AP World History - World Map Review
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Eastern Europe
Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Russia, Romania, Bulgaria, Yugoslavia
Western Europe
France, Great Britain, Germany, Spain, Italy, etc.
Latin America
All of South America & Mexico
West Africa
Ghana, Mali, Songhai
Mesoamerica
Mexico and central America: Nicaragua, Guatemala, Panama, El Salvador
Middle East
Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Syria, Turkey, Jordan, Lebanon
Southeast Asia
Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos
South Asia
India, Pakistan
East Asia or Far East
China, Korea, Japan
Oceania
Australia, Pacific Islands
Sub-Saharan Africa
Ghana, Mali, Songhai, Congo, South Africa
Andean Region
Peru, Columbia, Ecuador, Bolivia
1
North America
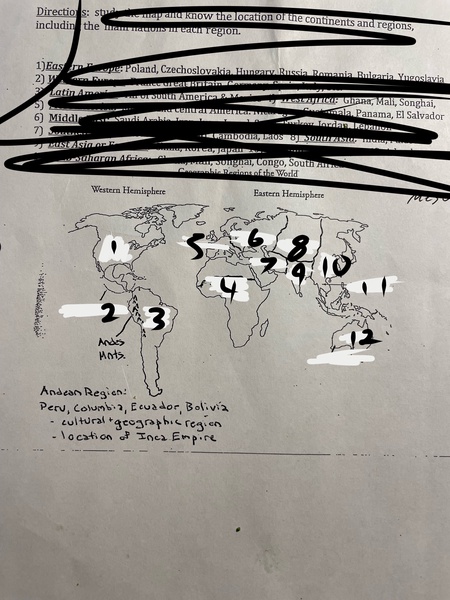
2
Mesoamerica
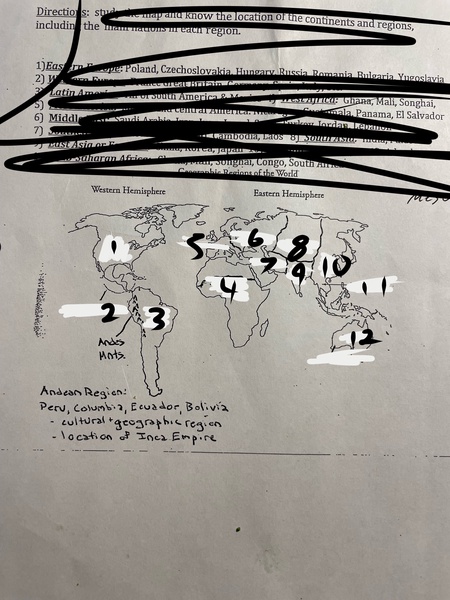
3
Latin America
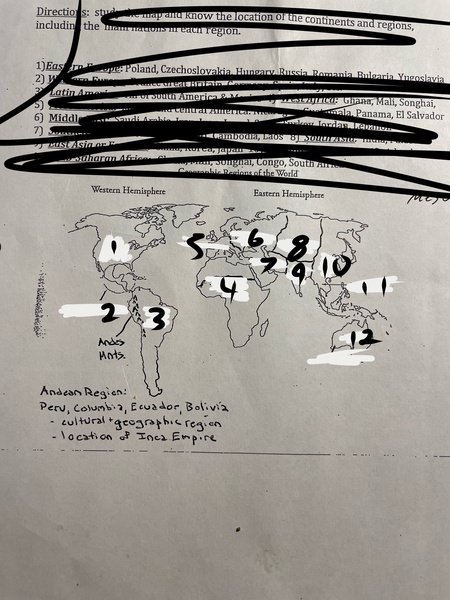
4
Sub-Saharan Africa
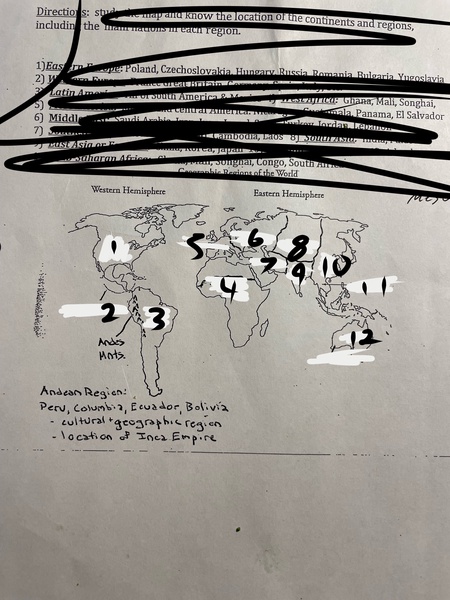
5
Western Europe
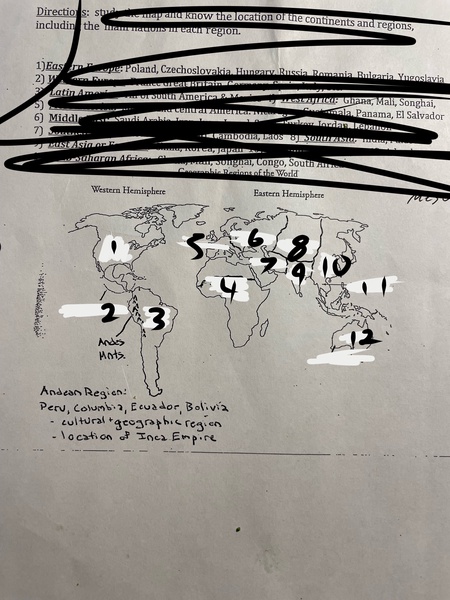
6
Eastern Europe
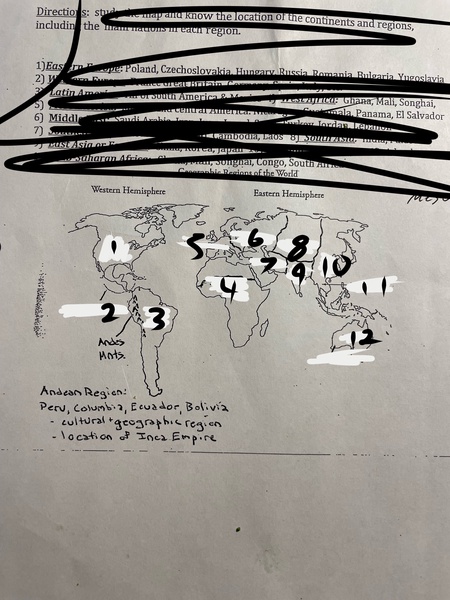
7
Middle East
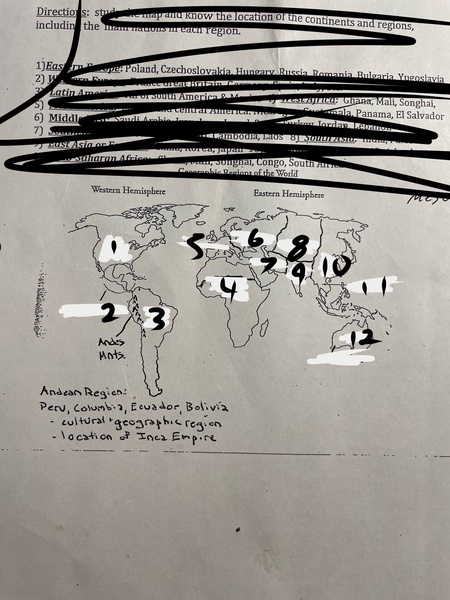
8
Central Asia
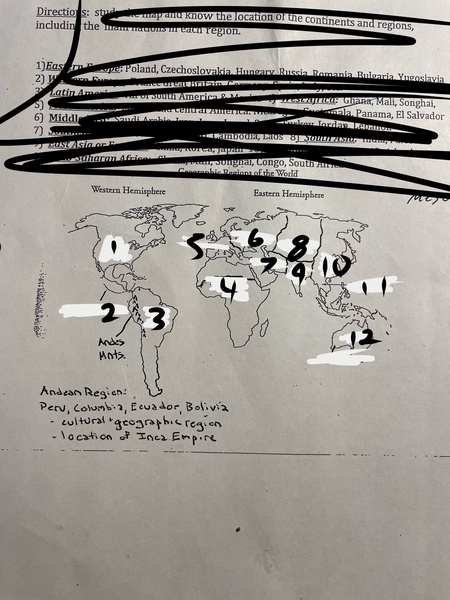
9
South Asia
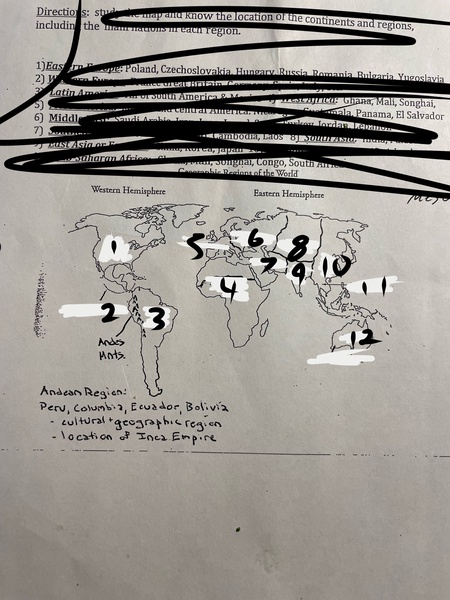
10
East Asia
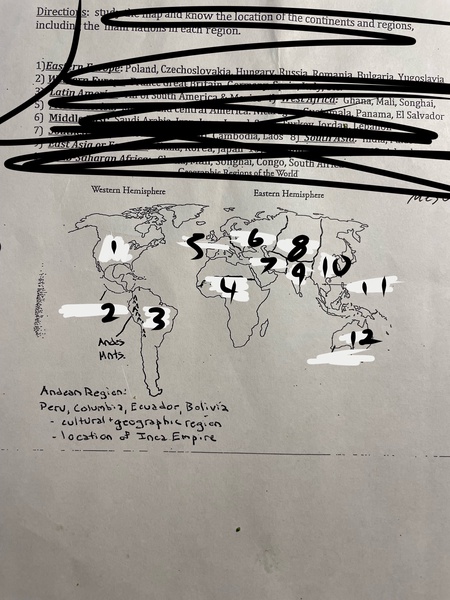
11
Southeast Asia
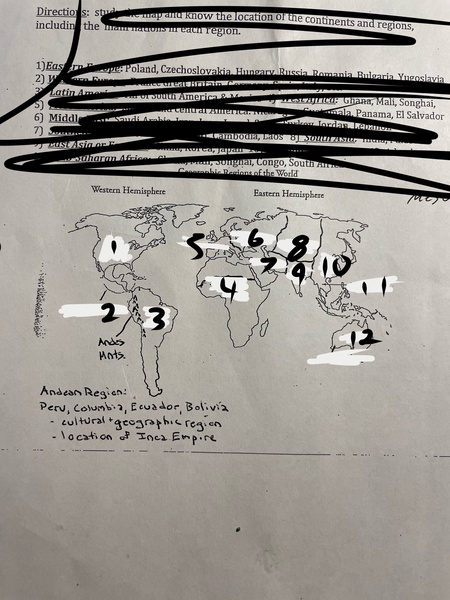
12
Oceania
The 2 sects/schools of Buddhism
“Theravada” and “Mahayana”
Why Confucianism isn’t a religion
It doesn’t address gods or the spiritual world
What were the answers to the disorder China faced during the “Spring-Autumn” period and “The warring states period”
Legalism, Confucianism, Daoism
Buddhism and Hinduism similarities
The idea that ordinary life is an illusion
the concepts of karma and rebirth
the goal of overcoming the incessant demands of the ego
the practice of meditation
the hope for a final release from the cycle of rebirth
Differences between Buddhism and Hinduism
Buddhism rejects religious authority of Brahmans and use of rituals, Buddhism based individual spiritual development
Buddhism rejects Hinduism’s caste system, all people can find nirvana at any level
Describe the evolution of Christianity
—originated in the Middle East, in the roman province of Judeas
—founded by Jesus, a Jew and carpenter who claimed that he was the Messiah and the son of God.
—after his death “Christians” formed a religion around Jesus’ teachings
—After many years of persecution from different emperors, the Emperor Constantine becomes a supporter of Christianity and stops the persecution
—Christians build churches to organize their religion
—Emperor Theodosius 1 makes Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire
Characteristics of Greek intellectual/philosophical traditions
emphasis on human logic and “reason”: establishing facts and verifying facts, using intellect, determine truth, falsehoods
Question current wisdom
Disregard roles of gods, search for non-religious explanations for the world and how it functions