WEEK 15 - ABD Cav and GI Tract Intro
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
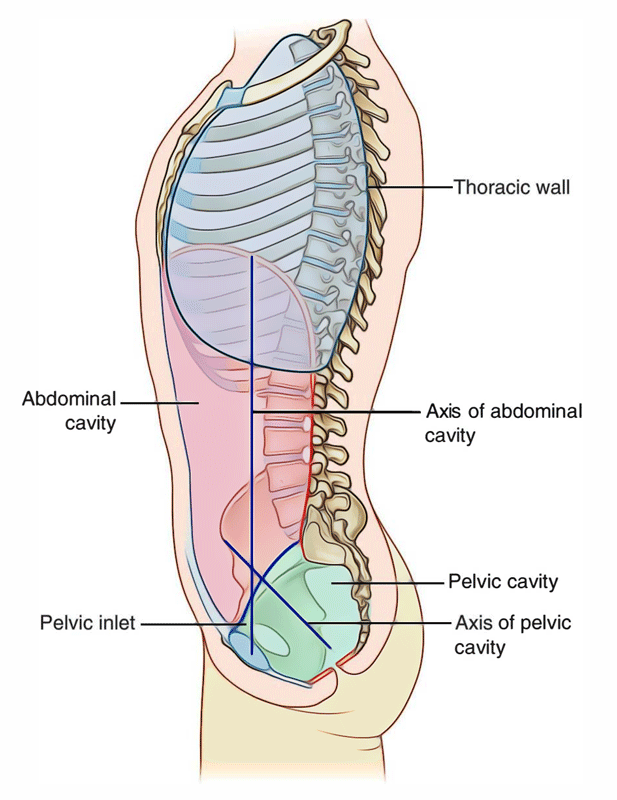
Superior ABD Cavity Boundaries
Diaphragm
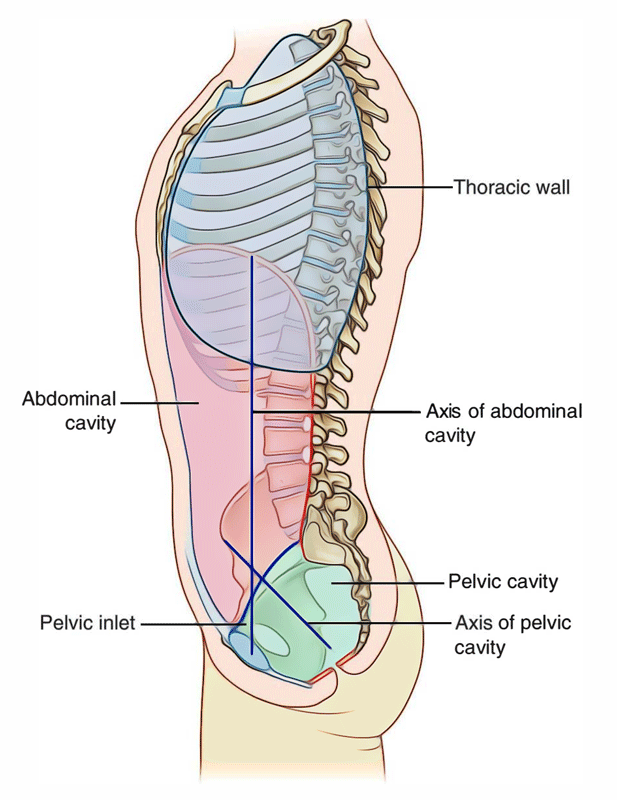
Inferior ABD Cavity Boundaries
Pelvic Inlet
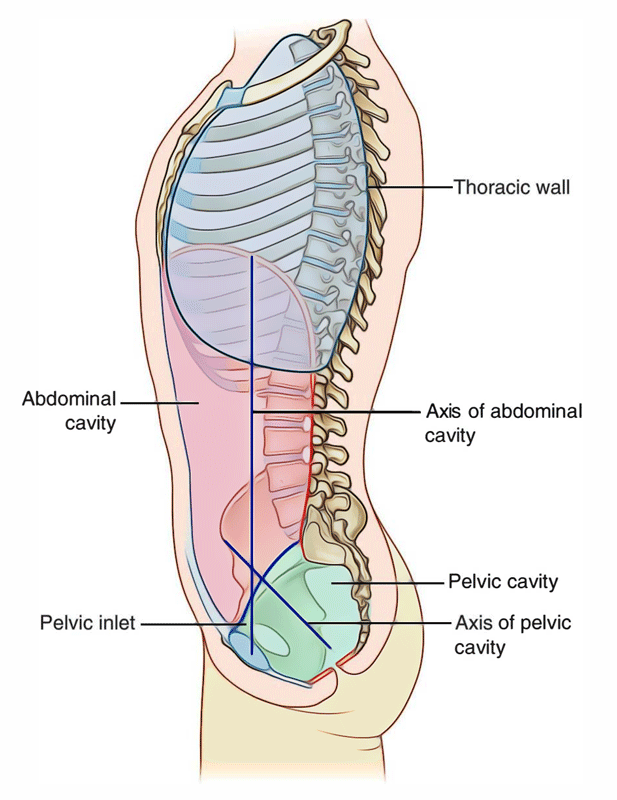
Ant/Post/Lat ABD Cavity Boundaries
Abdominal walls
Layers of the ABD Wall
skin
superficial fascia
muscles
Transversalis (connective tissue)
Extraperitoneal fascia (fat)
Parietal Peritoneum
ABD Cavity Organs
stomach and intestines
kidneys and ureters
liver, gallbladder, pancreas
spleen
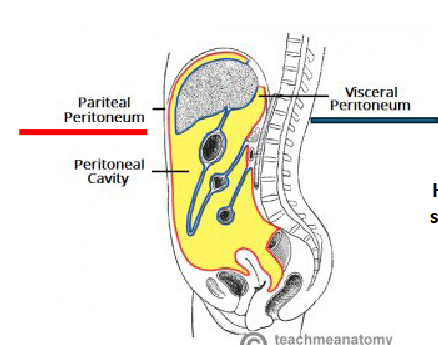
peritoneum
Serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity walls and covering many of the abdominal visceral organs
types of peritoneum
parietal peritoneum
visceral peritoneum
parietal peritoneum
lines the walls of the abdominal cavity
visceral peritoneum
package visceral organs
Intraperitoneal organs
definition
example
Organs that are ALMOST entirely enclosed by visceral peritoneum
stomach
retroperitoneal organs
definition
example
Organs localized in the retroperitoneal space (outside of peritoneal cavity)
kidneys
mesentery
definition
function
double layer / fold of peritoneum (continuity of visceral + parietal)
Suspend and anchor intraperitoneal organs to the posterior abdominal wall
Mesenteries of the ABD cavity
MESENTERY OF THE SMALL INTESTINE (small intestine → post. abd wall)
TRANSVERSE MESOCOLON (transverse colon → post. abd wall)
SIGMOID MESOCOLON (sigmoid colon → post. abd wall)
peritoneal cavity
Potential space between parietal and visceral layers of peritoneum
Retroperitoneal Space
located behind the peritoneum and in front of the transversalis fascia
Retroperitoneal Organs
SAD PUCKER
S – suprarenal (adrenal gland)
A – aorta/IVC
D – duodenum (2nd and 3rd parts)
P – pancreas (except tail)
U – ureters
C – colon (asc. and desc.)
K – kidneys
E – esophagus
R – rectum
Peritoneal Fluid
location
function
found within the the peritoneal cavity
provides essential lubrication and allows sliding of viscera
without friction or irritation
Curvatures of the Stomach
Lesser Curvature (medial)
Greater Curvature (lateral)
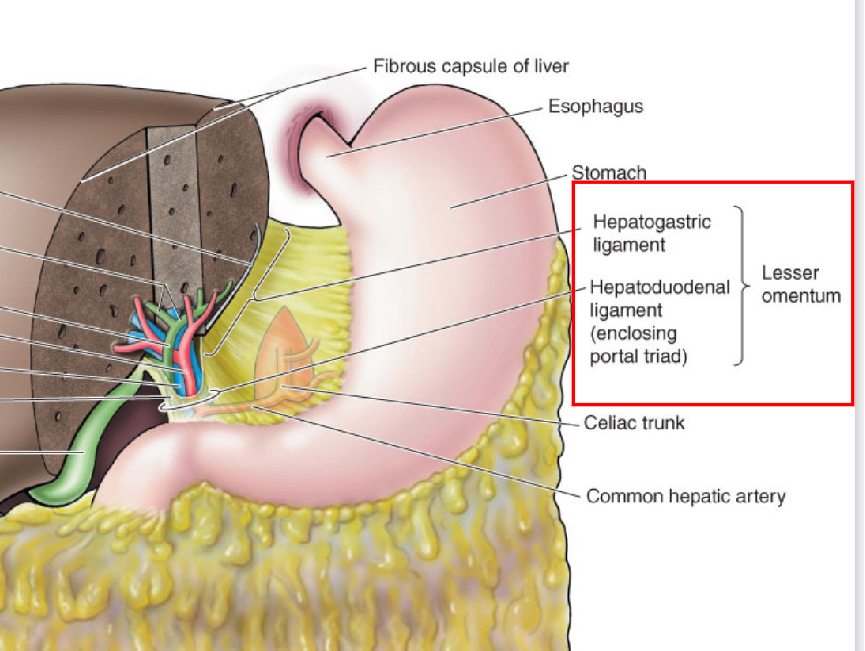
Lesser Omentum
Mesentery extending between the liver and the lesser curvature of the
stomach and proximal 1st part of duodenum
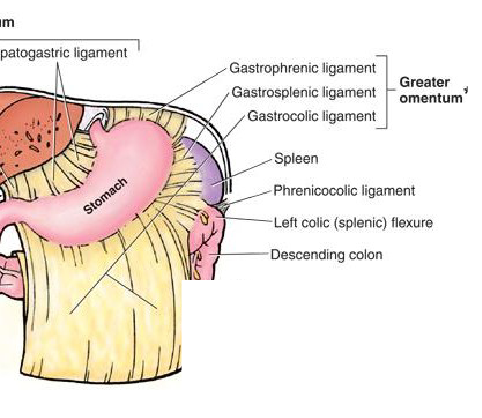
Greater Omentum
generally, location for at storage, passageway for vessels and, physical and immune protection
Mesentery that form an “apron” draping off the greater curvature of the
stomach
ligaments of the greater omentum
gastrophrenic lig (stomach → diaphragm)
gastrosplenic lig (stomach → spleen)
gastrocolic lig (stomach → duo, intestine)
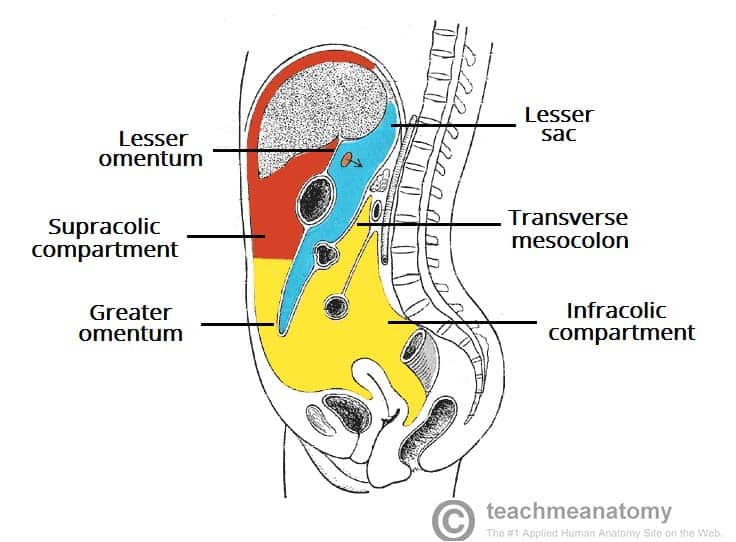
Sacs of the ABD
division of the peritoneal cavity
greater sac
lesser sac / omental bursa
omental foramen / foramen of winslow / epiploic foramen
small opening in the abdomen that connects the greater sac to the lesser sac
greater sac
extends from the diaphragm to the pelvic cavity (majority of abd cav)
compartments of the greater sac
Supracolic Compartment
subphrenic
subhepatic
Infracolic Compartment
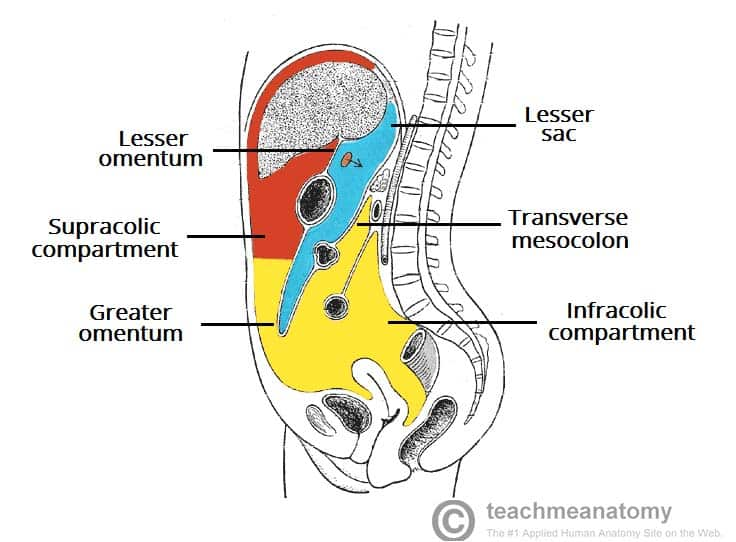
Lesser Sac location
posterior to the lesser omentum and the stomach but anterior to the pancreas
Pouches of the ABD Cavity Floor
pouches in between pelvic organs that formed as the parietal peritoneum drapes over them
Male Pouches / cul-de-sacs
rectovesical pouch = between bladder and rectum
Female Pouches / cul-de-sacs
vesico-uterine pouch = between bladder and
uterusrecto-uterine pouch of douglas = between uterus and rectum
GI Tract Composition
mouth
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
anus
Accessory Organs of GI Tract
teeth
tongue
salivary glands
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
main function of oral cavity
first step in digestion through the secretion of saliva
main function of esophagus
Propulsion of food bolus to stomach by PERISTALSIS
main function of stomach
stores food and continues the digestion (little) that started in the mouth
Intestines Function
small: where most of digestion occurs (and finishes)
large: absorption of water and formation of feces
main function of rectum
temporary storage for stool until it's ready to be eliminated through the anus