Genetic Code, Protein Synthesis Biochem
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Genetic Code
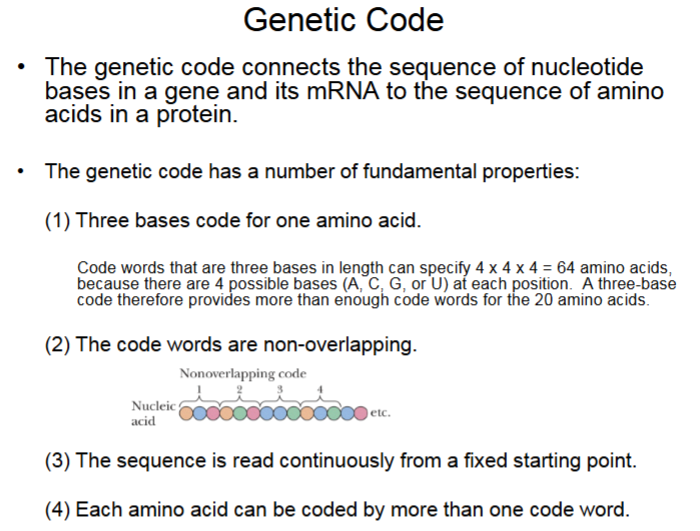
There are multiple code words for 1 amino acid. 1 Base coding only has 4 options. 2 Base coding gives 16 options (4×4). 3 base coding gives 64 options (4×4×4) for all 20 amino acids.
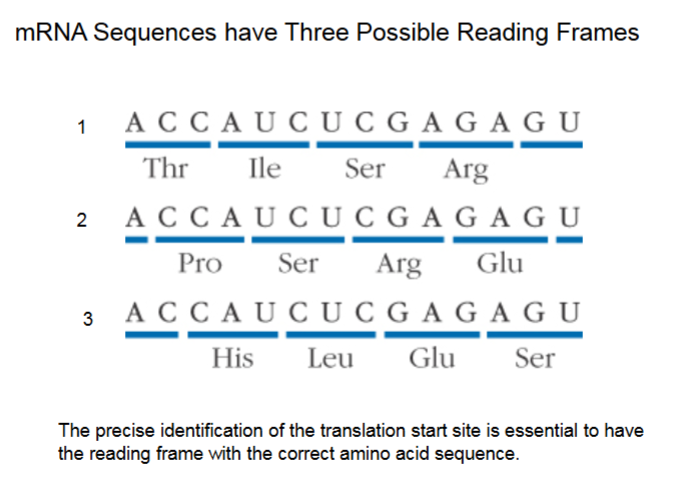
mRNA Sequences have Three Possible Reading Frames
Illustrates point of starting at the same point every time.
Translation begins NOT at start (5’) of mRNA, but when the AUG code (also code for methionine) is read off.
It ends when stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is read, not at end of mRNA (3’).
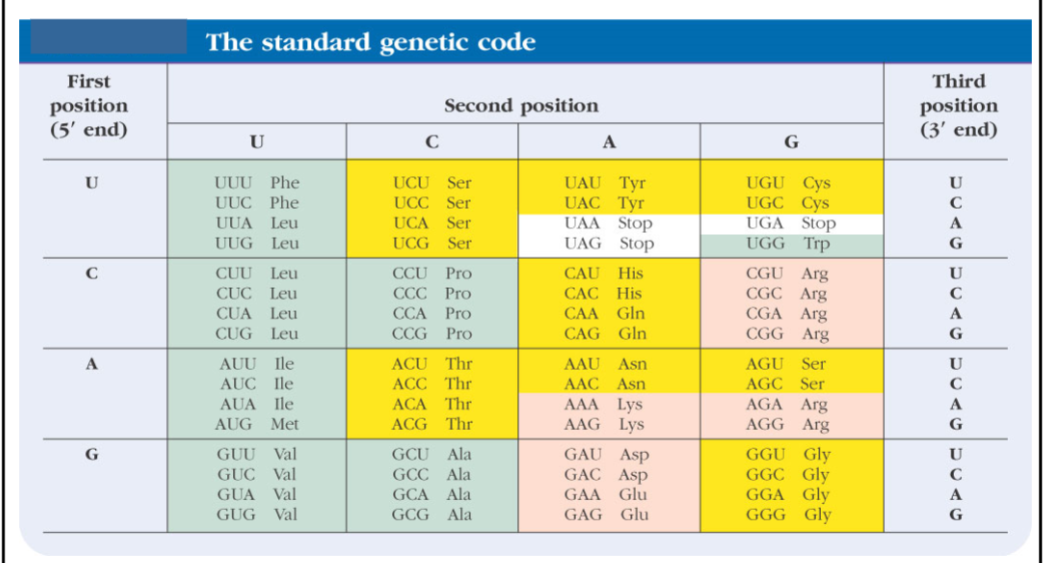
The Standard Genetic Code
Chemically similar amino acids have similar code words (see Asp, Glu).
Green = hydrophobic amino acids
Yellow = polar amino acids
Red = charged amino acids
The table has all possible 3 base ACUG code words.
Amino acids with 6 code words: Leu, Ser, Arg
Amino acids with 1 code word: Met, Trp
Amino acids with 4 code words: Most common, similar code words are usually different at the last position.
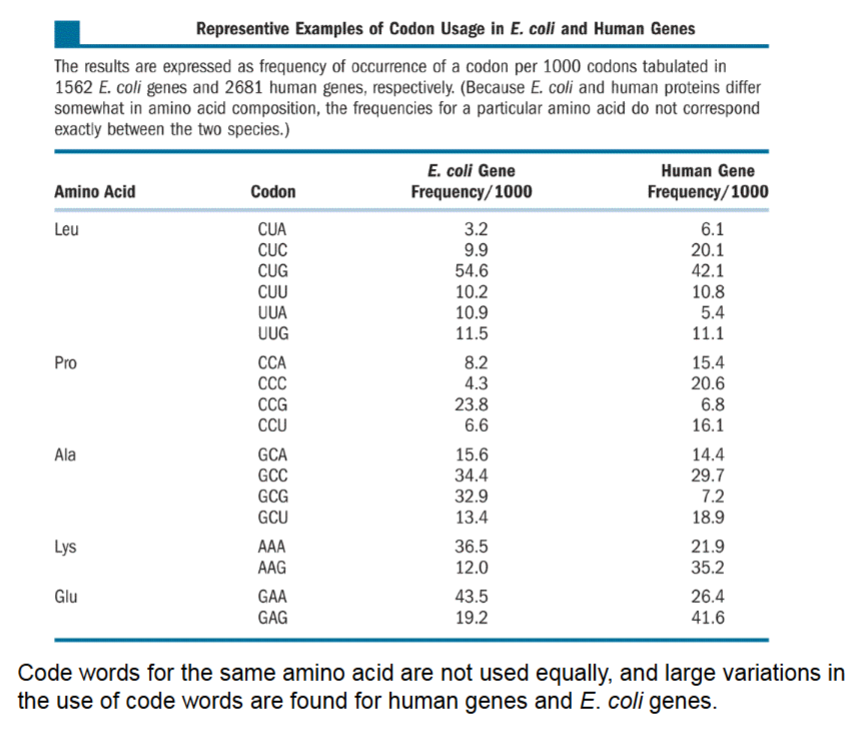
Representative Examples of Codon Usage in E. Coli and Human Genes
If an amino acid can have multiple code words, are they all used equally? No,
Can’t predict code words from trends, see Lys/Glu in E. coli versus humans.
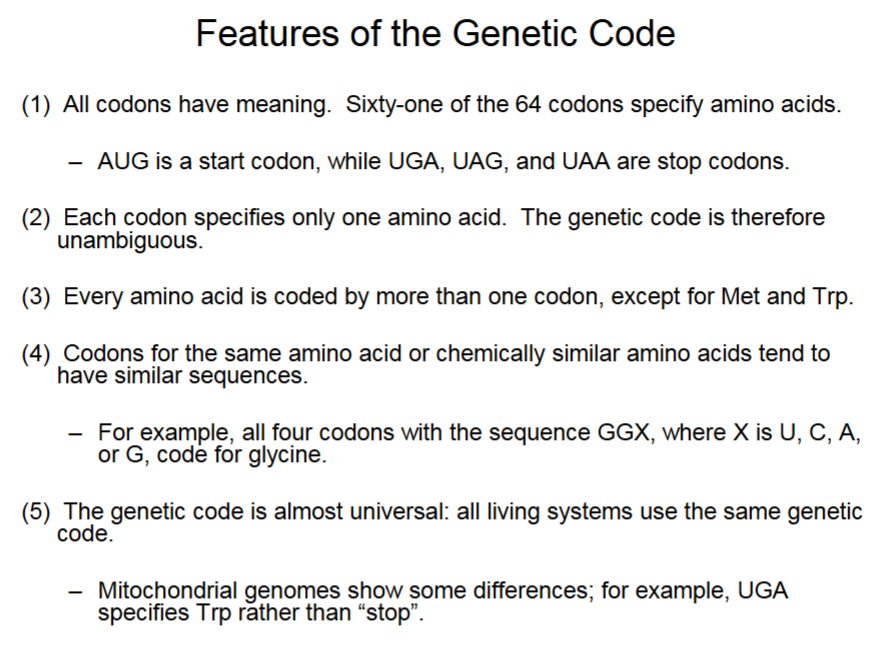
Features of the Genetic Code
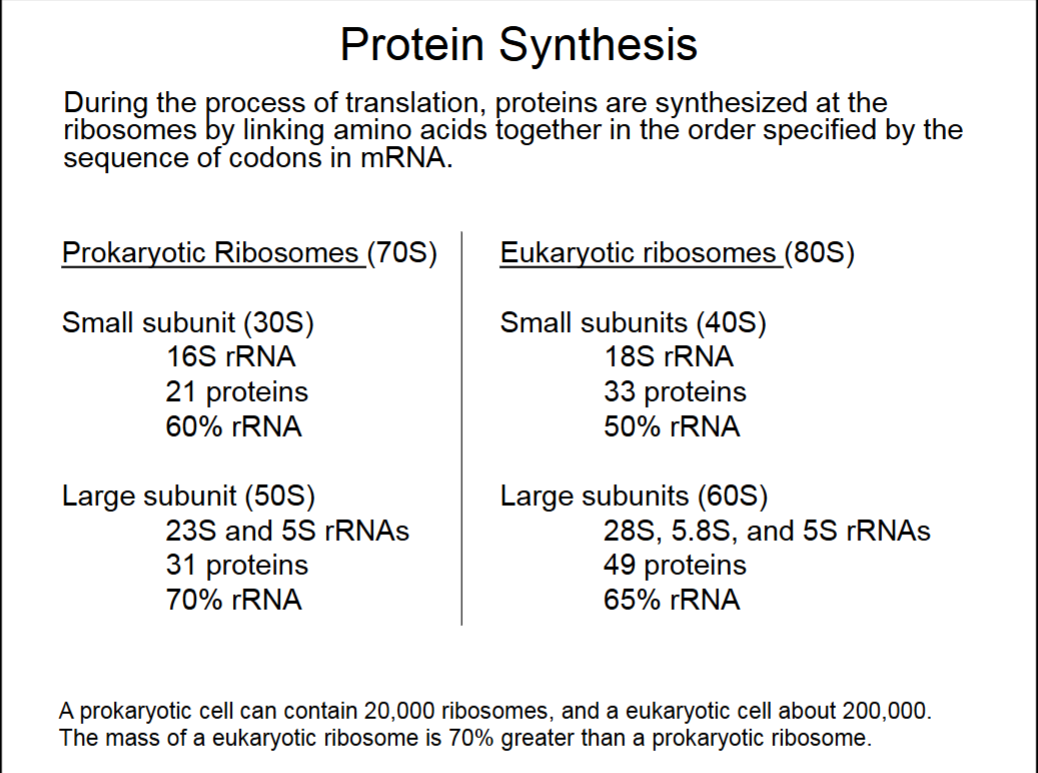
Protein Synthesis
Ribosome binds to mRNA from 5’ end.
Just 1 rRNA in small subunits, yet still 50-60% of subunit. Similarly with large subunits, ribosomes are very rRNA rich.
Ribosomes are made of protein complexes and rRNA.
S values refer to speed at which ribosomes pellet in a centrifuge (sedimentation rate).
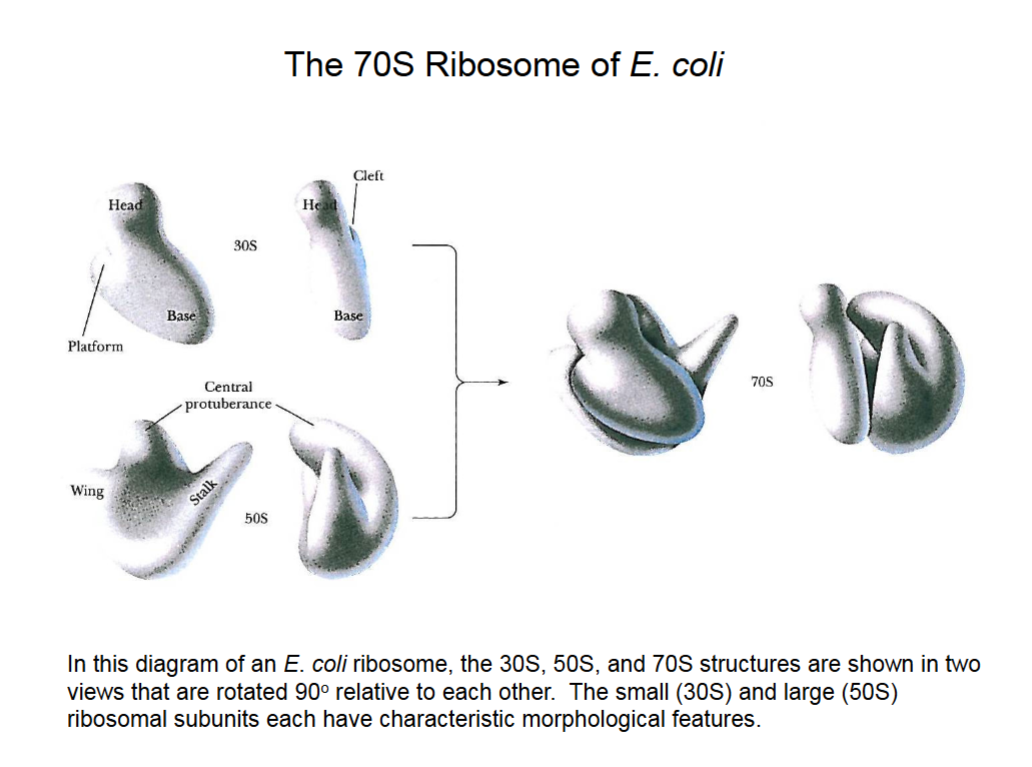
The 70S Ribosome of E. coli.
The far right picture has a gap through which mRNA will string, and amino acids will also enter the gap and be linked to the protein chain.
Mechanism of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis has three phases: initiation, elongation and termination.
Initiation
Involves binding of mRNA to the small and large ribosomal subunits, and binding of an initiator tRNA.
Elongation
Includes the formation of all peptide bonds of the growing polypeptide chain (amide bond between carbonyl and amino ends).
Termination
Occurs when a “stop” codon is reached along the mRNA, which leads to the release of the completed polypeptide.
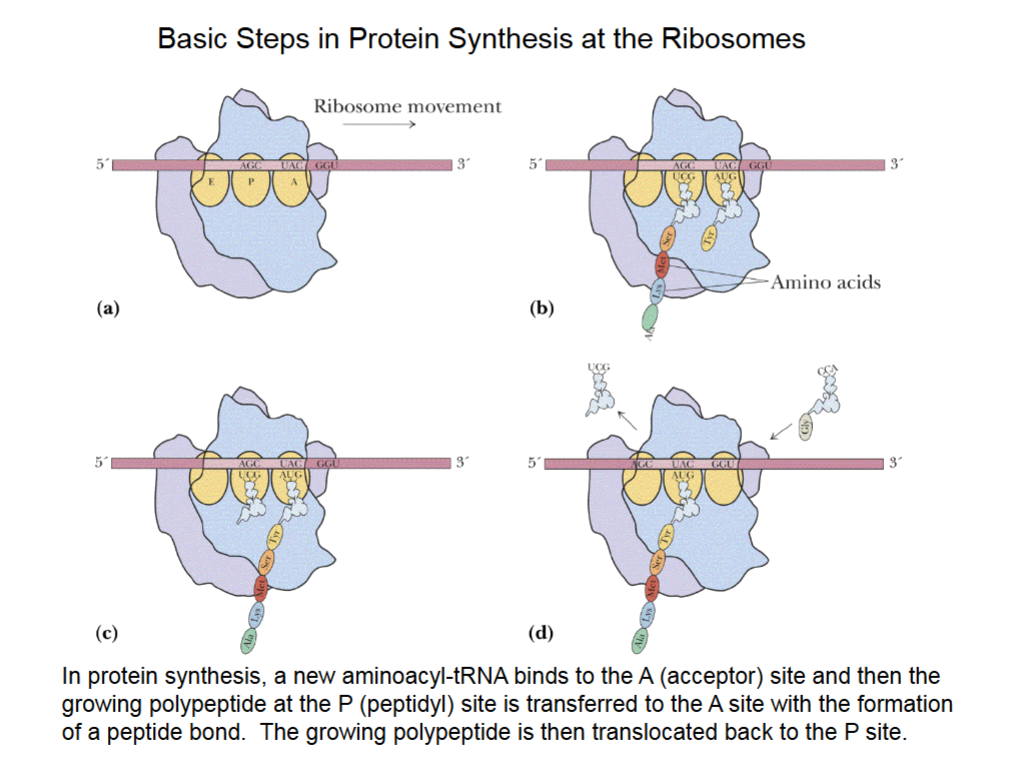
Basic Steps in Protein Synthesis at the Ribosomes
mRNA is between the 2 subunits of ribosome contacting A, P, E sites.
A is acceptor site, P is peptidyl site and E is exit site.
P site is where protein chain is synthesized, held in place by 3 H-bonds between the codon of an mRNA and the anticodon of the tRNA.
Protein chain moves back to A site to bind amino acid from the tRNA.
Sliding ribosome over mRNA, tRNA w/ protein moves from A to P, and another tRNA can be added to A site to begin process anew.
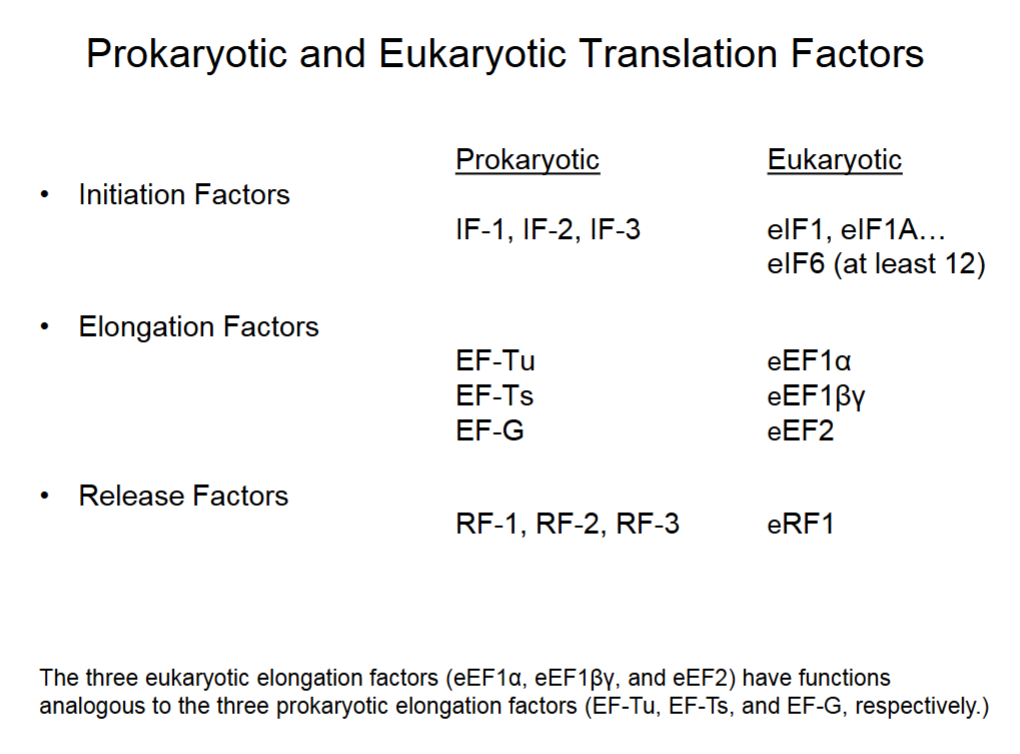
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Translation Factors
Other proteins found in both eukaryotic/prokaryotic cells to facilitates protein synthesis.
Prokaryotes have 3 initiation, elongation, and release factors each.
Eukaryotes have at least 12 initiation, 3 elongation and 1 release factors.
Eukaryotic elongation factors 1:1 with prokaryotic’s.
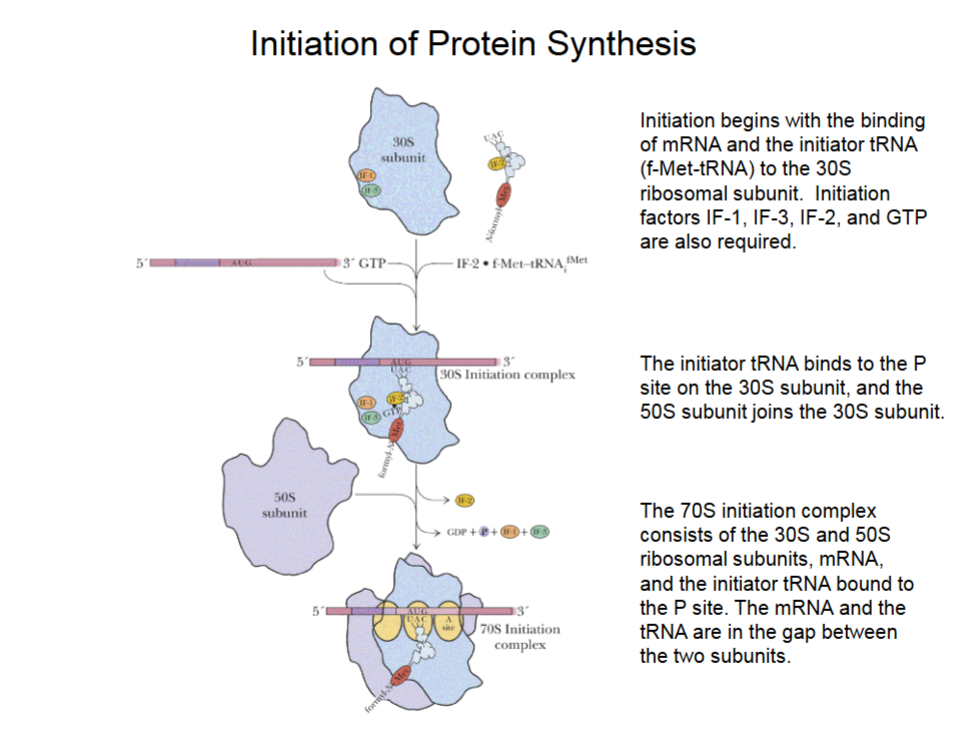
Initiation of Protein Synthesis
mRNA binds such that the first AUG (start code word) binds to the P site.
IF-1 and IF-3 bind to 30S subunit, IF-2 binds to initiator tRNA bringing in the first methionine.
GTP breakdown to GDP powers joining of components.
50S subunit joins 30s to make 70S initiation complex (also w/ initiator tRNA and mRNA in gap between ribosome subunits)
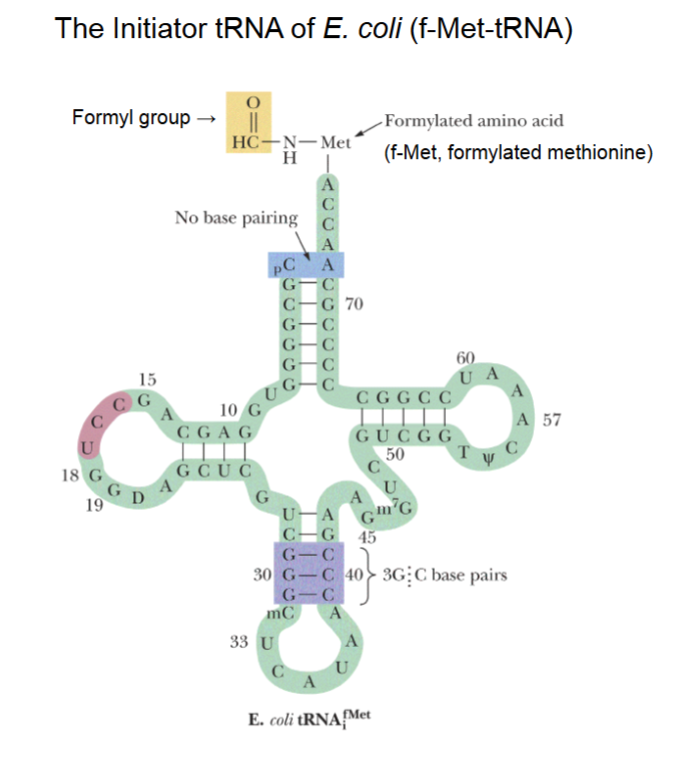
The Initiator tRNA of E. coli (f-Met-tRNA)
2 methionine tRNAs, the regular and the special initiator.
Initiator tRNA has 3’ end with acceptor stem with methionine covalently linked temporarily.
A formyl (aka aldehyde) group bound to the NH (amino group) of methionine, which blocks N-terminal (amino) end such that amino acids can only be added to the carbonyl group.
5’-CAU-3’ anticodon of tRNA
3’-GUA-5’ mRNA codon
(aka 5’-AUG-3’ start code word)
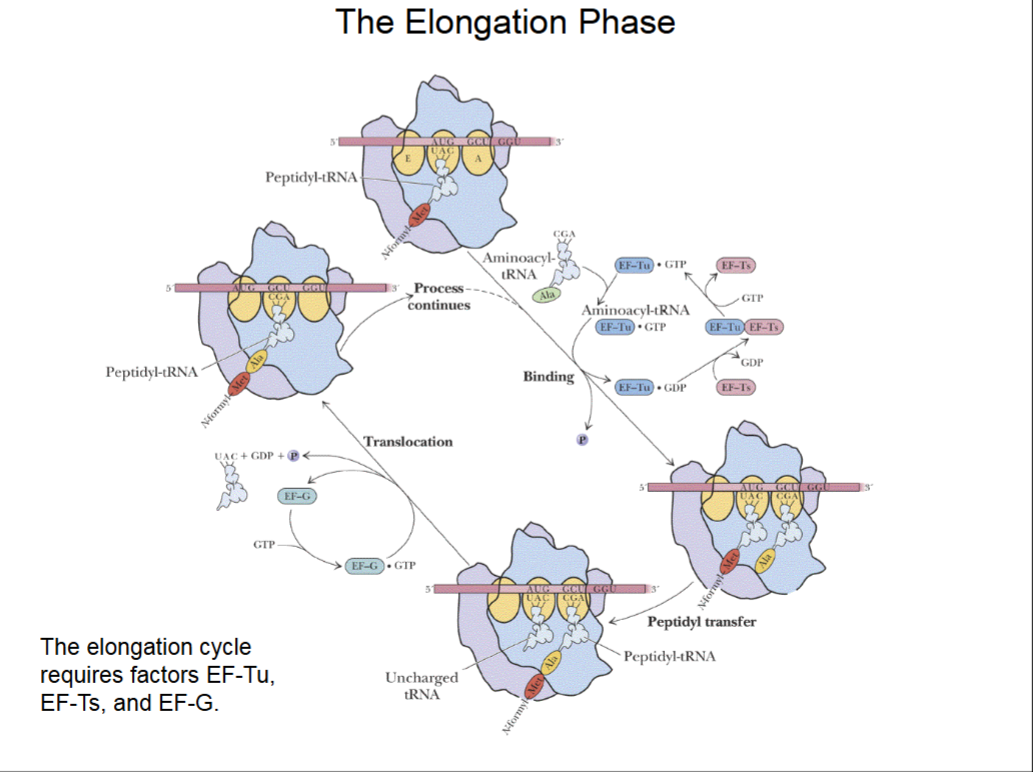
Peptide-Chain Elongation
Binding of a new aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site is brought about by elongation factor EF-Tu. Elongation factor EF-Ts recycles EF-Tu,
Peptidyl transfer is the step that forms the peptide bond between the new amino acid and the growing polypeptide chain.
The peptidyl transferase activity is not due to a protein enzyme, but to an RNA enzyme activity of the “peptidyl transferase center” of the 23S rRNA of the 50S subunit. RNA enzymes are known as ribozymes.
The process continues with the binding of the next new aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site.
The Elongation Phase
Methionine rRNA at P site, a new tRNA w/ amino acid wants to come in to A site.
The tRNA needs help of activated transition factor EF-Tu, activated by GTP, to slide into A site. A spent GDP is left.
EF-Ts removes GDP from EF-Tu and replaces it with GTP to activate it again.
Peptidyl transfer brings amino acid chain over to A site and elongates the chain.
Translocation moves ribosome 3 bases to right on mRNA. Needs an activated EF-G (activated by GTP, which is then spent into GDP) to occur.
After which, A site is open ot bind another tRNA.
RATE OF TRANSLATION:
Prokaryotes: ~20 aa/sec
Eukaryotes: ~8 aa/sec
Slow b/c complex process
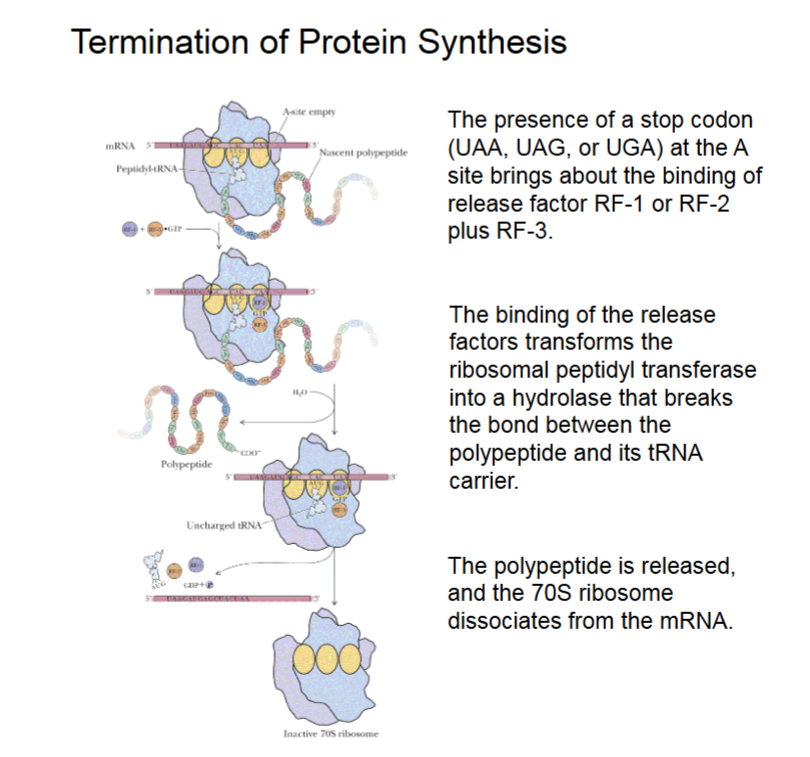
Termination of Protein Synthesis
The binding of release factors to the A site transforms the ribosomal peptidyl transferase, that forms the peptide bond between amino acids, into a hydrolase.
The peptidyl transferase then hydrolyzes the bond linking the polypeptide to its tRNA carrier, thereby releasing the polypeptide.
Stop codon signifies end of elongation (UAA, UAG, or AGA).
23S peptidyl transferase activity changed to hydrolase activity (breaking bonds, adding -H and -OH as ends).
Termination of Protein Synthesis (Visualized)
RF-1/RF-2 and RF-3 + GTP binding to A site from stop codon, this turns the transferase to hydrolase activity.
Polypeptide is broken from tRNA carrier.
Polypeptide released, 70S releases mRNA.
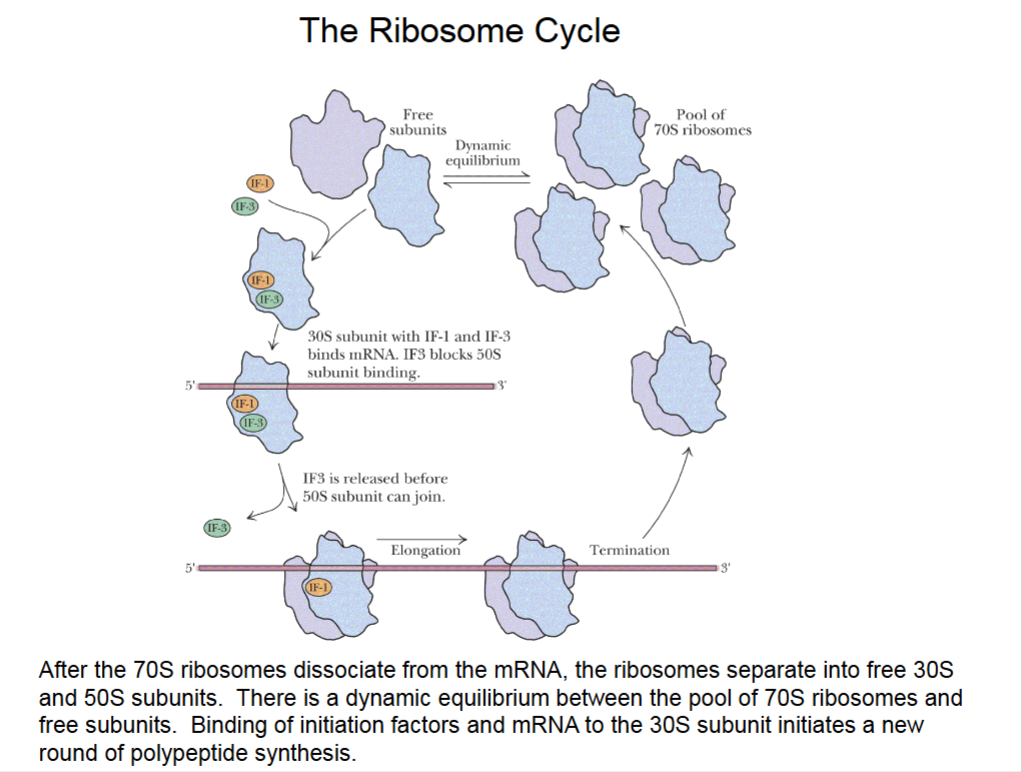
The Ribosome Cycle
Multiple ribosomes can bind to same mRNA.
Dynamic equilibrium between 70S and free subunits.
Free 30S subunits start initiation all over again.
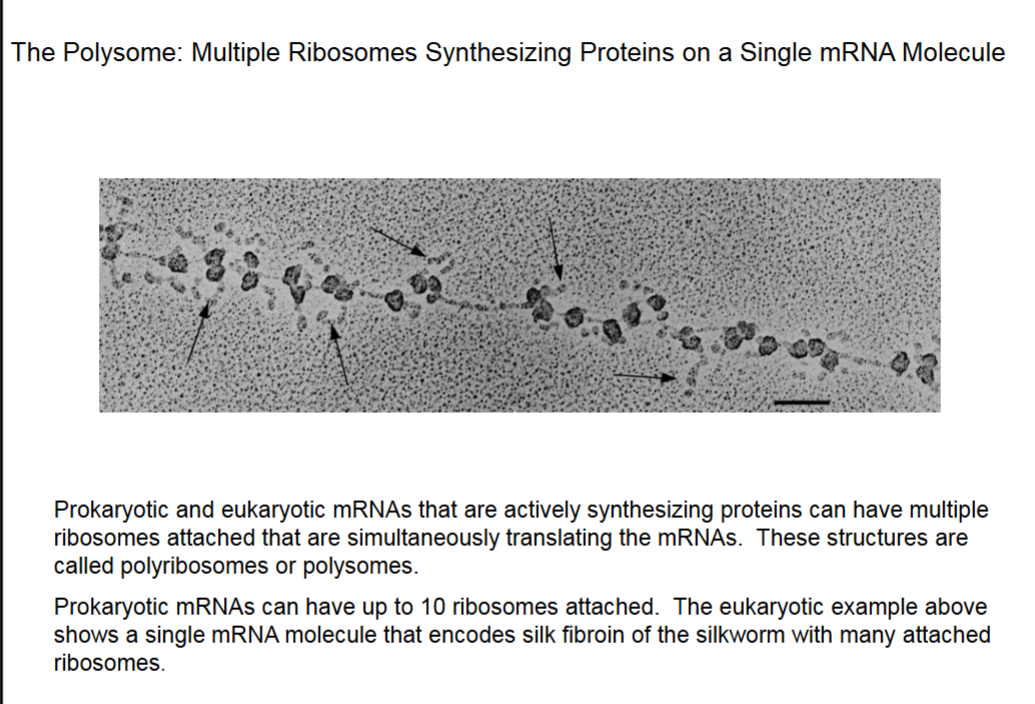
The Polysome: Multiple Ribosomes Synthesizing Proteins on a Single mRNA Molecule
This mRNA synthesizes fibroin (β-sheet).
Arrows point to synthesized proteins.
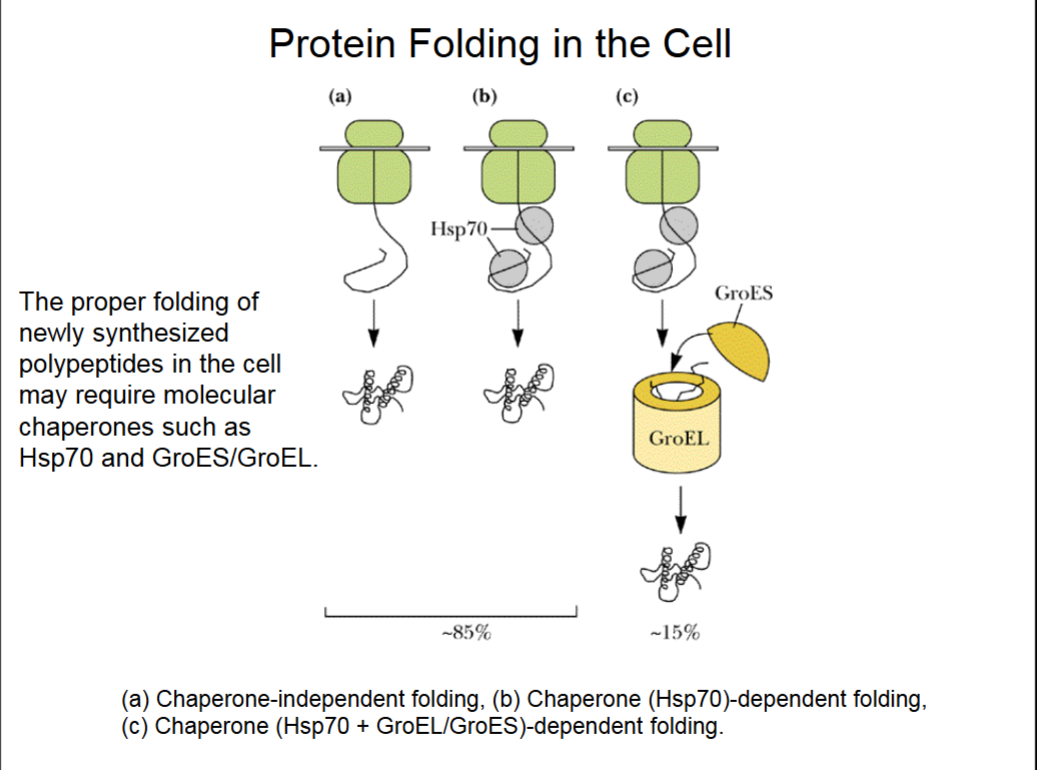
Protein Folding in the Cell