Interventional and Cath Lab Procedures
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what is an angiogram?
diagnostic examination of blood vessels by injecting them with contrast
what is an angioplasty?
treating blood vessels with balloons and stents following or during an angiogram
what is an embolisation?
procedure to deliberately occlude a blood vessel
when would an embolisation take place?
when there is too much blood flow e.g. in tumours
what does EVAR stand for?
endovascular aortic repair
what is an endovascular aortic repair?
treatment of an aortic aneurysm or dissection using stents
what is a fistulogram?
contrast imaging of fistulas
what is a fistula?
the surgical connection of an artery and vein in the arm to provide a suitable targe for dialysis
why are fistulograms needed?
fistulas may narrow and spasm or build up fatty deposits which restricts blood flow
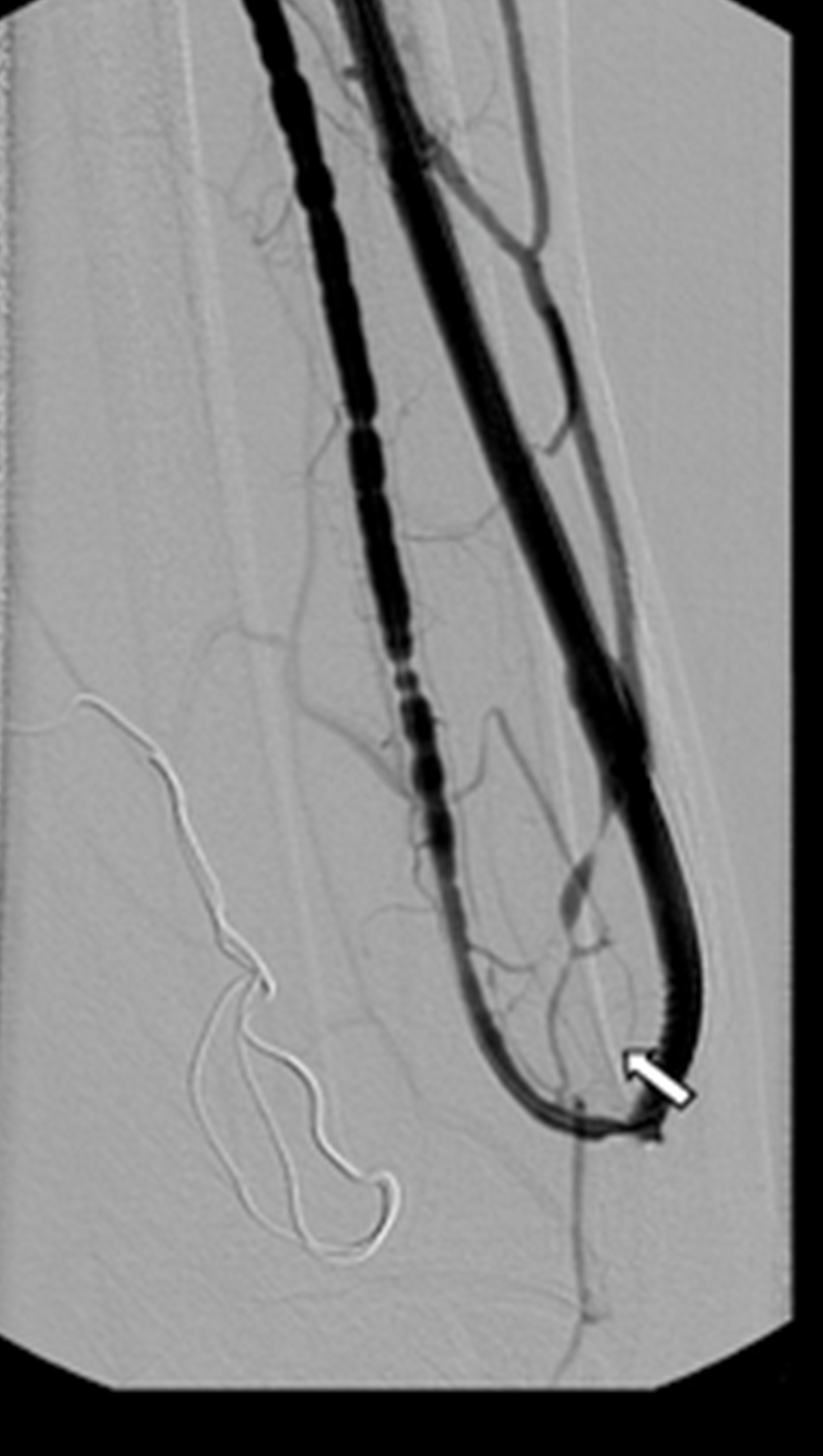
identify the interventional procedure
fistulogram utilising DSA
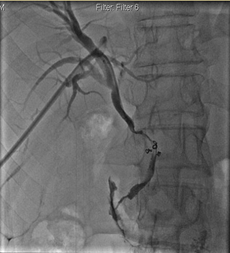
identify the interventional procedure
percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram
what is a nephrostomy?
insertion of a drain percutaneously into the kidney to drain urine to prevent hydronephrosis and infection
what is a PICC line insertion?
insertion of a central catheter from the arm, positioned in the vena cava
what is the benefit of radiographic guidance for line insertions?
can see location of lines to ensure correct placement
what is imaged during a nephrostomy?
the kidney and entire length of ureter to look for stones or blockages
what does a health vessel look like in an angiogram?
proximally wide then narrows distally
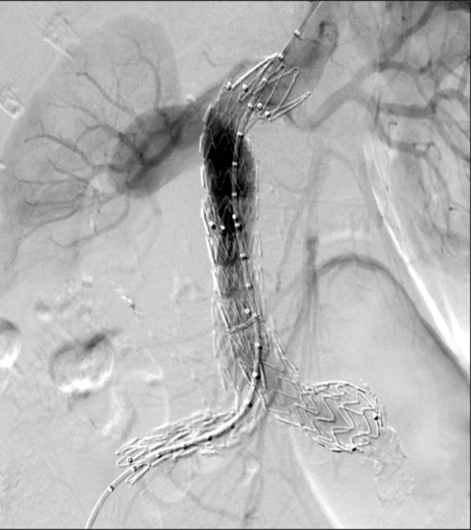
identify the interventional procedure
endovascular aortic repair
what are pump injector used for?
to inject large amounts of contrast in a controlled precise way
what are common cath lab procedures?
coronary angiogram, coronary angioplasty, cardiac ablation, pacemaker insertions, TAVI
what does TAVI stand for?
trans-catheter aortic valve insertion
what is a coronary angiogram?
examination of coronary arteries by injecting contrast
what is cardiac ablation?
treatment of arrythmia using heat or cold to produce scar tissue to make cardiac tissue insulators
what is a pacemaker?
device which maintains a safe heart rate for a patient with atypical sinus rhythm
what are the different types of pacemakers?
permanent or temporary
how do pacemakers work?
probe in atria senses if electrical activity is occurring then delivers one itself if not detected
where is a pacemaker usually inserted?
in the left shoulder or pectoral region
what are some contraindications of having the pacemaker on the left side?
fistula on the same side or lymph nodes removed due to breast cancer
how are specialist pacemakers like CRT-Ds different to normal pacemakers?
have an implanted cardiac defibrillator attached which can activate if an MI is detected
what kind of patients would have CRT-D pacemakers?
patients with high risk of cardiac arrest due to ventricular fibrillation outside of the hospital
why are TAVIs carried out?
to replace an non-functional aortic valve with a prosthesis
where are the catheters inserted for a TAVI?
through the femoral arteries
what are the procedural steps to a TAVI?
aortograms with contrast used to find the valves
a wire is fed through the left ventricle to guide the prosthetic
a balloon is inflated to open up the prosthetic
balloon is deflated and removed, catheters are removed
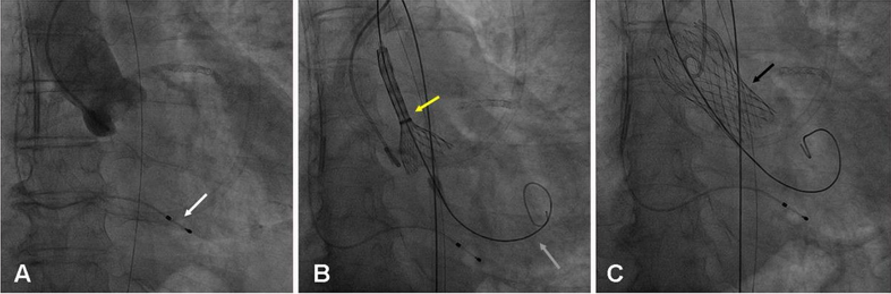
what cath lab procedure is shown?
trans-catheter aortic valve insertion
why are anticoagulants used in interventional procedures?
reduces formation of thromboses
what are the benefits of interventional radiography?
procedures can be therapeutic as well as diagnostic
what are the disadvantages to interventional radiography?
use of higher exposure factors, more contrast used, some procedures are temporary solutions before a larger surgical intervention,