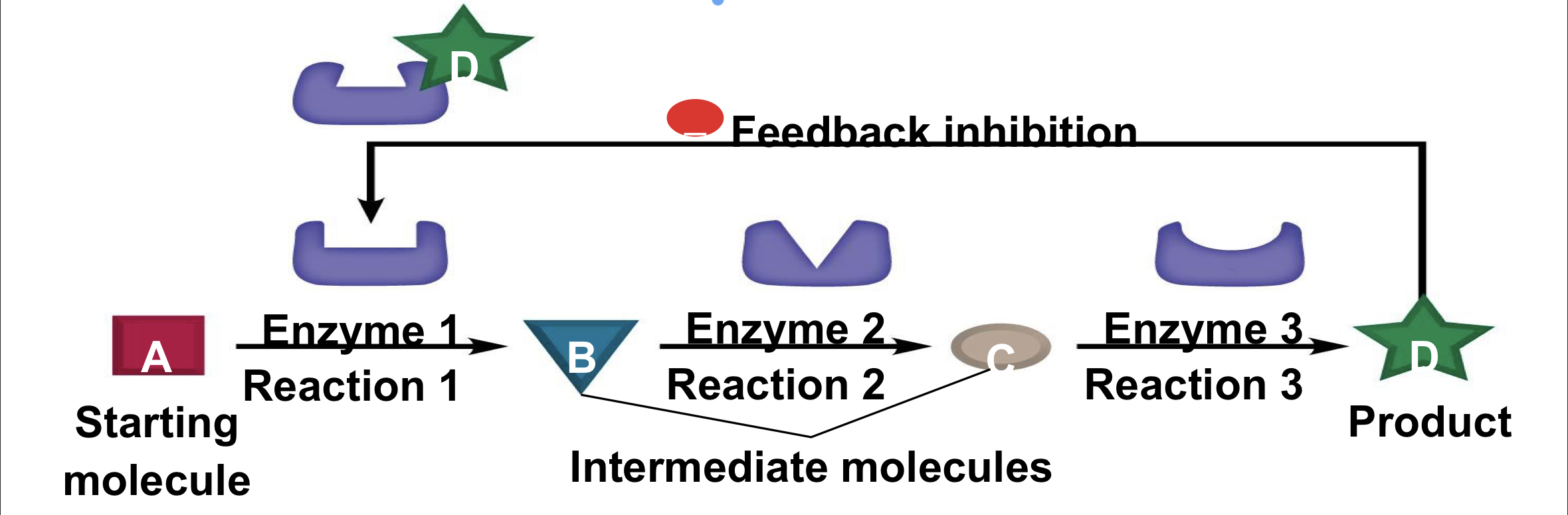
What is feedback inhibition?
* helps regulate metabolism
* Product of reaction is the inhibitor
* Product of reaction is the inhibitor
77
New cards
What are some uses for enzyme inhibitors?
Enzyme inhibitors have also been developed as
pesticides, deadly poisons for chemical warfare, and Beneficiary drugs
pesticides, deadly poisons for chemical warfare, and Beneficiary drugs
78
New cards
What are cofactors?
* non protein helpers for catalytic activities
* They may be organic or inorganic
* They bind to the enzyme permanently or reversibly
* Some inorganic cofactors include zinc, iron, and copper
* They may be organic or inorganic
* They bind to the enzyme permanently or reversibly
* Some inorganic cofactors include zinc, iron, and copper
79
New cards
What are coenzymes?
Are organic cofactors that include vitamins or molecules derived from vitamins