Fixed Income (Formulas)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Full Price

Converting from from 90 day to 360 day
365/90 times Price change
If given %DR then it would be the 90/360 (or whatever convention) times %DR
The outcome is divided by 100 - the outcome itself
If given price values then it is the same as 365/90 times Price Change
The price change is actually divided by FV not PV
FRN Discount/Required Rate
It is not the YTM but rather the YTM = MRR (Market Rate) + DR
Forward rates from spot rates
2Y1Y (In 2 years, the one year forward rate is)
= (3 year spot)³ / (2 year spot)²
Spot rates from forward rates
Multiple the one year spot by one year forward rates up until the year you are calculating and root by the year you are calculating
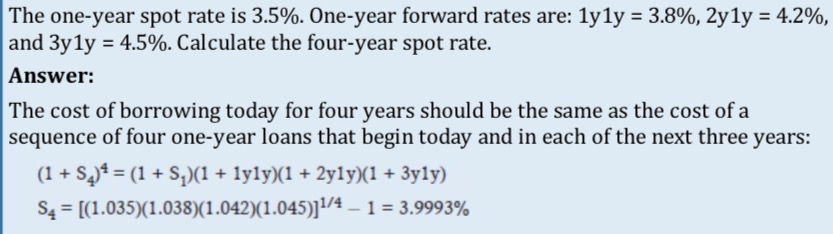
Par rate (The coupon rate which sets the price to 100)

approximate percentage change in bond price
= –modified duration × ΔYTM
.Modified duration (ModDur)

approximate modified duration
Can also be calculated by rearranging the approx change in bond price formula
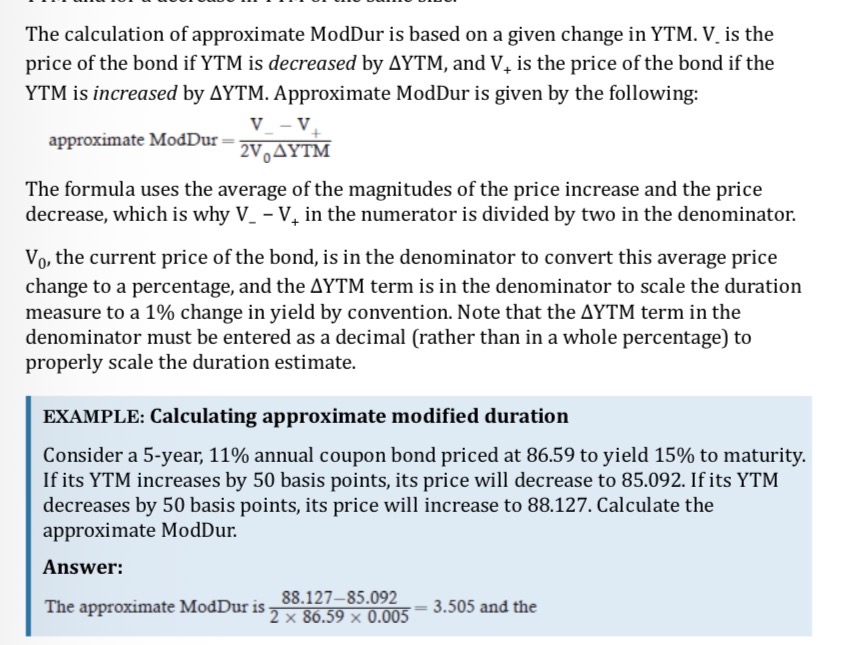
approximate percentage change in bond price
−ModDur × ΔYTM
Based on a ModDur of 3.50, in response to an 0.5% increase in YTM the price of the bond should fall by approximately 3.50 × 0.5% = 1.75%.
Money duration
= annual ModDur × full price of bond position
Convexity
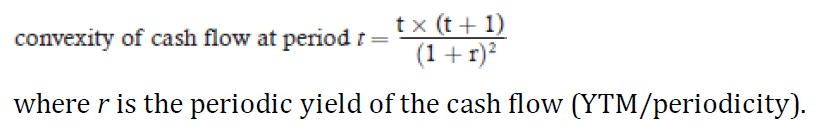
Better way of understanding formulas
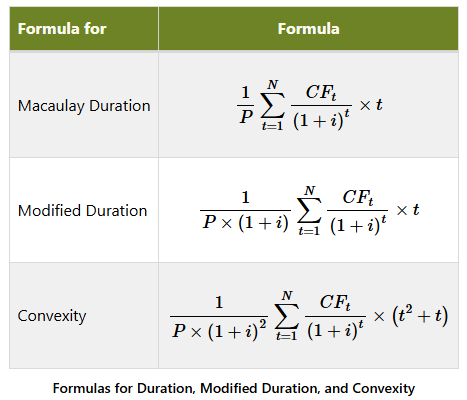
Apx convexity
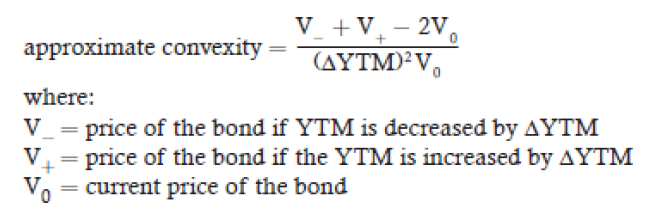
percentage price change of a bond for a specified change
in yield, given the bond’s duration and convexity.
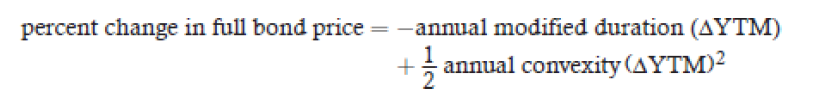
money convexity
annual convexity × full price of bond position
money duration and money convexity to estimate the change in price of a
bond as follows
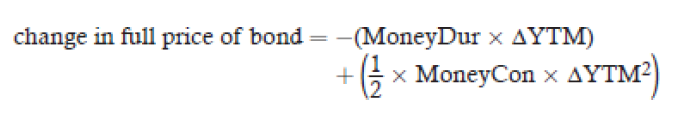
Convexity effect
1/2 × convexity × (ΔYTM) ²
expected loss =
probability of default × loss given default
Bond’s recovery rate
proportion of a claim an investor will recover if
the issuer defaults. The proportion an investor will not recover, or one minus the
recovery rate, is known as loss severity.
expected exposure or exposure at default i
the difference
between the amount the investor is owed (principal and accrued interest) and the value
of the collateral available to repay the inve
credit migration risk
the risk that a credit rating downgrade will
decrease the value of the bonds and potentially trigger other contractual clauses.