AP Biology Unit 5 - Heredity
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
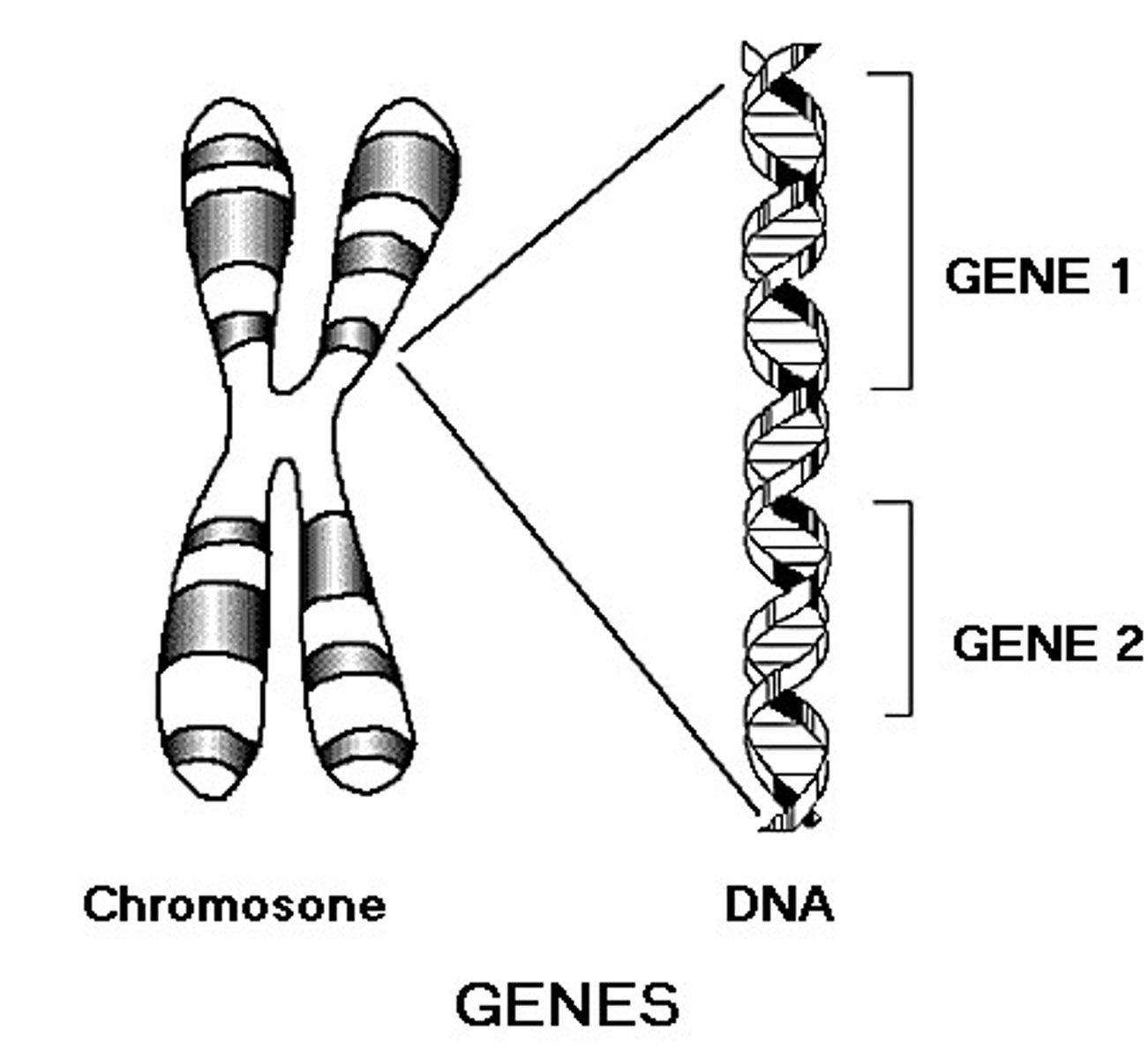
Genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
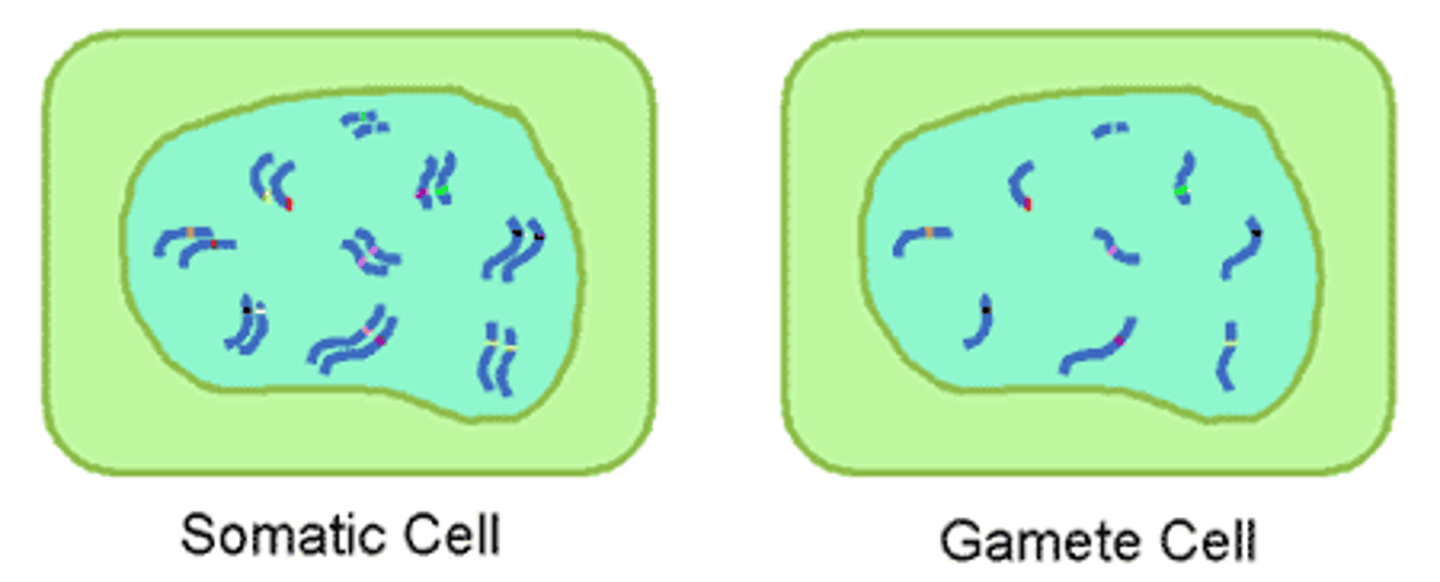
Gametes
reproductive cells
sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents
somatic cells
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
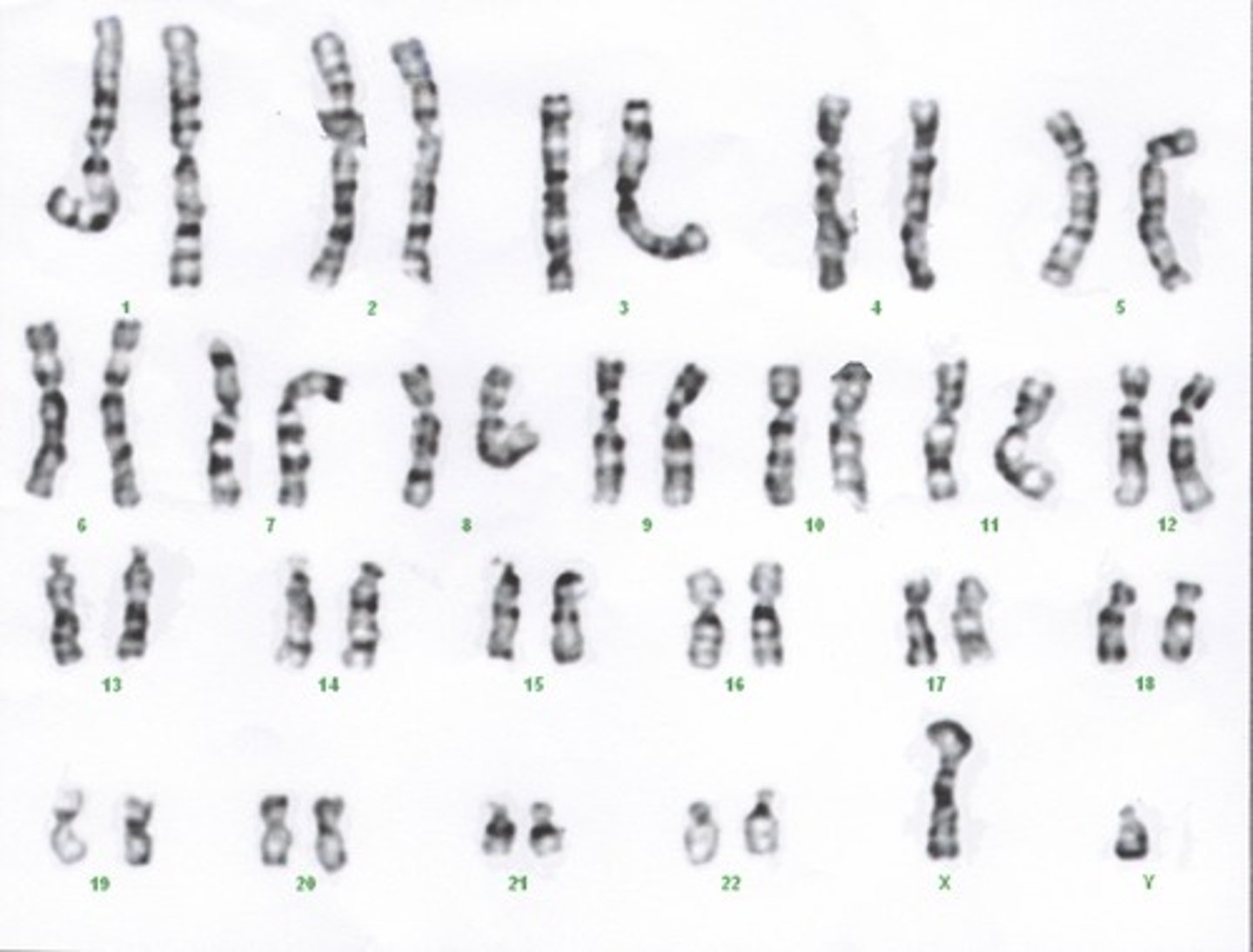
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
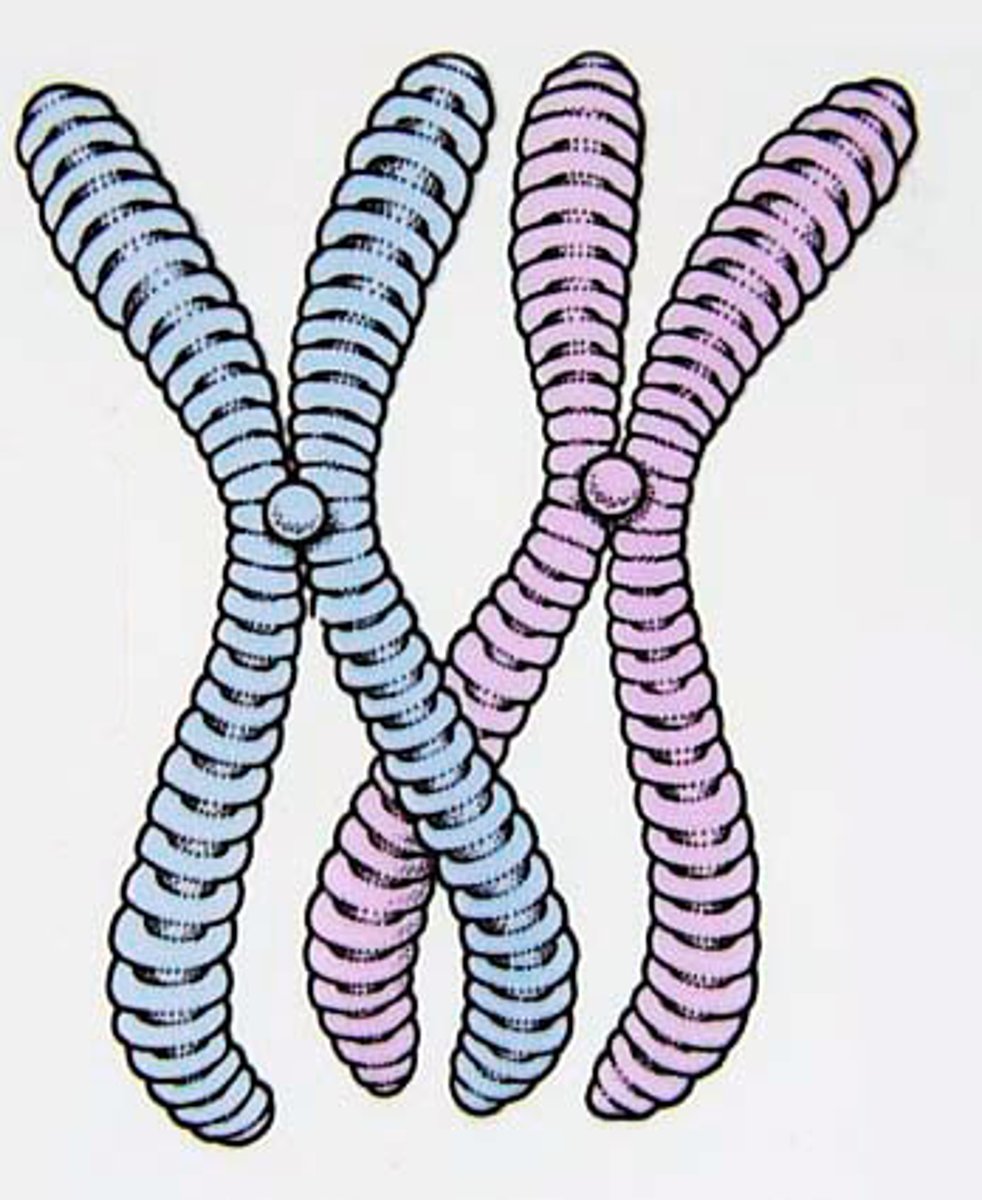
homologous chromosomes (homologs)
in a diploid organism, chromosomes that are similar in size, shape, and gene content
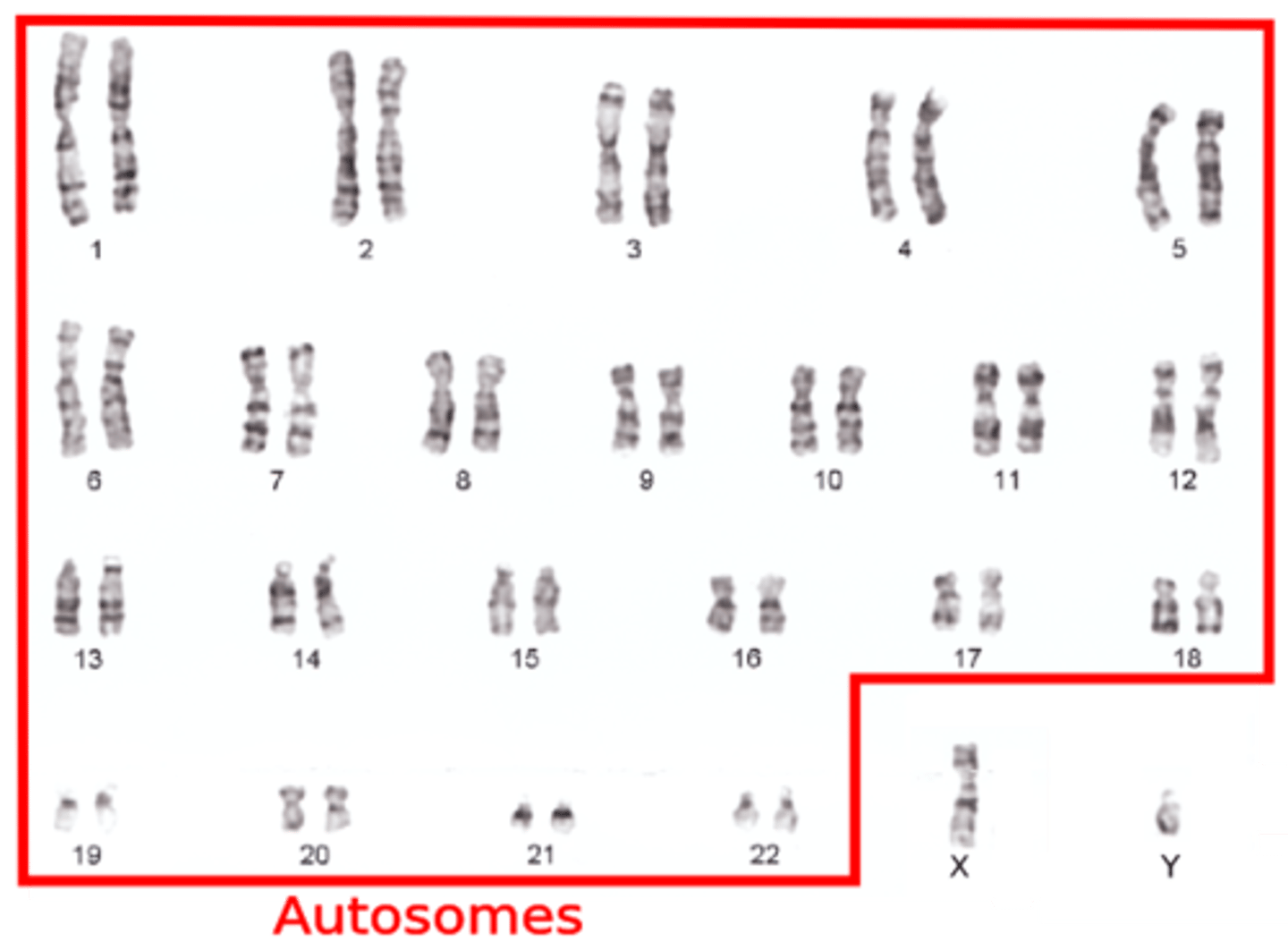
Autosomes
Chromosomes that are not directly involved in determining the sex of an individual.
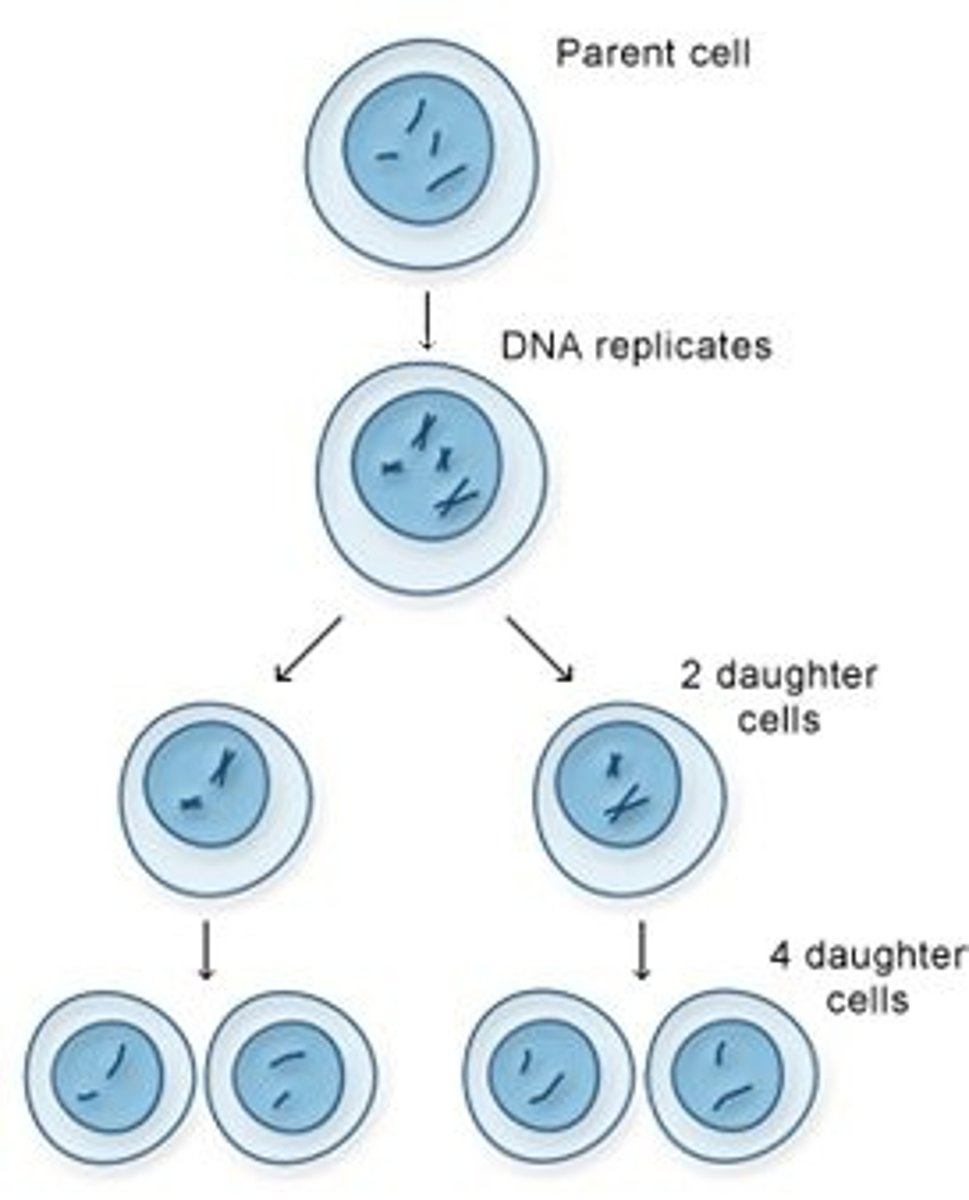
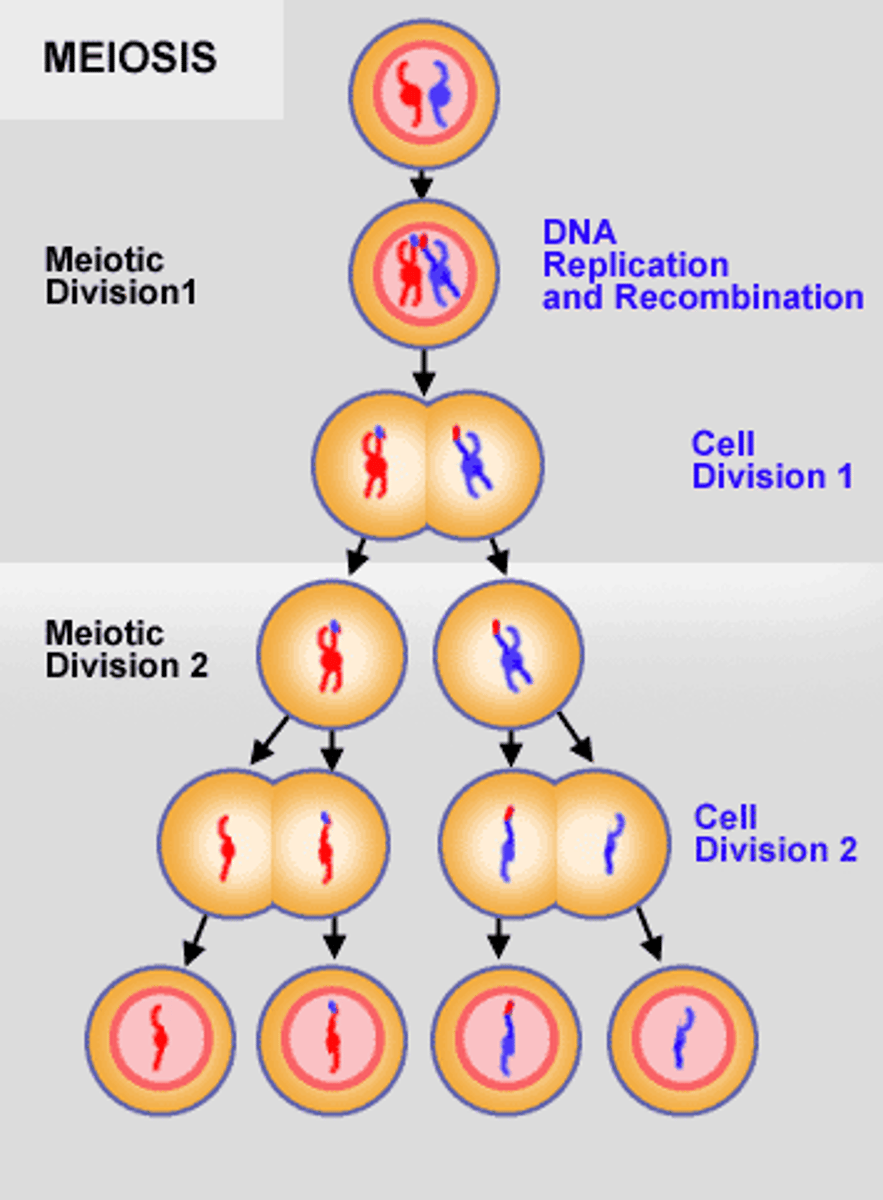
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
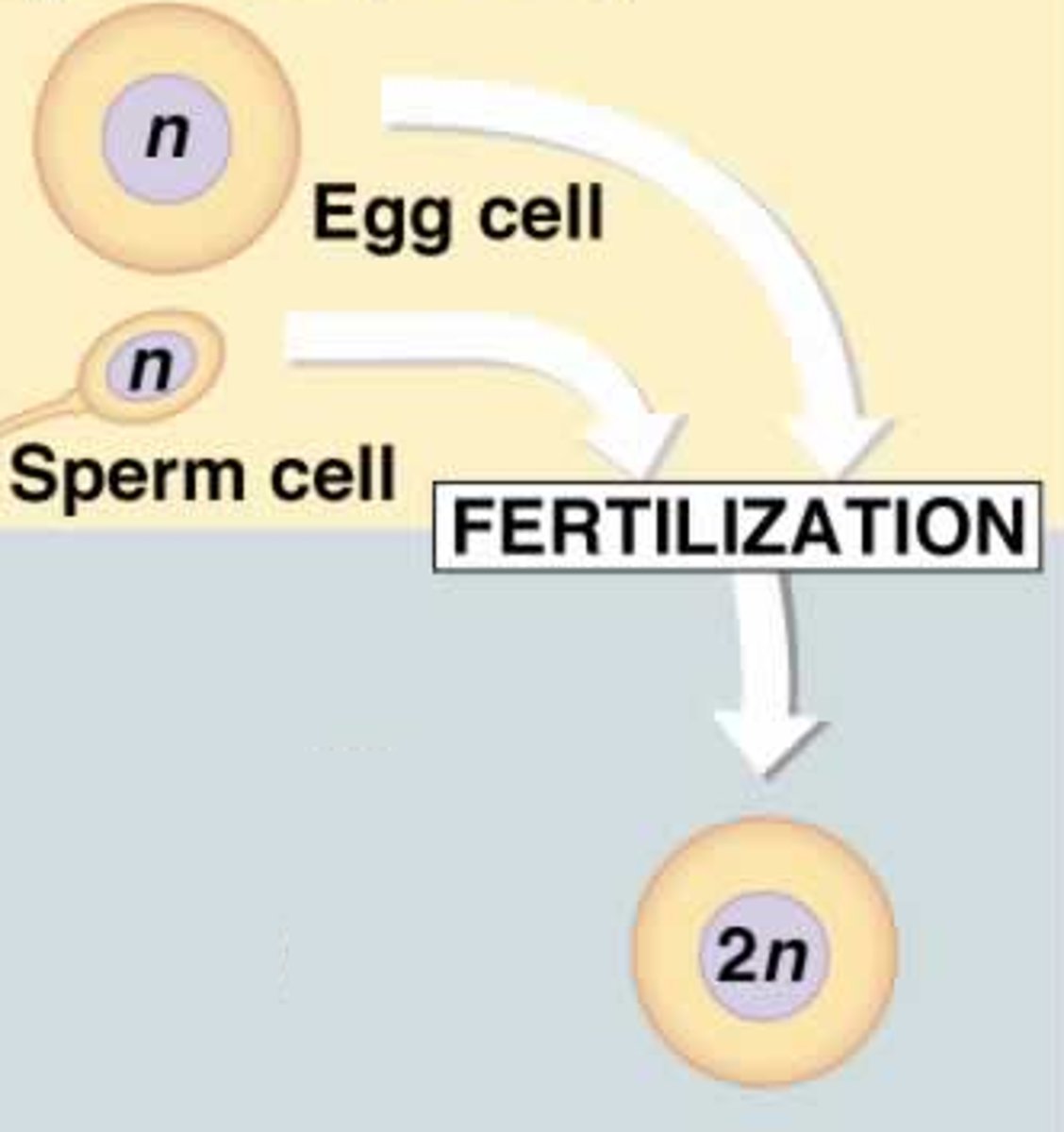
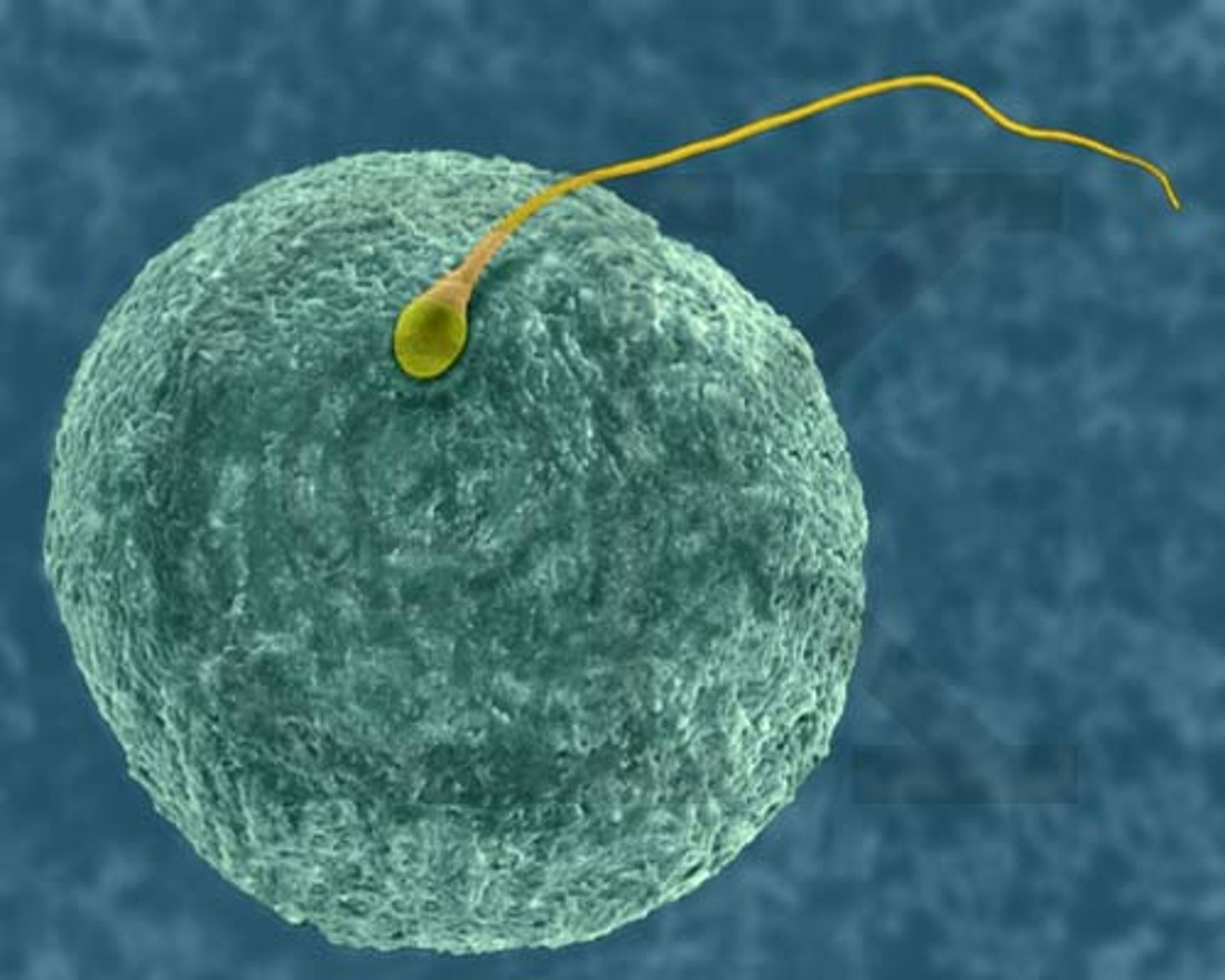
Fertilization
Process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell
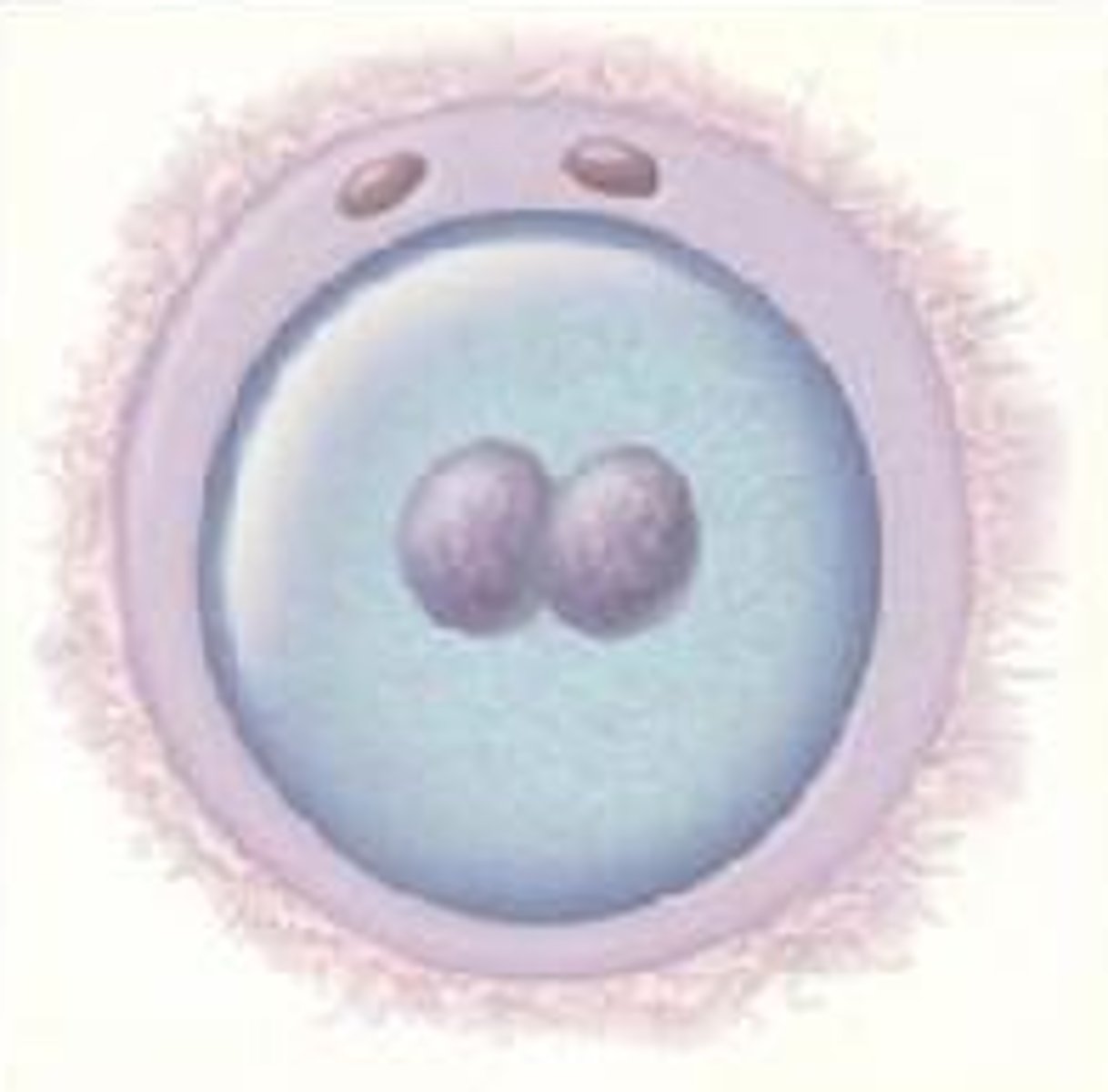
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
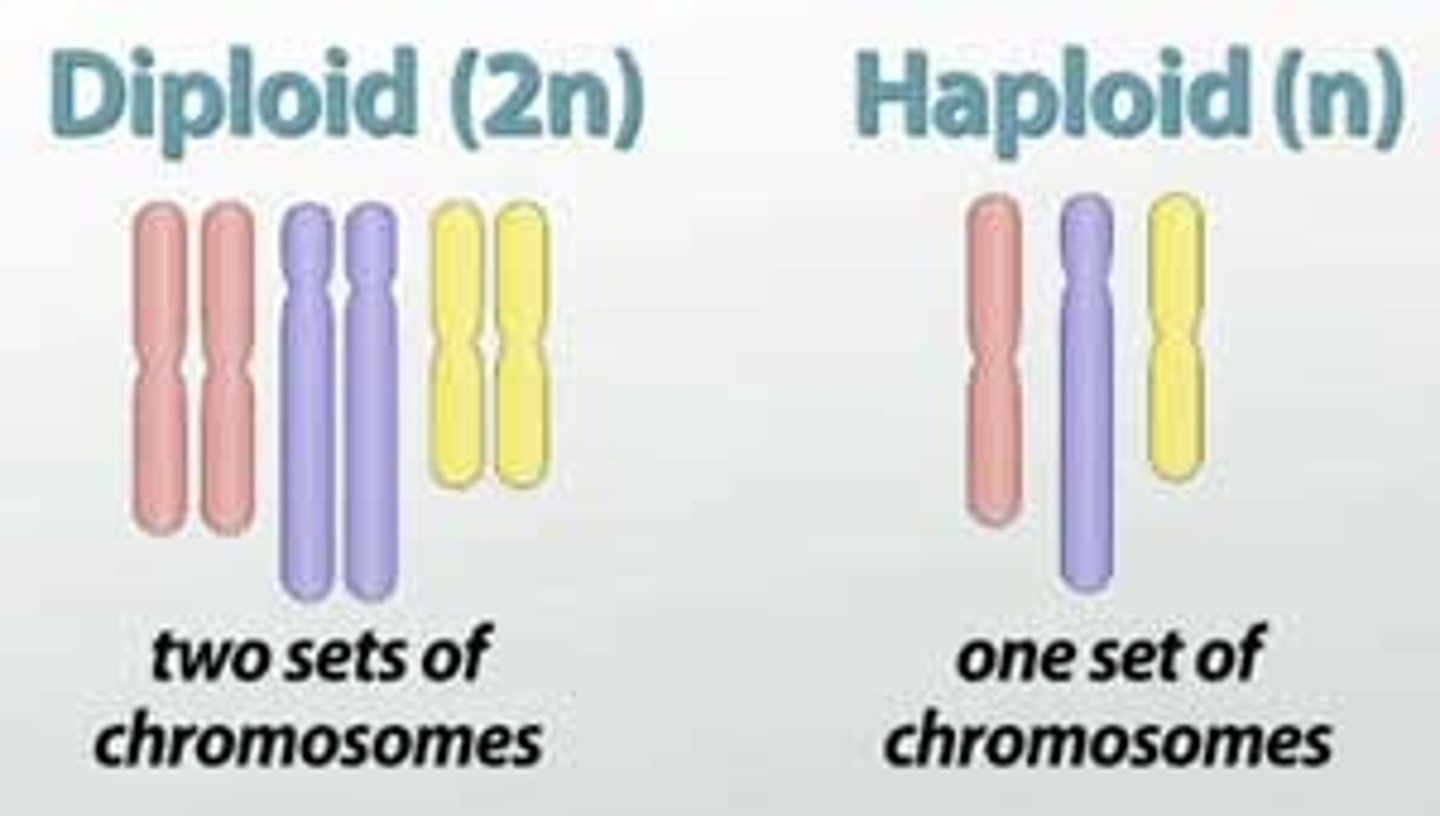
Diploid (2n)
two copies of each chromosome
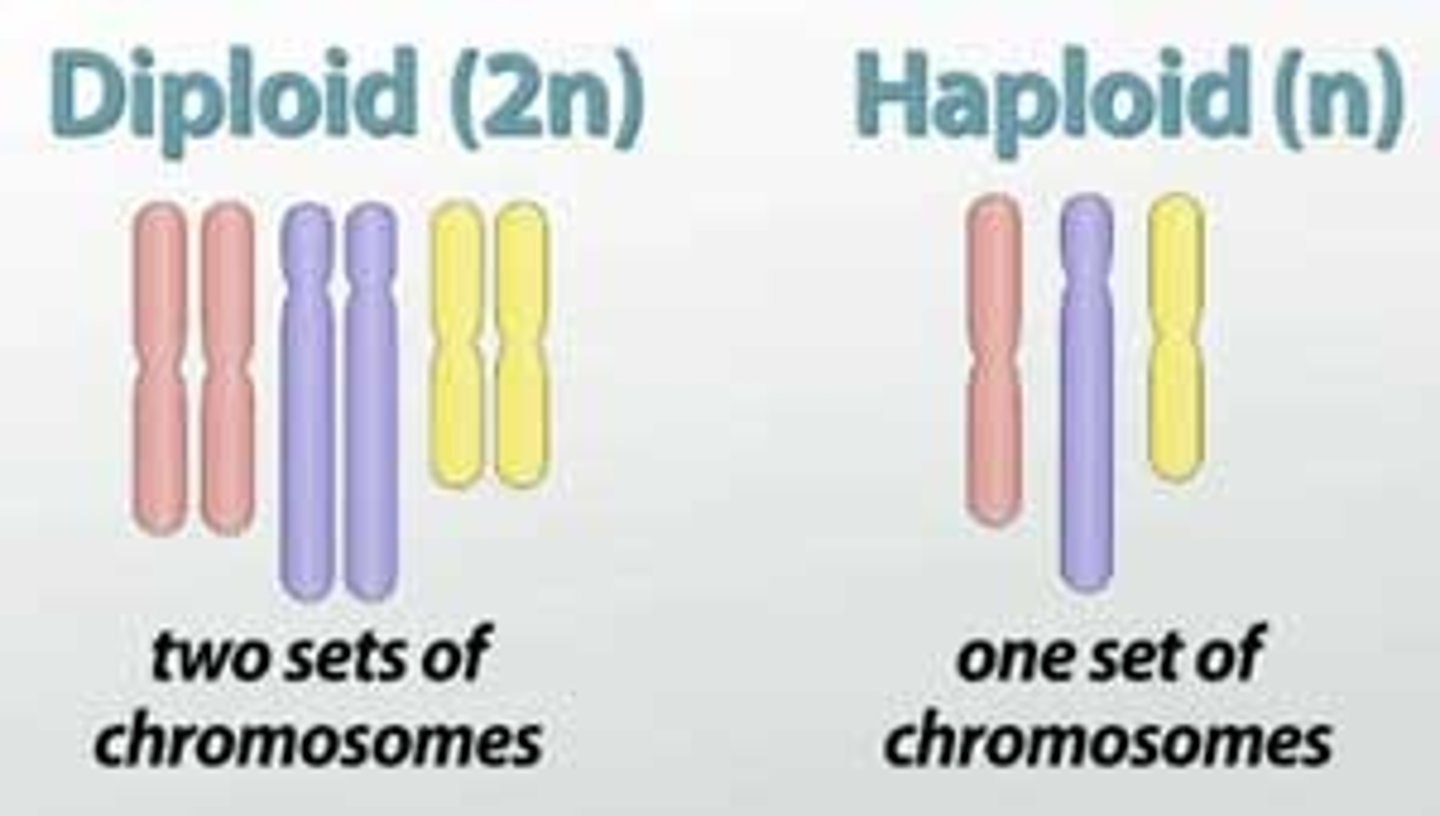
Haploid (1n)
one copy of each chromosome
daughter cells
the cells that result from a cell division
Meiosis 1
separates homologous chromosomes
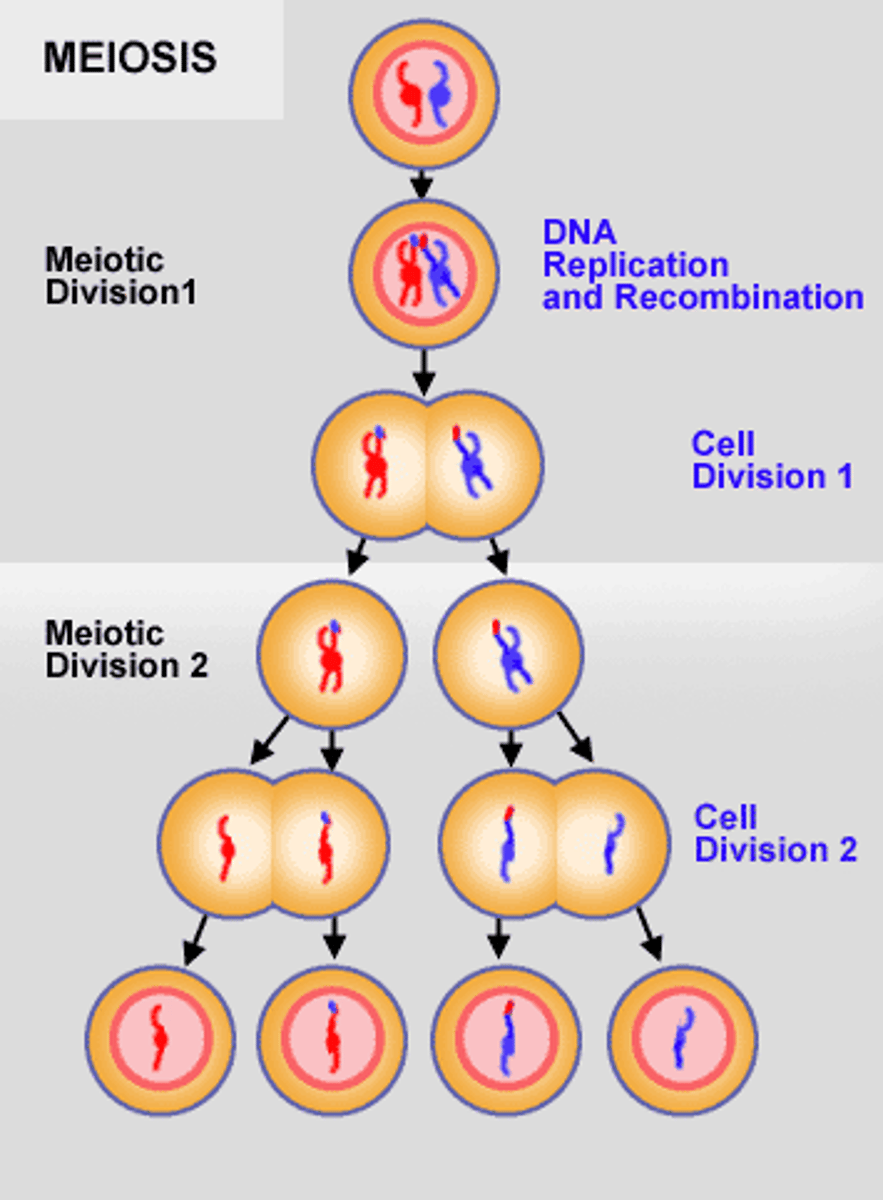
Meiosis 2
sister chromatids separate
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
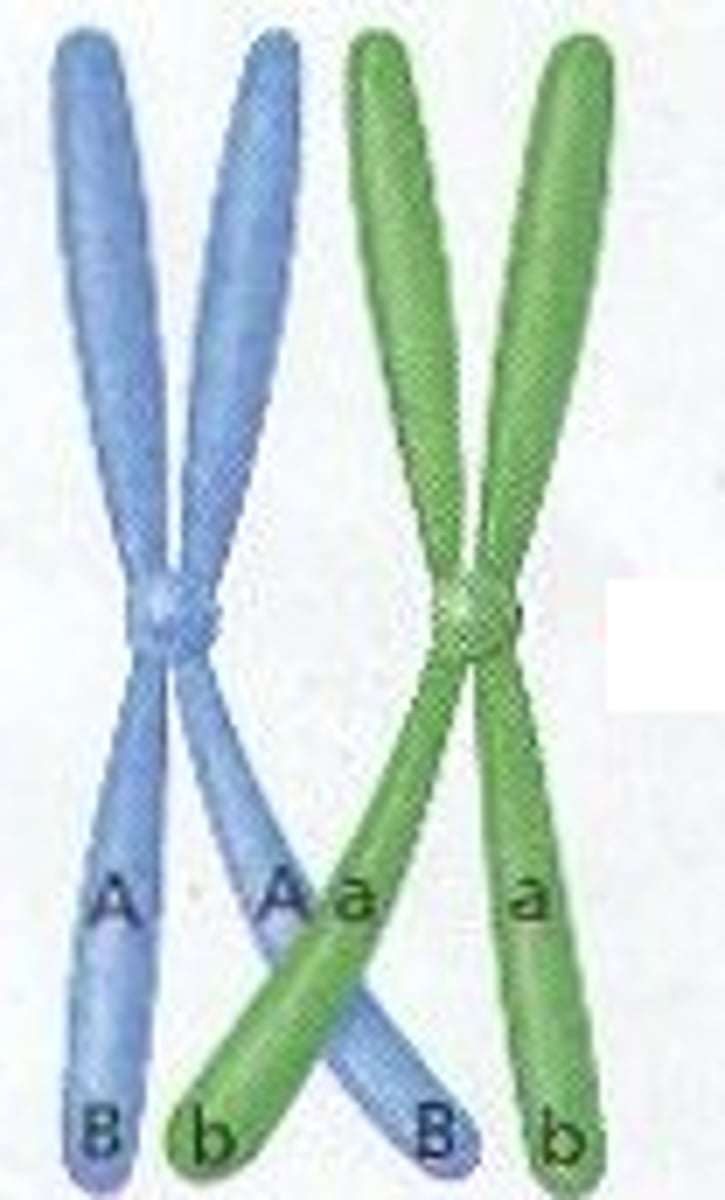
Tetrad
structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis
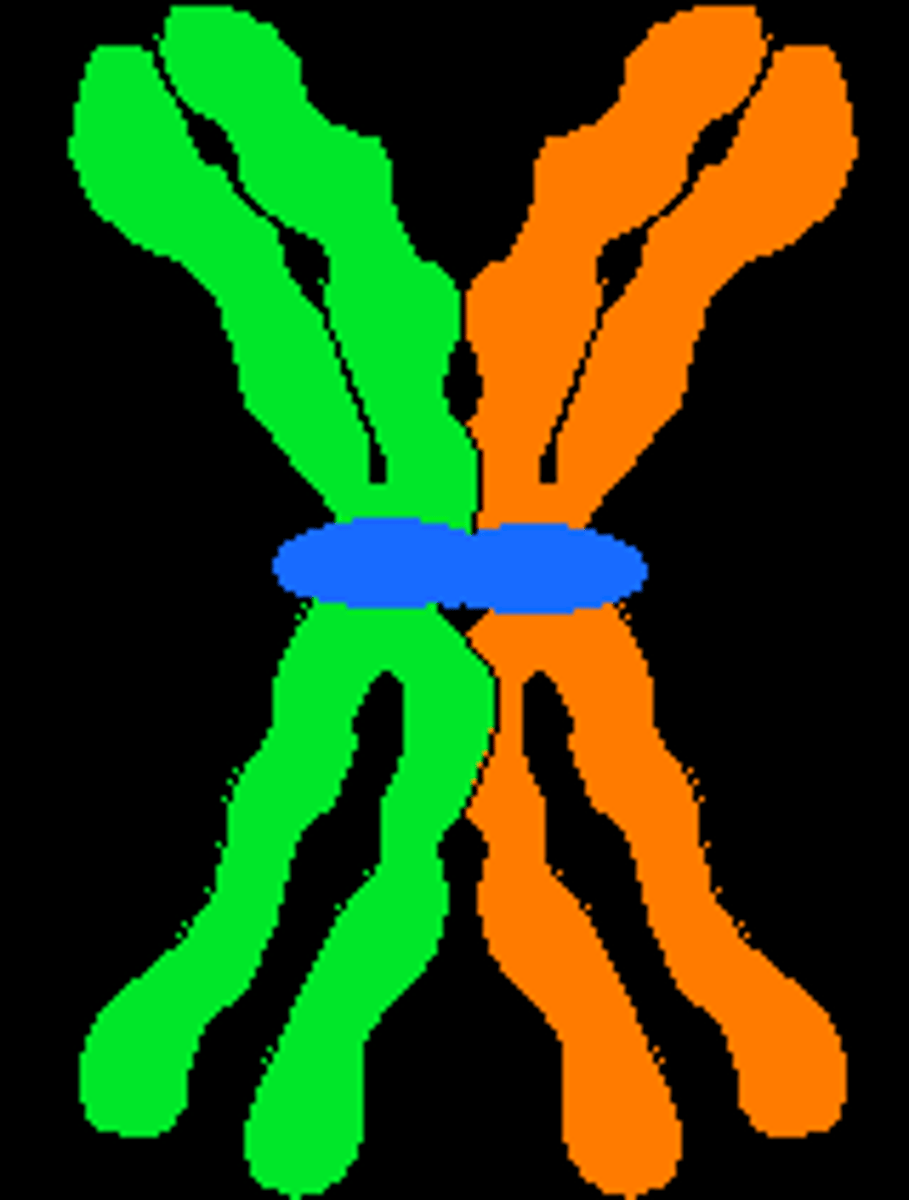
law of independent assortment
the law that states that genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
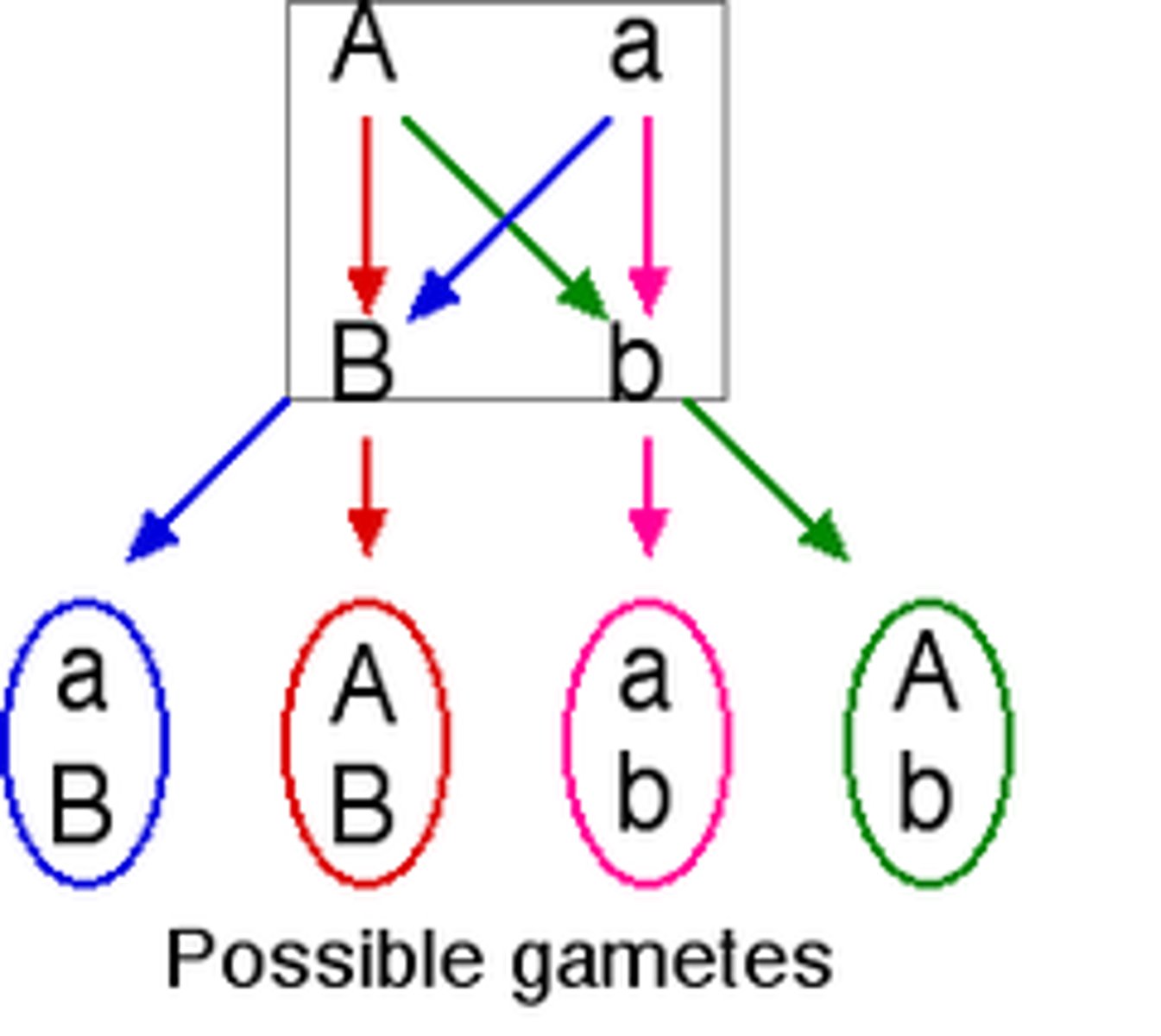
random fertilization
source of genetic variation caused by the unlimited number of possible sperm & egg combinations

P generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
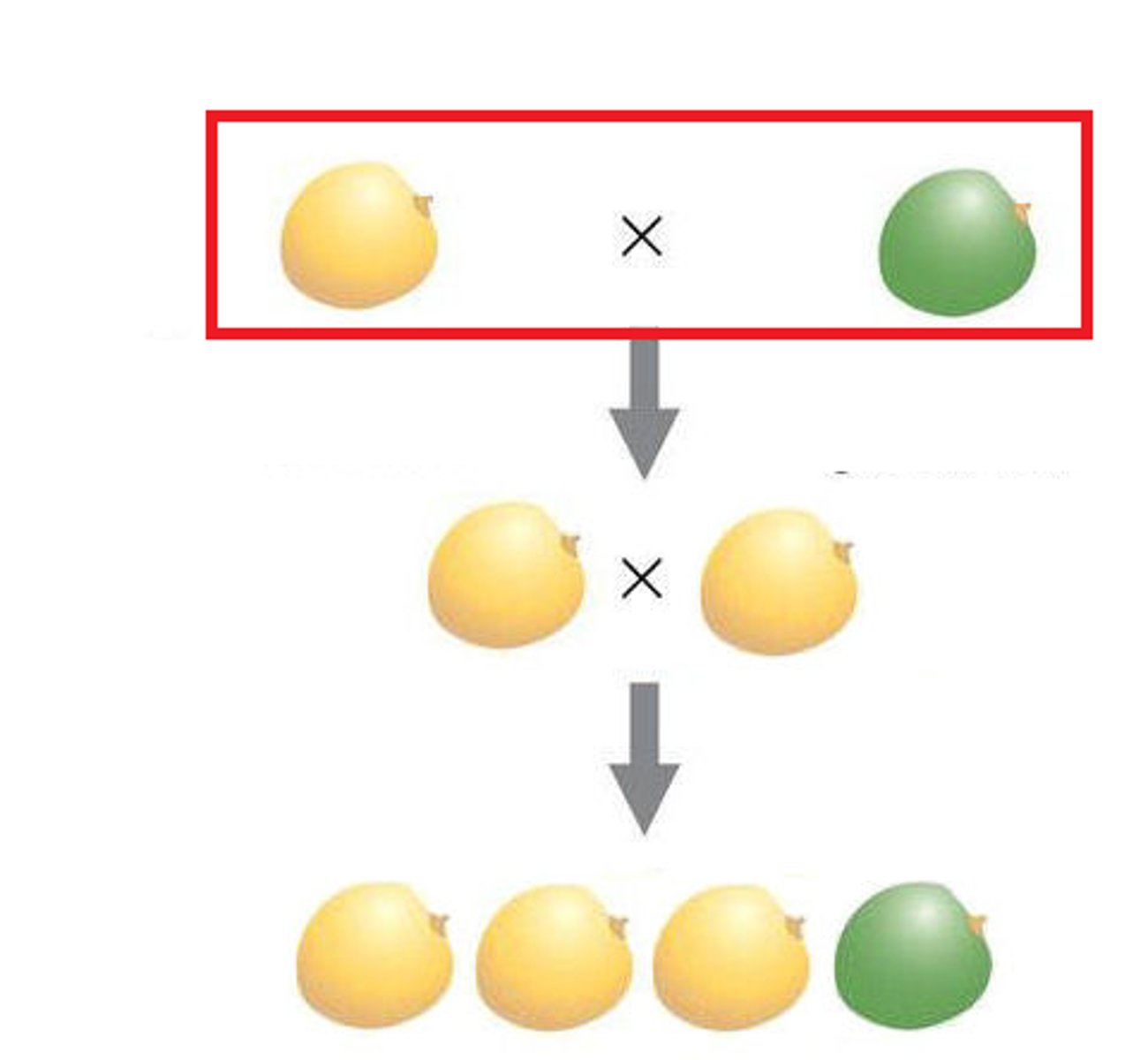
F1 generation (first filial generation)
offspring of the P generation
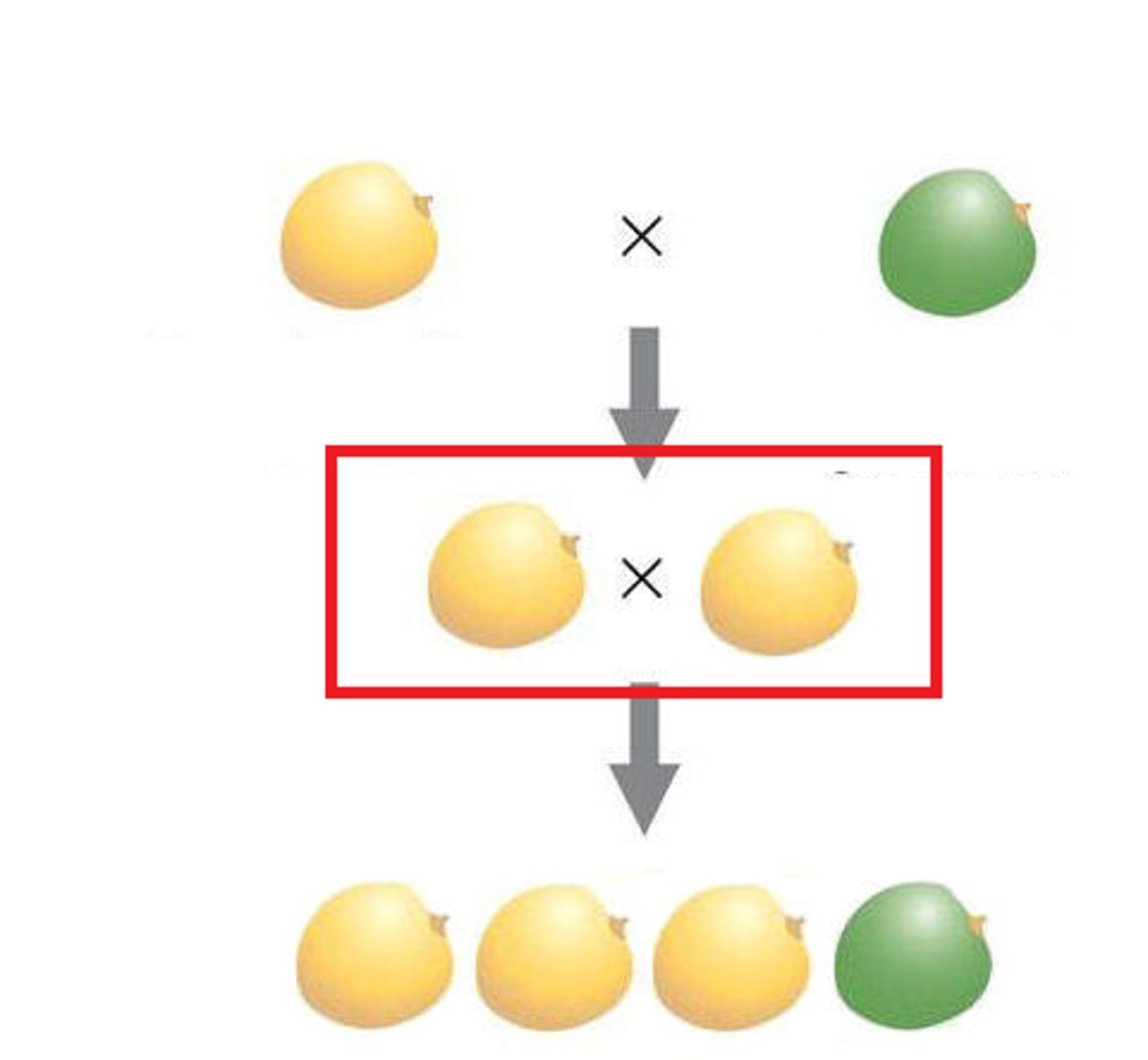
F2 generation (second filial generation)
offspring of the F1 generation
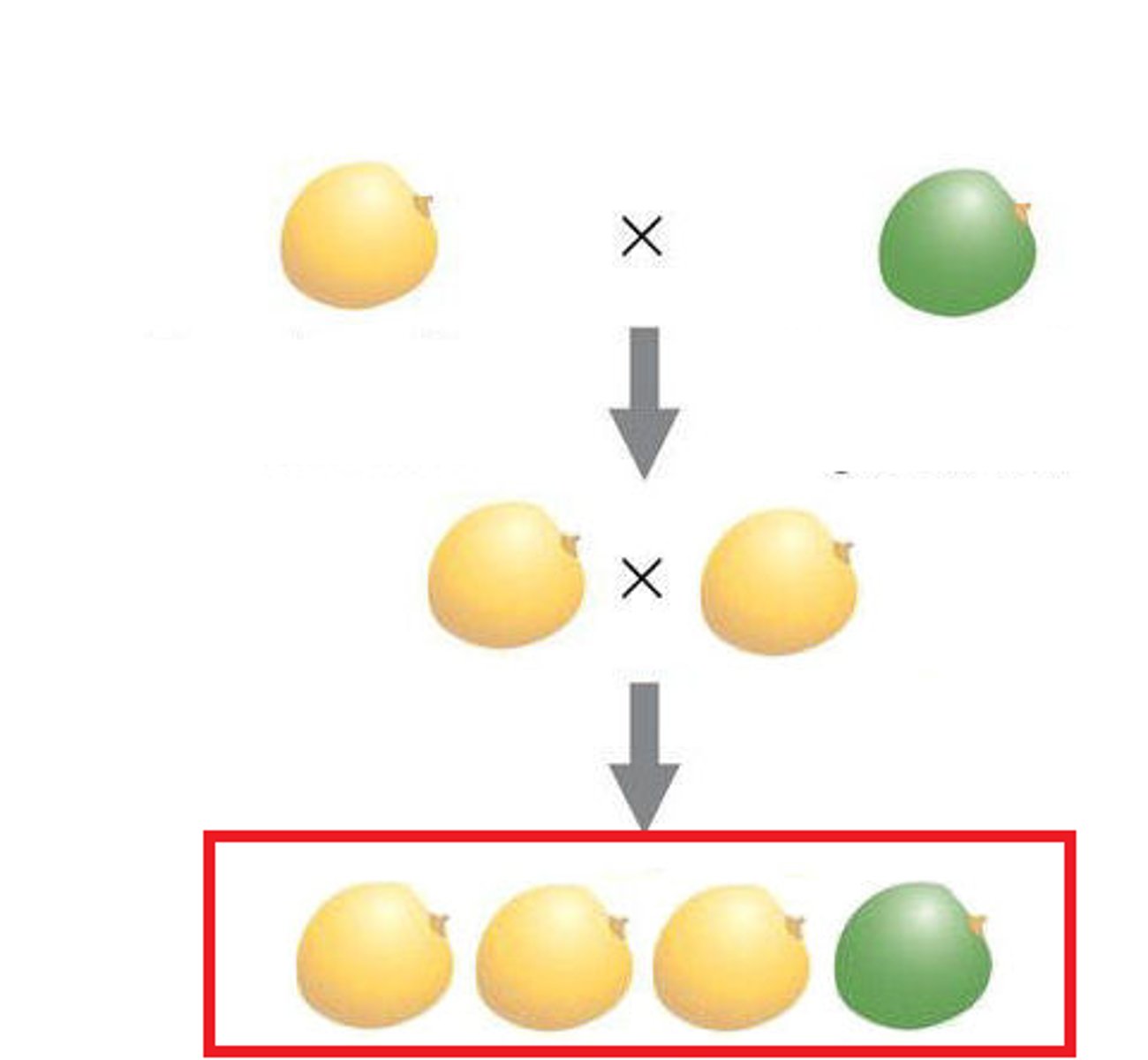
Alleles
different versions of a gene
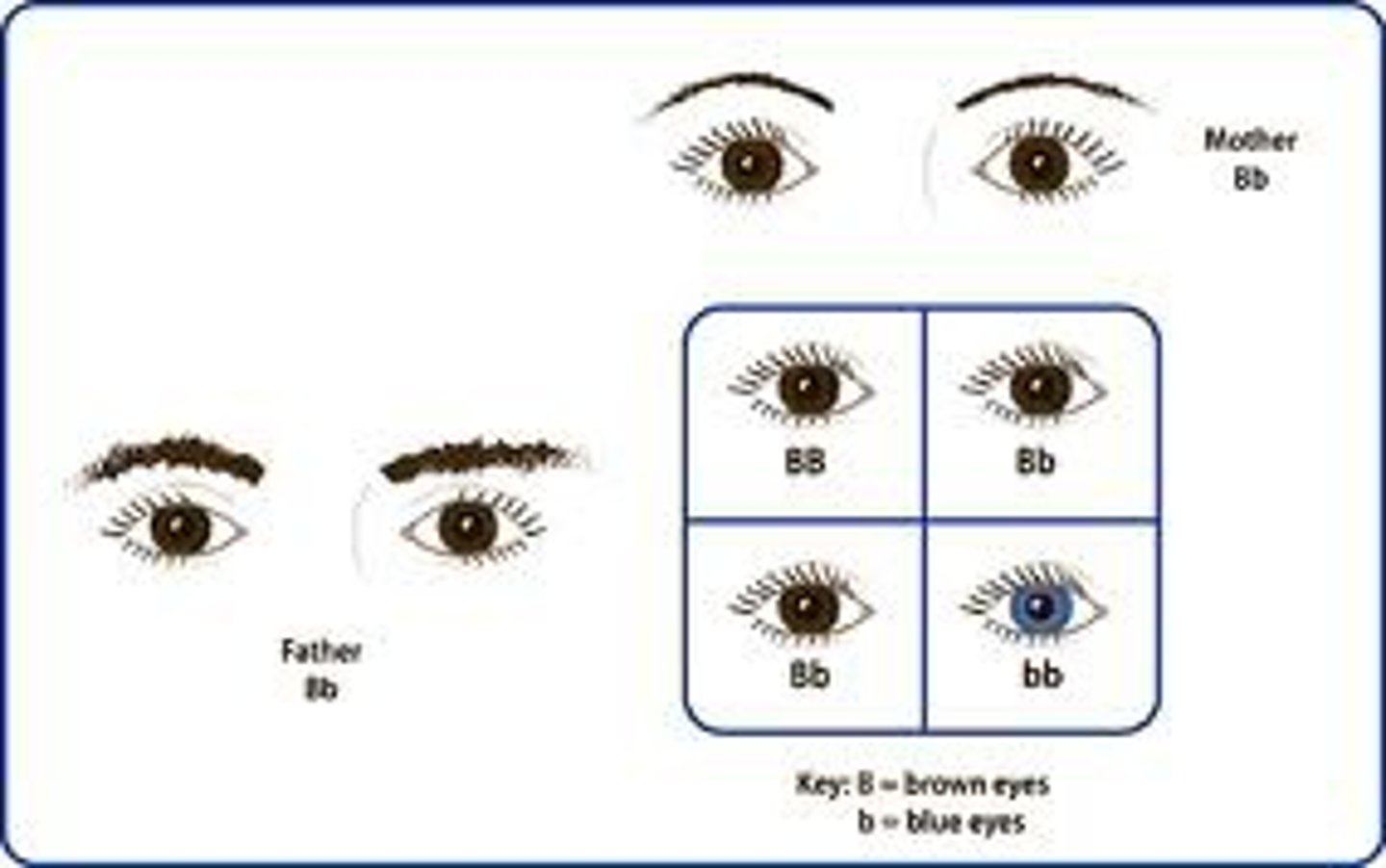
Dominant
An allele that is always expressed

Recessive
trait of an organism that can be masked by the dominant form of a trait
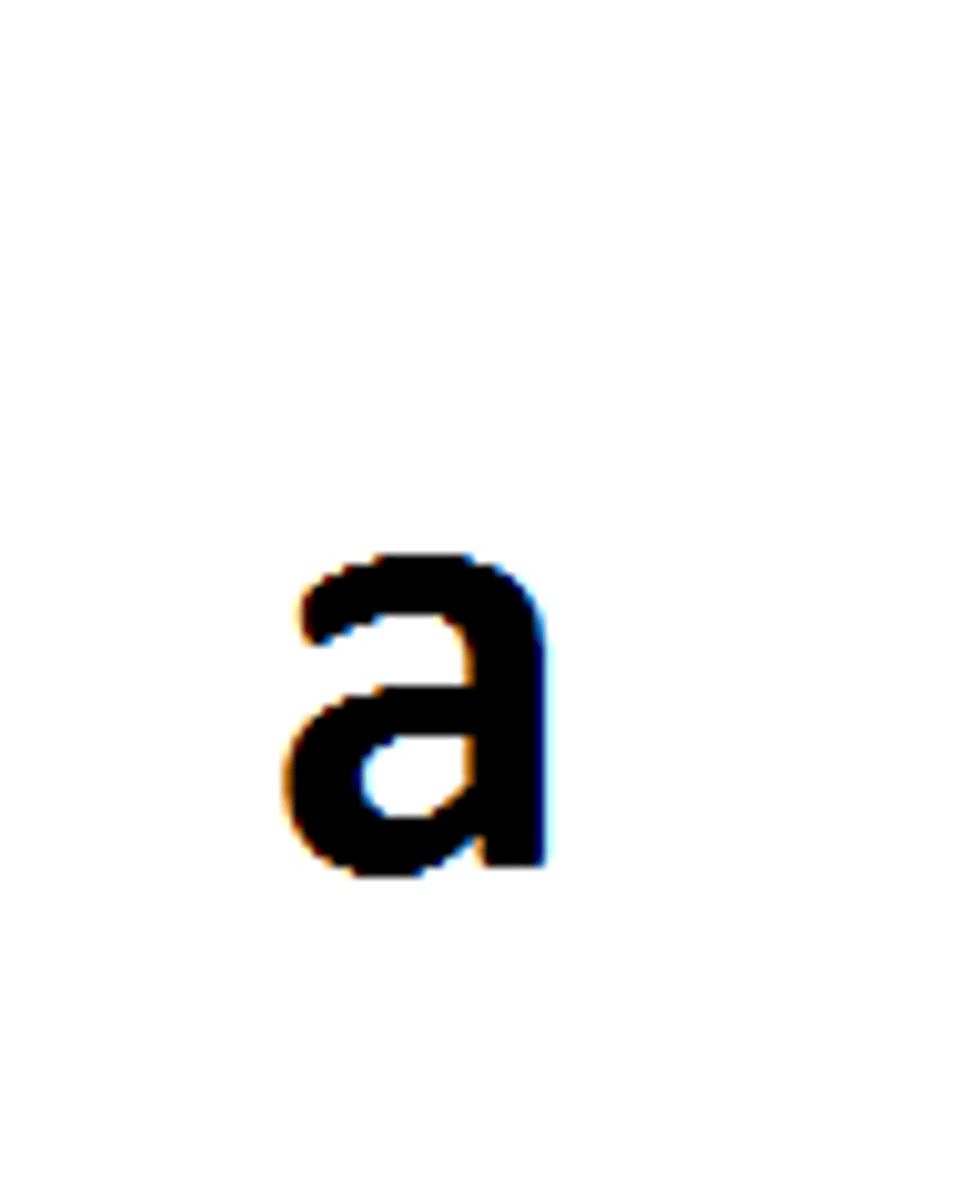
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
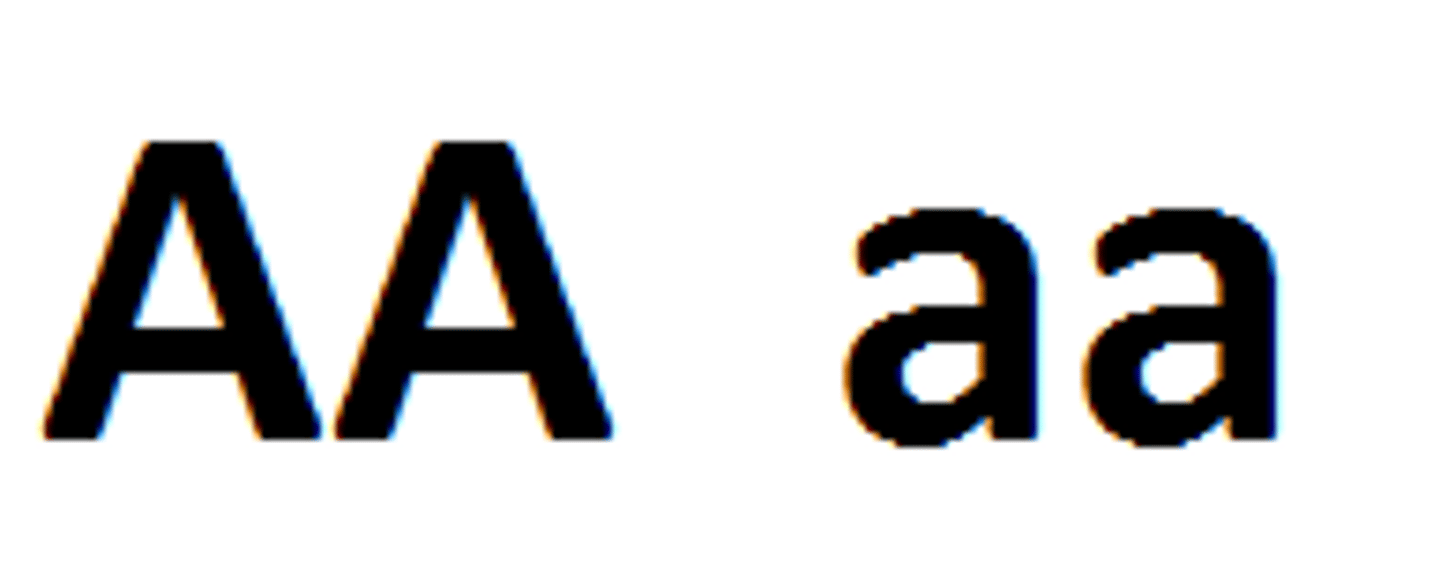
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait

Phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
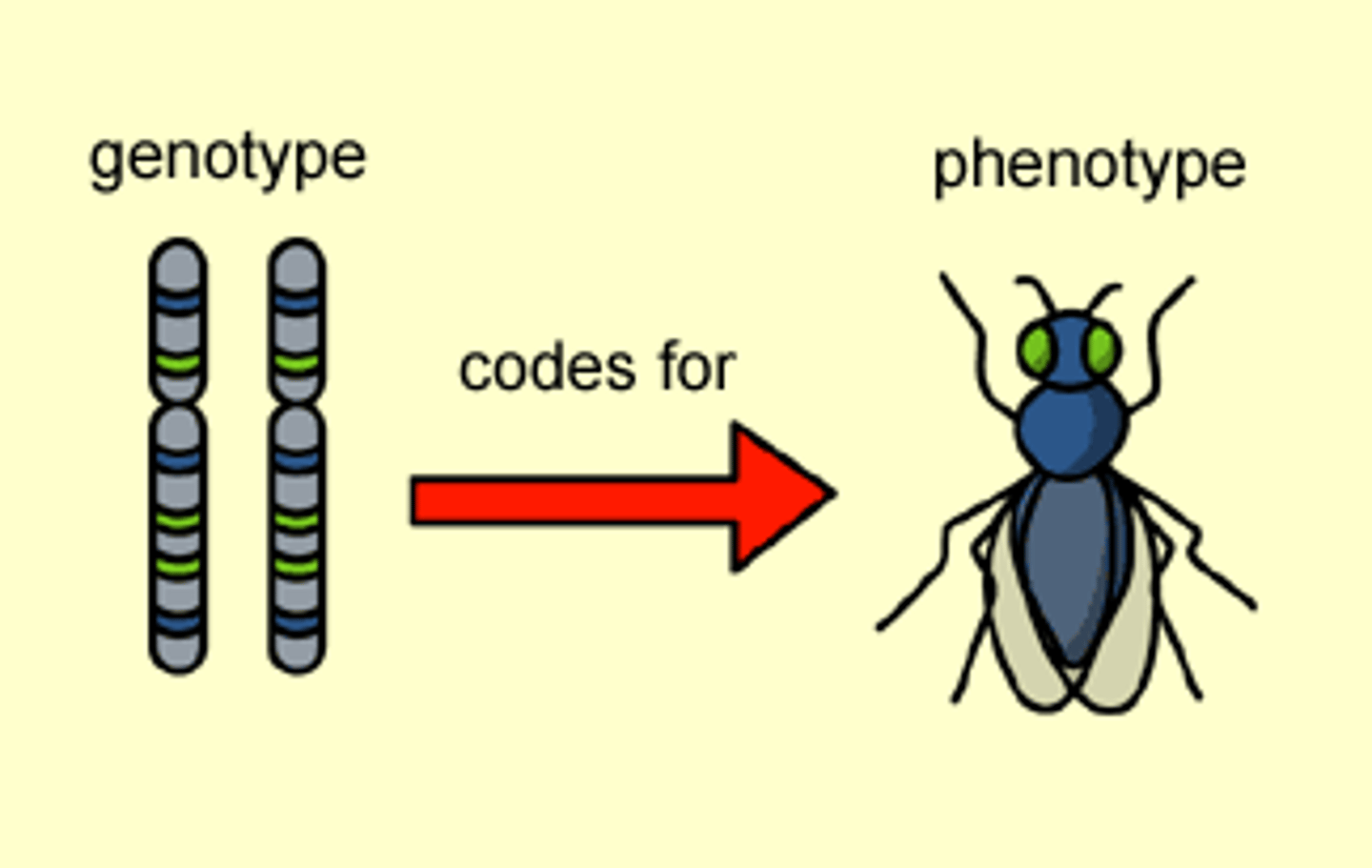
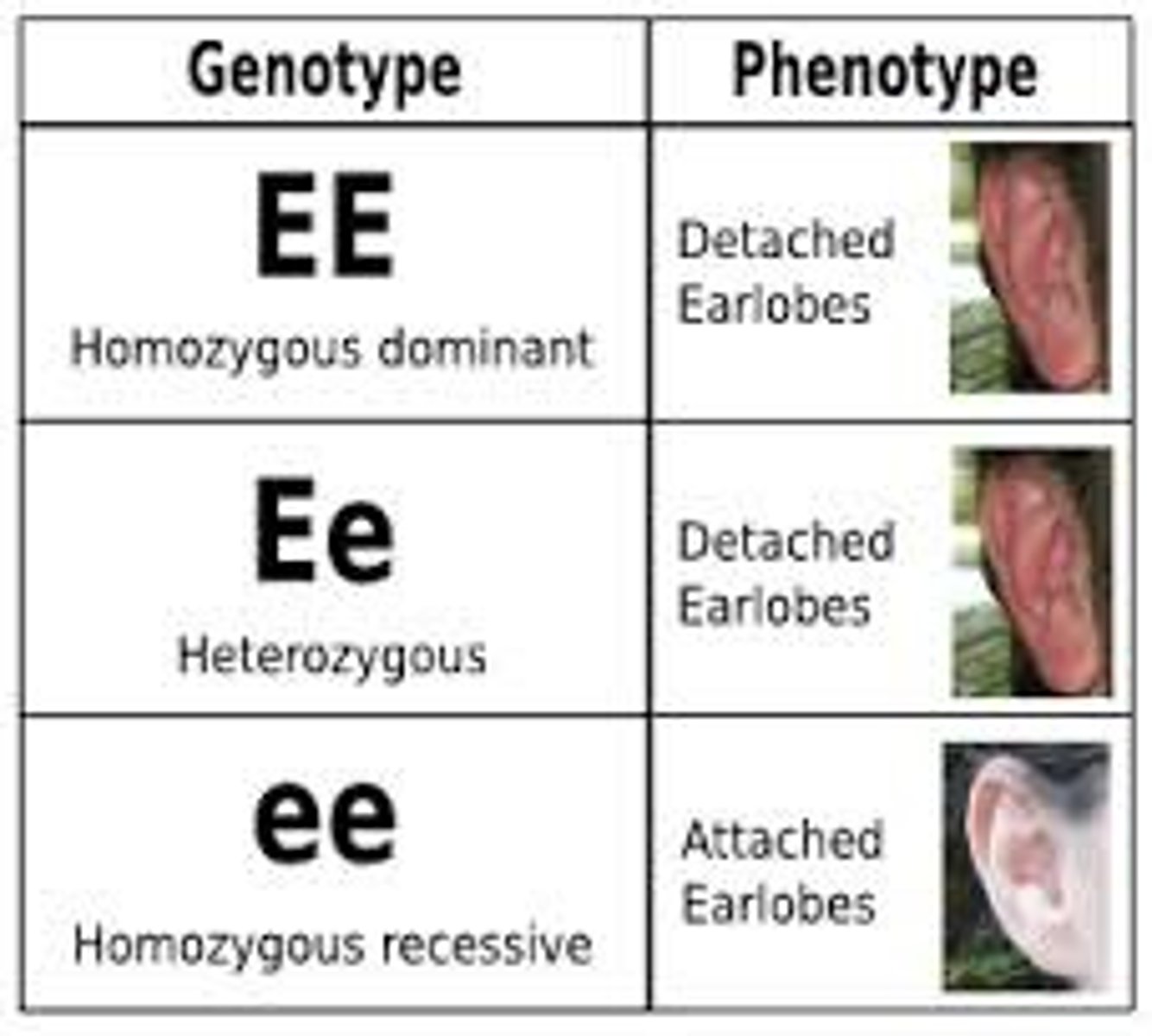
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
test cross
the crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
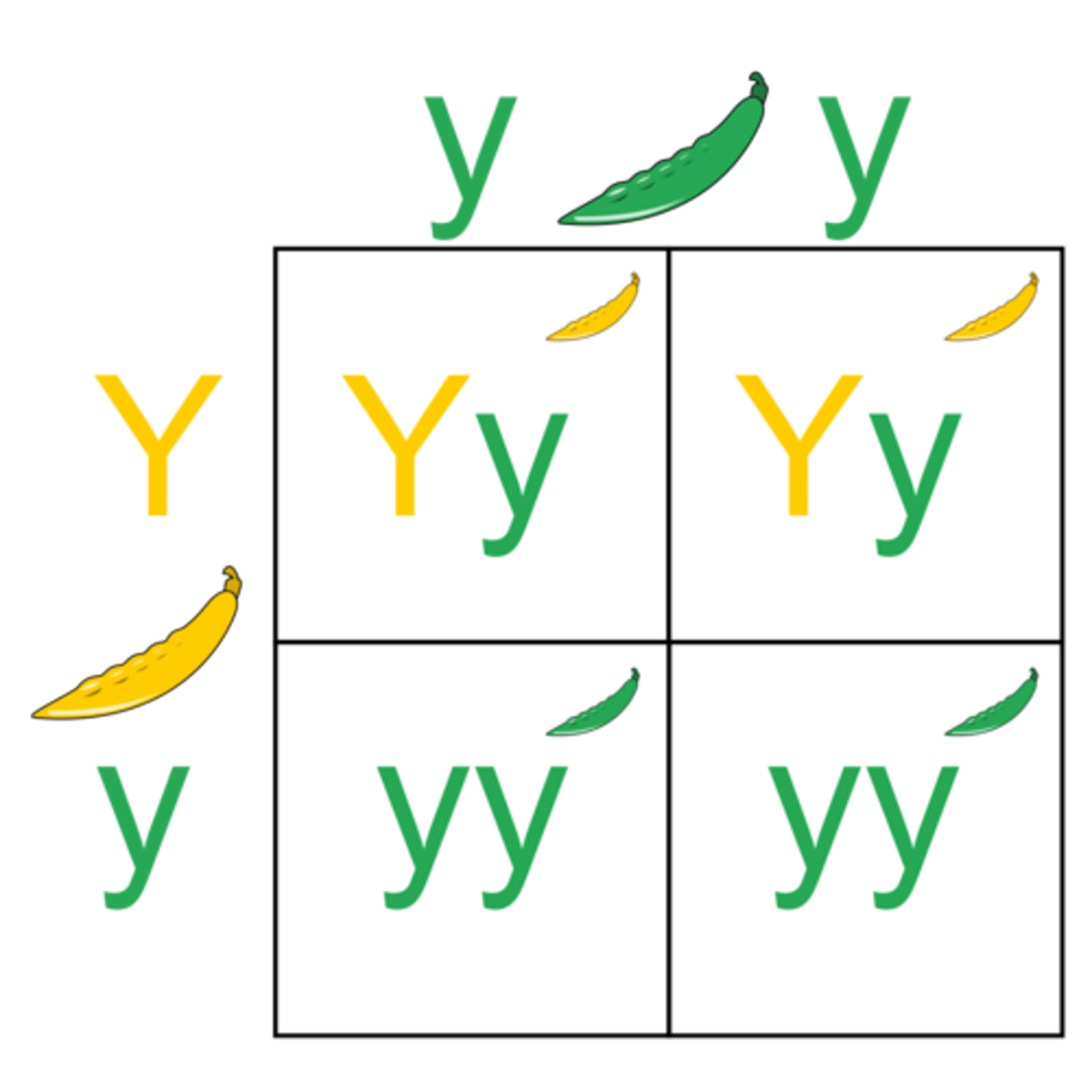
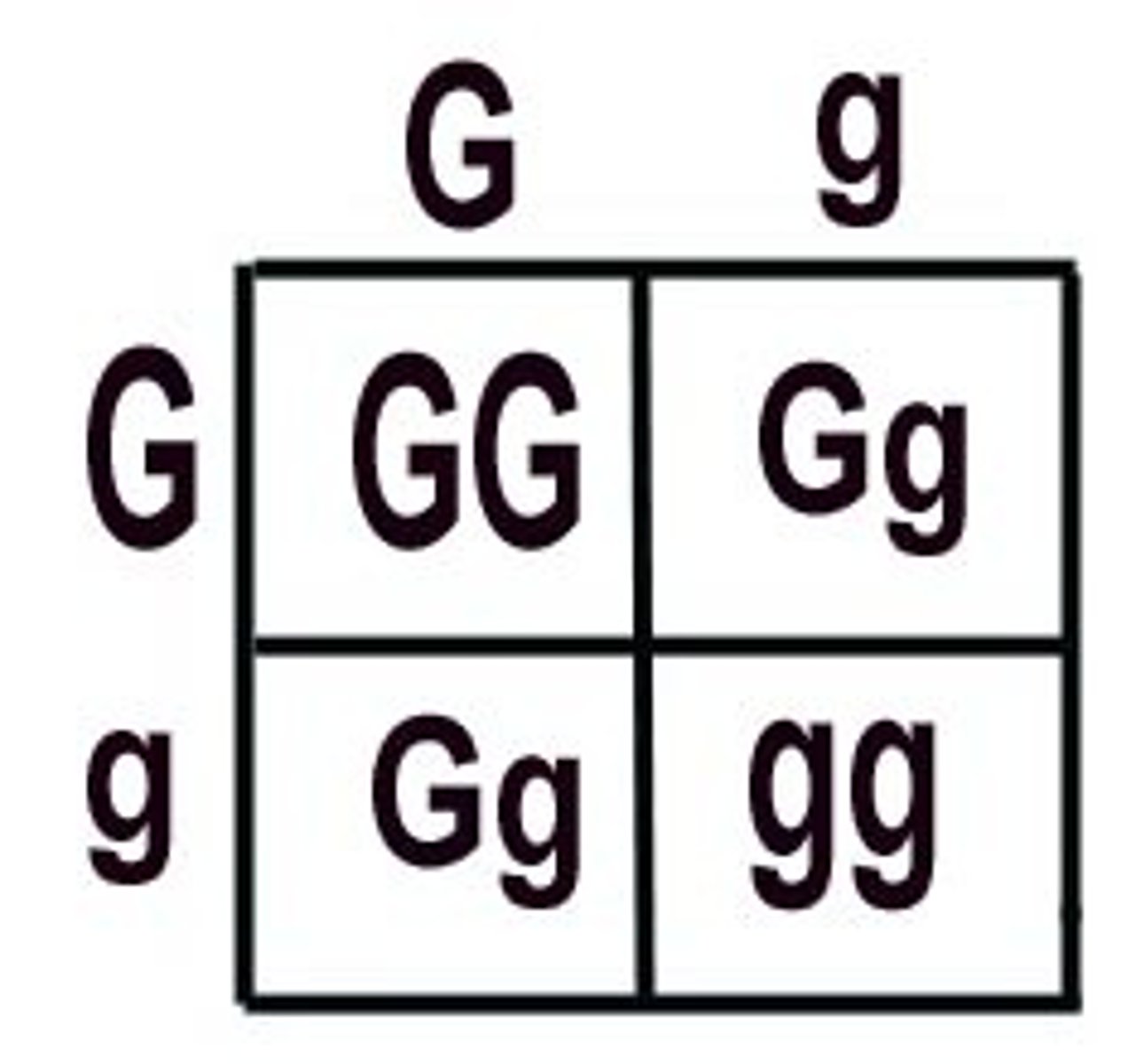
monohybrid cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
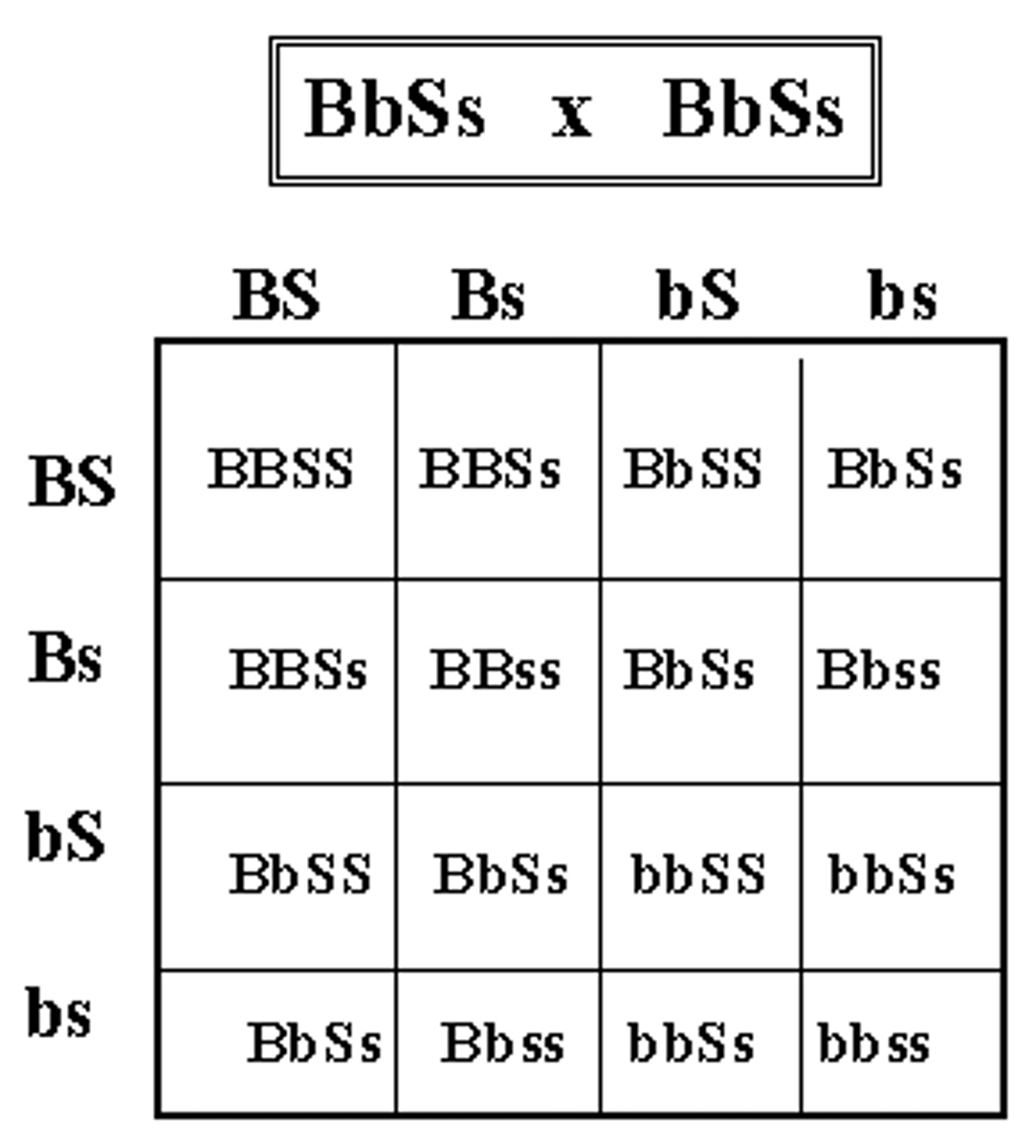
dihybrid cross
Cross or mating between organisms involving two pairs of contrasting traits
rule of addition
A rule stating that the probability that an event can occur in two or more alternative ways is the sum of the separate probabilities of the different ways.
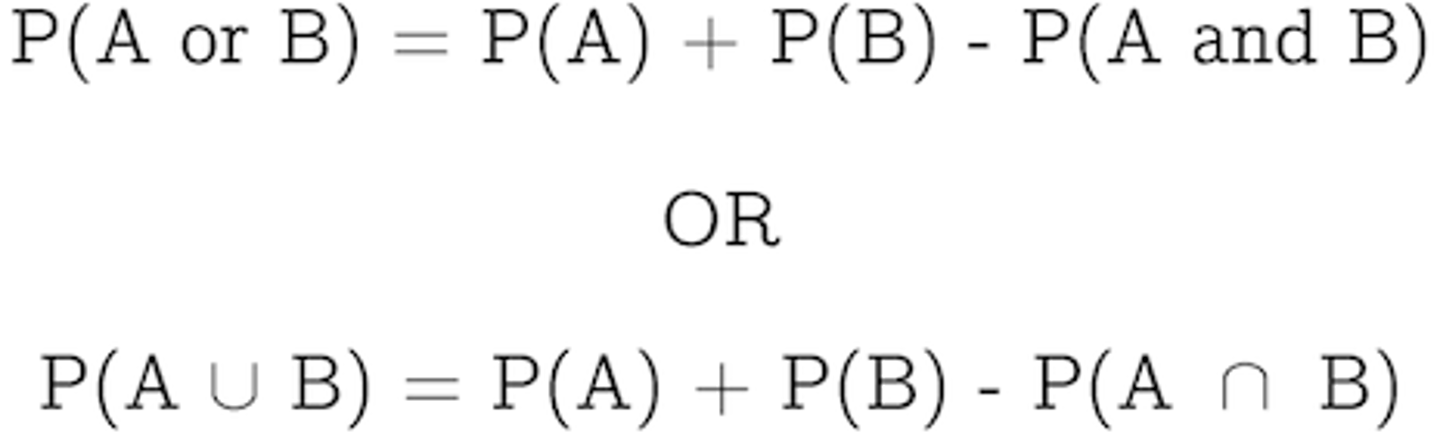
rule of multiplication
A rule stating that the probability of a compound event is the product of the separate probabilities of the independent events.
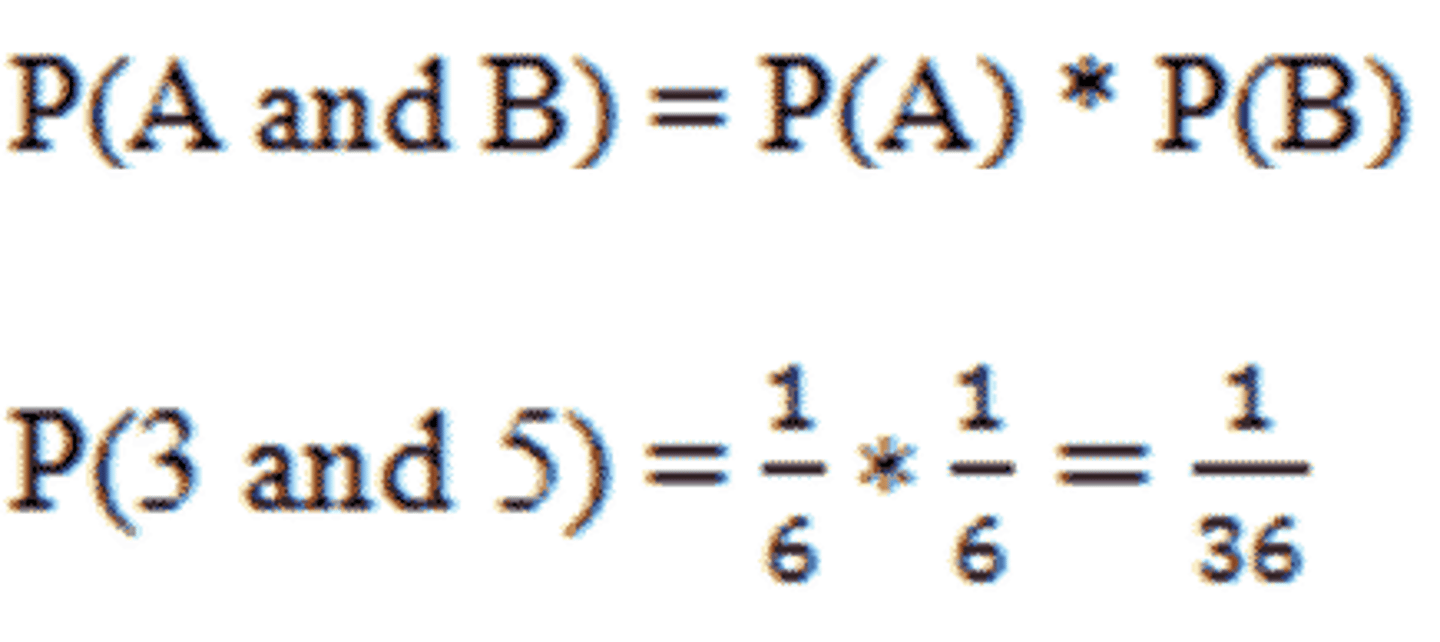
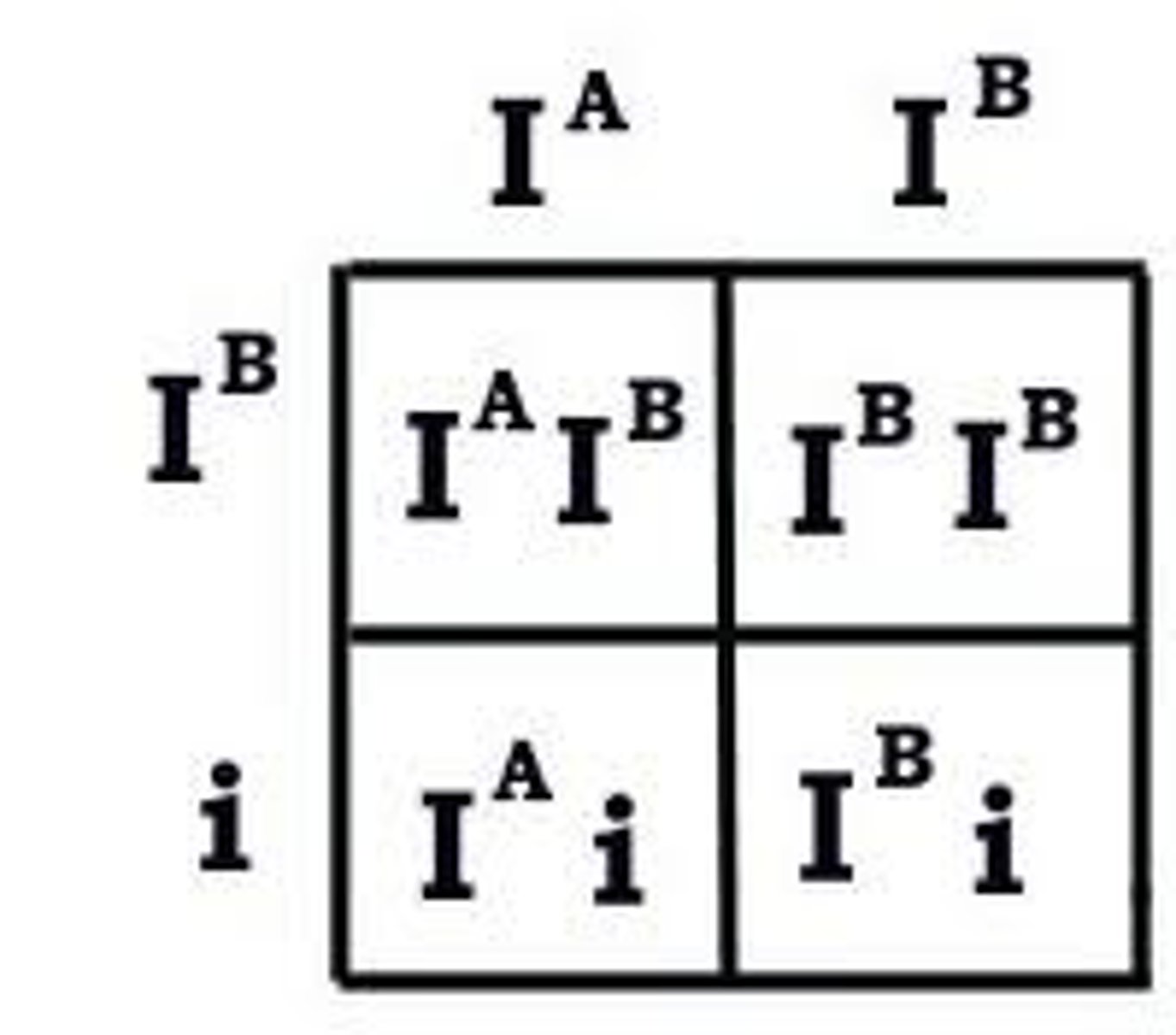
Codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
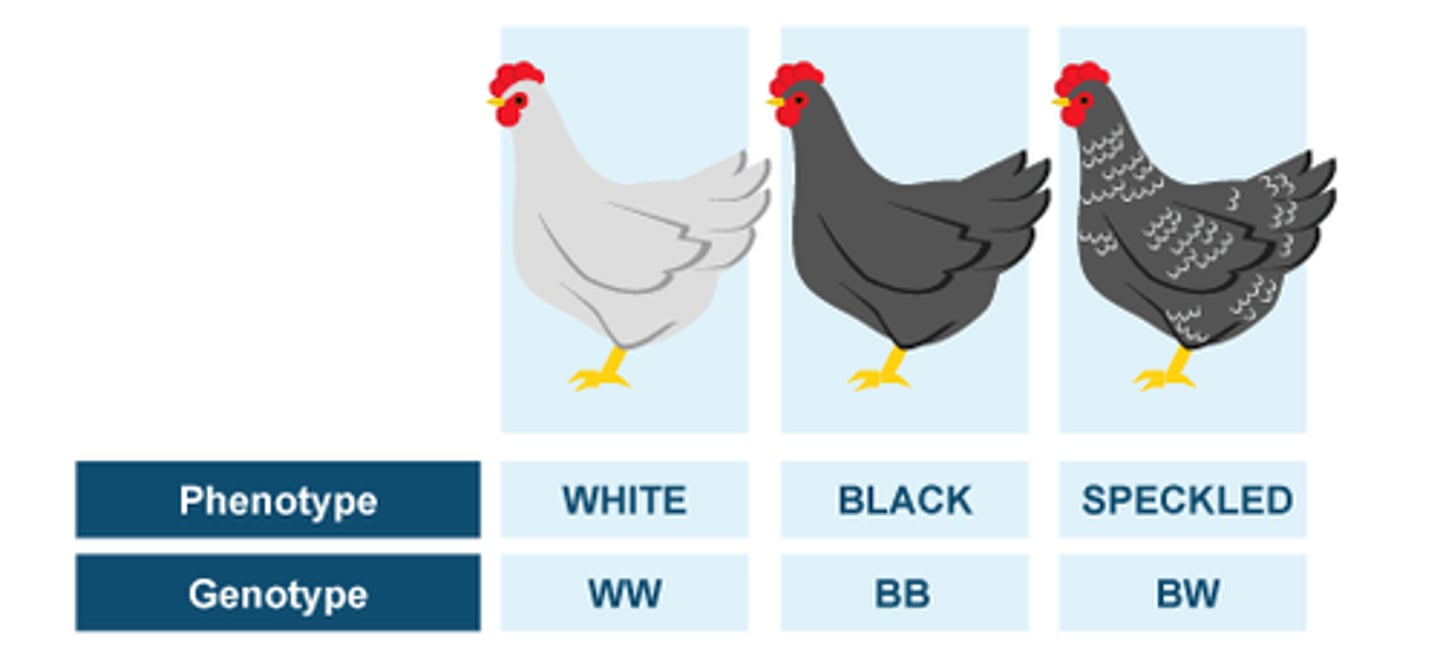
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
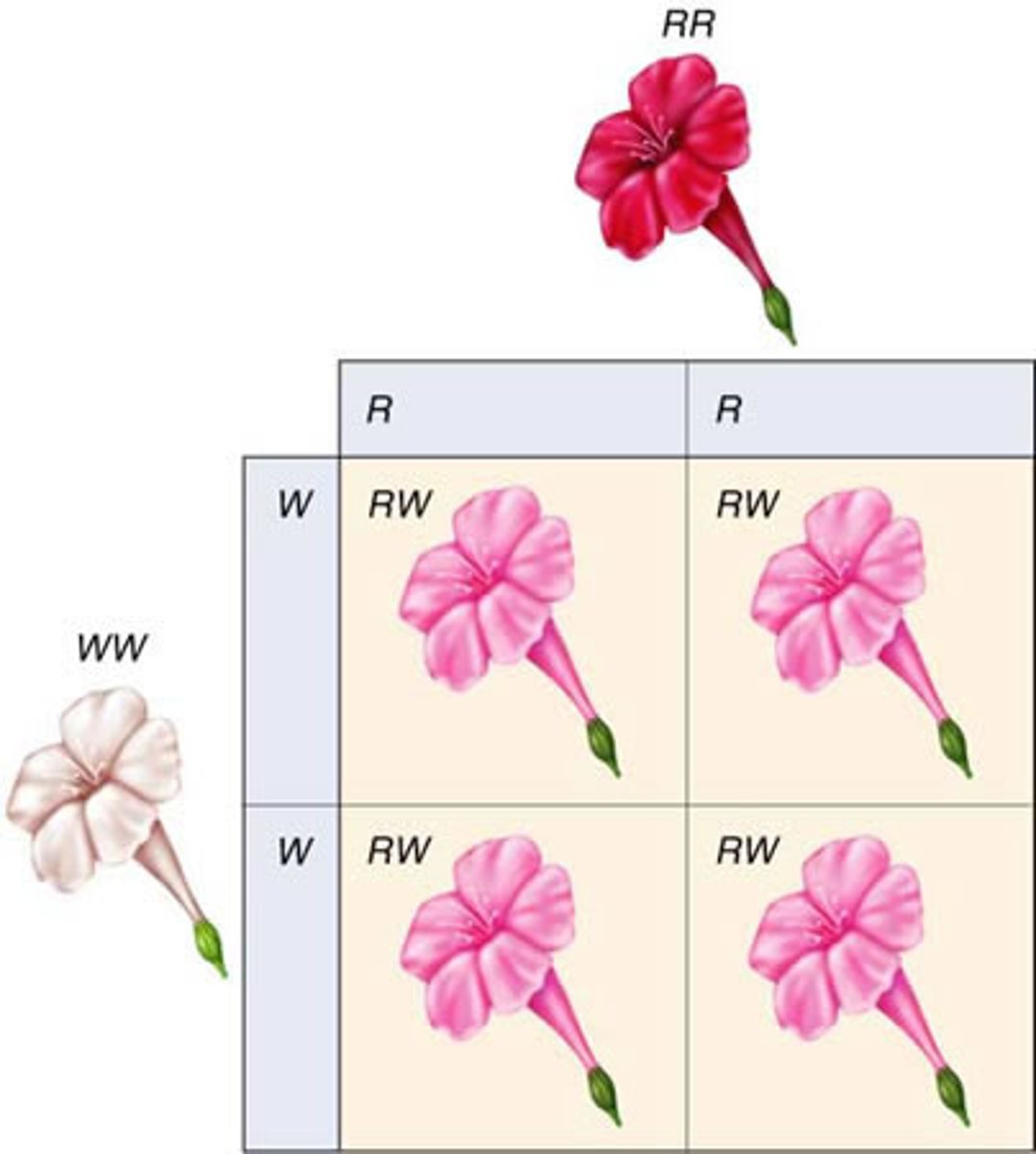
multiple alleles
three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait
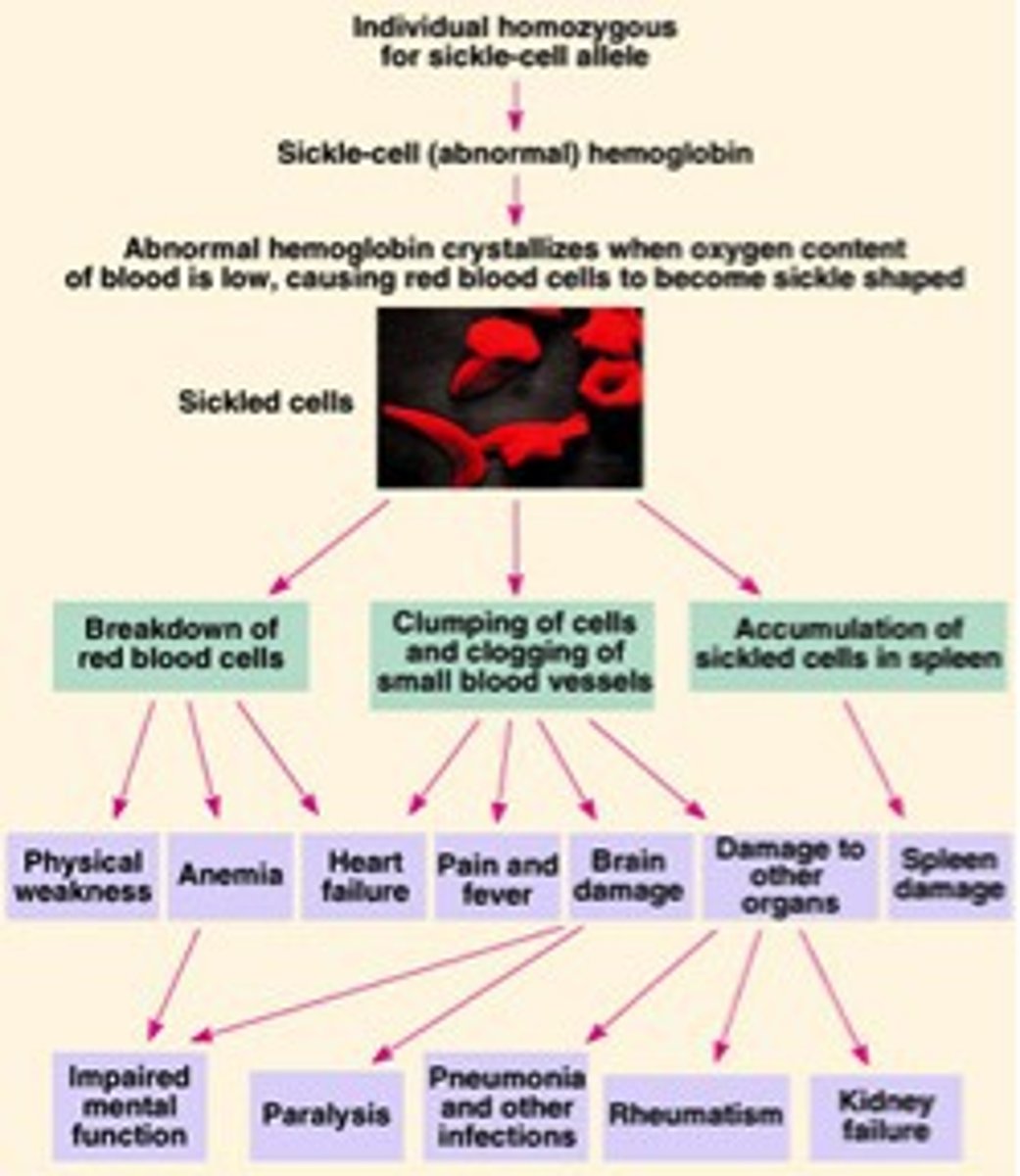
Pleiotropy
The ability of a single gene to have multiple effects.
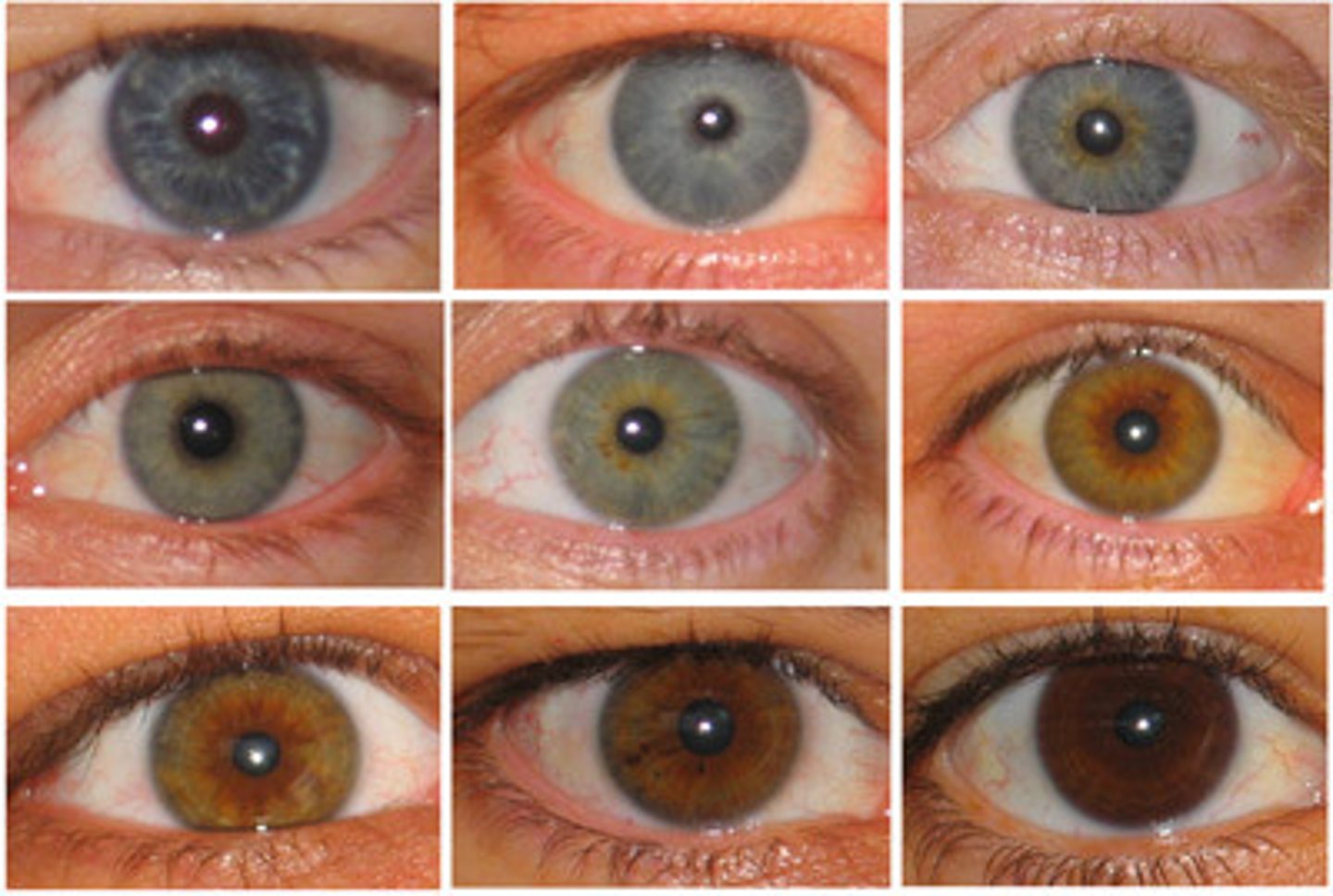
polygenic inheritance
combined effect of two or more genes on a single character
Pedigree
A chart or "family tree" that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait
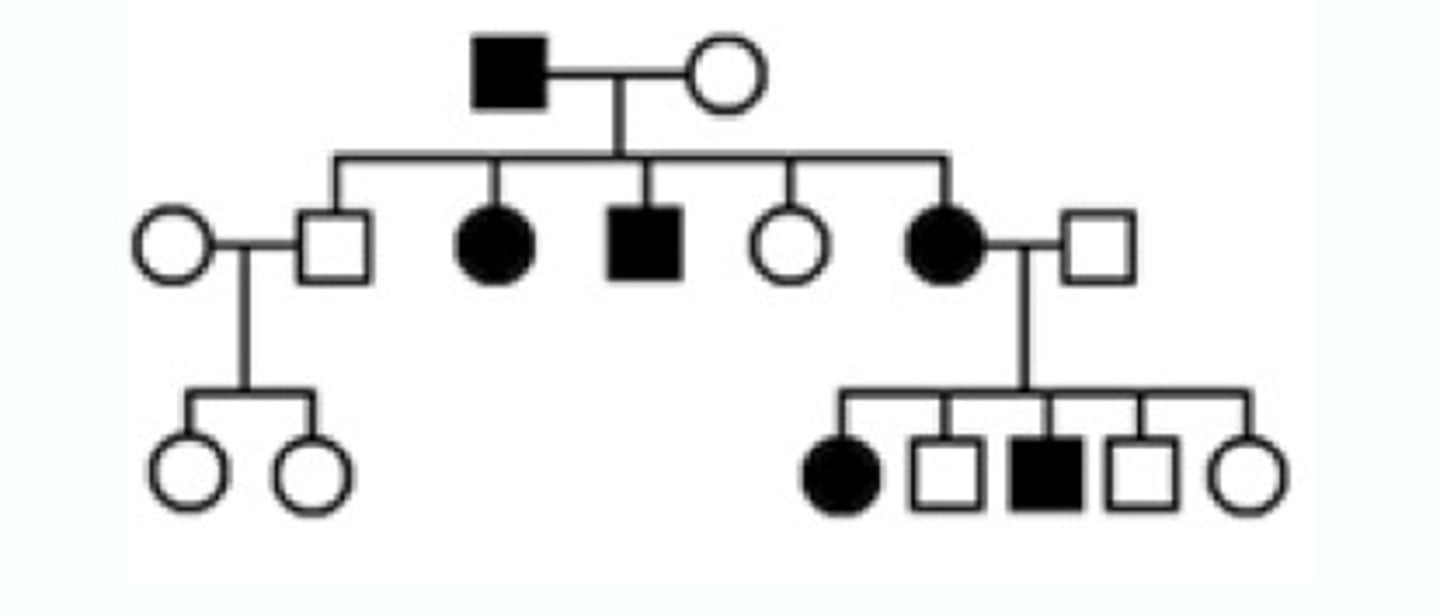
Sex-linked (X-linked)
An inheritance pattern in which traits are controlled by genes located on the X chromosome. Traits are more common in males.
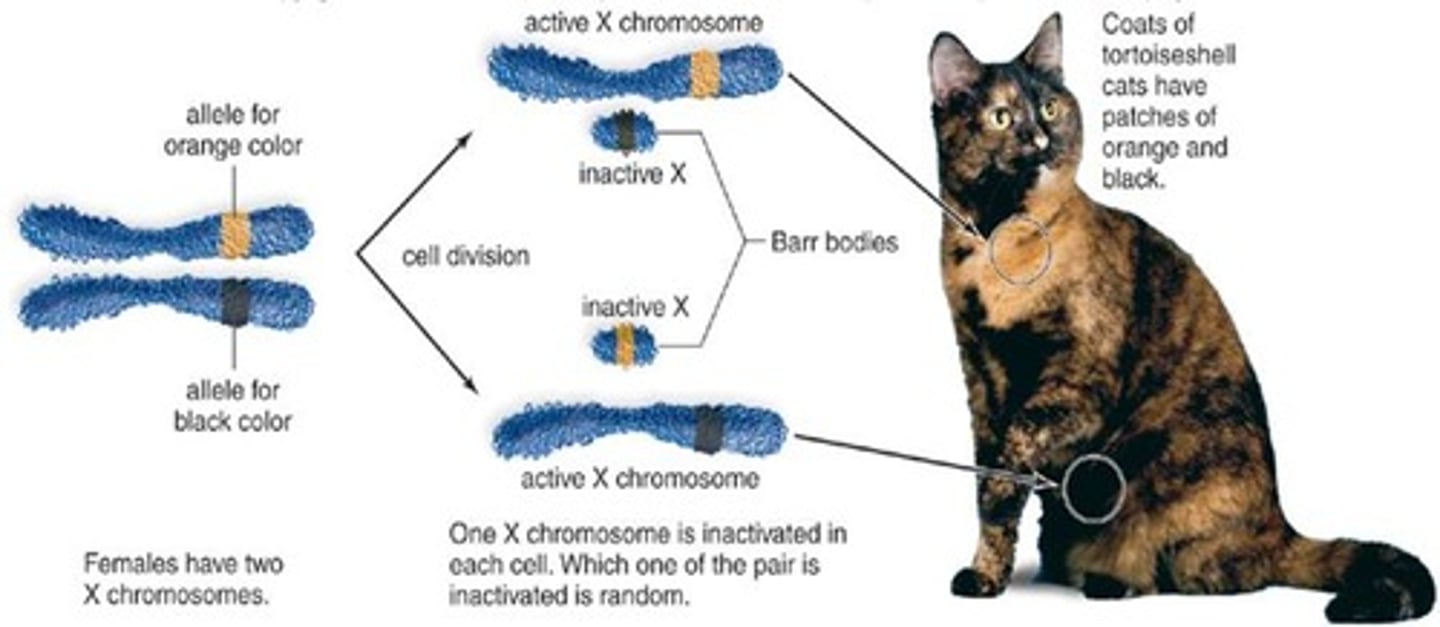
X inactivation
one of two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated and remains coiled as a Barr body
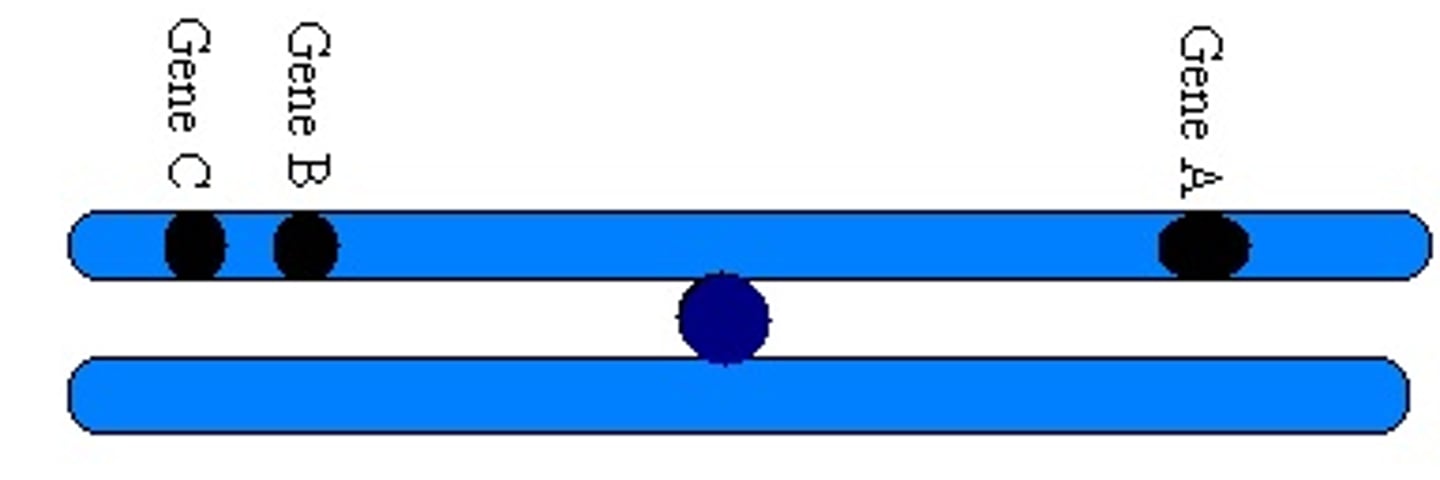
linked genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
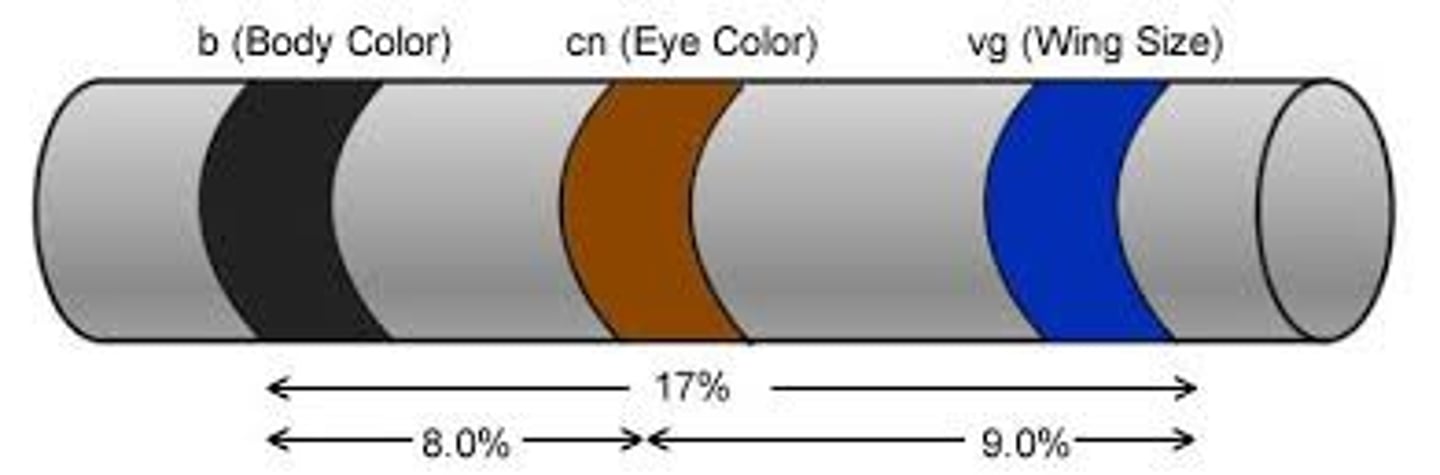
map unit
A unit of measurement of the distance between genes. One map unit is equivalent to a 1% recombination frequency.
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
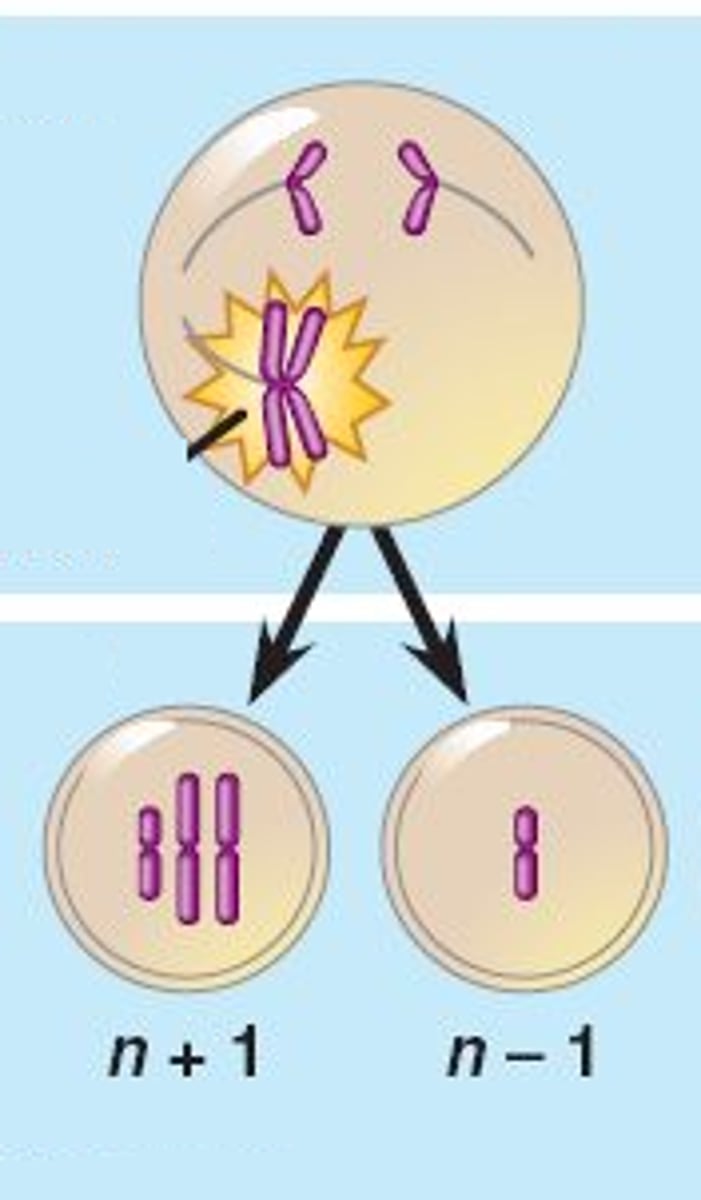
Aneuploidy
A chromosomal aberration in which one or more chromosomes are present in extra copies or are deficient in number.
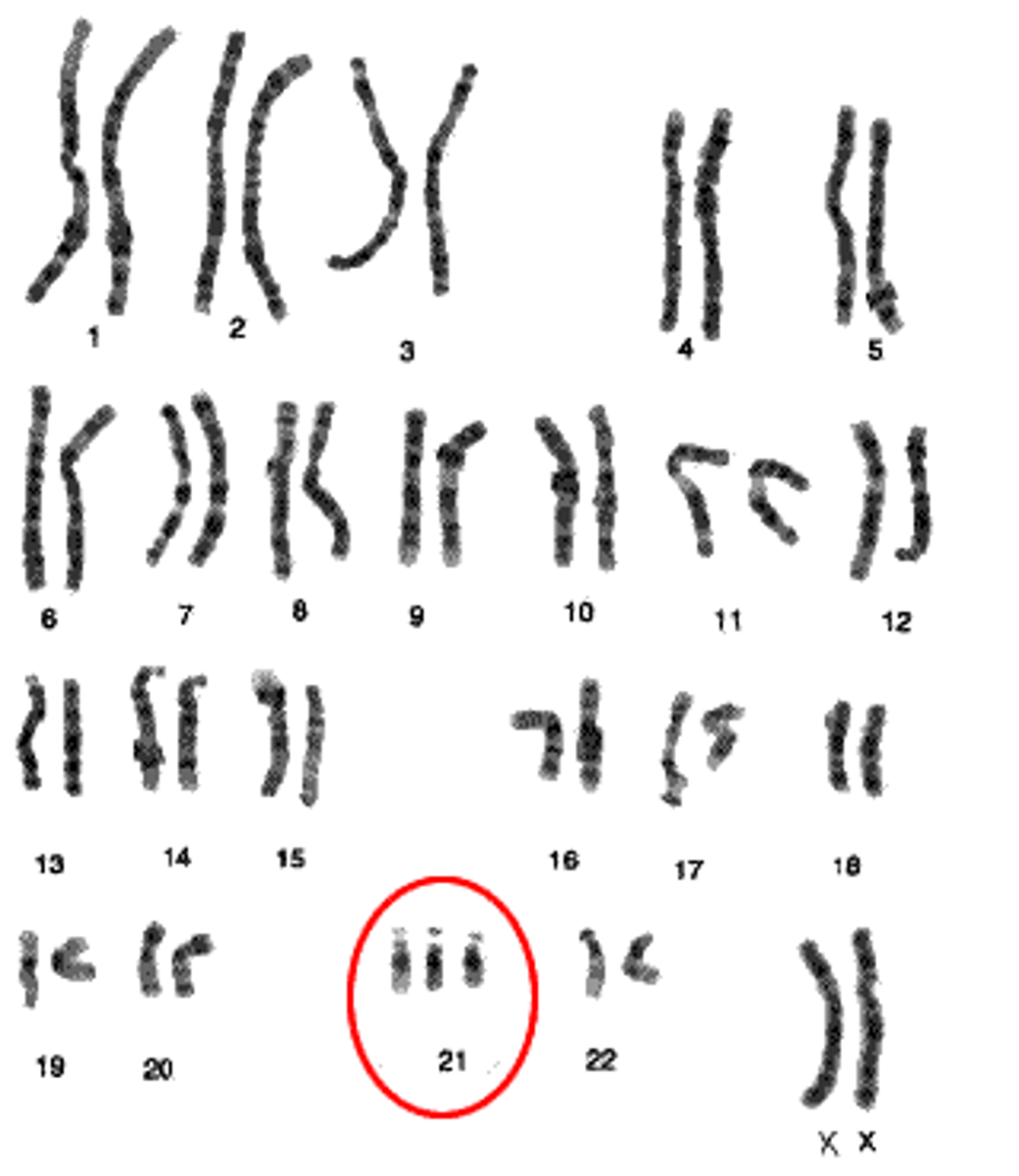
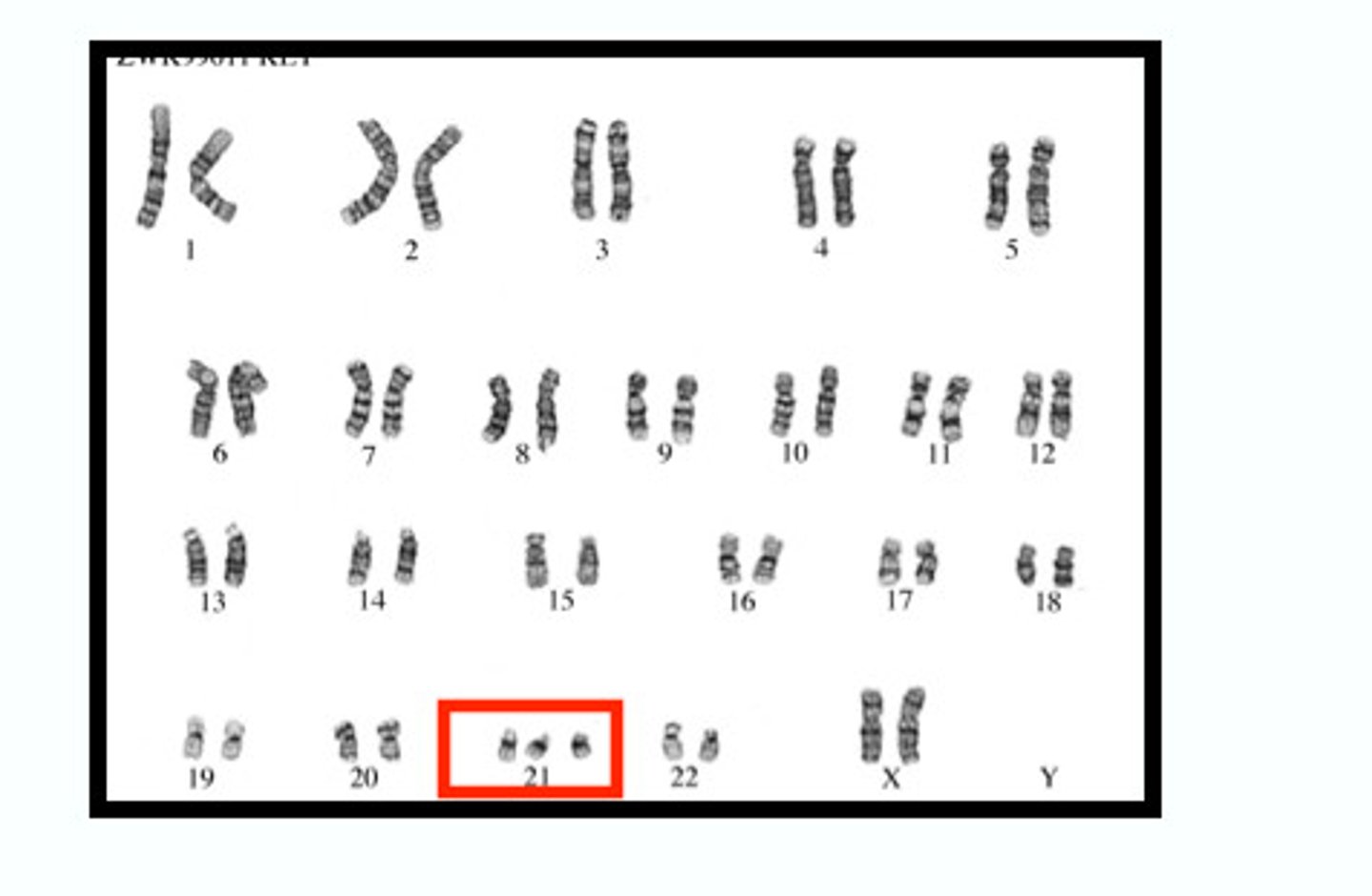
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome instead of 2
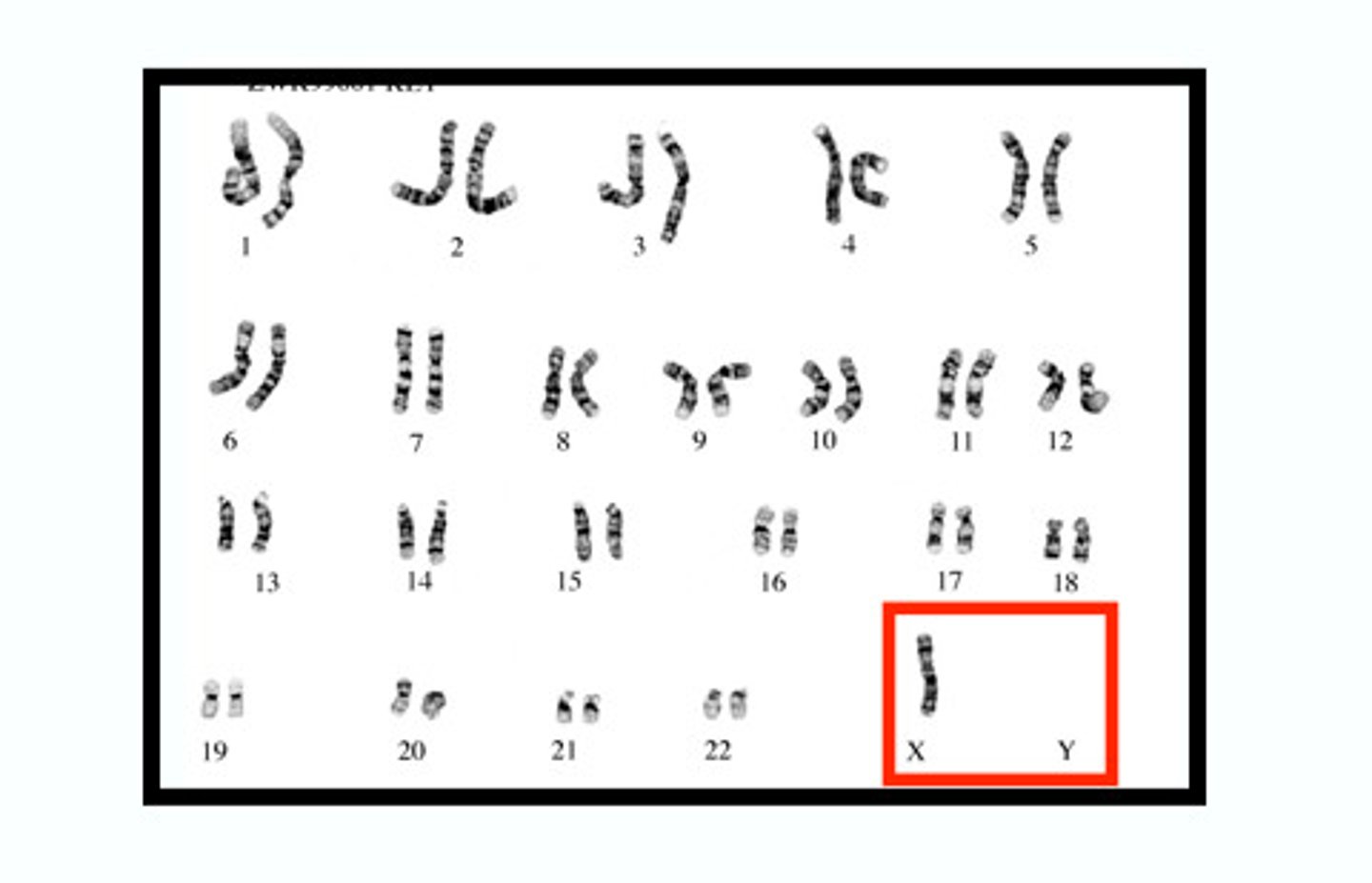
Monosomy
Chromosomal abnormality consisting of the absence of one chromosome from the normal diploid number
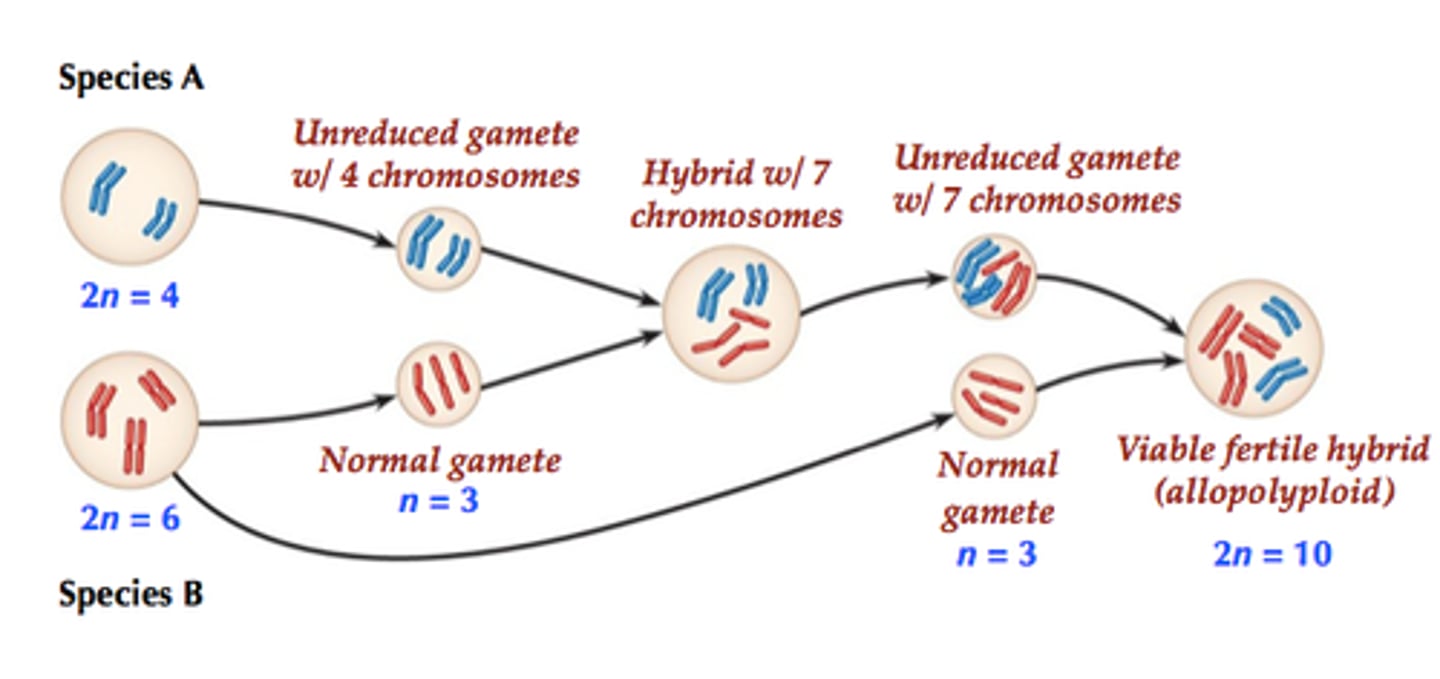
Polyploidy
condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
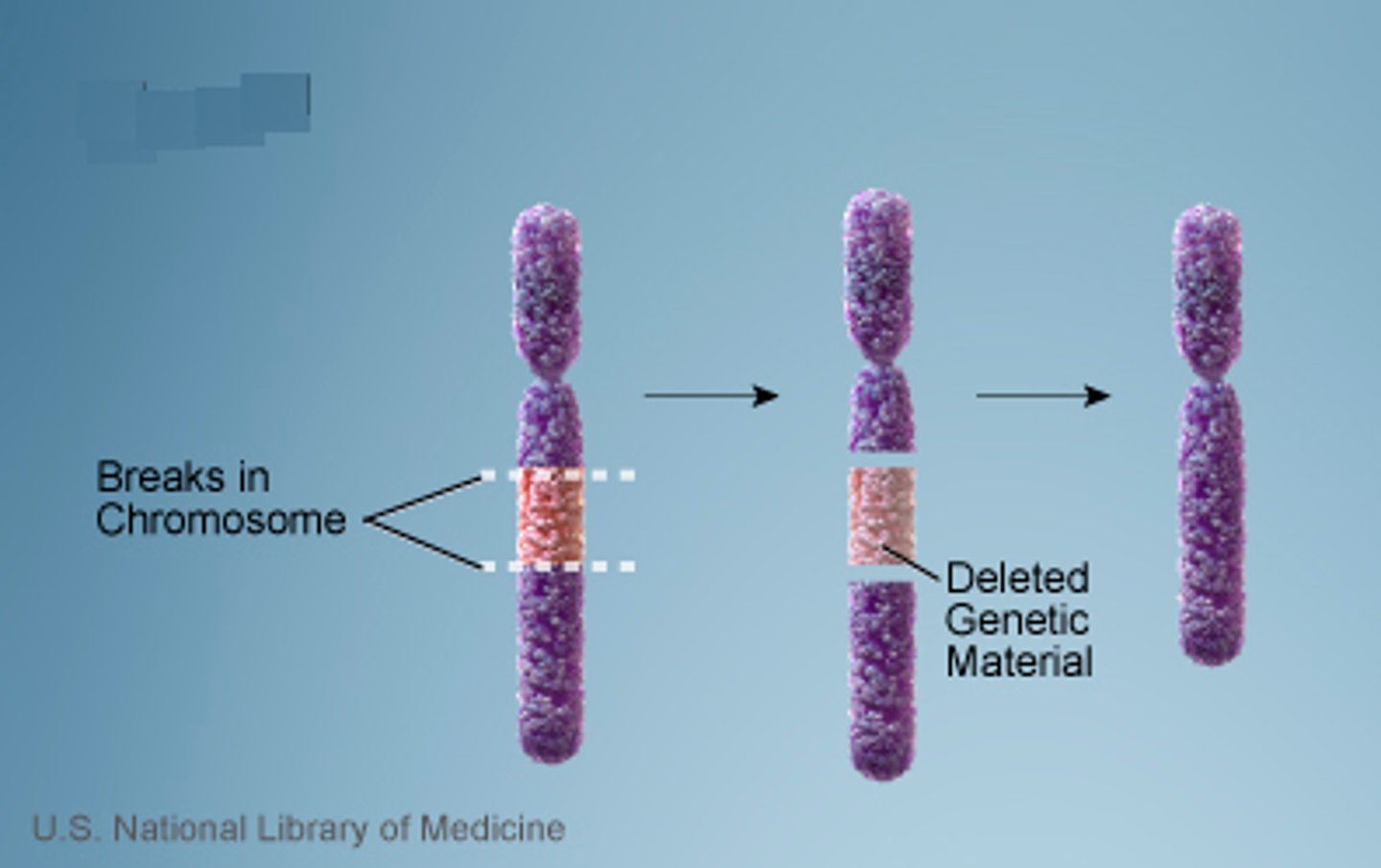
Deletion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.
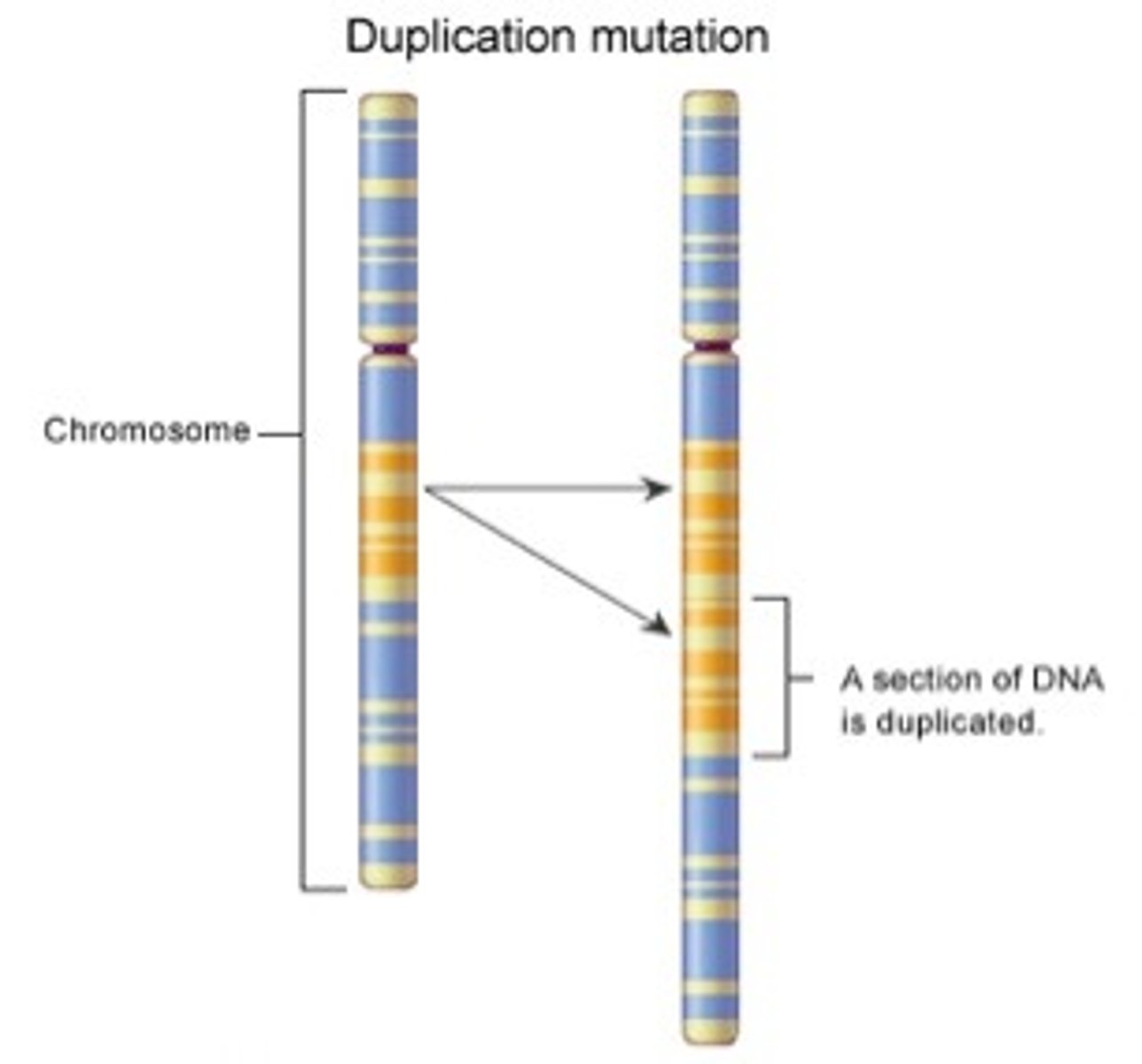
Duplication
change to a chromosome in which part of the chromosome is repeated
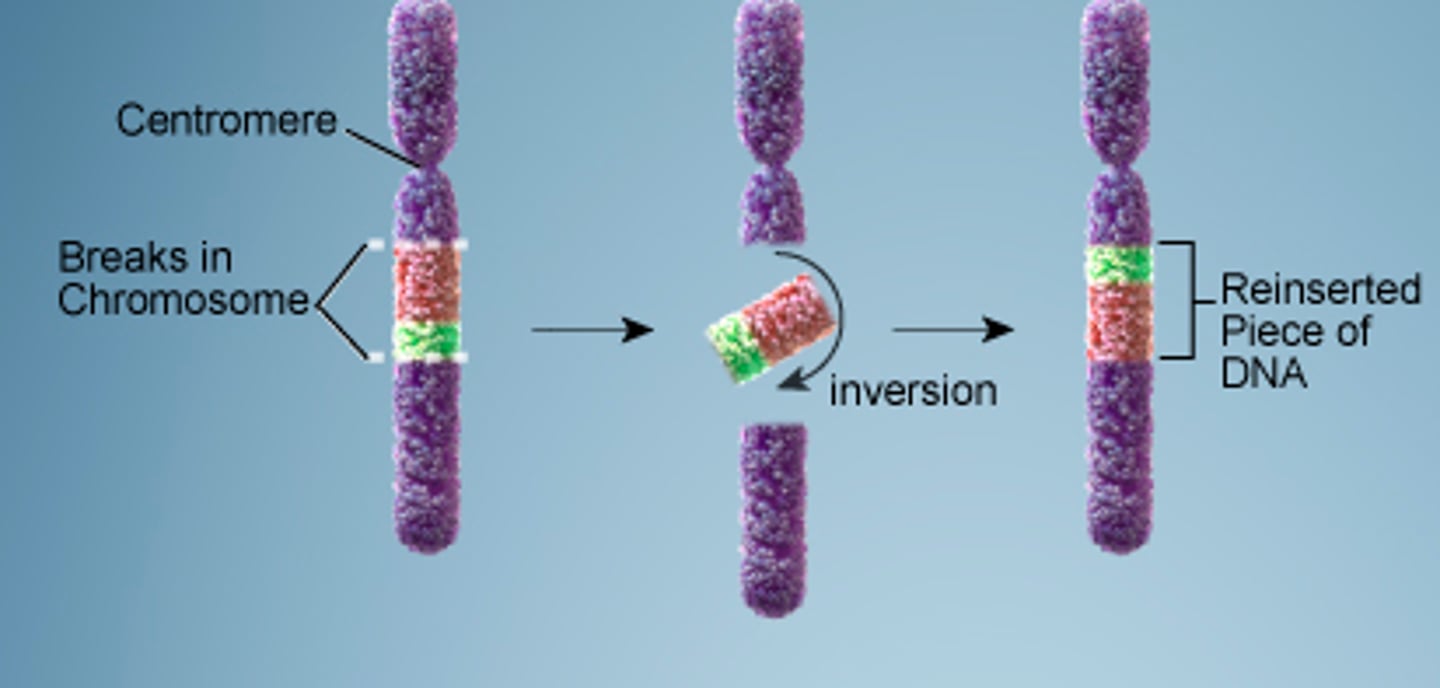
Inversion
A condition in which a section of a chromosome is reversed in direction
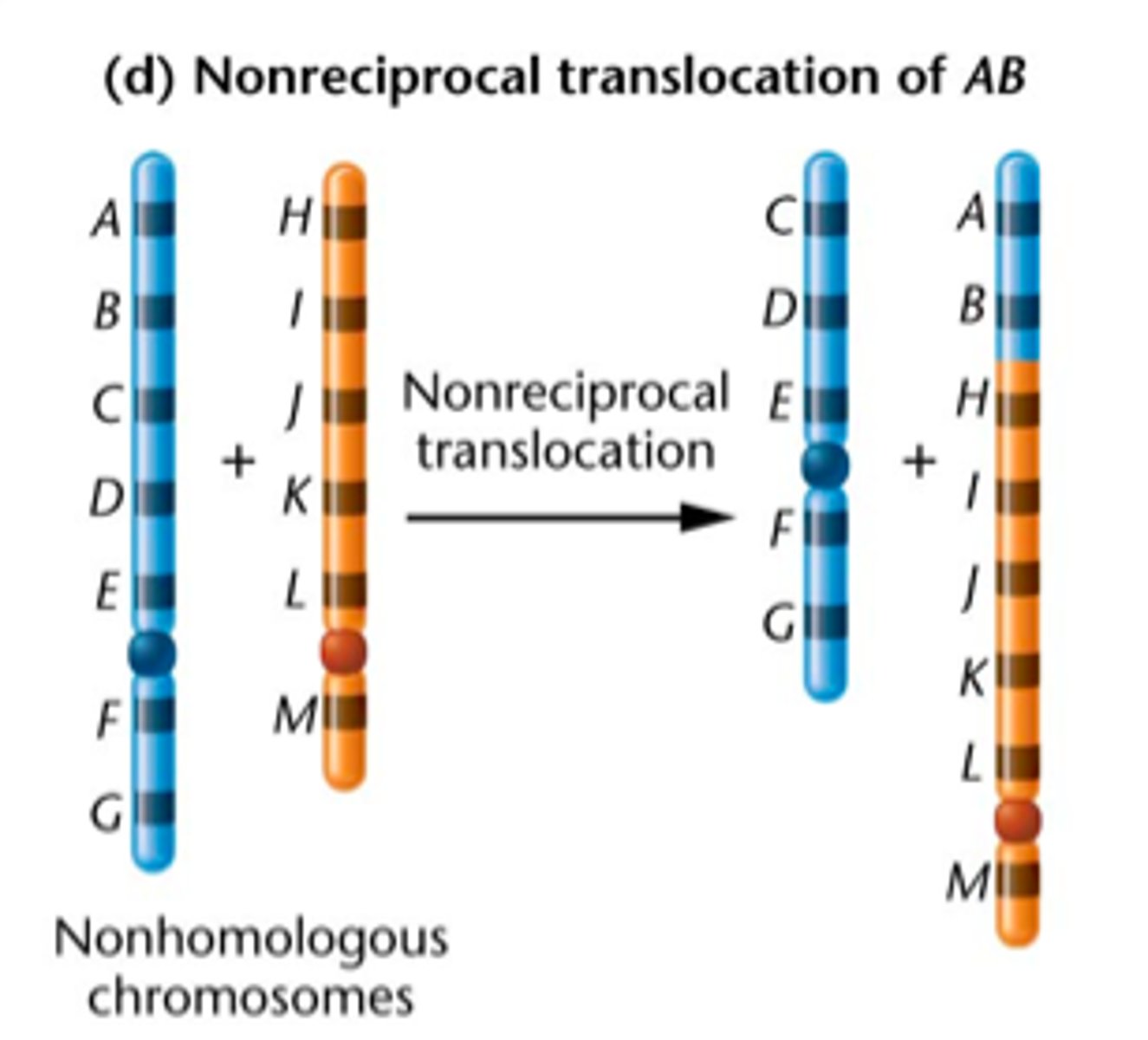
Translocation
The process in which a segment of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome.
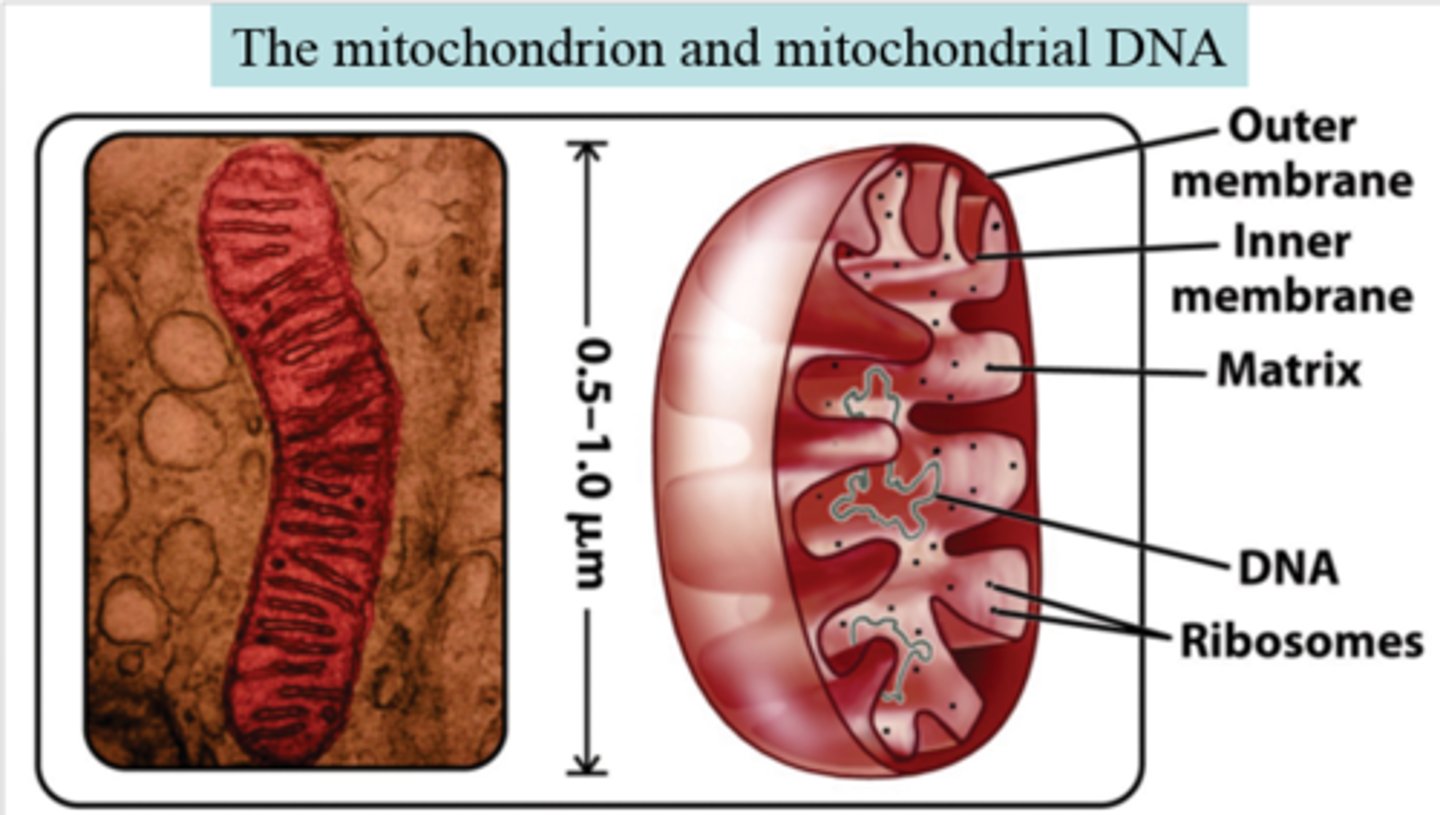
Non-nuclear DNA
mitochondria and chloroplasts contain small amounts of DNA separate from the nucleus